Exam 3 - CH 18: Blood & Formed Elements
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
The circulatory system is divided into which two systems?
Cardiovascular system
Lymphatic system
What are the functions of blood?
Transport mechanism for:
Nutrients
Signaling molecules
Respiratory gases (oxygen + carbon dioxide)
Waste products
Circulatory System: SEM of blood (Leukocytes, Erythrocytes, Platelets)
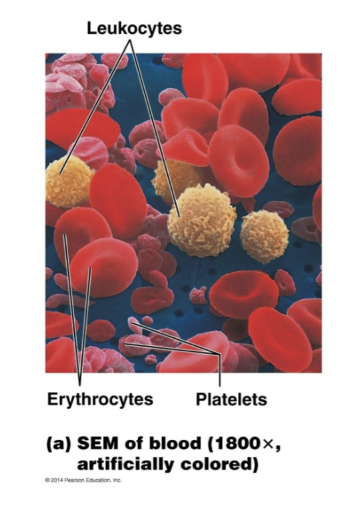
Blood transports:
• Oxygen from the lungs and nutrients
from the digestive tract
• Metabolic wastes from cells to the
lungs and kidneys for elimination
• Hormones from endocrine glands to
target organs
Blood prevents blood loss by:
• Activating plasma proteins and
platelets
• Initiating clot formation when a
vessel is broken
Blood maintains:
• Appropriate body temperature by
absorbing and distributing heat
• Normal pH in body tissues using
buffer systems
• Adequate fluid volume in the
circulatory system
Blood prevents infection by:
• Synthesizing and utilizing antibodies
• Activating complement proteins
• Activating WBCs to defend the body
against foreign invaders
Functions of the circulatory system include:
Transport (wastes, nutrients, hormones, gases)
Protection (immune components)
Regulation (pH, ion concentration)
Body temperature regulation
What is the blood volume of males?
5-6 liters
What is the blood volume of females?
4-5 liters
Which cellular and liquid components are found in blood?
• Blood cells—formed elements
• Plasma—liquid portion of blood
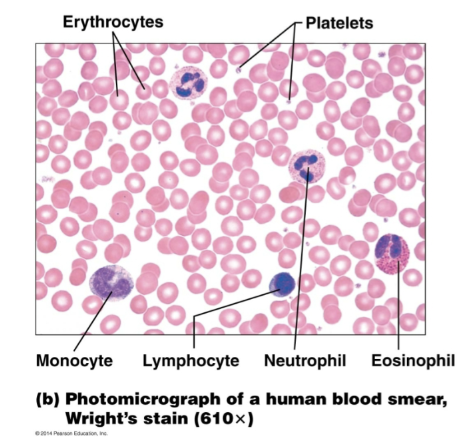
Composition of Blood: Blood smear (Erythrocytes, Platelets, Monocyte, Lymphocyte, Neutrophil, Eosinophil) → won’t be tested on?
What is the pH of blood? (Important to remember)
7.35 - 7.45 (Slightly alkaline)
If pH is off, components that dissolve in blood would be affected.
The shape of proteins/enzymes would change.
What is the temperature of blood?
38C (100F this is higher due to internal temp being slightly higher than surface temp).
Blood accounts for approximately how much of body weight?
8% of body weight
What is Hematocrit?
The measure of % RBC (red blood cells)
• Males: 47% ± 5%
• Females: 42% ± 5%
What is the buffy coat? Where is it found?
Portion of blood composed of leukocytes and platelets.
• Present at the junction of plasma and RBCs
Hematocrit (Plasma, Buffy Coat, RBCs)
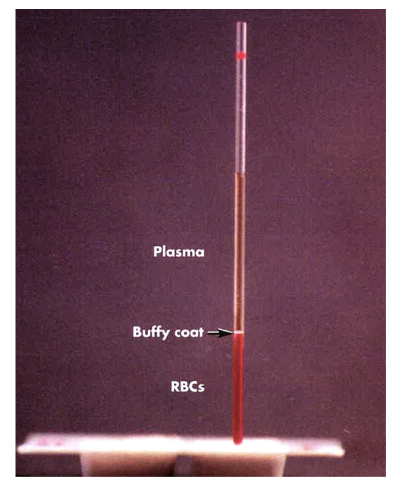
The percentage of blood volume that consists of erythrocytes is known as the __________.
hematocrit
Figure 18.8: Stages of differentiation of blood cells in the bone marrow
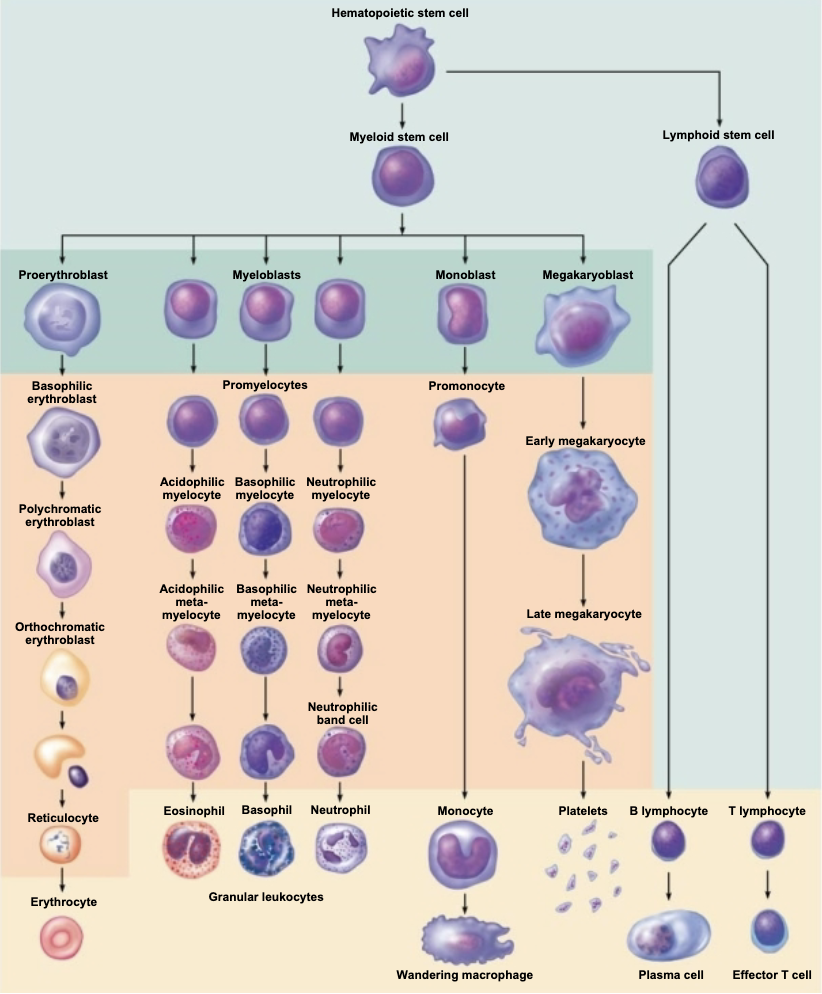
Two things to know:
everything except t and bc cells
T and B cells come from the lymphoid lineage
You get natural killer cells from the lymphoid lineage
What are the formed elements of blood?
• Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets make up the formed elements
• Only WBCs are complete cells
• RBCs have no nuclei or organelles, and platelets are just cell fragments
How long do the formed elements of blood survive in the bloodstream? (Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets)
Most formed elements survive in the bloodstream for only a few days.
Most blood cells do not divide but are renewed by cells in the bone
marrow.
Erythrocytes, lymphocytes, and platelets are _________?
formed elements
Before birth, where does blood cell formation take place?
In the fetal yolk sac, liver, and spleen
By the seventh month of formation in embryo/fetal development, ________ is the primary hematopoietic area?
red bone marrow
Where do blood cells develop from?
mesenchyme-derived cells called blood islands
formation in embryo and fetal development. (idk if we need to memorize)
All formed elements arise from the common _____ ______ ____ ____?
pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell
What are the two lineages that hematopoietic stem cells develop along?
What determines these lineages?
(1) Myeloid lineage - Myeloid stem cells - Give rise to all other blood cells
(2) Lymphoid lineage - Lymphoid stem cells - Give rise to lymphocytes
“Signals are what determines these lineages.”
Formation of Formed Elements of Blood (not sure to memorize either)
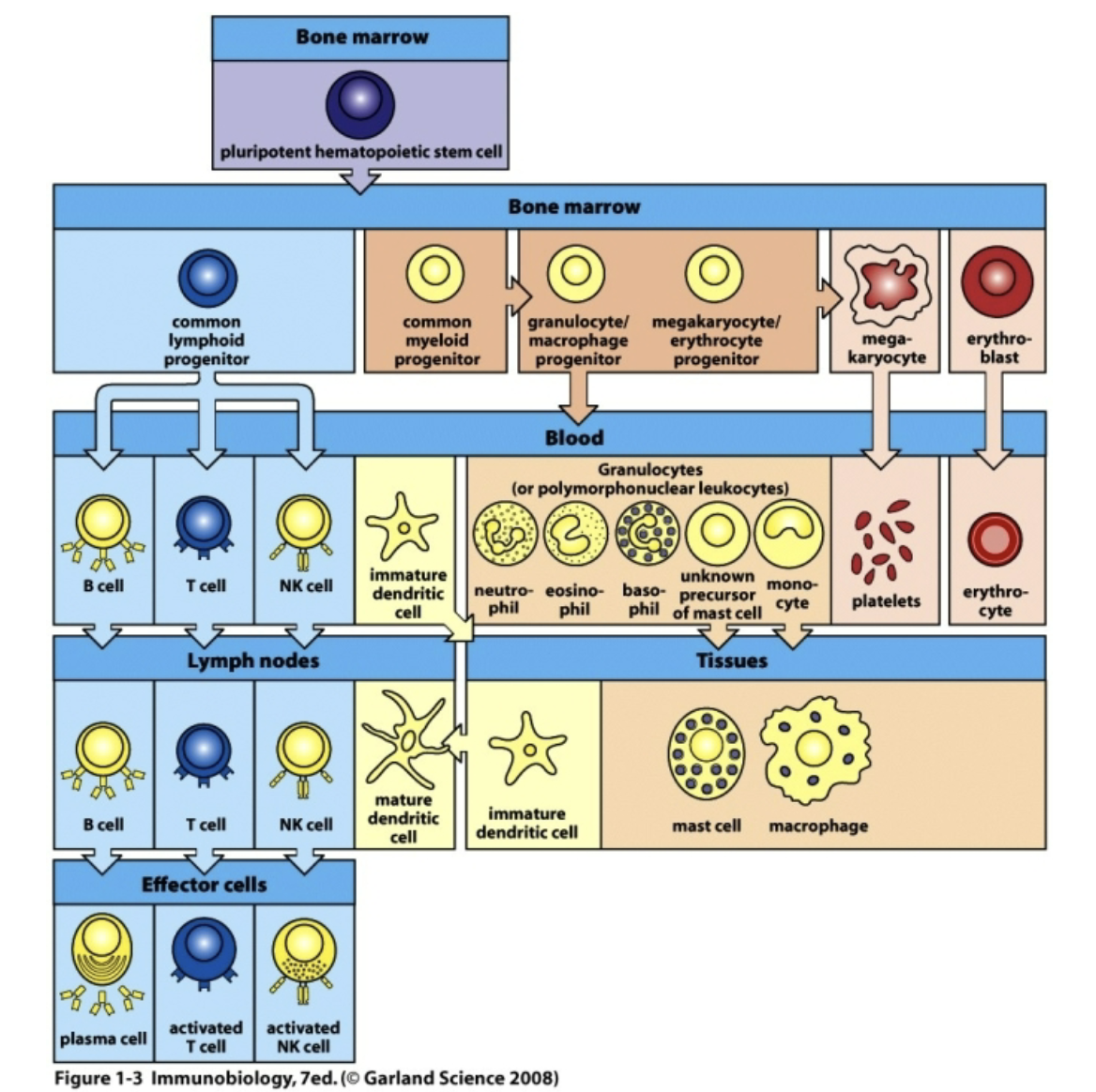
Q: Blood stem cells give rise to which two lines of progenitor cells?
myeloid stem cells & lymphoid stem cells
Q: Which celll do NOT develop from the differentiation of myeloid stem cells?
lymphocytes
In what order do blood cells develop?
Mesenchyme → Blood Islands → Pluripotent
TRUE or FALSE: All lymphocytes are leukocytes, but not all leukocytes are lymphocytes.
True: All lymphocytes are leukocytes.
Lymphocytes are specific, not in the same lineage.
Figure 18.7: Red Bone Marrow
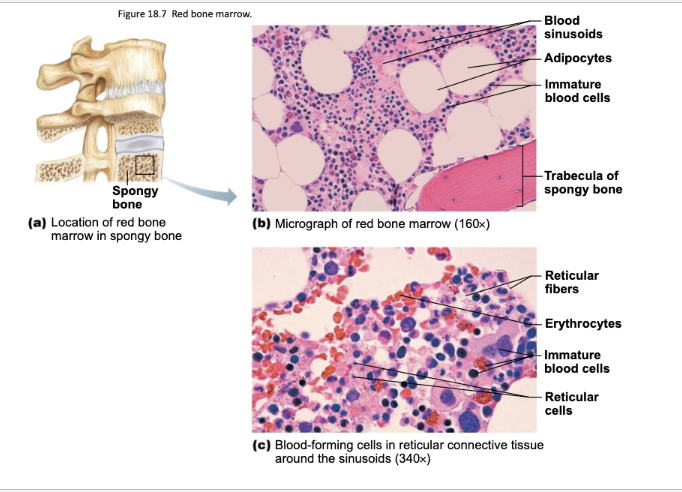

Where is bone marrow located?
Within all bones.
Where is red marrow located in adults?
• Between the trabeculae of spongy bone of axial skeleton
• Pelvic and pectoral girdles
• In proximal epiphyses of the humerus and femur
What is the function of red marrow?
Actively generates new blood cells.
Contains immature erythrocytes.
TRUE or FALSE: Yellow marrow is dormant.
True
Where is yellow marrow located?
Long bones of adults.
Contains many fat cells.
for every cell, it requires growth factors
mature blood cells should have lost its nucleus
What is hematopoiesis? Where does it occur?
The production of the formed elements that occurs in the red bone marrow.
• Other tissues (spleen and liver) are also
hematopoietic in developing
embryo/other mammals.
• The pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell
gives rise to all formed elements
• Growth factors stimulate the
differentiation and proliferation of the
formed elements from this stem cell.
Red blood cells lack ____ and ____. They do not undergo _____.
Nuclei & Organelles; Mitosis.
• Erythrocytes (red blood cells; RBCs) are derived from ______.
the myeloid lineage
The pluripotent stem cell differentiates into a common myeloid progenitor.
Mature erythrocytes:
• Do not contain a nucleus or
organelles
• Contain abundant hemoglobin for
oxygen transport
• Have a concave disc shape
A hemocytoblast is transformed into a _____________.
proerythroblast
Proerythroblasts develop into early ________.
erythroblasts
The developmental pathway of erythrocytes consists of three phases:
• 1 – ribosome synthesis in early erythroblasts
• 2 – Hb accumulation in late erythroblasts and normoblasts
• 3 – ejection of the nucleus from normoblasts and formation of reticulocytes
Reticulocytes then become mature erythrocytes
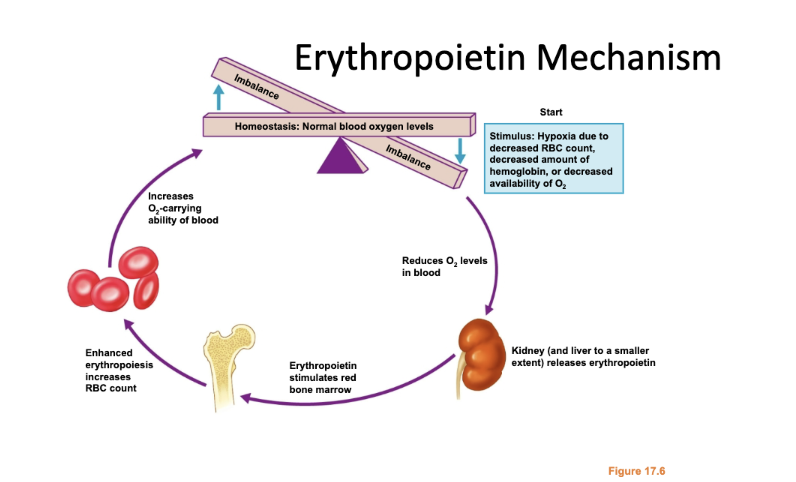
Erythropoietin Mechanism

Hemoglobin is a protein that is responsible for?
transportation of oxygen
Hemoglobin is a preferred method of oxygen _________, and most oxygen is transported bound to it.
transportation
The transportation of carbon dioxide occurs as _________?
bicarbonate
• This is the result of carbonic anahydrase, an enzyme that creates this buffering system.
• Hemoglobin has a low affinity to carbon dioxide.
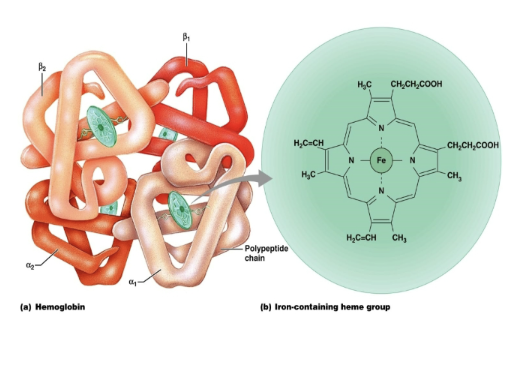
Hemoglobin is made up of the protein ______, bound to the red heme pigment.
globin
Heme contains iron portion that binds ______.
oxygen
What are the 4 polypeptide chains that make up the protein portion (globin)?
• Two alpha chains
• Two beta chains
Hemoglobin (Hb) Structure

What are antibodies made from?
B cells.