CSD class 16
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Muscles of the Soft Palate: Speech
Close the velopharyngeal opening, or velopharyngeal port, for all oral sounds
Muscles of the Soft Palate: Swallowing
Close off the velopharyngeal port so that food and liquid do not enter the nasal cavity
What sounds cause the soft palate to be depressed
/m/, /n/, and “ng”
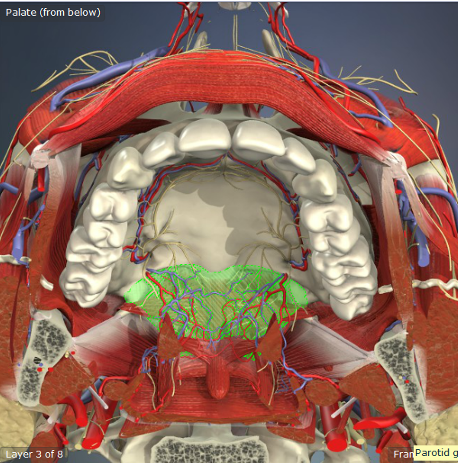
Soft Palate or Velum
A combination of muscles, palatine (=palatal) aponeurosis, nerves, and blood supply covered by mucous membrane lining
Palatine Aponeurosis
Makes up the mid-front portion of the soft palate
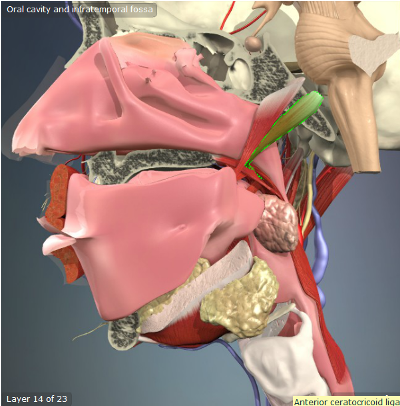
Levator Veli Palatini
Origin: Temporal Bone; Eustachian Tube
Insertion: Palatine Aponeurosis
Action: Elevates Soft Palate
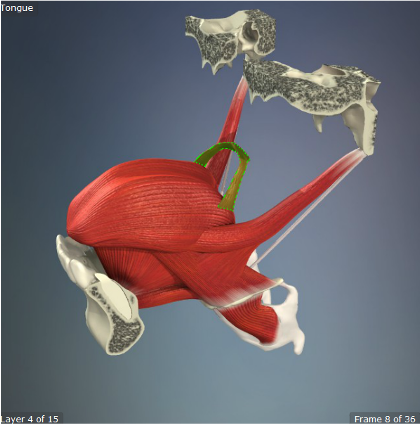
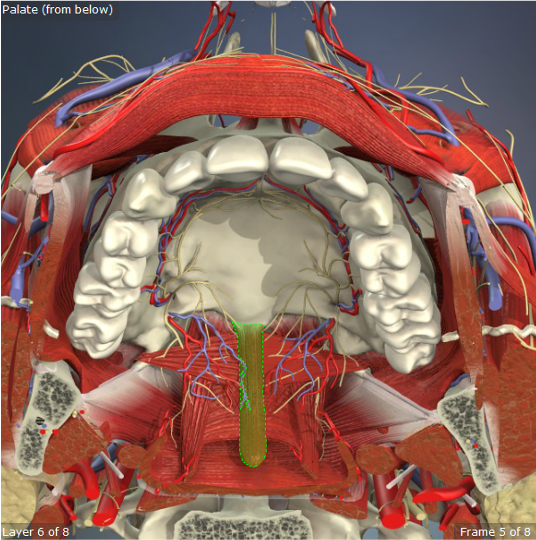
Palatoglossus
Origin: Palatine Aponeurosis
Insertion: Sides of Tongue
Action: Pulls soft palate toward tongue, elevates back of tongue
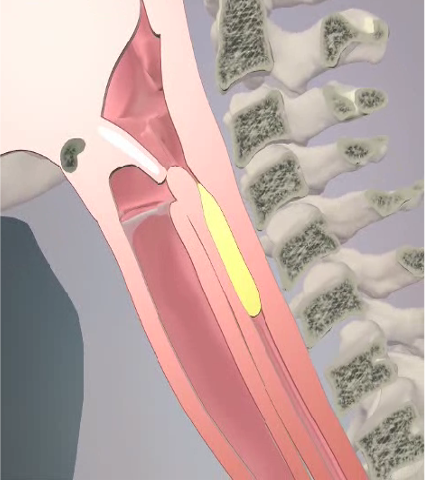
Palatopharyngeus
Origin: Palatine aponeurosis and posterior margin of hard palate
Insertion: Upper border of thyroid cartilage
Action: Narrows the pharynx, lowers the soft palate
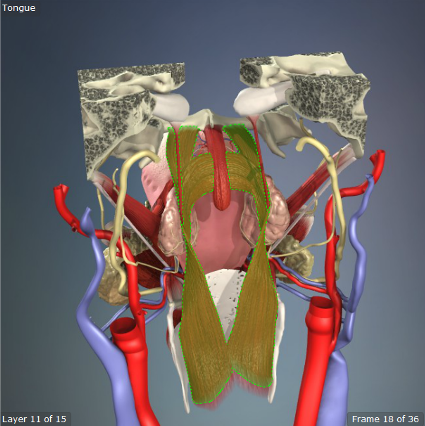
Tensor Veli Palatini
Origin: Sphenoid Bone, Eustachian Tube
Insertion: Palatine Aponeurosis
Action: Dilates the Eustachian Tubes, tenses soft palate
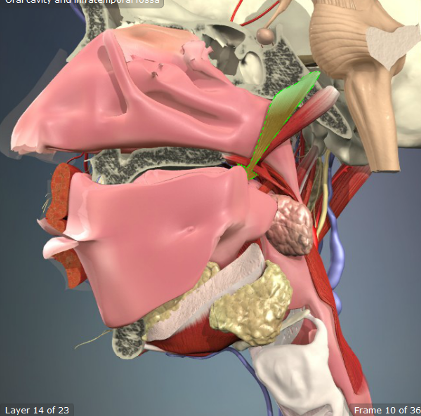
Muscularis Uvulae
Origin: Posterior Nasal Spine
Insertion: Palatine Aponeurosis
Action: Adds bulk and stiffness to velum
Swallowing
A complex process
A large series of neuromuscular systems and movements are involved for the process to be initiated and executed properly
Mastication
Chewing
Deglutition
Swallowing
Phases of Swallowing
Oral Preparatory Stage (mastication)
Oral Stage (propulsion of bolus)
Pharyngeal Stage (pharyngeal swallow)
Esophageal Stage (esophageal transit)
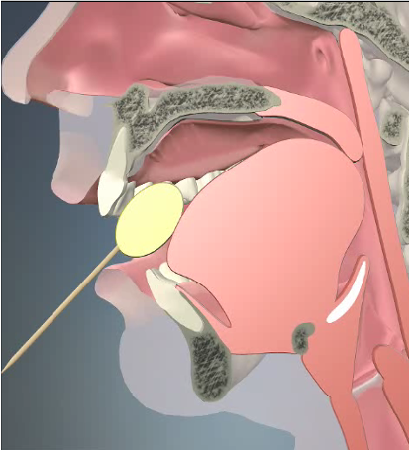
Oral Preparatory Phase
Voluntary control, goal of preparing the bolus to begin digestion and transport through the swallowing mechanism
Mastication
Food is mixed with saliva to form a bolus in preparation for swallowing
Oral Phase
Voluntary control
The initiation of this phase of swallowing is marked by tongue movement that results in posterior transport of the bolus into the pharyngeal cavity
It begins with the tip of the tongue is placed at the alveolar ridge
Respiration ceases during this phase of swallowing to maintain adequate airway protection
Soft palate is elevated
Tongue is depressed and pulled backward
The anterior portion of the tongue is elevated to the hard palate and squeezes the bolus backward
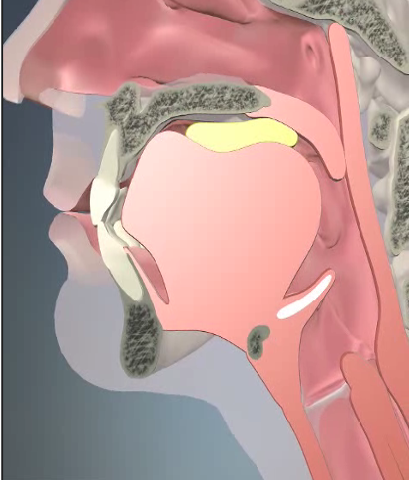
Pharyngeal Phase
Involuntary and Voluntary
Involuntary: Once initiated, it cannot be reversed
Voluntary: Complex and sequential control of muscles to protect airway from bolus
Initiated about the time when the bolus head is passing any point between the anterior faucial pillars and the ramus of the mandible
The bolus passes from the pharynx into the esophagus, taking less than one second
Respiration ceases reflexively at this point
Velum is elevated
Tongue is retracted
Lips are sealed
A tight seal is formed to protect the airway
The bolus passes over epiglottis through the pyriform sinuses to the esophagus
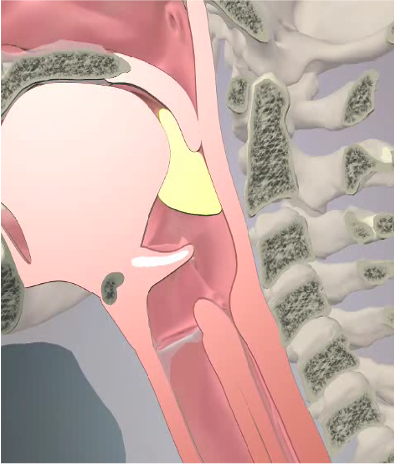
How to protect the airway
Vocal folds are closed
False vocal folds are closed
Epiglottis is depressed
Larynx is elevated
Esophageal Phase
Involuntary
The bolus is transported down the esophagus into the stomach during the esophageal phase
Swallowing involves peristaltic (wavelike) movement of the bolus through the esophagus