MCAT Biology: Renal and Digestive systems
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
major excretory organs
colon, liver, kidneys
colon function
eliminates solid waste (material that is not eaten but not absorbed into the blood)
liver function
Eliminates hydrophobic waste (material that is eaten and absorbed into the blood but too hydrophobic to dissolve in the plasma)
kidney function
Eliminate hydrophilic waste (material that is eaten and absorbed into the blood and dissolved in the plasma). Filters blood, regulates blood pressure, pH, osmolarity, volume and ion concentration.
main urinary organs
kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys
adrenal gland medulla secretes
epinephrine
The adrenal gland cortex secretes
cortisol and aldosterone (A cort)
smooth muscles in the urinary tract
ureter, bladder, urethra, and internal urinary sphincter
skeletal muscles in the urinary tract
external urinary sphincter
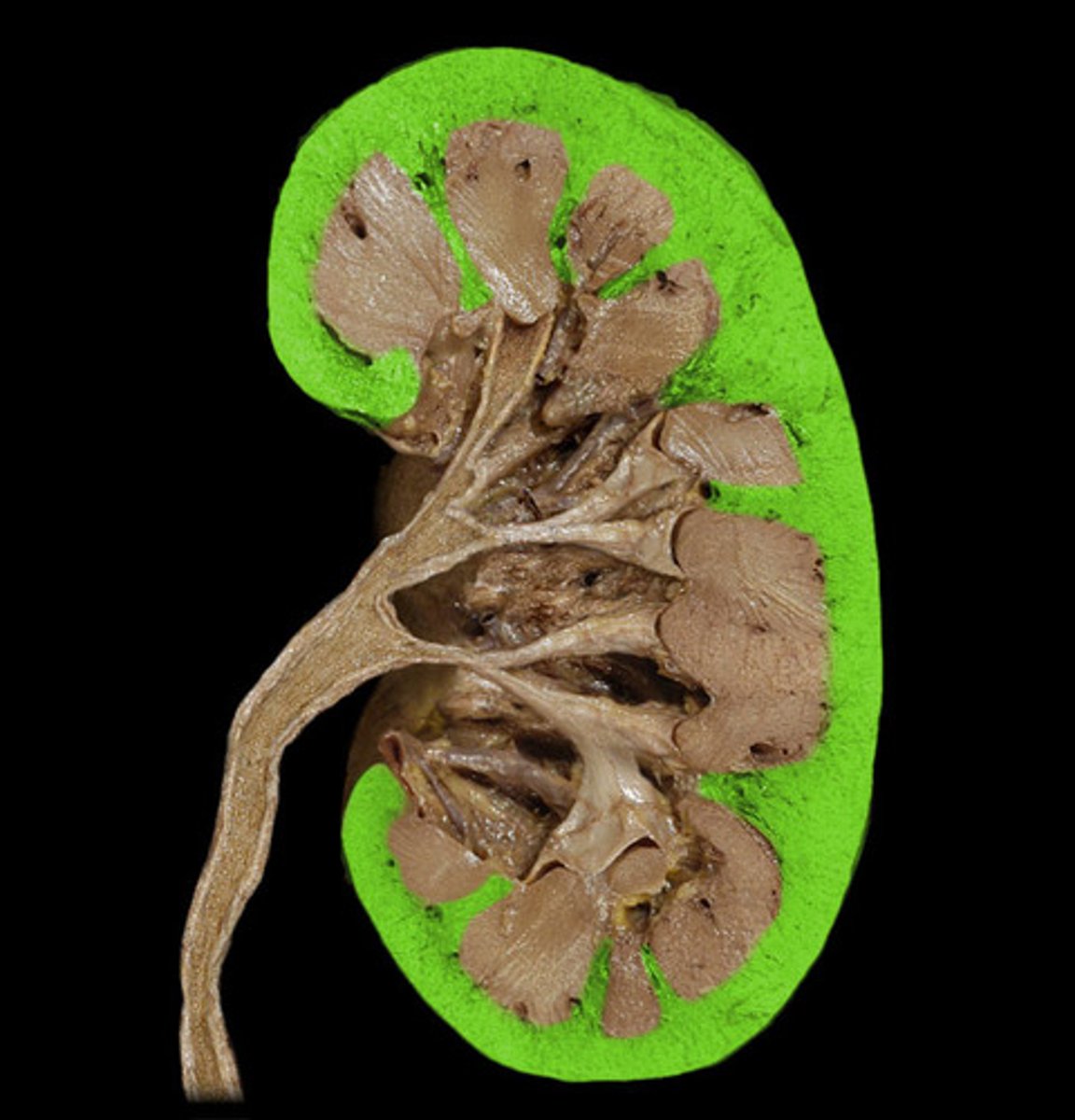
kidney cortex
outermost layer of the kidney that has a normal osmolarity
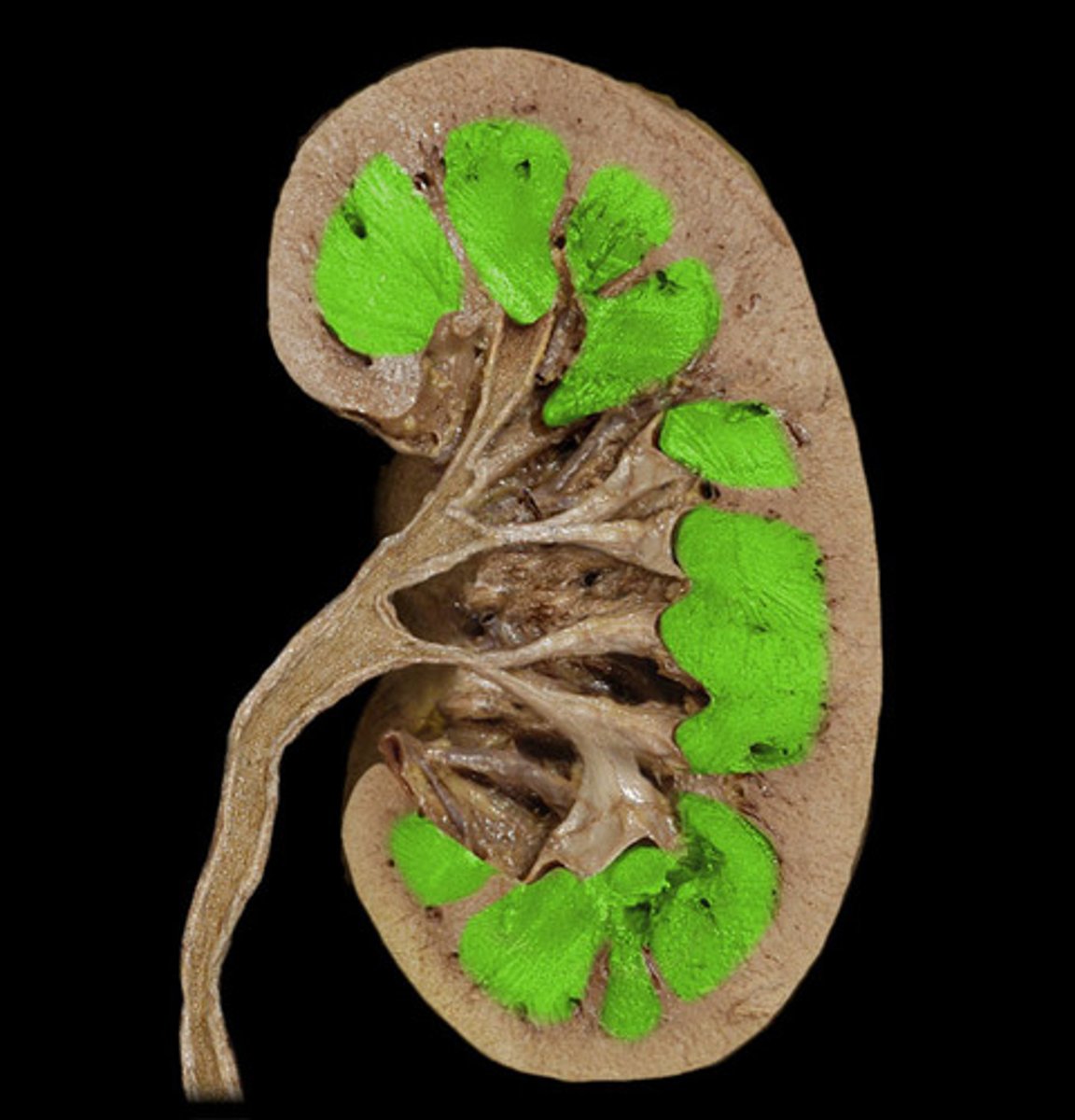
kidney medulla
The deeper region of the kidney contains the loop of Henle regions of the nephrons. Increasing osmolarity towards the center
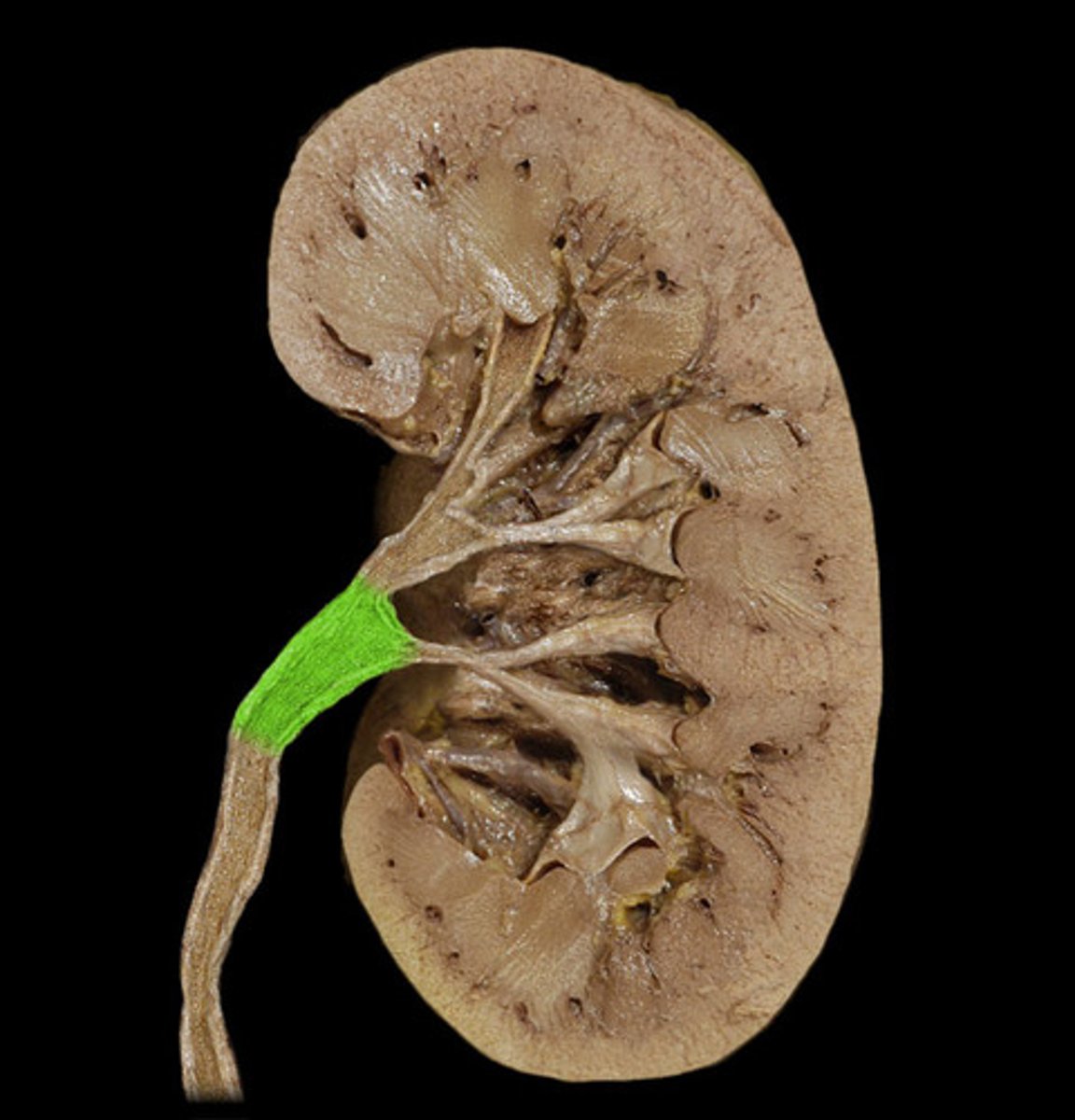
renal pelvis
central collecting region in the kidney
the three processes to produce urine
filtration, reabsorption, secretion
filtration
moving blood plasma across the glomerulus membrane using blood pressure
reabsorption
Move a substance (ions, bicarbonate, glucose, amino acids, water) from the filtrate to the blood
secretion
move a substance (drugs, toxins, creatine, protons, nitrogen waste) from the blood to the filtrate
afferent arteriole
The small artery that carries blood toward the capillaries of the glomerulus.
efferent arteriole
The small artery that carries blood away from the capillaries of the glomerulus.
glomerulus
a small network of capillaries encased in the upper end of a nephron, where the filtration of blood takes place
vasa recta
capillary bed that surrounds the nephron. all molecules reabsorbed or secreted are from the vasa recta
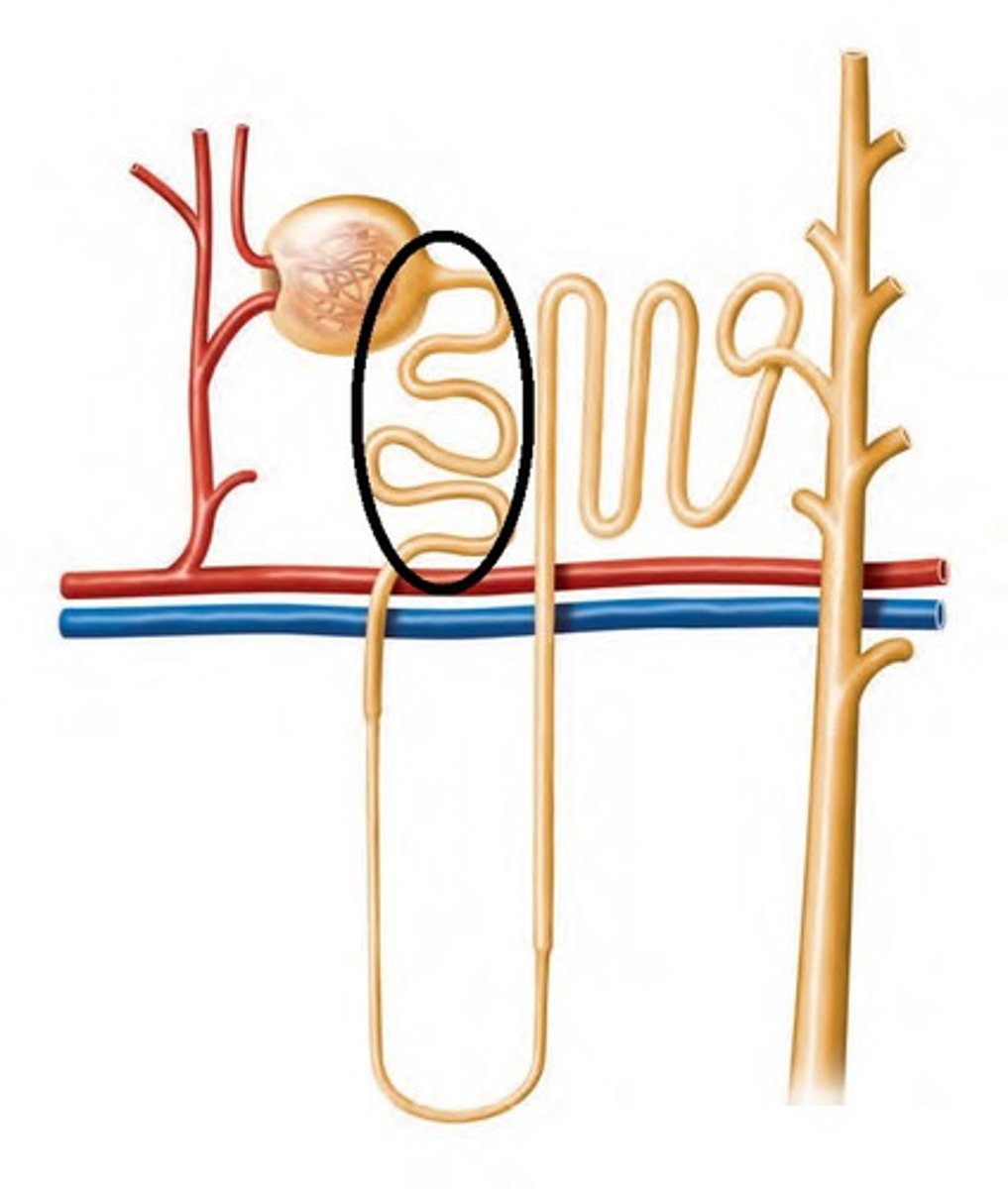
proximal convoluted tubule
The first section of the renal tubule that the blood flows through; reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients, as well as secretion of H+, nitrogen waste, and drugs.
descending loop of henle
The increasing osmolarity in the medulla causes water to exit the loop, increasing the osmolarity of the filtrate.
ascending loop of henle
Portion of the nephron not permeable to water. A filtrate flows up the ascending loop through a decreasing concentration of the medulla, salt (NaCl) is actively pumped out of the filtrate, decreasing the filtrate concentration
distal convoluted tubule
Between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct, Selective reabsorption and secretion occur, most notably to regulate the reabsorption of Ca2+
collecting duct
The portion of the nephron where water reabsorption is regulated via antidiuretic hormone (ADH); ADH levels = blood osmolarity
comparing urine and blood
Whatever is happening in the urine, the opposite is happening in the blood
Whatever is happening to volume, the opposite is happening to concentration/molarity
renin-angiotension system
If blood pressure falls, kidney secretes renin. Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. ACE converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II which causes systemic vasoconstriction and an increase in aldosterone release
aldosterone on blood pressure
increases the number of Na+/K+ ATPases in the nephron to increase blood osmolarity. ADH causes water reabsorption to increase blood volume and pressure.
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
contact point between the afferent arteriole and the distal convoluted tubule. The afferent arteriole is a baroreceptor and senses when pressure is low. The distal tubule is a chemoreceptor that senses when the filtrate is low and causes the release of renin and the dilation of the afferent arteriole.
ANP blood pressure regulation
High blood pressure causes the atria of the heart to stretch, causing the right atrium to release atrial natriuretic peptide. ANP causes vasodilation and inhibits renin and aldosterone release.
Kidney pH regulation
secretes H+ or reabsorbs bicarbonate to engage in the blood buffer system as needed
SNoW DRoP
Southern- DNA
Northern- RNA
Western- Protein
alimentary canal
digestive tube that extends from the mouth to the anus
accessory organs
feed into the alimentary canal
role of bile
EMULSIFICATION of fats. The breakdown of large lipid globules assists in their absorption
gallbladder function
store and concentrate bile and releases bile due to CCK release from small intestine
endocrine role of pancreas
to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
Exocrine role of the pancreas
releases bicarbonate, and various pancreatic digestive enzymes (proteases, lipases, etc.),
pancreatic protease activation
trypsinogen is activated by enterokinase produced by small intestine
mucosa
An innermost layer of the alimentary canal wall breaks down food and absorbs nutrients. Protection from harmful ingested products and produces mucus to lubricate.
submucosa
layer of connective tissue under the mucosa in the alimentary canal wall. Blood vessels absorb amino acids and sugars to deliver them to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. where lymph vessels absorb fats
enteric nervous system
The nervous system of the gastrointestinal tract. It controls secretion and motility within the Gi tract and is linked to the central nervous system.
circular muscle
layer of muscle around the alimentary canal wall that mixes food with digestive juices and segments them into bolus
longitudinal muscle
The outer layer of smooth muscle in the wall of the digestive tract. When the longitudinal muscle contracts the tube shortens (peristalsis)
peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
function of the mouth
mastication, taste food, form a bolus, lubrication
components of saliva
lysozyme: kill bacteria, amylase: startch digestion, lingual lipase: fat disgestion
function of the esophagus
Moves food from the mouth to the stomach. Begins as skeletal muscle then becomes smooth muscle
cardiac sphincter
at the connection between the esophagus and stomach that keeps food in the stomach. By the heart.
function of the stomach
store food and slowly release to small intestine, also to digest polypeptides into tri and di peptides.
gastric glands
Exocrine glands in the stomach wall that secrete gastric juice into the stomach. made up of mucus cells, parietal cells, and chief cells
pyloric sphincter
connects the stomach to the small intestine and regulates release
parietal cells
exocrine secretion of HCl into the stomach
chief cells
exocrine secretion of pepsinogen (further activated by HCl)
G cells
endocrine secretion of gastrin due to the presence of food. This increases the activity of salivary and gastric glands and increases the GI tract motility
function of the small intestine
break nutrients into monomers and absorbs them
regions of the small intestine
duodenum (first 5%), jejunum (middle 40%), ileum (last 55%)
surface area of the small intestine
HUGE due to plicae folds in mucosa, villus folds in the plicae and microvilli folds in the villus
enterokinase
exocrine secretion of the small intestine that triggers the activation of pancreatic proteases from the zymogen form (trypsinogen to trypsin)
brush border enzymes
exocrine digestive enzymes from the small intestine
enterogastrone
endocrine secretion of small intestine due to large meal and will slow digestion
CCK
endocrine secretion of the small intestine released to due to fats and triggers the release of bile from the gallbladder
Secretin
endocrine secretion of the small intestine that is released due to low pH and causes the pancreas to release bicarbonate.
function of the large intestine
store and form feces and reabsorb water when dehydrated
bacteria in the large intestine
The body's "natural flora" prevents the spread of bad bacteria. Produces 50% of vitamin K (for clotting) and gas
ileocecal valve
regulates the movement from the small to large intestine
internal/external anal sphincters
Regulate the release of feces. smooth/skeletal muscle control