Organic Chemistry - Functional Groups/Hydrocarbons/Intermolecular Forces
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Alkane
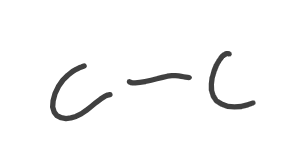
Alkene
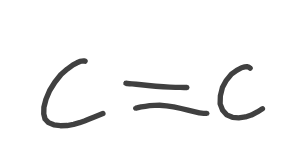
Alkyne
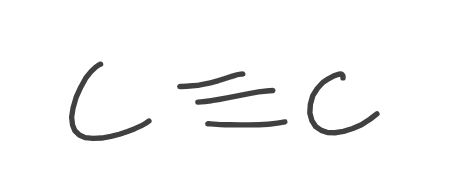
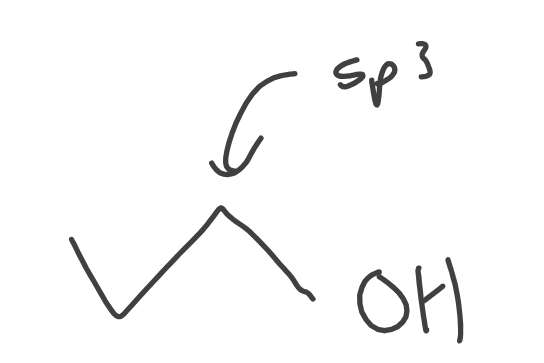
Alcohols
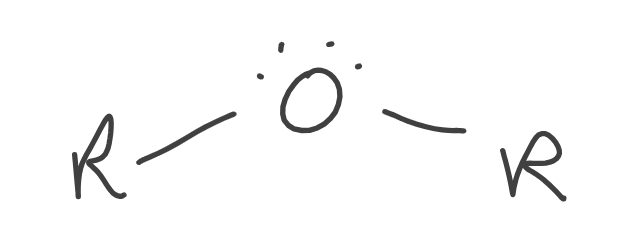
Ether
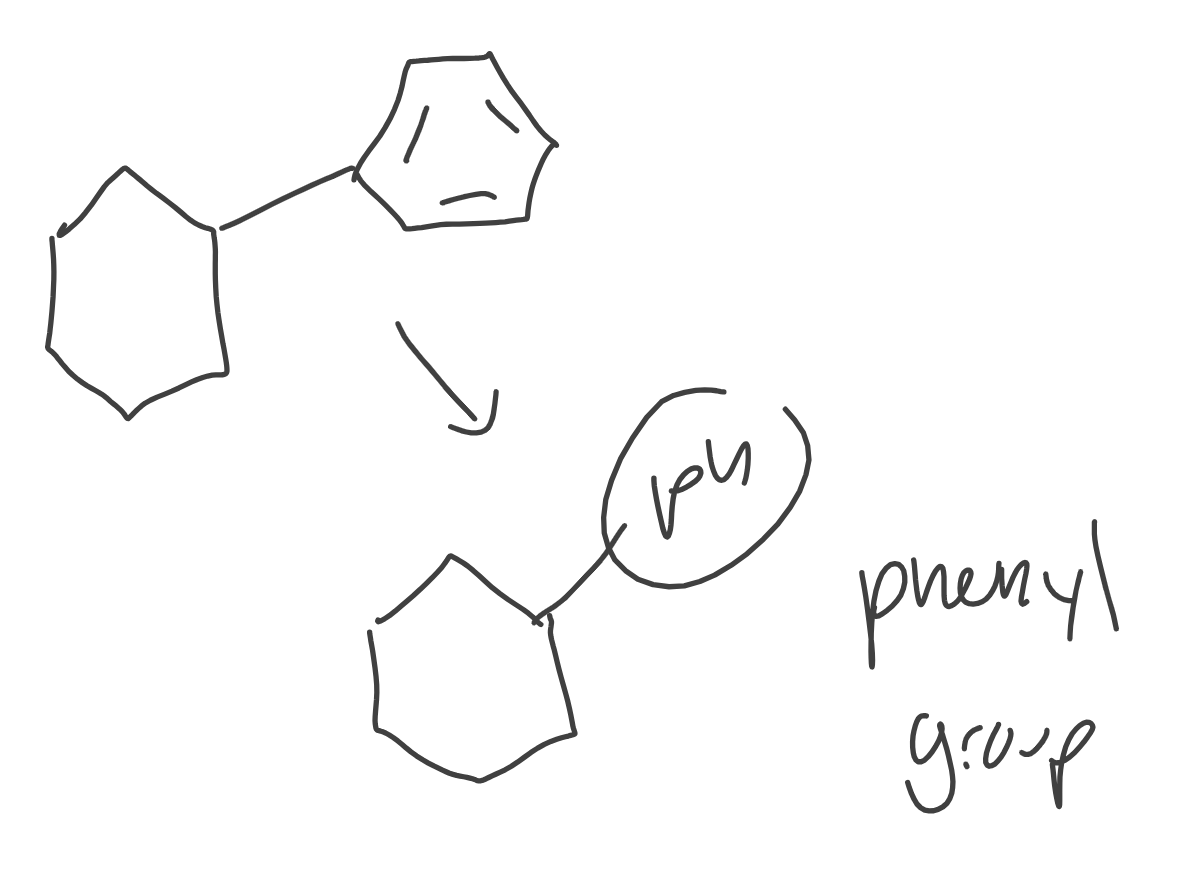
Phenyl Group
Alkyl Halides
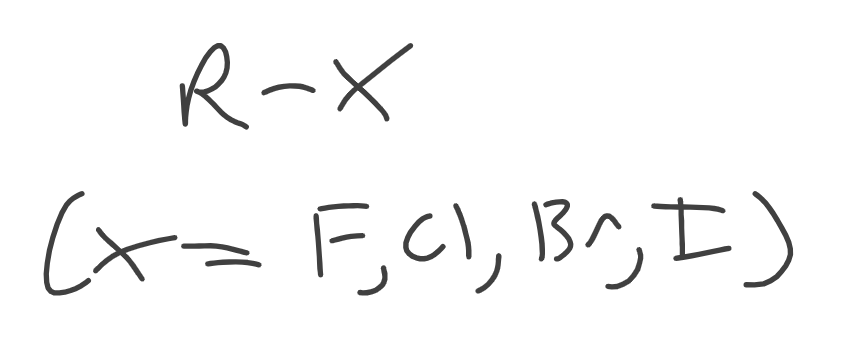
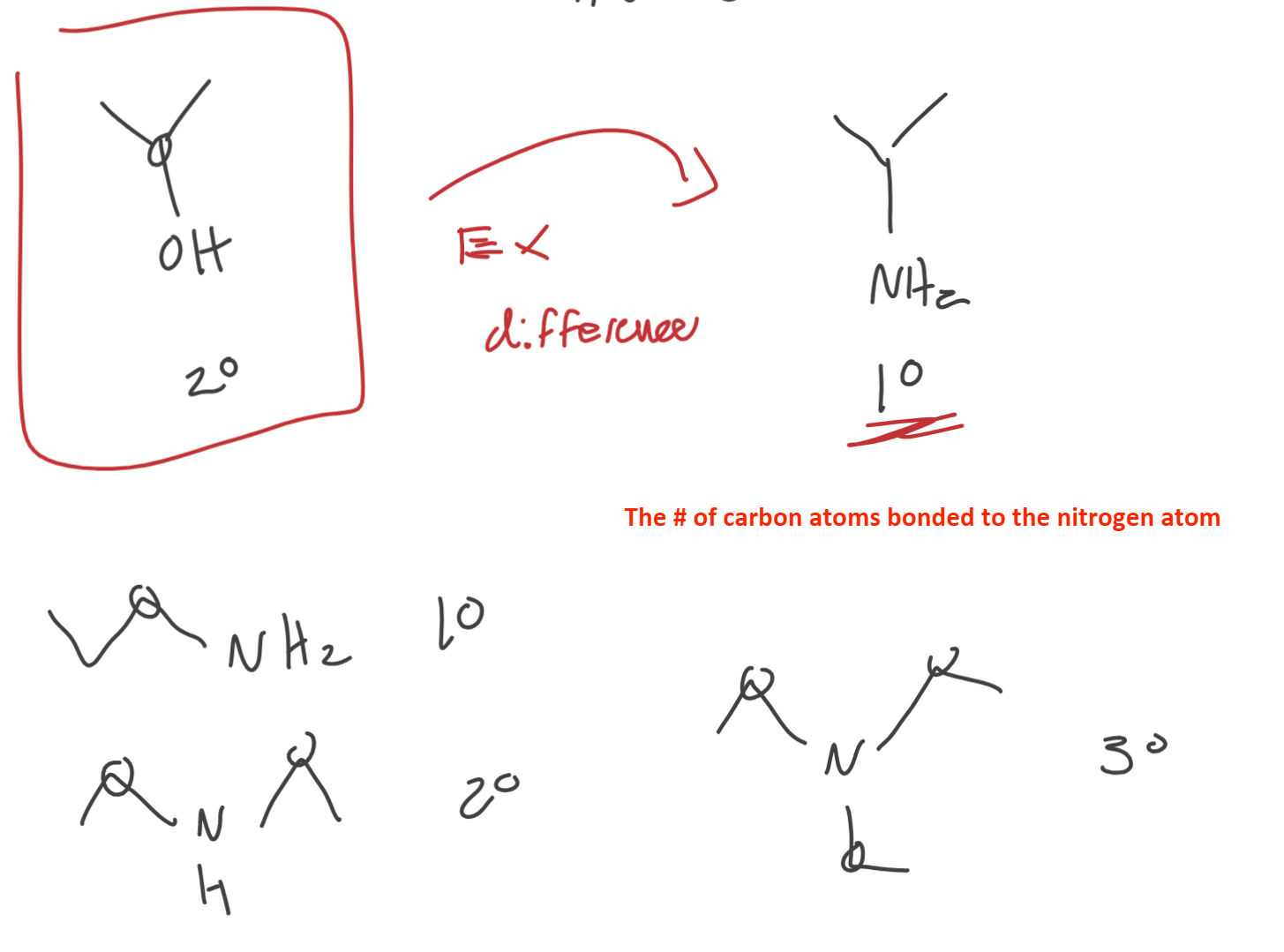
Amine
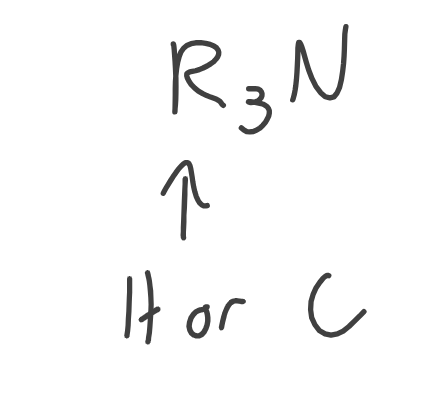
What’s special about amine?
It’s degree (1st, 2nd, 3rd) is based on the number of carbons BONDED to the NITROGEN atom.
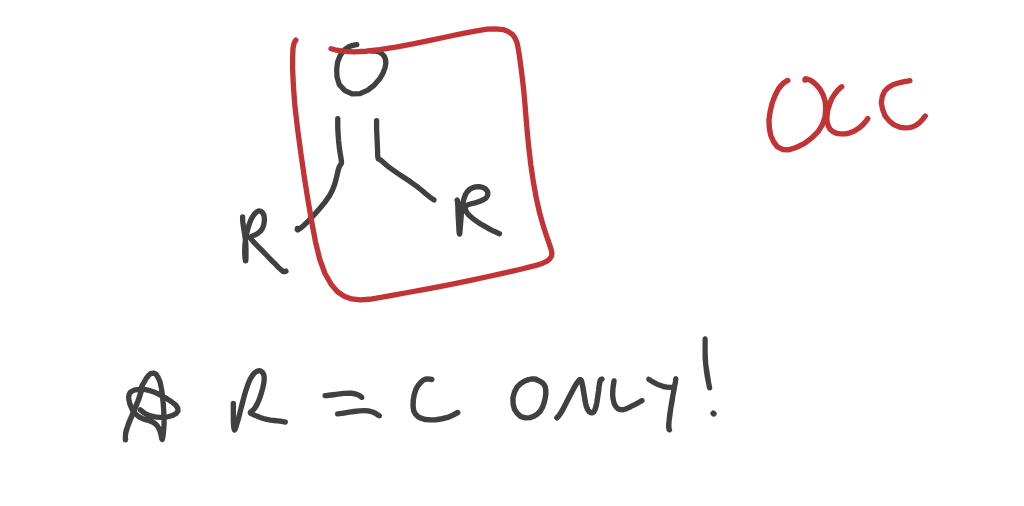
Ketones
R = C ONLY
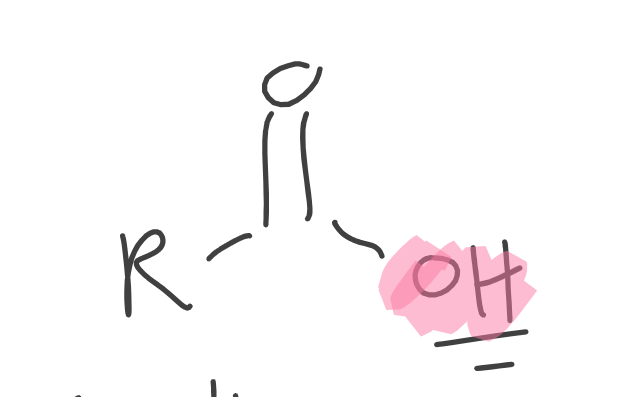
Carboxylic Acids
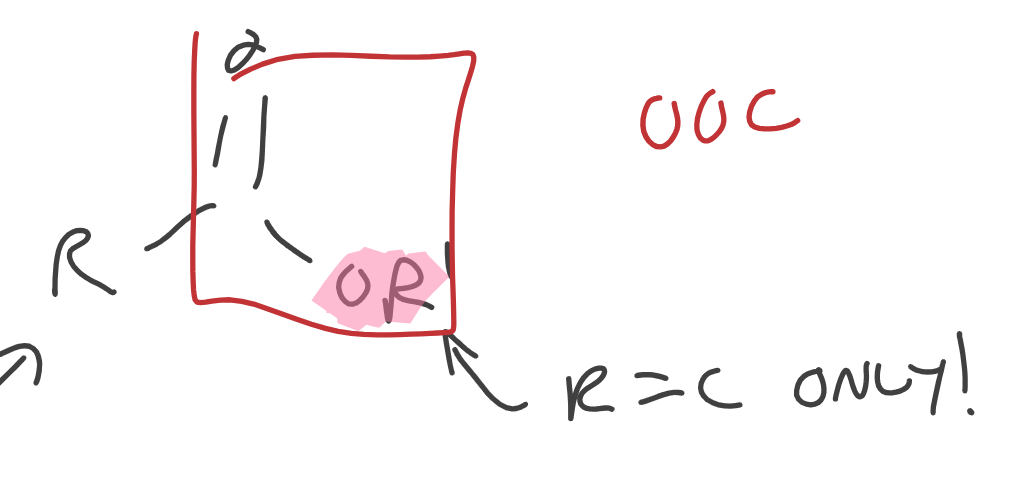
Esters
R bonded to O can ONLY be C
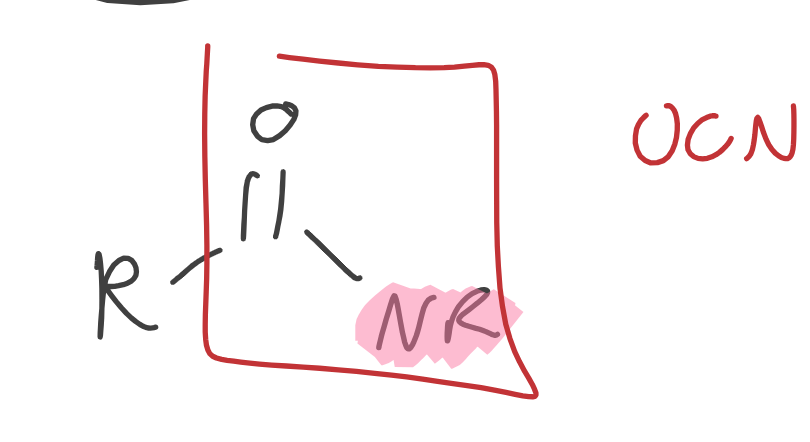
Amides
Contains Nitrogen
Aldehyde
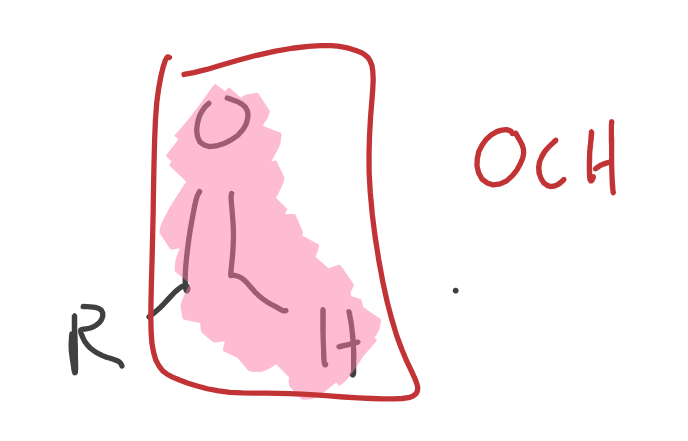
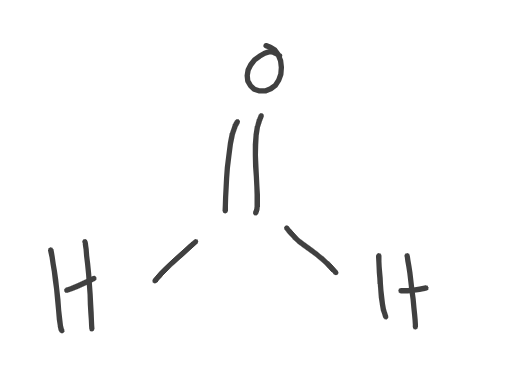
What is this Aldehyde?
Formaldehyde
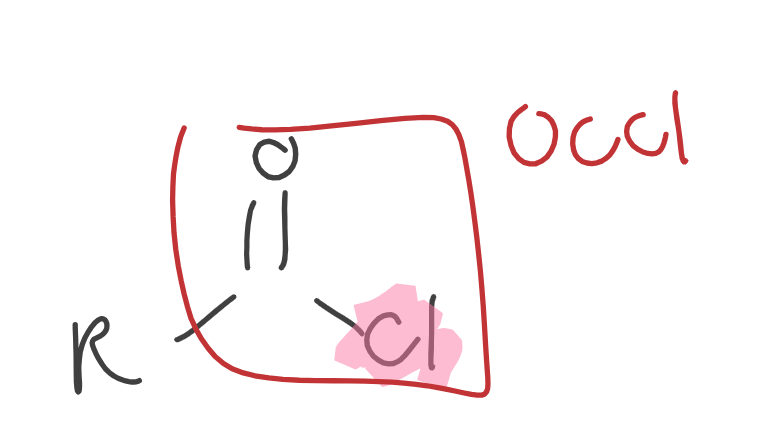
Acid Chlorides
R = C ONLY
Nitriles
Contains a triple bond C to N
R is sp³ hybridized only
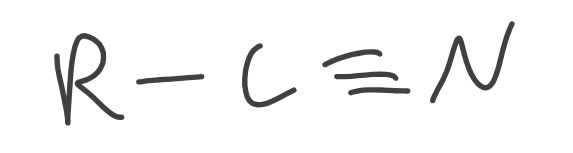
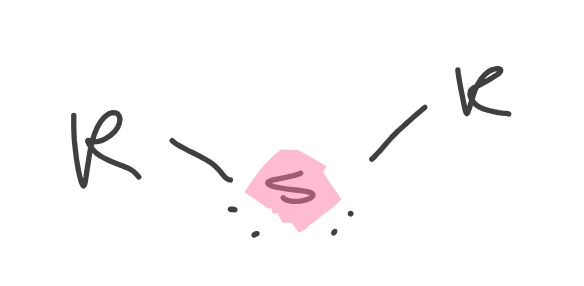
Sulfide
Contains sulfur
Van der Waals forces
Also called London forces
All compounds exhibit vdw forces
Strength depends on surface area
Ex: I2 > F2
Iodine is larger
Branched compounds are weaker than one long chained compound
Smaller chains are weaker than longer chains
Dipole-Dipole
Between two polar molecules
Stronger than vdw
Hydrogen Bonding
H is directly bonded to O, N, or F
Molecules that can hydrogen bond to other molecules like itself must have an N—H or O—H bond
Molecules that can hydrogen bond to water must have an O, N, or F bonded to an H with a lone pair