Chemistry Exam - Mixtures, Properties, Gravimetric Analysis
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
is hydrogen a metal, non metal or a metalloid
non metal
mnemonic to remember where the non-metals start
cats purr softly, enjoying, itchy, restful naps
do reactive elements exist as uncombined elements in nature?
no. for example reactive sodium is seen as NaCl but not by itself as Na
what is reactivity?
describes how readily an element reacts with another to form compounds
elements are reactive if they gain, donate or share electrons with other elements (so not noble gases)
what are the physical properties of a semi-metal/metalloid
they have some metallic properties and some non metal properties
what are the physical properties of a non-metal?
non malleable
non-ductile
dull in appearance
less dense than metals
poor conductor of heat and electricity
what are the physical properties of a metal?
hard
solid at room temp (except mercury)
high melting point
shiny
great conductor of electricity and heat (copper)
dense
ductile
malleable
what is the purpose of gravimetric analysis
determines the percentage of each element that makes up a specific compound
define ductile
ability for a material to stretch and bend into long, thin wires without breaking
define solubility
the ability of a solute to dissolve in a solvent to form a solution.
define viscosity
a substance resistance to flow
eg. water - low viscosity (flows very easily)
eg. honey - high viscosity (takes longer to come out of its bottle)
define malleable
ability to be changed into different shapes
what is melting point
the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid.
what is boiling point
the temperature at which a liquid boils and becomes vapour
define explosive
the ability to produce an explosion
define pyrophoric
has the ability to ignite when exposed to air
define combustibility
material that can catch on fire easily
define oxidiser
ability to strip an electron off another substance, gaining one for itself
define corrosive
the ability to destroy other substances in a chemical reaction
what is radioactivity (chemical property)
how the nucleus of an atom will change over time
what is flammability
how a substance will react in an open flame
list different chemical properties
flammability
reactivity
corrosive
oxidiser
combustible
toxicity
explosive
pyrophoric
chemical stability
what is a chemical property?
a change which can not be seen unless a reaction occurs. It is the breaking and forming of bonds
list different physical properties
melting point
boiling point
malleable
colour
smell
texture
density
solubility
ductile
viscosity
what is a physical property?
a property that can be observed, measured or a change of matter occurs (solid-liquid-gas)
Homogeneous mixture
A mixture with uniformly distributed properties, where components are evenly combined. can mix together
Heterogeneous mixture
A mixture composed of non-uniformly distributed components which are unevenly combined. can not mix together
Solutions
Homogeneous mixtures in which the dissolved particles are invisible to the naked eye, consisting of one solvent and at least one solute.
Solvent
a substance present in higher concentrations that dissolves a solute to form a solution.
Solute
The substance present in lower concentrations that dissolves in a solvent to form a solution.
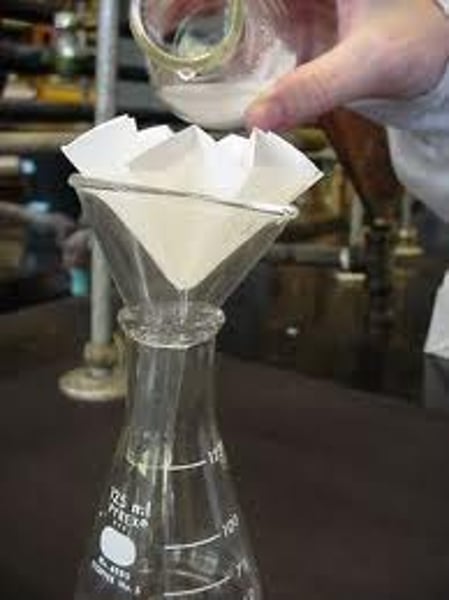
Filtration
A separation technique where solids are separated from fluids using a filter that allows fluid to pass but solid particles to hold
separates insoluble substances from soluble substances

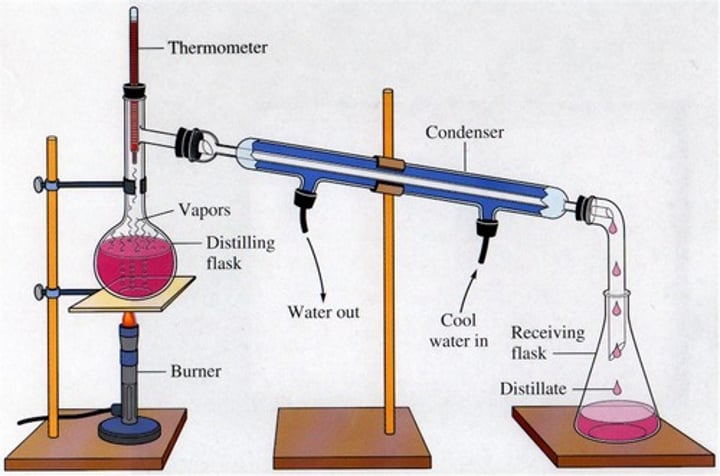
Distillation
A separation technique where two miscible liquids are separated by their boiling points, often used to turn saltwater into fresh water.
- one component turns into gas and is cooled back into a liquid using a condenser
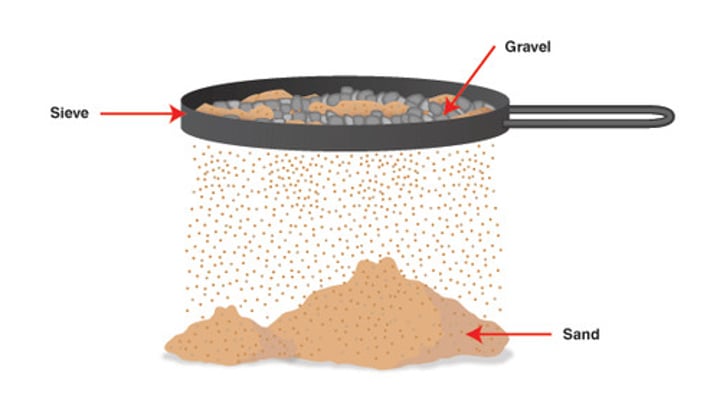
What method would be utilised to separate gold and sand?
A heterogeneous mixture of gold and sand, physically separable using a sieve due to uneven combination of components.
What method would be utilised to separate seawater?
The process of using distillation to separate salt and water in a homogeneous mixture.
what is a mixture?
two or more elements or compounds that are physically bonded but not chemically combined, thus can be separated
what are the similarities between a homogenous mixture and a heterogenous mixture
- both are types of mixtures
- both are physically bonded
- can be separated using physical separation techniques
define physical change
a change of matter from one form to another without a change in chemical properties
what are examples of a physical change?
- changing between a solid, liquid or gas
- physically separating components
- dissolving
- precipitating
Sieving
A separation technique where particles are separated by size. a sieve is used to separate the smaller particles
Density
mass/volume
Name one example of objects having the same mass but different densities
a 1kg textbook has the same mass as 1kg of feathers. When they are both thrown into the ocean, the book will sink and the feathers will float as they both have different densities.
Sedimentation
process of heavier solid particles settling to the bottom of the container.
- separates solids from liquids
- less dense at the top, more dense at the bottom
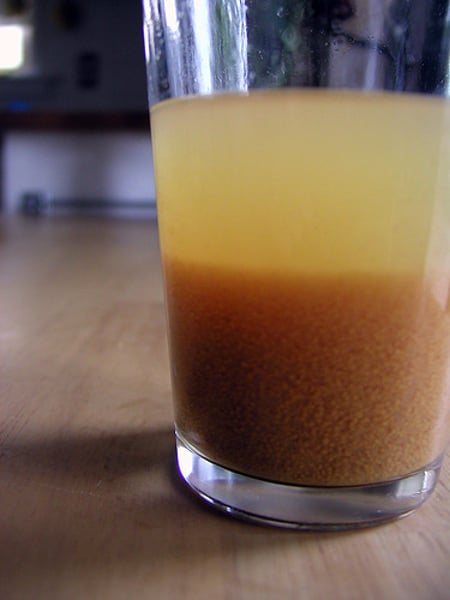

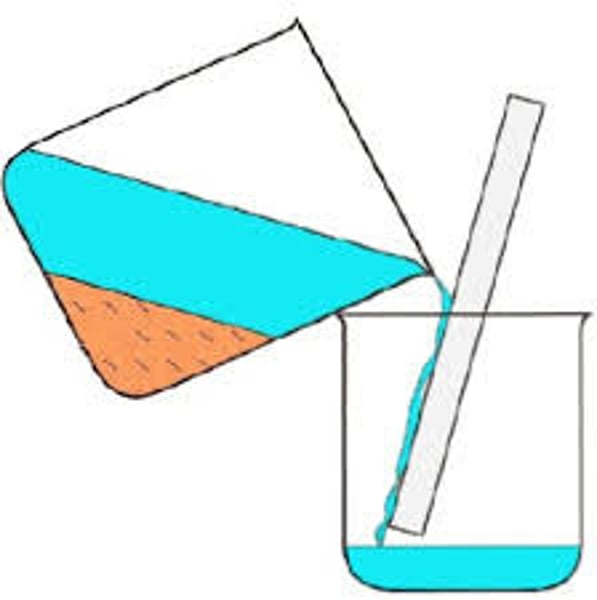
Decantation
A method of separating solid insoluble particles from a liquid by leaving the particles to settle and pouring off the liquid.
define miscibility
the ability of a liquid solute to dissolve in a liquid solvent. forms a homogeneous mixture
define immiscible
the inability of two liquids in each other regardless of the proportions they are mixed in. forms a heterogenous mixture
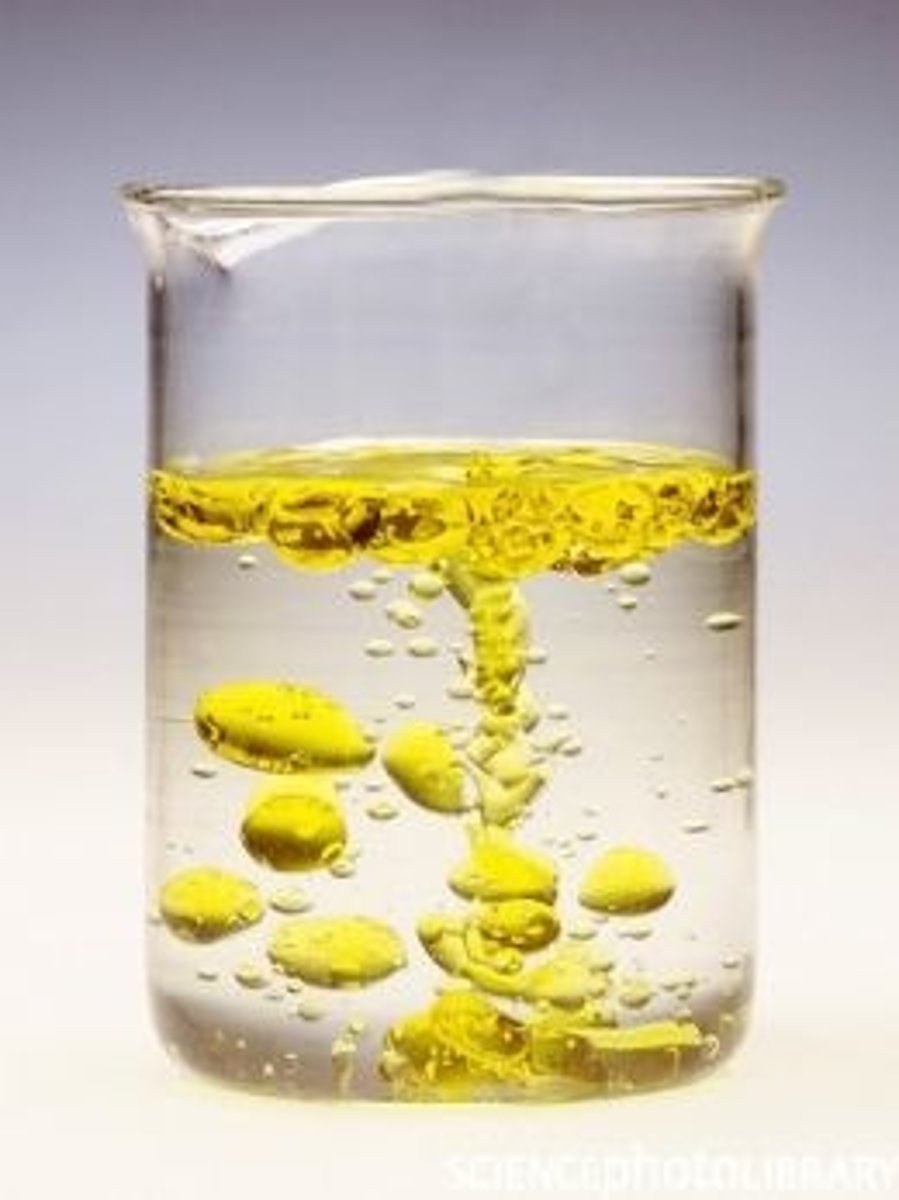

provide an example of a miscible mixture
salt and water
provide an example of a immiscible mixture
oil and water
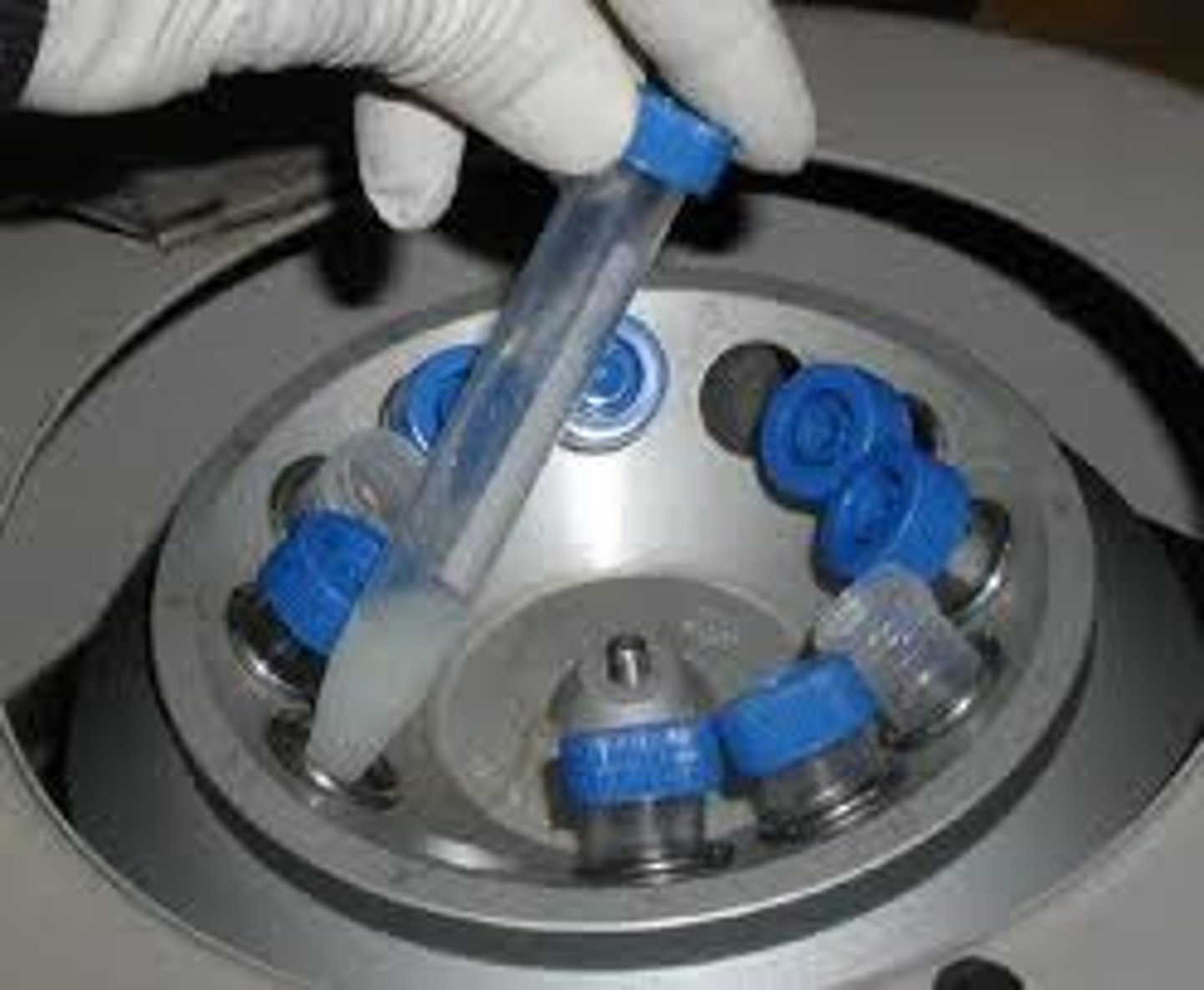
Centrifugation
process of separating out particles of different sizes and densities by spinning them at high speed in a centrifuge.
- like sedimentation but faster
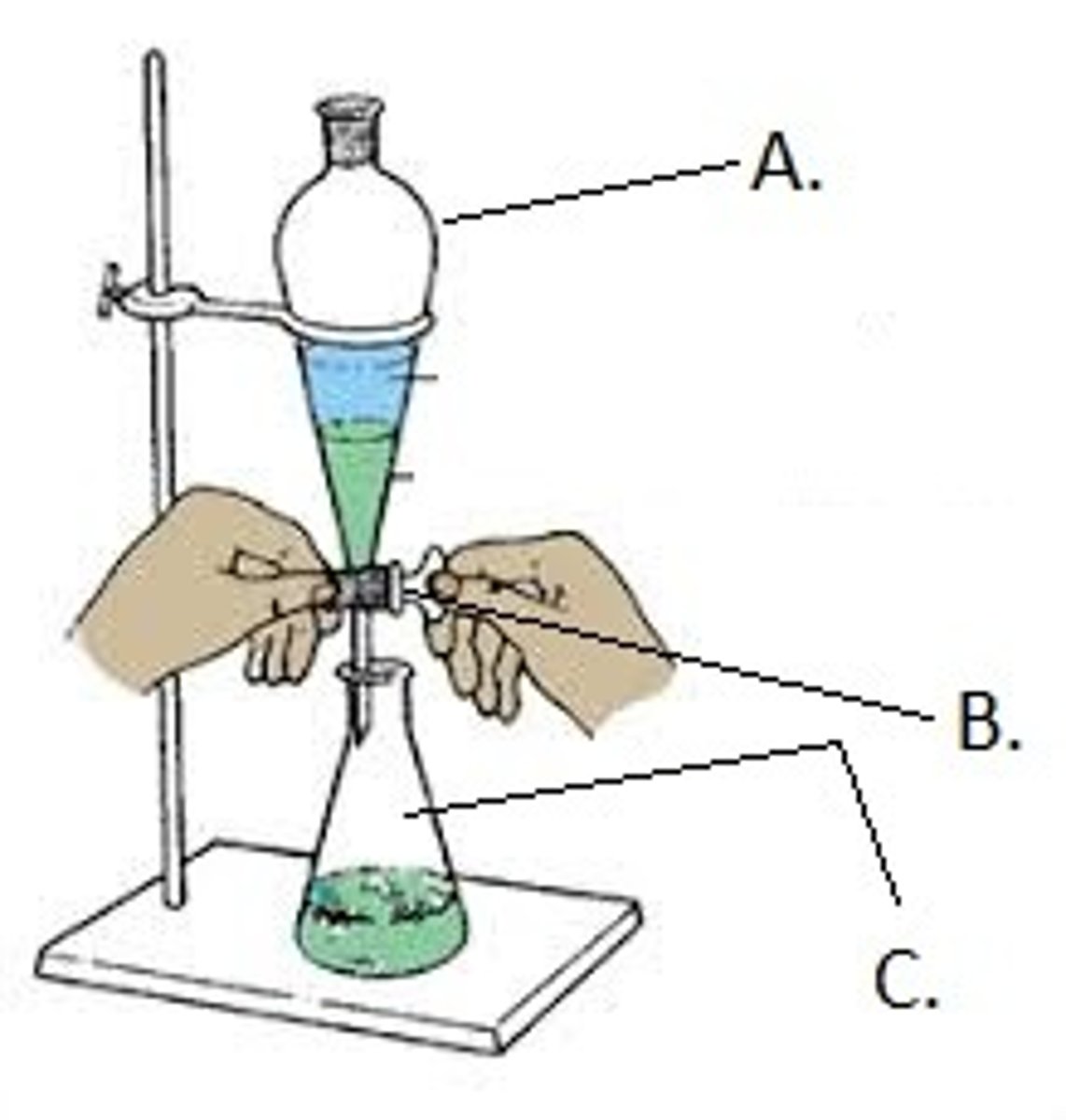
Separation Funnel
lab glassware that separates two immiscible liquids of different densities
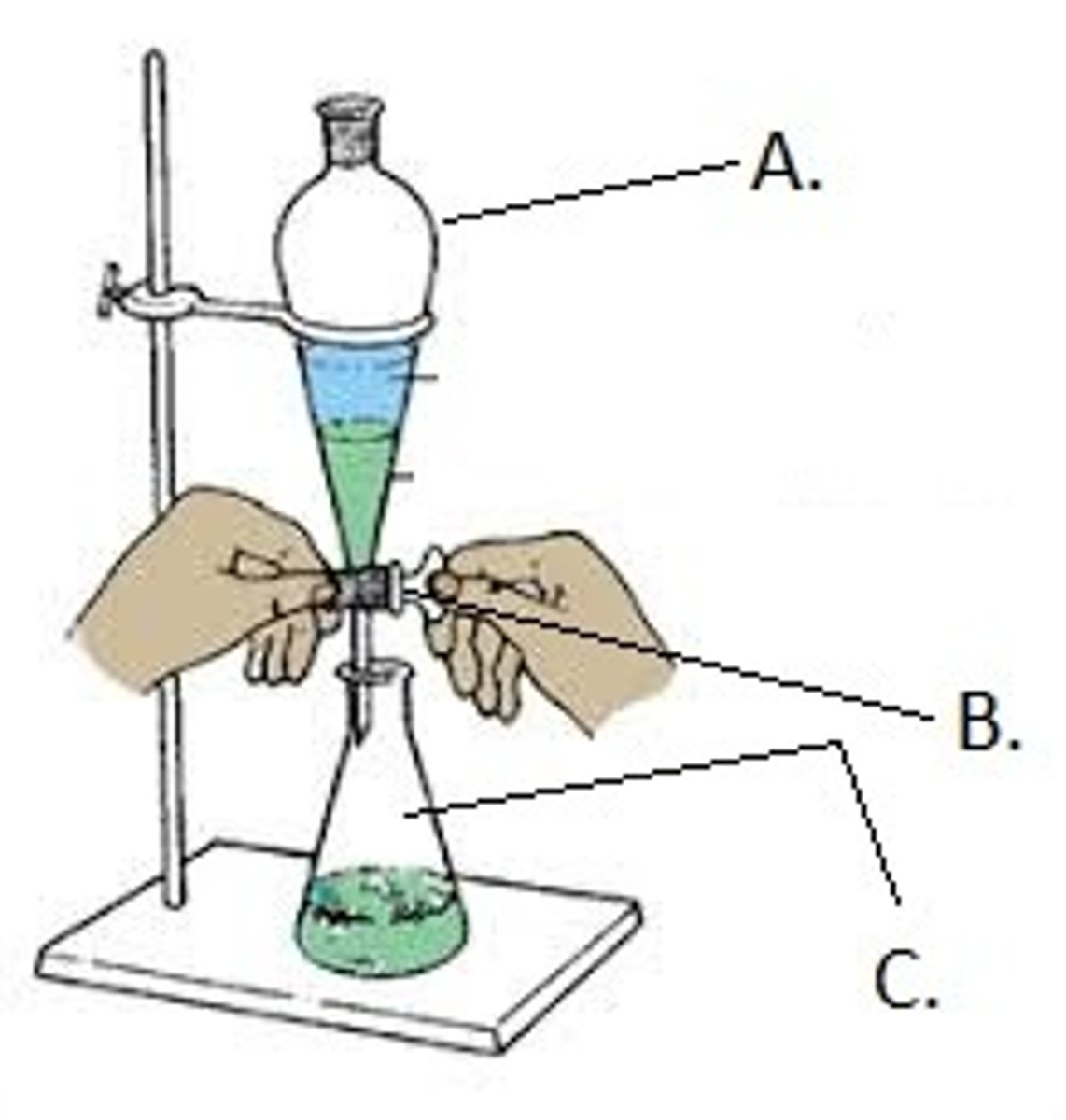
what steps are taken to use a separation funnel
1. pour mixture
2. shake mixture
3. leave to settle (dense liquid will settle to the bottom, less dense liquid will float to the top)
4. the denser liquid is then dripped out by a tap, leaving the less dense liquid in the funnel
Melting Point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid, or a liquid to solid (freezes)

Boiling Point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas

Freeze Concentration
Separation technique that depends on a difference in melting point. The temp of the mixture is put below melting point for only ONE component. one substance freezes, the other remains a liquid
Evaporation
separation technique where a mixture is heated so that one component is turned to a gas
(commonly used when there is a large difference between boiling points of a soluble solid and a liquid in a mixture)
Name one difference between evaporation and distillation
- evaporation is used to collect the substance that does not evaporate (stable)
- distillation is used to collect the substance that evaporates easily (volatile)