Ch 4 - Information Gathering: Interactive Methods
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Interviewing. What kinds of information should be sought in interviews?
An info gathering interview is a directed conversation with a specific purpose that uses a question and answer format
Get opinions of interviewee and feelings about the current state of the system, organizational and personal goals, and informal procedures for interacting with information technologies
SEEK OPINIONS
CAPTURE FEELING
GOALS PROJECT FUTURE
HCI CONCERNS
Five Steps in Interview Preparation
1) Reading Background Material
Corporate web, annual report, newletter or publications
Optomize time you spend in interviews
2) Establishing Interviewing Objectives
4-6 key areas concerning HCI, info processing, and decision making behavior about which you will want to ask questions
Usefulness of system, how it fits in physical aspects, how it suits users’ cognitive capabilities, engaging, system is rewarded, information sources, formations, etc
3) Deciding Whom to Interview
People at all levels
4) Preparing the Interviewee
Call ahead and allow interview time to think about the interview
Email questions ahead of time to allow the interviews time to think over their responses
Zoom, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams, etc
5) Deciding on Question Types and Structure
Open and closed questions, Probes
Pyramid, funnel, and diamond structure
List two popular video-conferencing platforms. What is “Zoom fatigue”?
Two video conferencing options are Google Meet and Zoom. Zoom fatigue is that overusing video conferencing can lead to exhaustion in unexpected ways. In person and online meetings should be kept 45 minutes.
Question Types
Open Ended
Those such as “What do you think about putting all the managers on an intranet?”
Option is open
Closed Ended
Closed responses
Dichotomous closed question
This type of question limits the interviewee even further by allowing only a choice on either pole (yes/no,true/false)
Probes
The purpose of a proble is to go beyond the inital answer to get more meaning, to clarify, and to draw out and expand on the interviewwe’s point
Open-Ended Questions. List eight benefits and five drawbacks of using them? When are open-ended questions appropriate for use in interviewing?
Benefits:
1) Puts the interviewee at ease
2) Allowing the interviewer to pick up on the interviewee’s vocabulary, which reflects
3) Providing richness of detail
4) Revealing avenues of further questioning that otherwise may go untapped
5) Making the interview more interesting for the interviewee
6) Allowing more spontaneity
7) Making phrasing easier for the interviewer
8) Using them in a pinch if the interviewer is caught unprepared
Drawbacks:
1) Asking questions that may result in too much irrelevant details
2) Possibly losing control of the interview
3) Allowing responses that may take too much time for the amount of useful information gained
4) Potentially seeming that the interviewer is unprepared
5) Possibly giving the impression that the interviewer is on a “fishing expedition,” with no real objective for the interview
Define what is meant by closed interview questions. List six benefits and four drawbacks of using them. When are closed-ended questions appropriate for use in interviewing?
Benefits:
Saving Time
Easily comparing interviews
Getting to the point
Keeping control over the interview
Covering lots of ground quickly
Getting to relevant data
Drawbacks:
Boring for the intervieww
Failing to obtain rich detail
Failing to address the main ideas for the preceding reason
Failing to build rapport between interviewer and interviewee
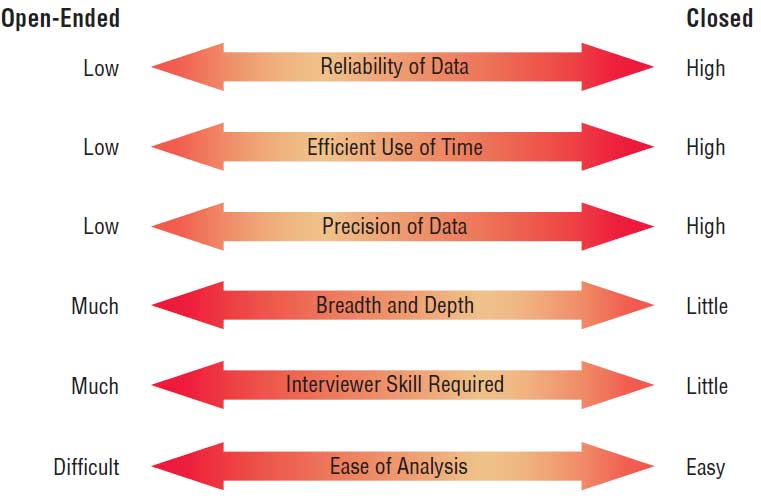
What is a probing question? What is the purpose of using a probing question in interviews?
Probes allow a systems analyst to follow up on questions to get more detailed responses. These examples were selected from different interviews and are not shown in any particular order
Arranging Questions in a Logical Sequence
Using a pyramid structure
Using a Funnel structure
Using a diamond-shaped structure
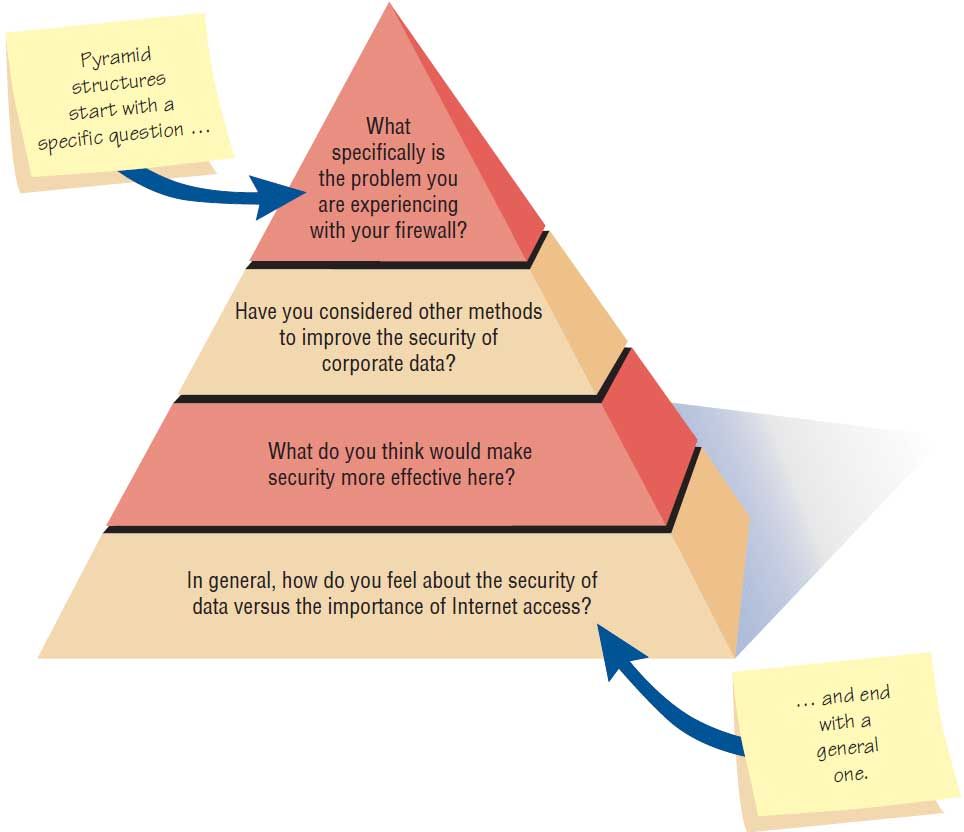
Define what is meant by pyramid structure. When is it useful to employ this structure in interviews?
Interview begins with very detailed, often closed, questions. The interviewer then expands the topics by allowing open-ended questions and more generalized responses.
Uses
Interviewee needs to warm up to the topic
Ending determination about the toic
Define what is meant by funnel structure. When is it useful to employ this structure in interviews?
Begins with generalized, open-ended questions and then narrowing the possible responses by using closed questions. The interview structure can be thought of as funnel shaped, as depicted
Uses
Easy, nonthreatening way to begin an interview
When interviewee feels emotional about the topic and needs freedom to express those emotions
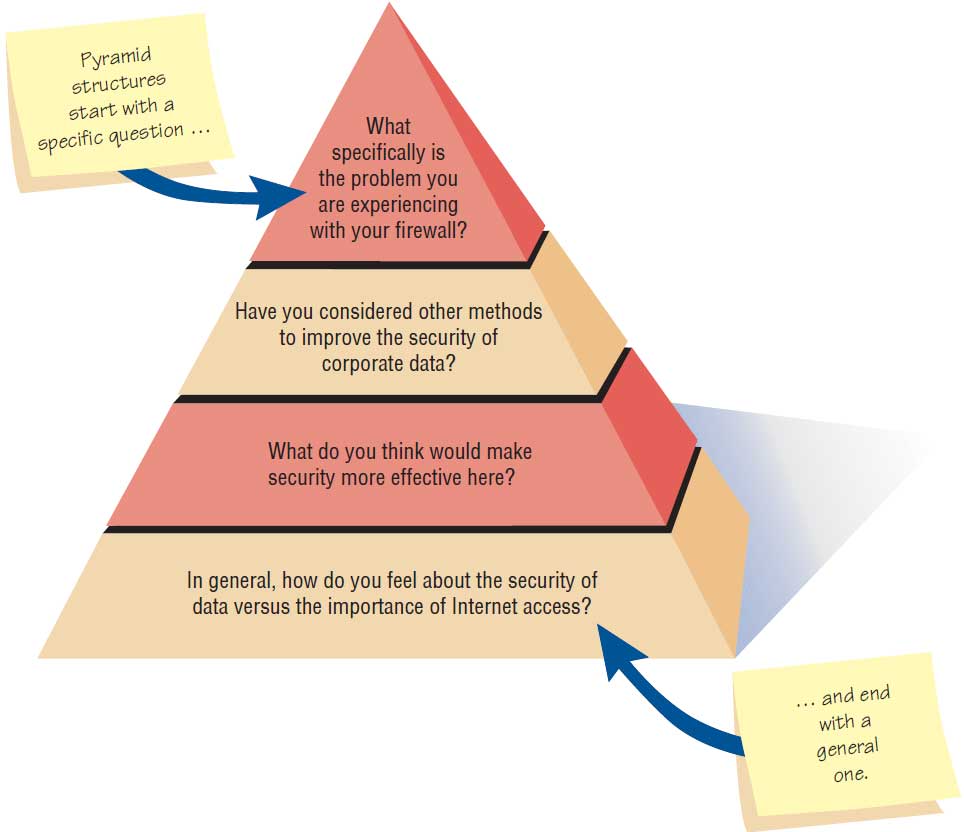
Define what is meant by diamond-shaped structure. When is it useful to employ this structure in interviews?
This structure entails beginning in a very specific way, then examining general issues, and finally coming to a very specific conclusion
Uses:
combines the strengths of the other two approaches but has the disadvantage of taking longer to implement than either other structure
Summarize and provide feedback on your overall impressions
Inform the interviewee about the subsequent steps to take and what you and other team members will do next.
Ask the interviewee with whom you should talk next
Writing the Interview Report
Written ASAP, Better quality data
Note main points and own opinions
Follow up meeting review the report
Listening to Stories. What are seven elements common to stories told by users in the organization?
Stories are made up of elements
Reasons for telling stories
1) The call to adventure
Problem stats with a reason an opportunity was noticed or problem needed addressing
2) The quest
There is something worth finding or achieving
3) The struggle
Who the storyteller names as villains
Obstacles
4) The transformation
Storyteller reveal their own weaknesses. The storyteller describes overcoming this weakness
5) The resolution
6) The Moral
Tells others how to behave
7) The epilogue
What are the four reasons users tell stories to analysts?
Experiential stories
Describe what life is like in the org
Explanatory stories
Suggest that there is an explanation for behavior or a reason for the decisions made
Validating stories
Convince people that the org made the correct decision, or they are used to express and maintain the existing values of the org
Prescriptive stories
Childhood fables, suggest how everyone in the org should behave
Define joint application design (JAD).
Focus group. Technique that allows analyst to accomplish requirements analysis and design the user interface with the in a group setting
Cut time required for personal interviews
improve the quality of the results of information requirements assessment
Create more user identification with IS as a result of the participative processes
Who is Involved?
Analysts, users, executives
Outside management consultant to serve as a session leader
Observes who are analysts or techical experts
Where?
2 to 4 day sessions off-site
Executive centers
Group decision support facilities that are available at major universities
Video call
List the situations that warrant use of JAD in place of personal organization interviews. (Conditions that support the use of JAD, Who is Involved?)
User groups are restless and want something new, not a standard solution to a typical problem
The org culture supports joint problem-solving behaviors among multiple level of employees
Forecaast that the number of ideas generated via one-on-one interviews will not be as plentiful as the number of ideas possible from ann extended group exercise
Org workflow permits the absence of key personnel during. two-to four day block of time
List the potential benefits of using JAD. List the three potential drawbacks of using JAD as an alternative to personal interviews.
Benefits:
Time savings over traditional one-on-one interviews
Rapid development
Weigh the possibility of improved ownership of the IS (users involved early in systems projects)
Creative development of designs
Drawbacks:
Commitment of large block of time from all participants (2-4 day commitment)
Preparation for the JAD sessions is inadequate in any regard or the followup report is incomplete
Necessary organizational skills and org culture may not be sufficiently developed
Using Questionnaries. What kinds of information is a systems analyst seeking by using questionnaires or surveys?
Definition:
Info gathering technique that allows system analysts to study attitudes, beliefs, behavior, and characteristics of several key people in the organization who may be affected by the current and proposed systems
Planning for the Use of Questionnaires
1) Decide what you are attempting to gain through using a survey
2)Questionnaire better for quantifying vs Interviewing in depth analysis
Uses
People widely dispersed
Many ppl involved
Exploratory study
Certain about problems
Writing Questions
Open-Ended
Opinions
Closed
list all possible responses to ?
large sample
Word Choice
Using Scales in Questionnaires
Measurement
Validity and Reliability
Constructing Scales
List four situations in which the use of questionnaires is appropriate.
Designing Questionnaires
Question Order
List two reasons a systems analyst would use a closed question on a questionnaire.
List two reasons a systems analyst would use an open-ended question on a questionnaire.
Open-Ended
Opinions
When it’s impossible to list effectively all possible responses
When exploratory situation occurs
Closed
list all possible responses to ?
large sample
What are the two basic question types used on questionnaires?
Closed
Open
What are the seven guidelines for choosing language for a questionnaire?
Use language of respondents whenever possible. keep wording simple
Be specific
Keep questions short
Do not patronize respondents by talking down to them through low-level language
Avoid bias
Target questions to correct respondents
Ensure questions are accurate
Use software to check if reading level is appropriate
Define what is meant by scaling. What are two kinds of information or scales that systems analysts most commonly use?
The process of assigning number sor other symbols to an attribute or a characteristic for the purpose of measuring the attribute or characteristic
Nominal scales
Interval scales
What are nominal scales used for?
Used to classify things. A question such as the following uses a nominal scale:
What type of software do you use the most?
1 = a word processor
2 = a spreadsheet
3 = a database
4 = an email program
Give an example of an interval scale.
When should an analyst use an interval scale?
Examples are the farenheit and celsius scales
Intervals between each pair are equal, analyst should assume that the respondent perceives the intervals to be equal when they respond to this question:
Define reliability as it refers to the construction of scales.
Measures consistency
External consistency
Internal consistency
Define validity as it refers to the construction of scales.
Degree to which a question measures what the analyst intends for it to measure
Does it measure that?
List three problems that can occur because of careless construction of scales.
Leniency
Respondents who are easy raters
Central tendency
Problem that occurs when respondents rate everything as average
Halo effect
What four actions can be taken to ensure that a questionnaire’s format is conducive to a good response rate?
A. Allowing ample white space
B. Allowing adequate space for responses
C. Asking respondents to circle their answers
D. Using objectives to help determine format
Which questions should be placed first on a questionnaire?
Questions of importance to respondents go first.
Why should questions on similar topics be clustered together?
Similar topics should be clustered together to build a frame of reference for respondents.
What is an appropriate placement for controversial questions?
Controversial questions should be positioned after less controversial questions.
Administering Questionaries. List five methods for administering a questionnaire.
A. Convening all concerned respondents together at one time
B. Personally handing out blank questionnaires and taking back completed ones
C. Allowing respondents to self-administer the questionnaire at work and drop it in a centrally located box
D. Mailing questionnaires to employees and supplying a deadline, instructions, and return postage
E. Administrating the questionnaire electronically and receiving and storing the responses electronically
Requirements Prioritization
Definition:
Involves the client or customer as well. Interviewing and administering questionaires are not effective ways to ask a customers which features they desire
What considerations are necessary when questionnaires are web based?
When designing Web-based questionnaires, there must be ample space for open-ended questions and the appropriate use of check boxes, radio buttons, and drop-down menus. It is important to have both Submit and Clear buttons. The Web survey should provide a password system to help ensure confidentiality.

What are the six methods of requirements prioritization an analyst can use to help users prioritize software features?
Methods for RP:
Simple Ranking
Assign a 1 to most desirable requirement, assign a 10 to least desirable requirement
100-Token Method
How many tokens is a requirement?
Loses sight of which deparment, as it is anonymous
MoSCoW Method
Puts requirements into the four buckets
Must
Should
Could
Won’t
Urgent/Important Matrix
Horizontal X is meant to show urgency and the vertical y-axis represents importance
Analytic Hierarchy Processing (AHP)
Presents pairs of alternatives to participants and has the participant decide which of the two are most important.
Shown good results for large, important decisions
Q-Sorts
sorting a deck of cards of requirements into piles and therefore is similar to the 100-token and MoSCoW methods
No pressure on getting it right the first time. Requirements can be moved interactively from one pile to another
Issues associated with questionaries are avoided
Can identify participants that have similar attitudes by examing how they sorted the deck of requirements, even if they are from different departments or units
Which method is preferred for determining requirements prioritization?
MoSCow prioritization
List a drawback of each of the six requirements prioritization methods.
Simple Ranking
Con: Boring, Futile. Most people aren’t good at making and ordering a long list of any sort
100-Token Method
Con: It’s anonymous
MoSCoW method
Con: Once a requirement is considered a won’t requirement, it will never have a chance of being important.
Categories are too broad and hard to tell priorities within the large categories
Urgent/Important Matrix
Con: Analyst might also want to consider those requirements that are marked “Not important but urgent” so that additional goals can be met before the release date
Analytic Hierarchy Processing (AHP)
time consuming
March Madness
Q-Sorts
Con: All the requirements must be pre-printed on cards so that they can sorted easily
What are the four advantages of Q-sorting?
There is no pressure on getting it right the first time
By requiring the participants to sort statements into a forced normal distribution many of the problems associated with questionnaires (central tendency, leniency) can be avoided
An analyst can identify participants that have similar attitudes by examining how they sorted the deck of requirements, even if they are from different departments or units
Participants usually think it’s fun to arrange and rearrange these requirements from one pile to another
Human Computer Interaction
Ergonomic aspects, system usability, how pleasing and enjoyable the system is, and how useful it is in supporting individual tasks