CMSD 4010 Phonetics Exam 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Phonetics
study of perception of speech sounds
Language
a socially shared code that used arbitrary symbols and rule-governed combinations of symbols to represent ideas, thoughts, and feelings; comes from the mind
Speech
physical behavior that encompasses patterns of movement of speech structures and the pattern of acoustic vibration that these movements generate; comes from the mouth
Dialect
language & speech; different usage patterns of language; some more noticeable than others; confined to region or culture
Idiolect
a person’s own unique form of spoken language
What are some disorders that SLPs may encounter?
apraxia, aphasia, dysphagia, dysarthria, stuttering, developmental disorders, etc.
What are some developmental disorders?
ASD, Down Syndrome, Cleft Palate, Hard of Hearing/Deaf, speech sound disorders, language disorders, etc.
What are two speech sound disorders?
dysarthria and dysphagia
Morpheme
the smallest unit of language that carries meaning
Derivational morphemes
changes definition and/or part of speech; example: happy+ness
Inflectional morphemes
changes tense, number, comparison;-ed, -est, -s
8 inflectional morphemes
-ed (past tense)
-er (comparison)
-est (comparison)
-en (past perfect participle)
-ing (present tense)
-s (plural)
-’s (possessive)
-s (3rd person singular)
Free morpheme
carry a specific meaning when they appear alone
Bound morpheme
must be attached to other morphemes to produce a word with a specific meaning
Phoneme
a basic segment that has the linguistic functioning of distinguishing morphemes
Minimal pairs
differ by just one phoneme;
example: cat, mat, sat, fat, rat, bat
How many morphemes does ‘CATS’ have?
2
Syllable
a unit of speech that consists of one vowel or vowel-like element that may be accompanied by surrounding consonants
What 2 parts can syllables be broken into?
onset and rime
Onset
all the consonants before the vowel
Rime
the vowel & all the consonants after it
Rime can be split into what two parts?
-nucleus/peak
-coda
Nucleus
vowel-like element; the “peak”
Coda
consonants that come after the vowel
Grapheme
a letter or pattern that represents a single phoneme
Digraphs
-2 letters, 1 sound
-examples: ch, sh, th
Trigraphs
-3 letters, 1 sound
-examples: tch, dge
About how many graphemes are there?
250
Orthography
conventional spelling (i.e. with the alphabet)
About how many phonemes are there?
45
Free variation
can be exchanged for each other in a phonetics context
Complementary distribution
cannot be exchanged for each other in a phonetics context
Stress
the emphasis or prominence given to a syllable relative to other syllables
Primary stress
most emphasis
Articulators
-velum
-alveolar ridge
-mandible
-lips
-tongue
-vocal folds
Systems of speech sound production
-respiratory
-laryngeal
-subpharyngeal
What are the 3 cavities?
-oral
-nasal
-pharyngeal
What are the places of lingual articulation?
-interdental
-dental
-alveolar
-postalveolar
-palatal
-velar
-back
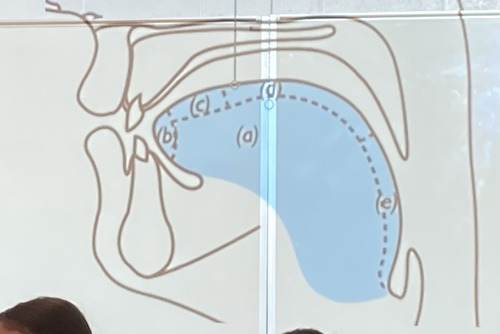
Name the parts of the tongue
a. body
b. tip (apex)
c. blade
d. dorsum
e. root
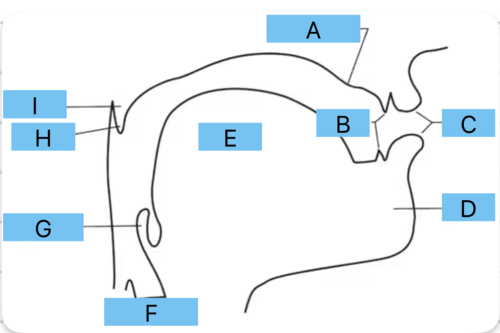
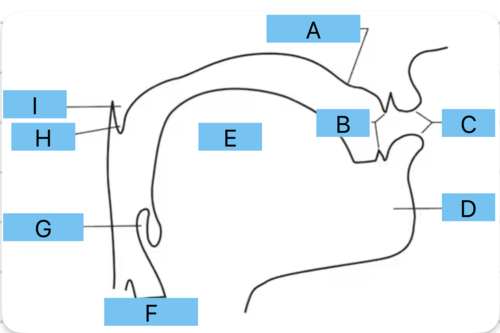
Identify a
alveolar ridge
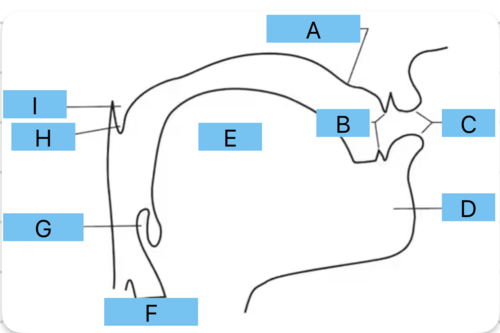
Identify b
teeth
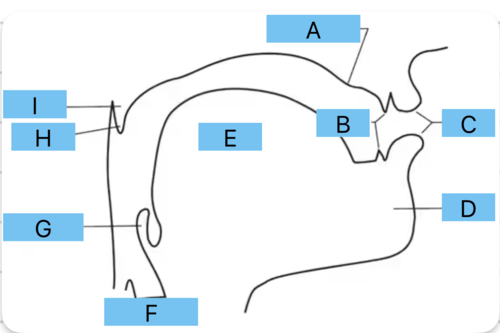
Identify c
lips
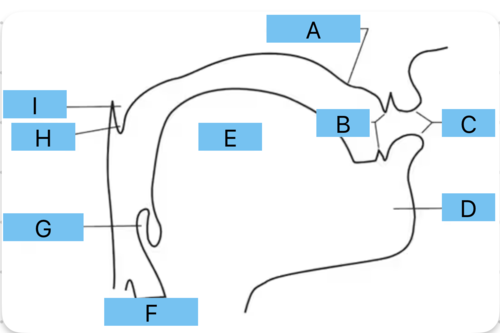
Identify d
mandible/jaw
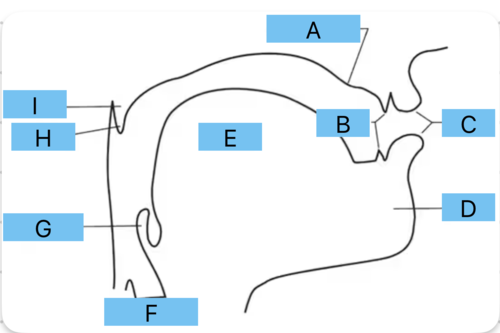
Identify e
tongue
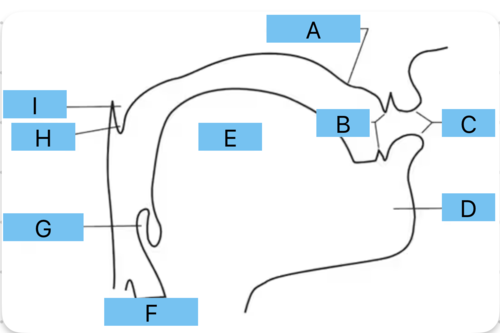
Identify f
vocal folds
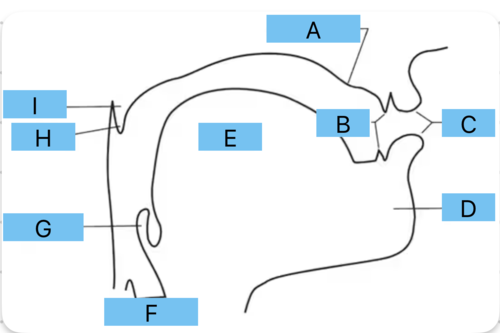
Identify g
epiglottis
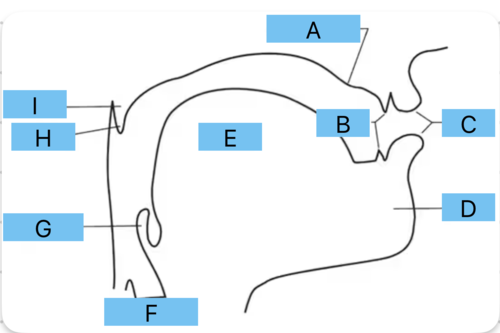
Identify h
uvula
Identify i
velum
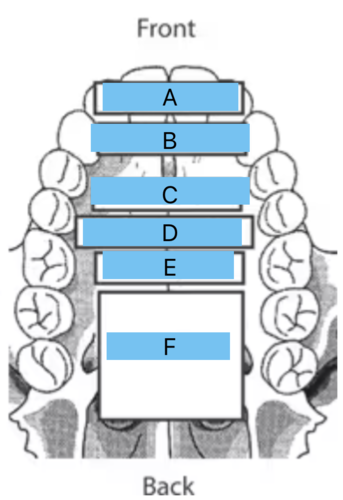
Identify all the places of articulation from A to F
a - interdental
b - dental
c - alveolar
d - postalveolar
e - palatal
f - velar
Graphemes
letters
Phonemes
sounds
Prevocalic
- used to indicate that a sound occurs before a vowel
- in the word ‘tub’, the /t/ sound is ____
Postvocalic
- indicates that a sound occurs after a vowel
- in the word ‘tub’, the /b/ sound is ____
Intervocalic
- a sound that occurs between two vowels
- in the word ‘alone’, the consonant represented by the letter ‘l’ is _____
What does IPA stand for?
International Phonetic Alphabet
A cvc syllable is composed of what?
- onset, nucleus, and coda
- tap
What is a CV syllable composed of?
- onset and nucleus
- to
Open syllables
syllables that end in a vowel, with no coda
Closed syllables
syllables that end in a consonant
Is ‘he’ and open or closed syllable?
open
Is ‘heat’ an open or closed syllable?
closed
Consonant clusters
sequences of consonants in a syllable