Lecture 18 HN204
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
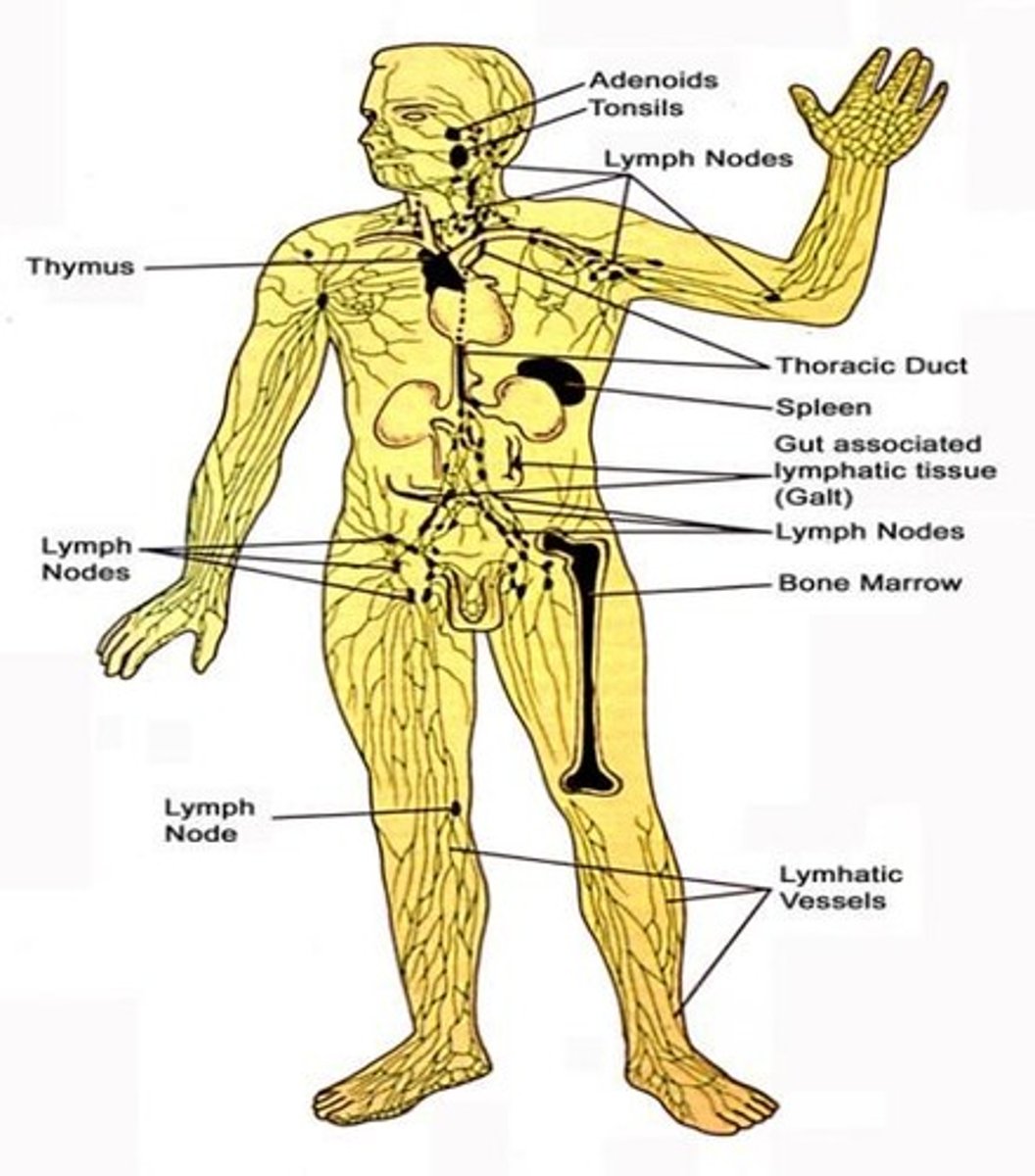
lymph definition
Interstitial fluid that has entered initial lymphatic vessels
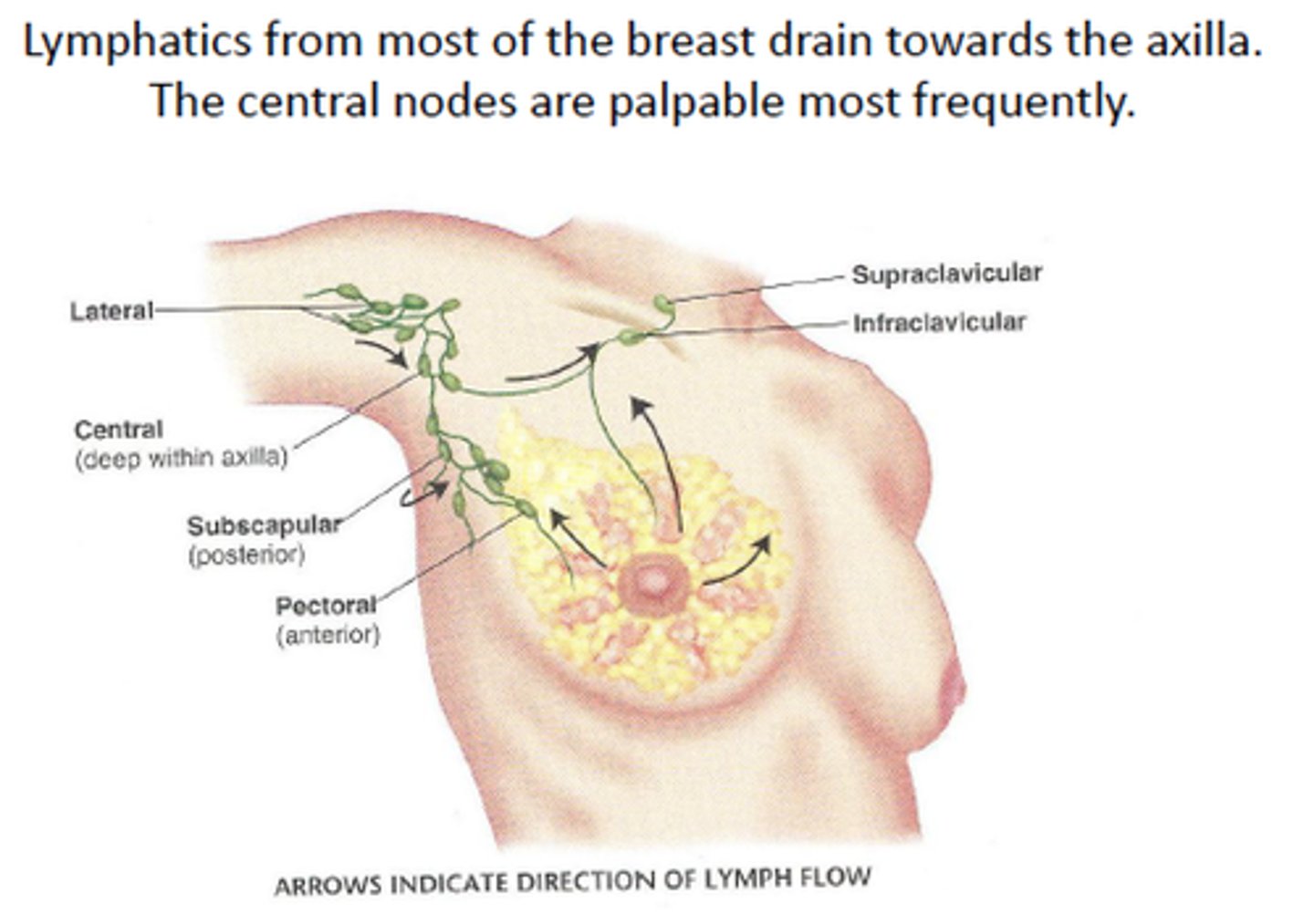
lymph nodes
along collecting lymph vessels
500 in body
filtration and immune activation
lymphoid tissue
primary and secondary lymphoid tissues
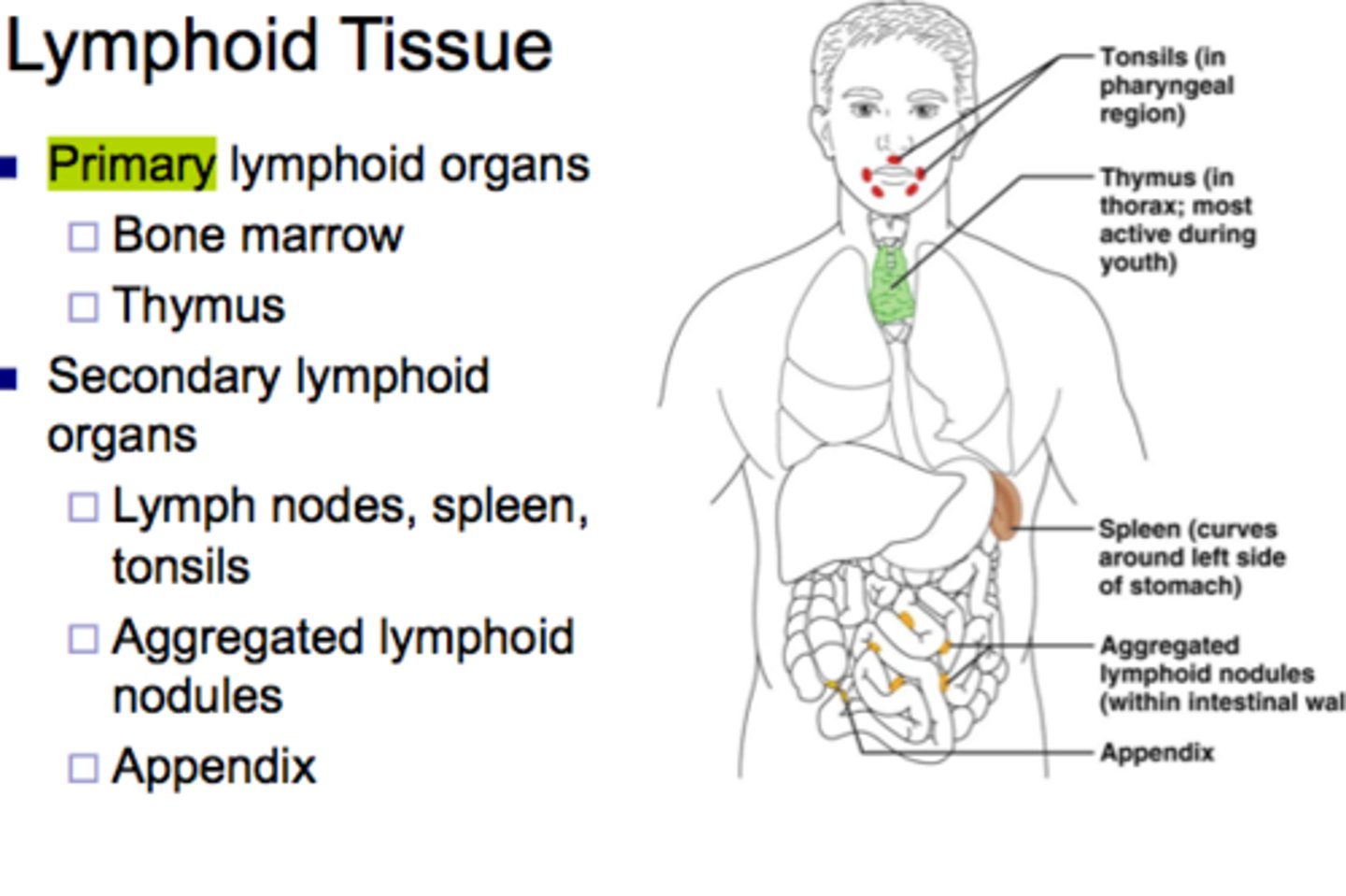
primary lymphoid tissues
bone marrow and thymus
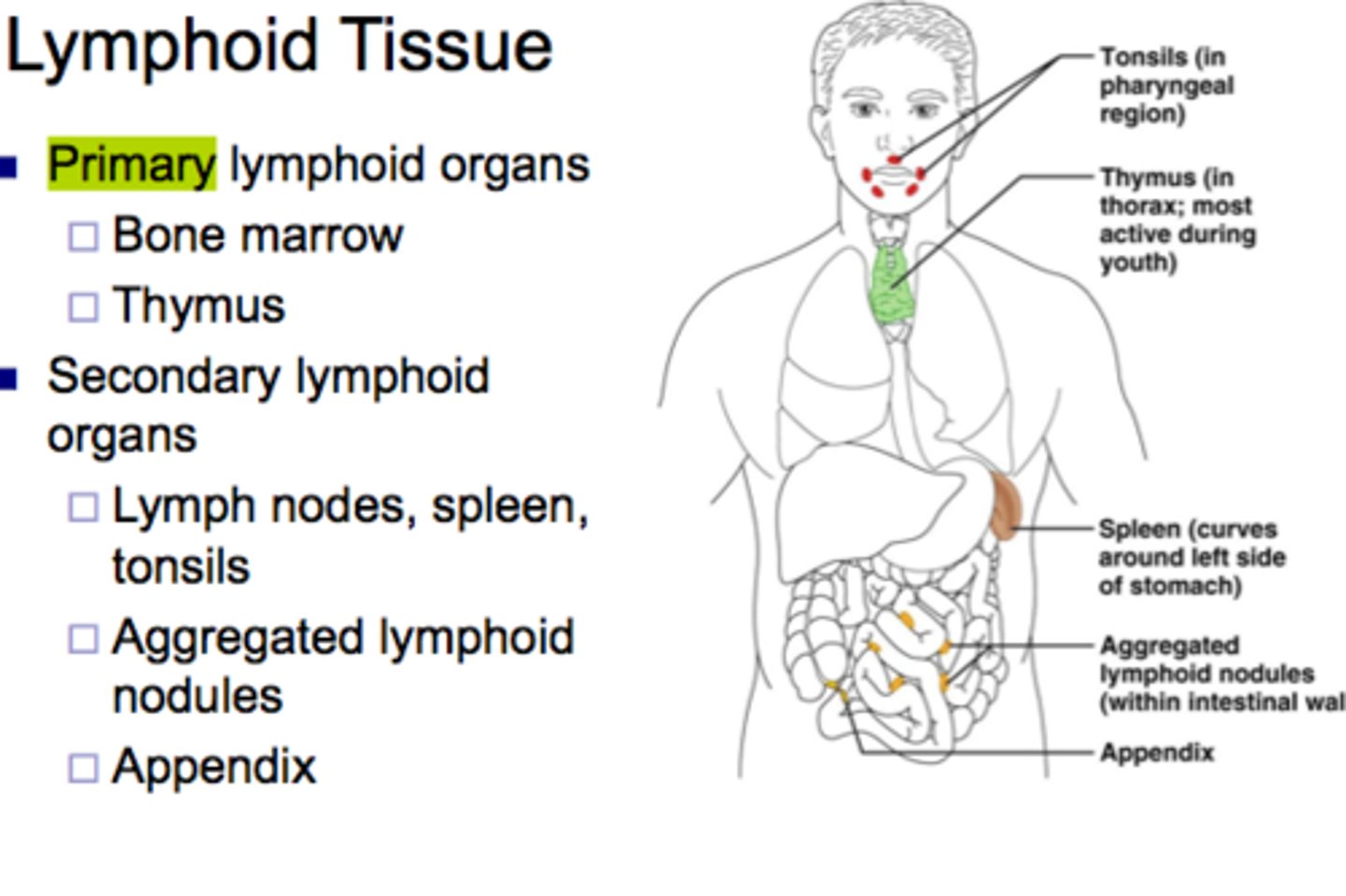
secondary lymphoid tissues
spleen. lymph nodes, tonsils, appendix, aggregated lymph nodules (Peyer's patches)
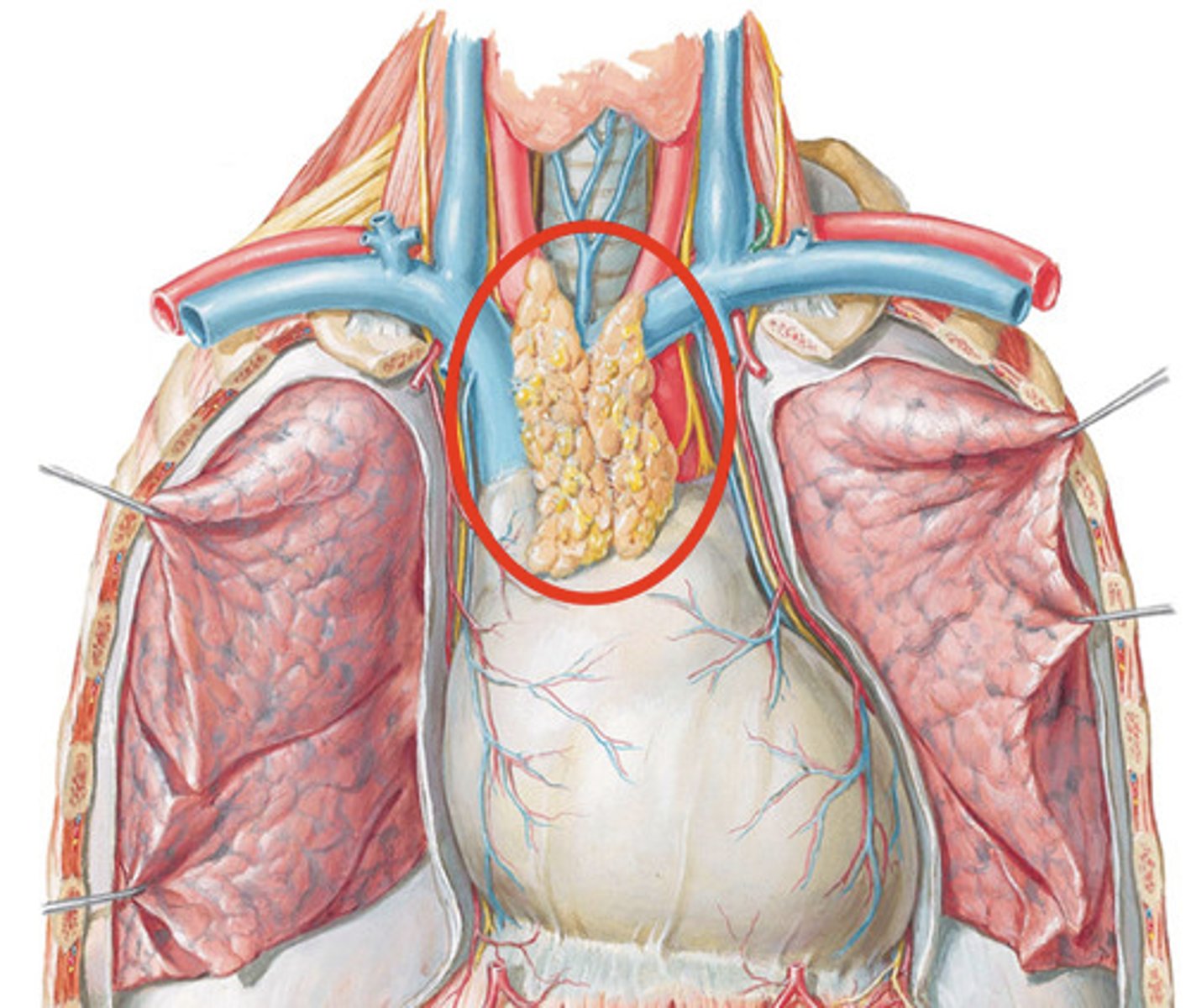
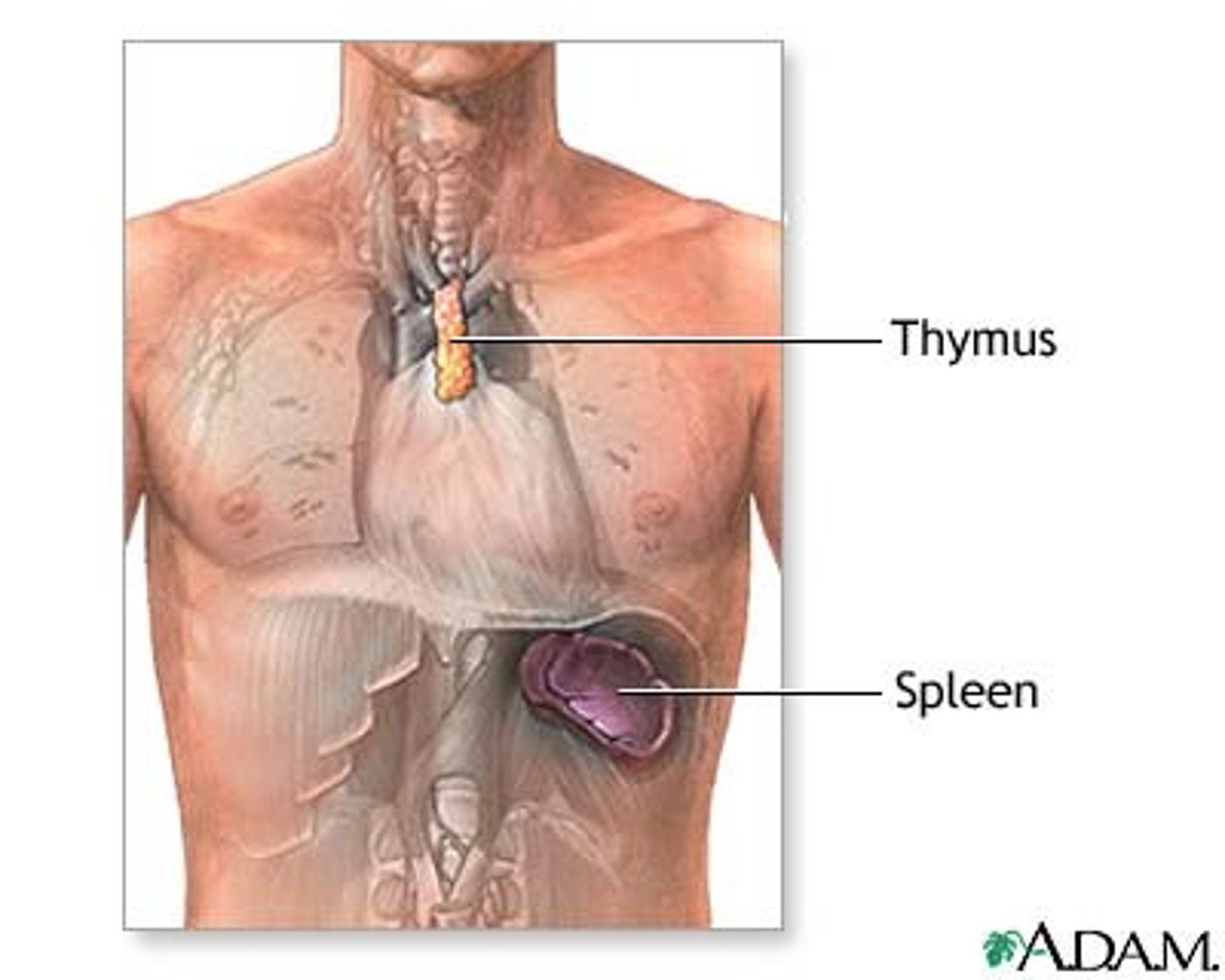
thymus
Gland in the thoracic cavity above the heart where T lymphocytes mature.
spleen
Organ near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
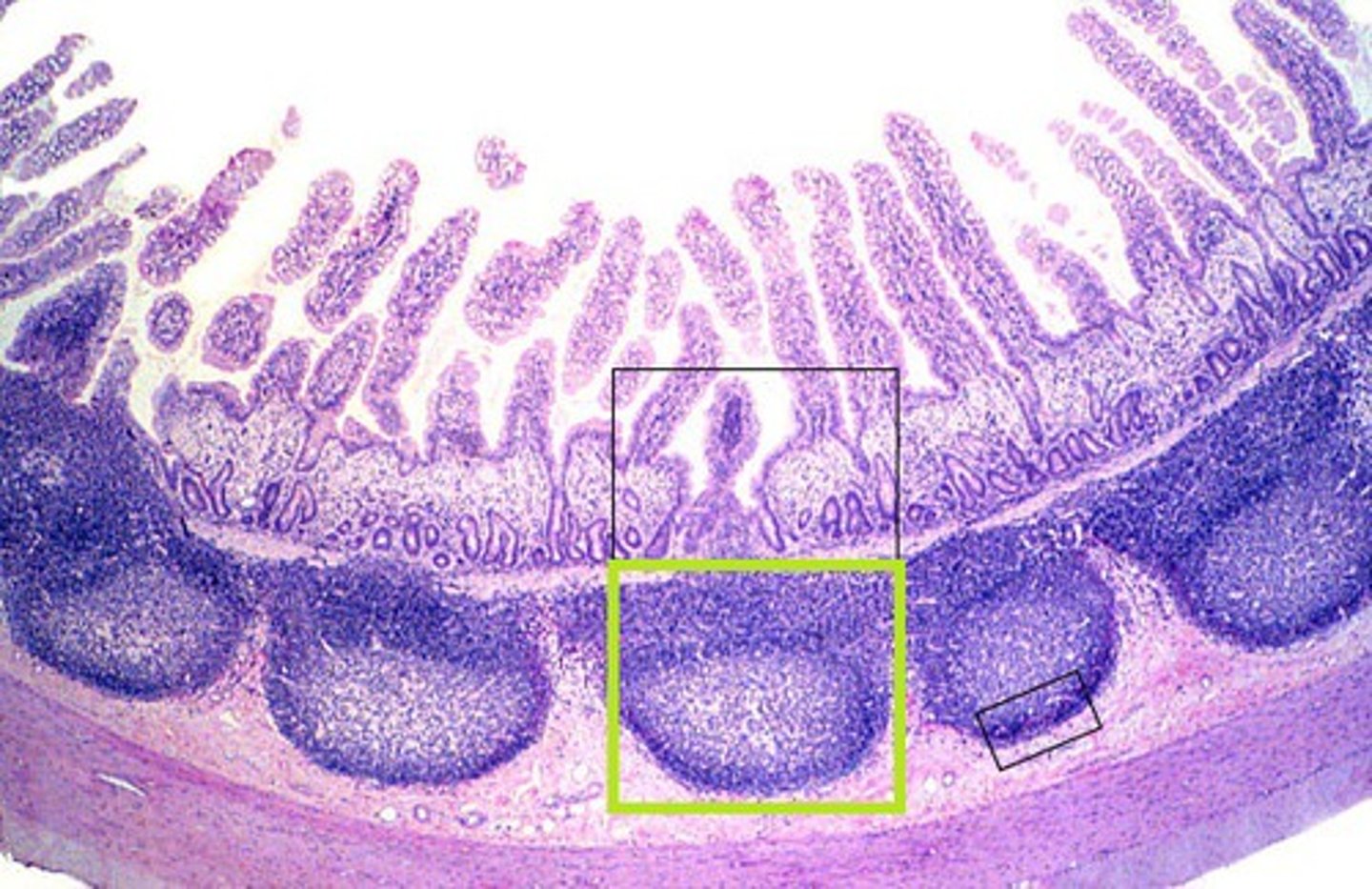
Aggregated lymphoid nodules (Peyer's patches)
clusters of lymphoid follicles in ileum (distal part) of small intestine
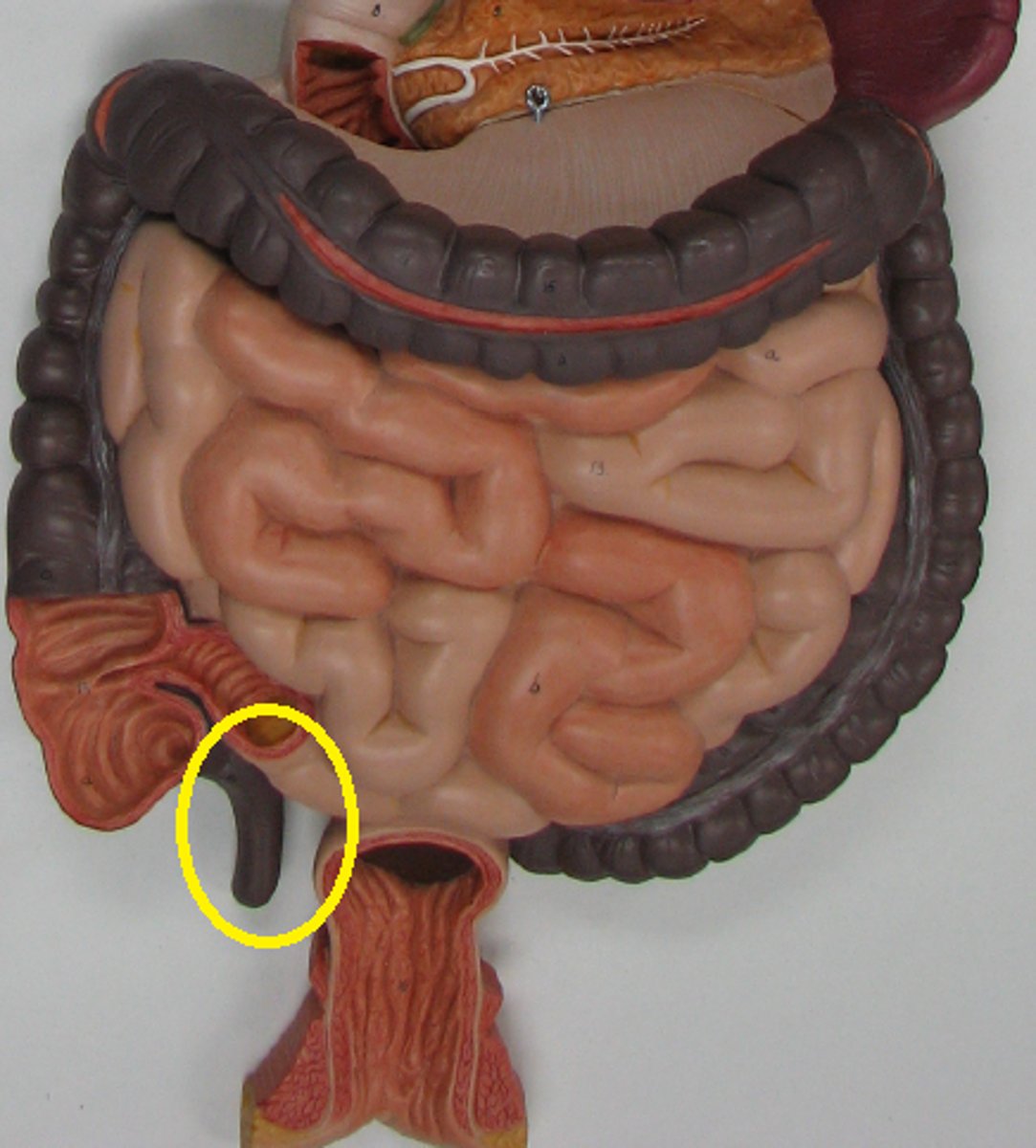
appendix
A small, fingerlike extension of the vertebrate cecum; contains a mass of white blood cells that contribute to immunity.
red bone marrow
produces blood cells, b cells originate and mature here
lymph capillaries are close to
circulating capillaries
fluid in blood is called
plasma
fluid in the tissue called
interstitial
fluid in the lymph vessels is called
lymph
2 types of pressure at the capillaries
hydrostatic and osmotic
hydrostatic
pressure exerted by liquid at rest
strongest
osmotic pressure
caused by albumin, draws fluid in
lymphatic pathway
lymphatic capillary
collecting lymphatic vessel
lymph node
larger lymphatic vessel
converges into lymphatic trunk
collecting duct
subclavian vein and internal jugular vein via the right lymphatic duct or thoracic duct
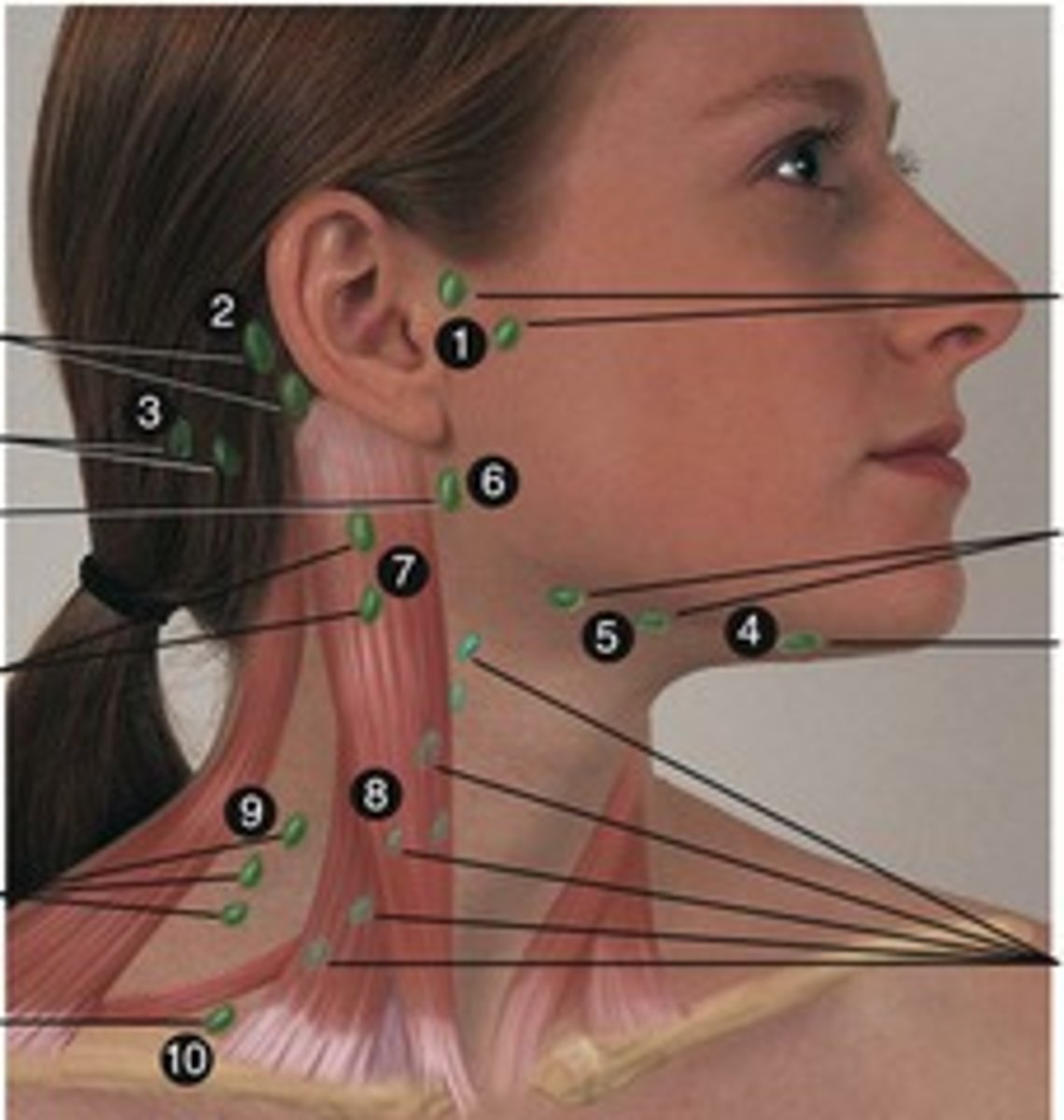
lymph node clusters
cervical, axillary, inguinal, tracheobronchial, aortic, and iliac
what is drained by the right lymphatic duct
right upper side of the body (shoulder, arm, chest)
what is drained by the left lymphatic duct
everything except right upper side of body
pathway from right jugular trunk
right jugular trunk
right lymphatic trunk
right subclavian vein
pathway from right subclavian trunk
right subclavian trunk
right lymphatic duct
right subclavian vein
pathway from right bronchomediastinal trunk
right bronchomediastinal trunk
right lymphatic duct
right subclavian vein
pathway from right lumbar trunk
right lumbar trunk
cisterna chyli
thoracic duct
left subclavian vein
pathway from left jugular trunk
left jugular trunk
thoracic duct
left subclavian vein
left subclavian trunk
left subclavian trunk
thoracic duct
left subclavian vein
left bronchomediastinal trunk
left bronchomediastinal trunk
thoracic duct
left subclavian vein
left lumbar trunk
left lumbar trunk
cisterna chyli
thoracic duct
left subclavian vein
edema
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces of tissues.
pitting edema
indentation left after examiner depresses the skin over swollen edematous tissue
sign of liver disease
not enough albumen
albumin
protein in blood; maintains the proper amount of water in the blood by draining capillaries
Bubonic Plague (Black Death)
swollen lymph nodes called bubos
lacteals
specialized lymph vessels in the small intestine that absorb fat into the bloodstream
chyle
white or pale yellow substance in lymph that contains fatty substances absorbed by the lacteals
Lymphangitis
inflammation of lymph vessels
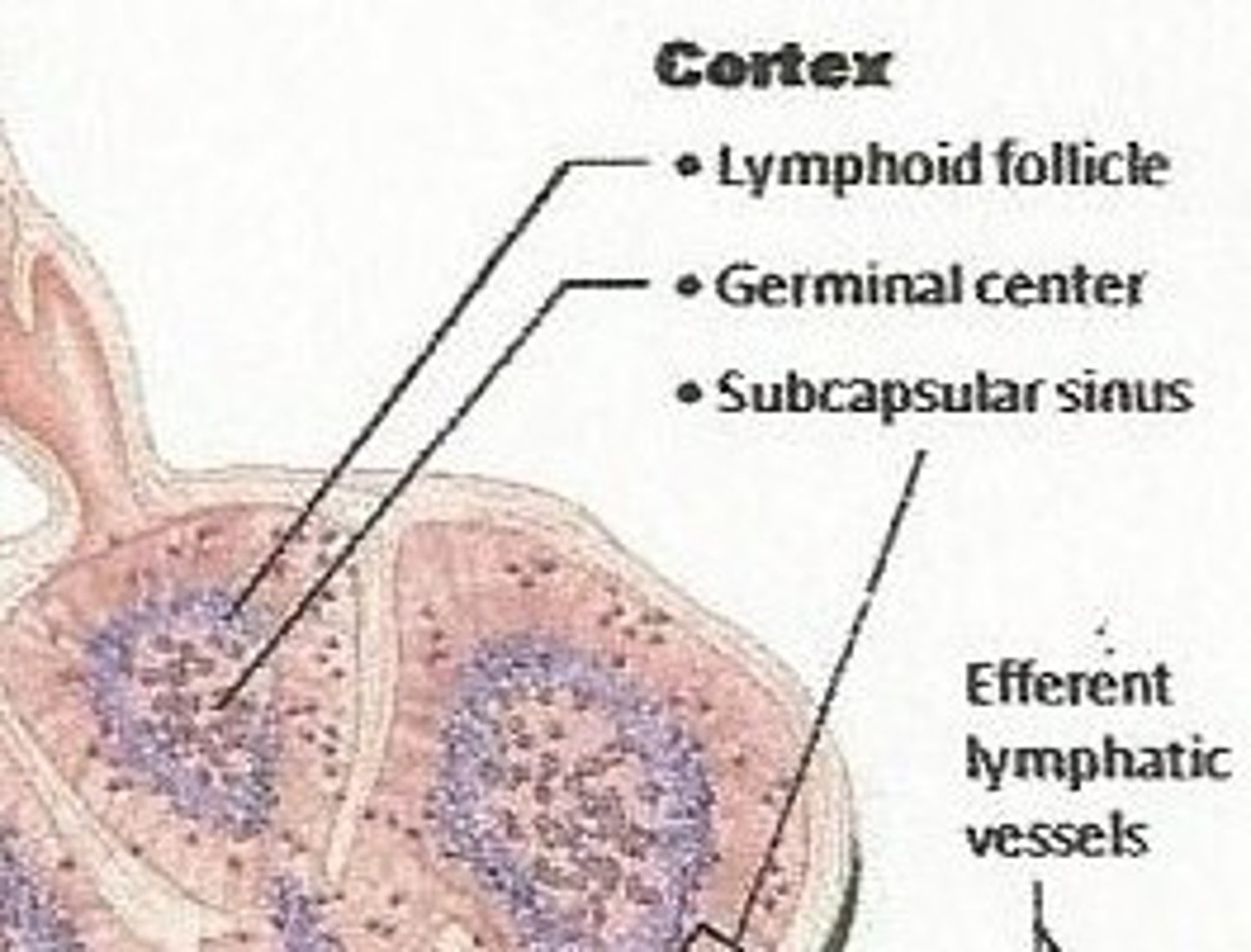
lymphoid follicles
solid, spherical bodies consisting of tightly packed lymphoid cells and reticular fibers
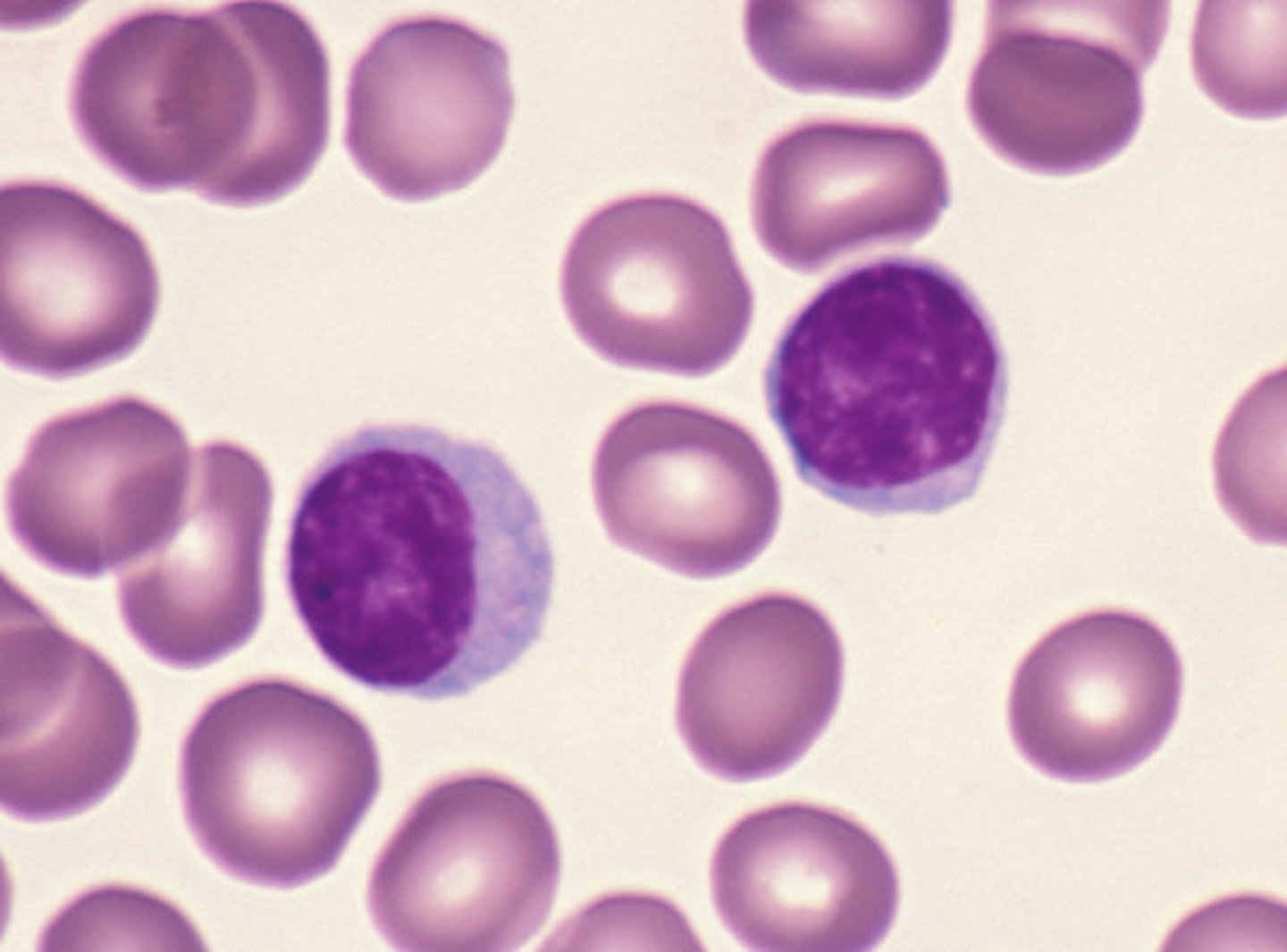
lymphocytes
2 types
b lymphocytes
t lymphocytes
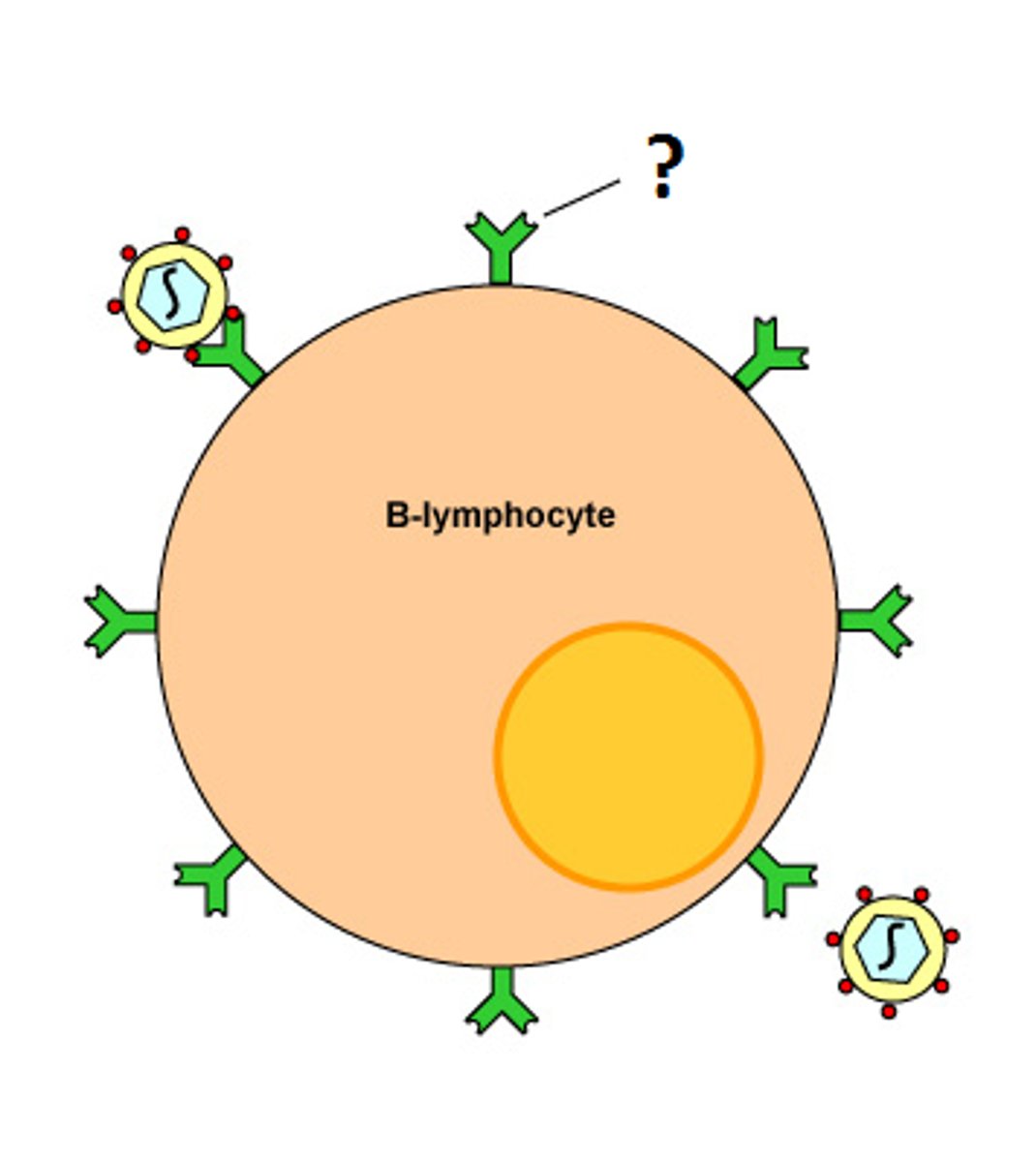
b lymphocytes
B lymphocytes form in the bone marrow and release antibodies that fight bacterial infections
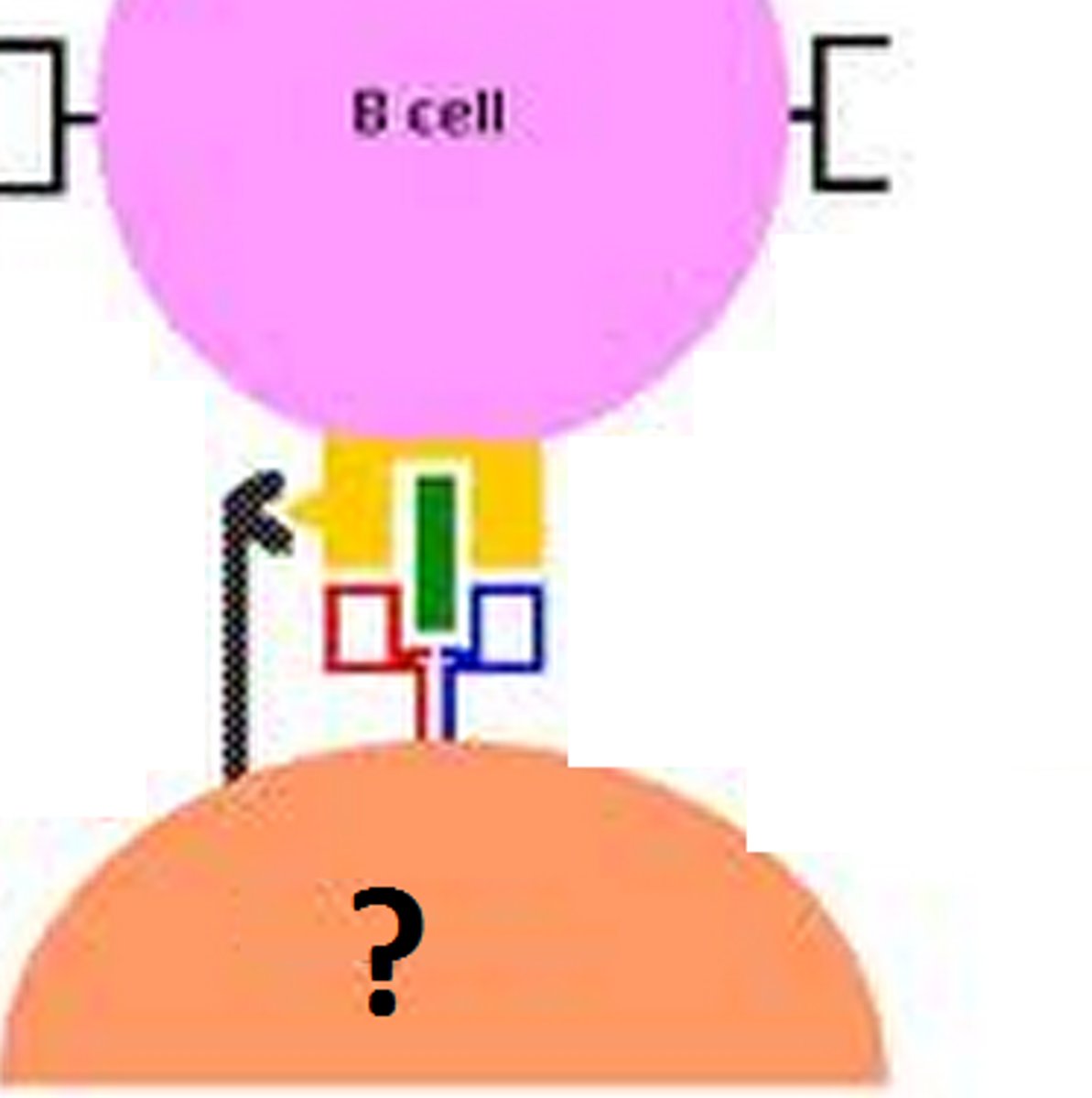
t lymphocytes
T lymphocytes form in the thymus and other lymphatic tissue and attack cancer cells, viruses, and foreign substances
mucosa associated lymph tissue MALT
part of the lymphatic system that monitors and produces an immune response against pathogens passing with food through the GI tract
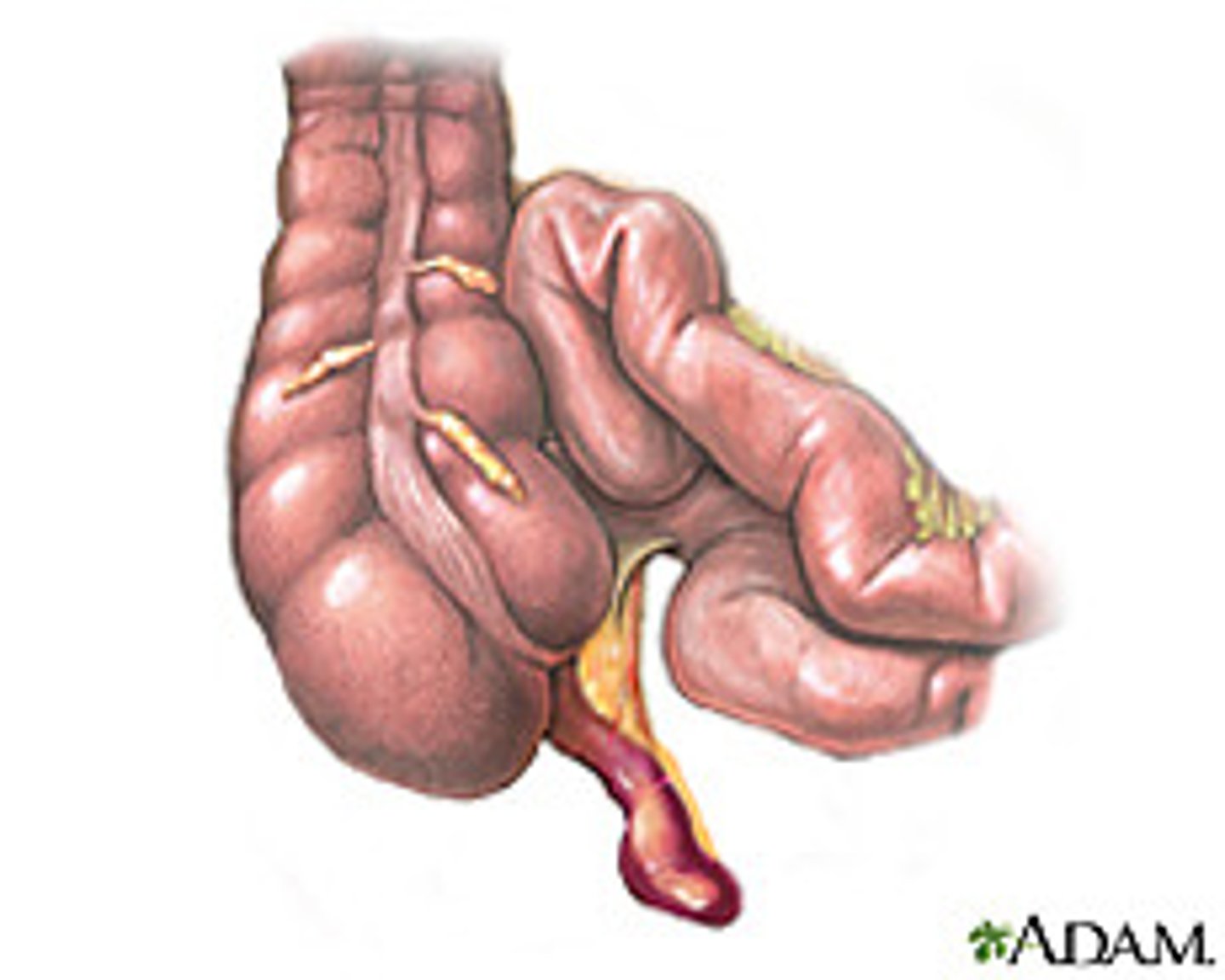
appendicitis
inflammation of the appendix
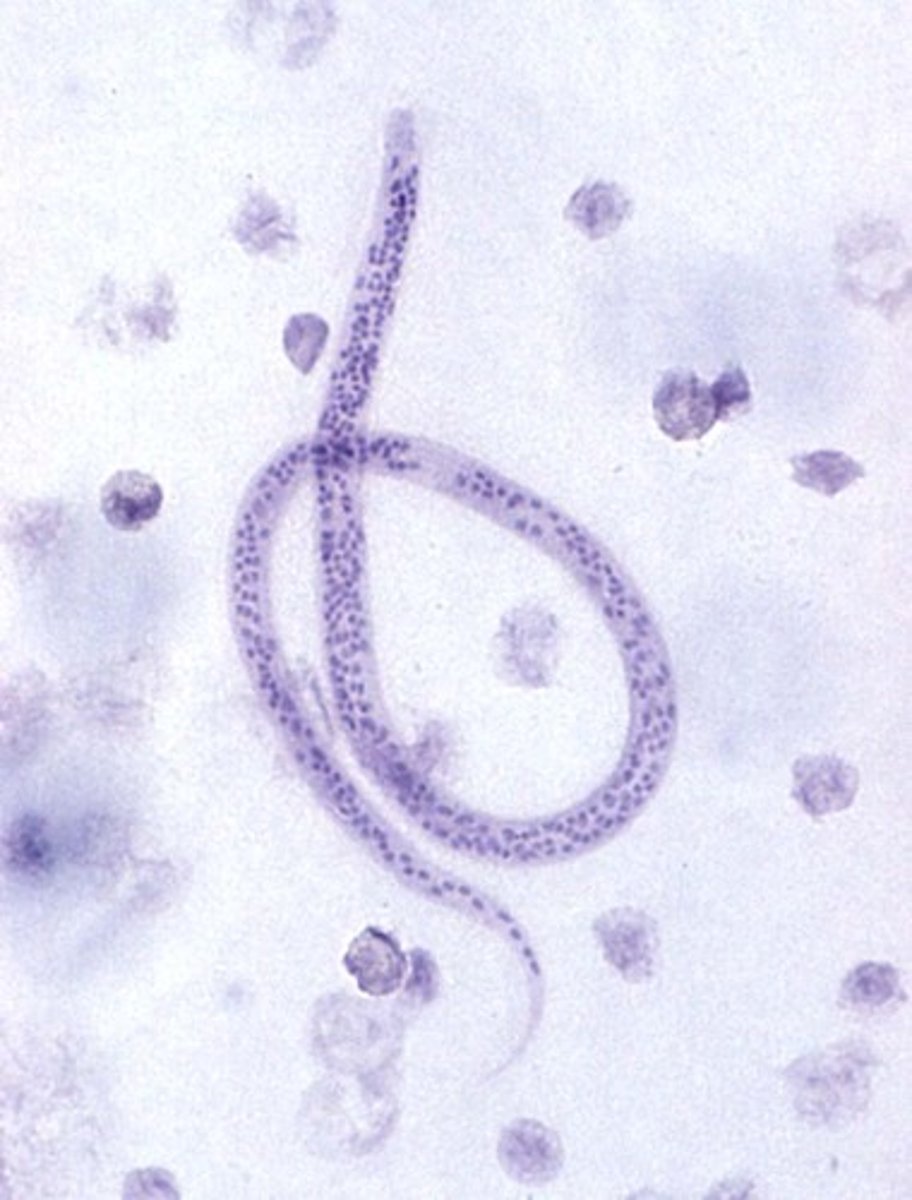
filariasis
infection of the blood and tissues of healthy individuals by worm embryos or filariae
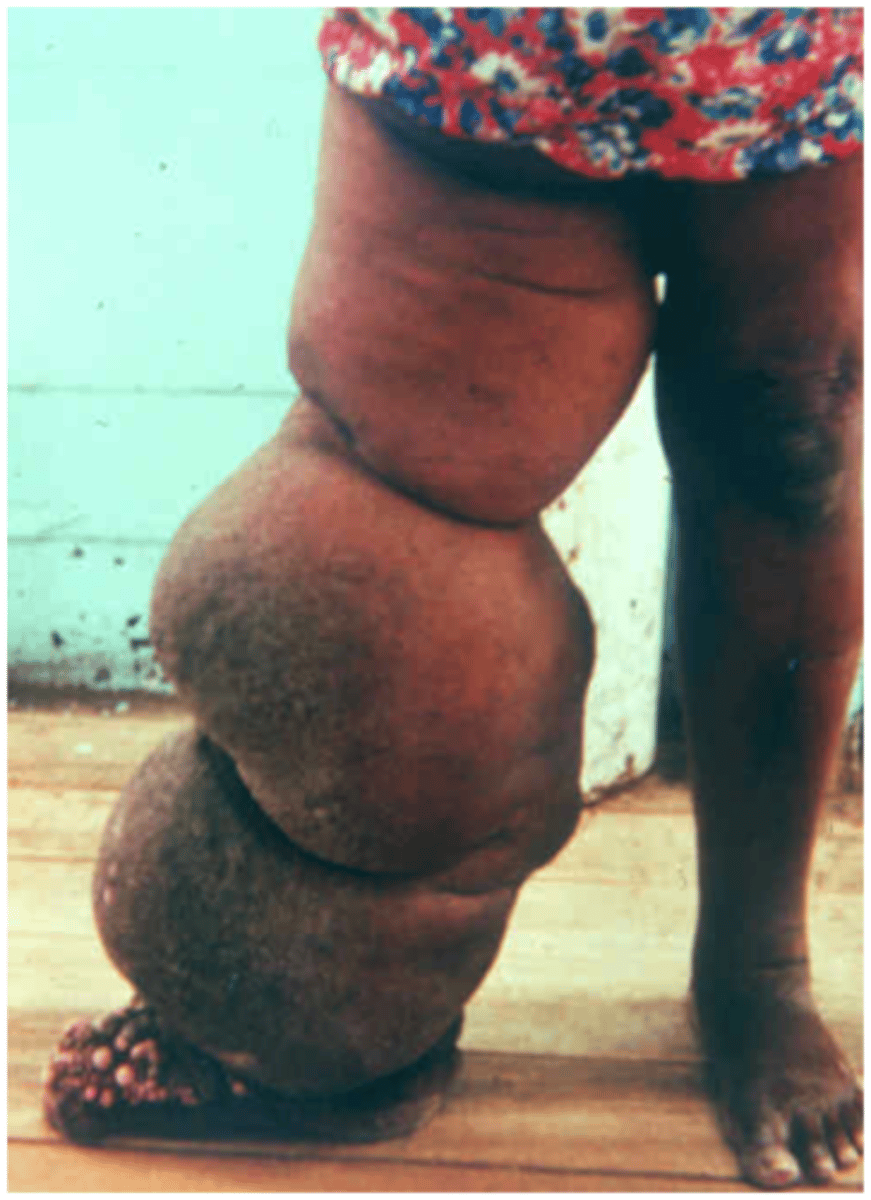
elephantiasis
results from blockage of lymphatic vessels that causes extreme tissue edema
effector cells
Muscle cells or gland cells that carry out the body's response to stimuli.
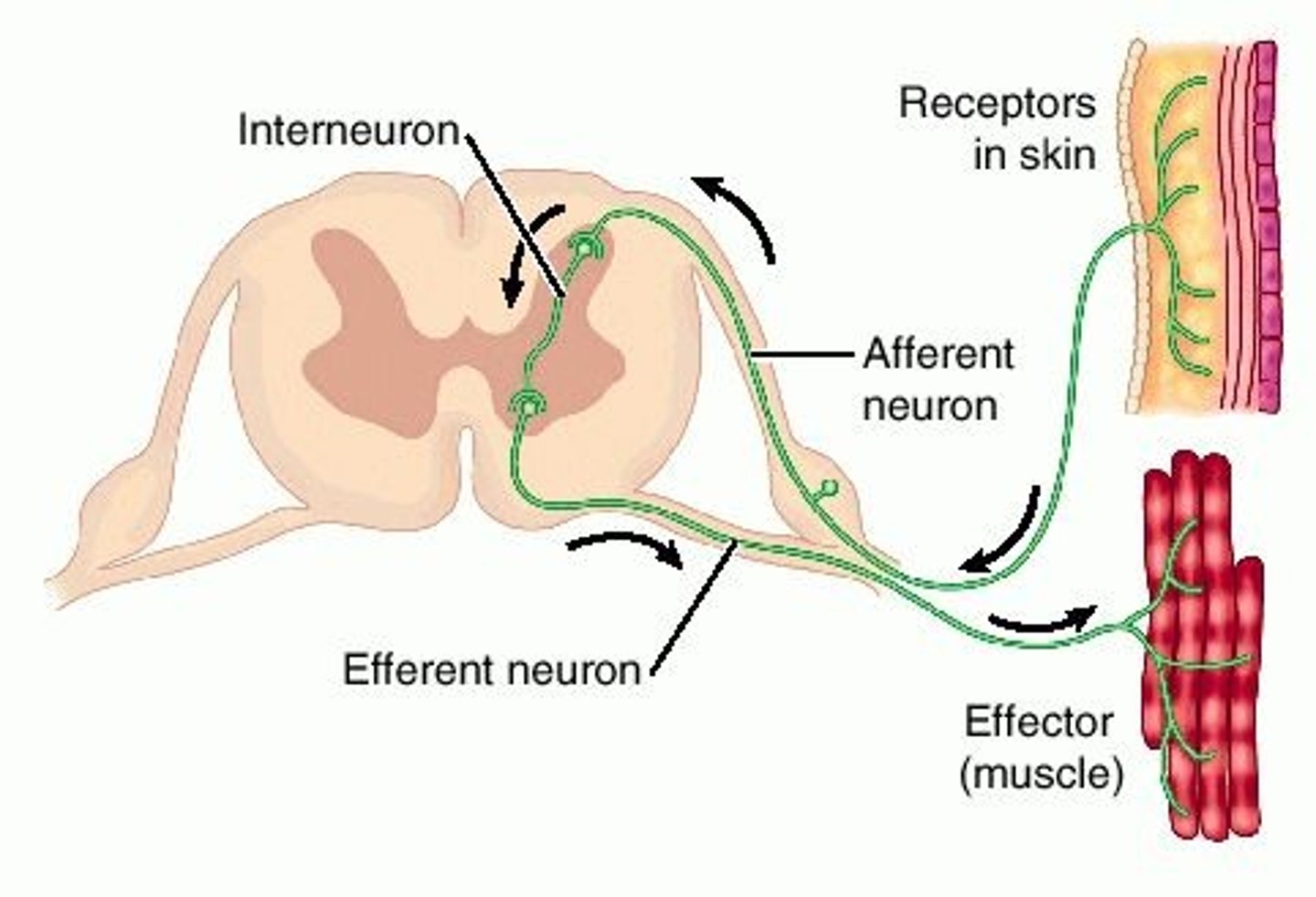
memory cells
General term for lymphocytes that are responsible for immunological memory and protective immunity.
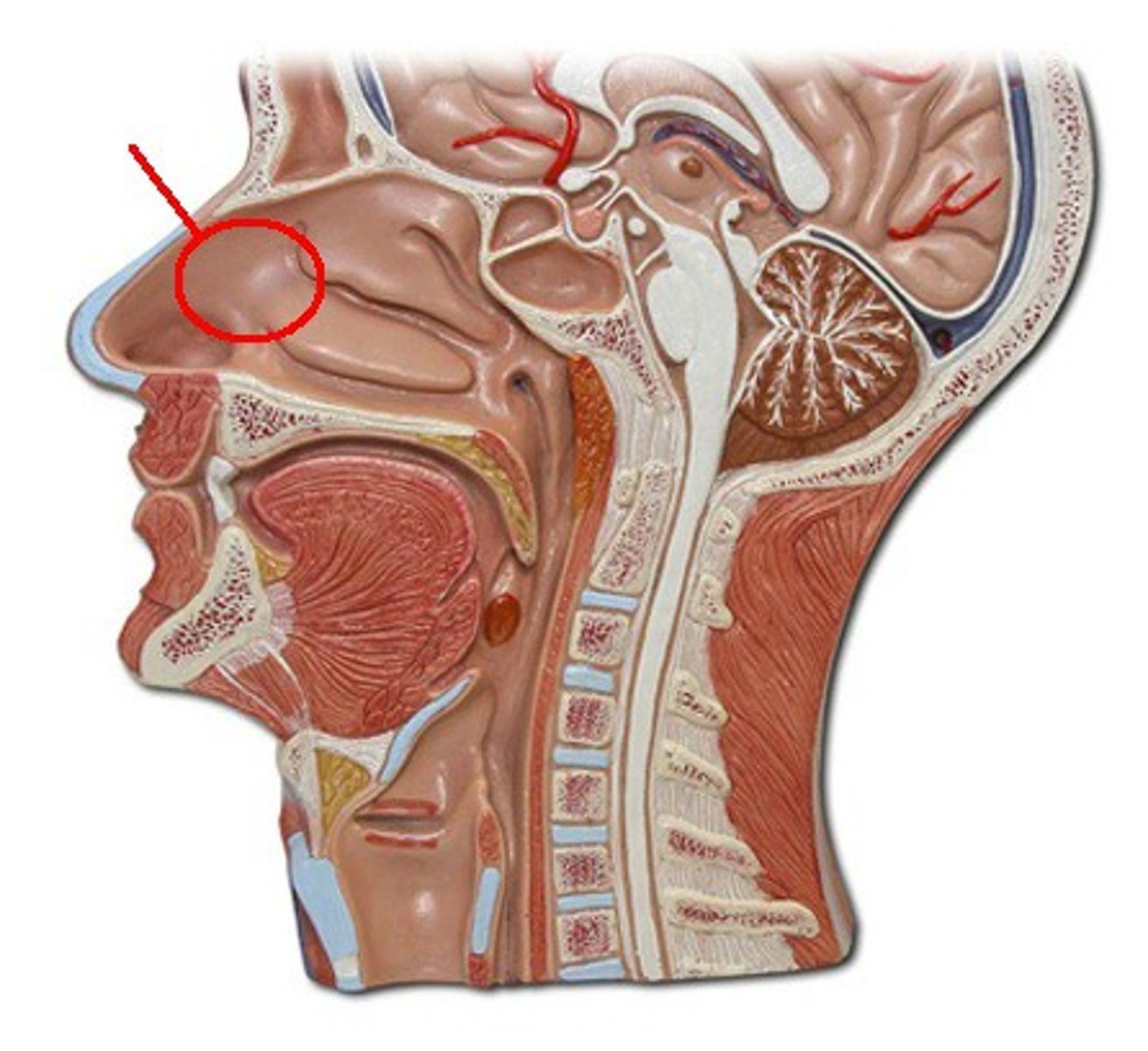
nasal cavity
hollow space behind the nose
nostril
one of the two channels of the nose
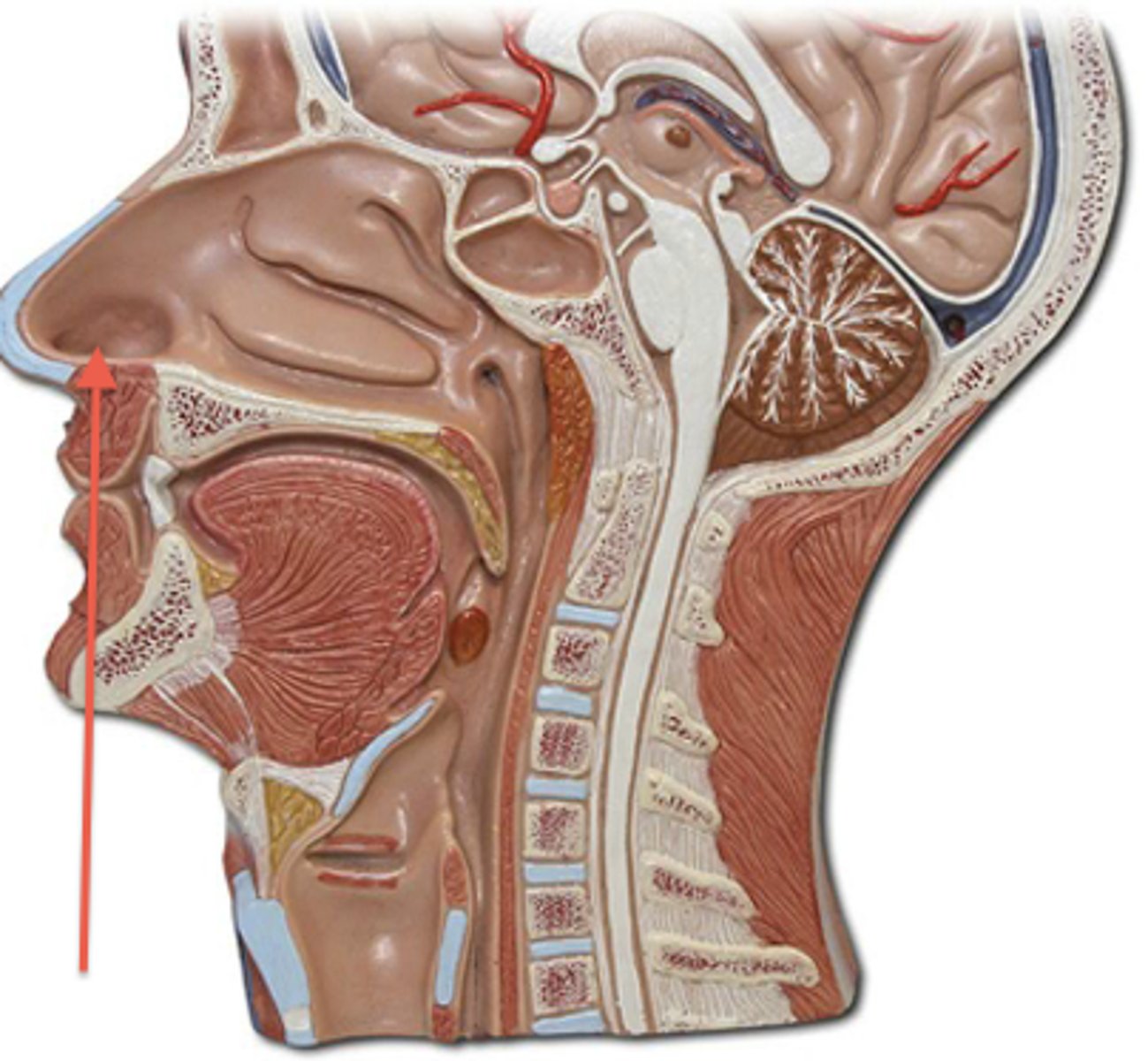
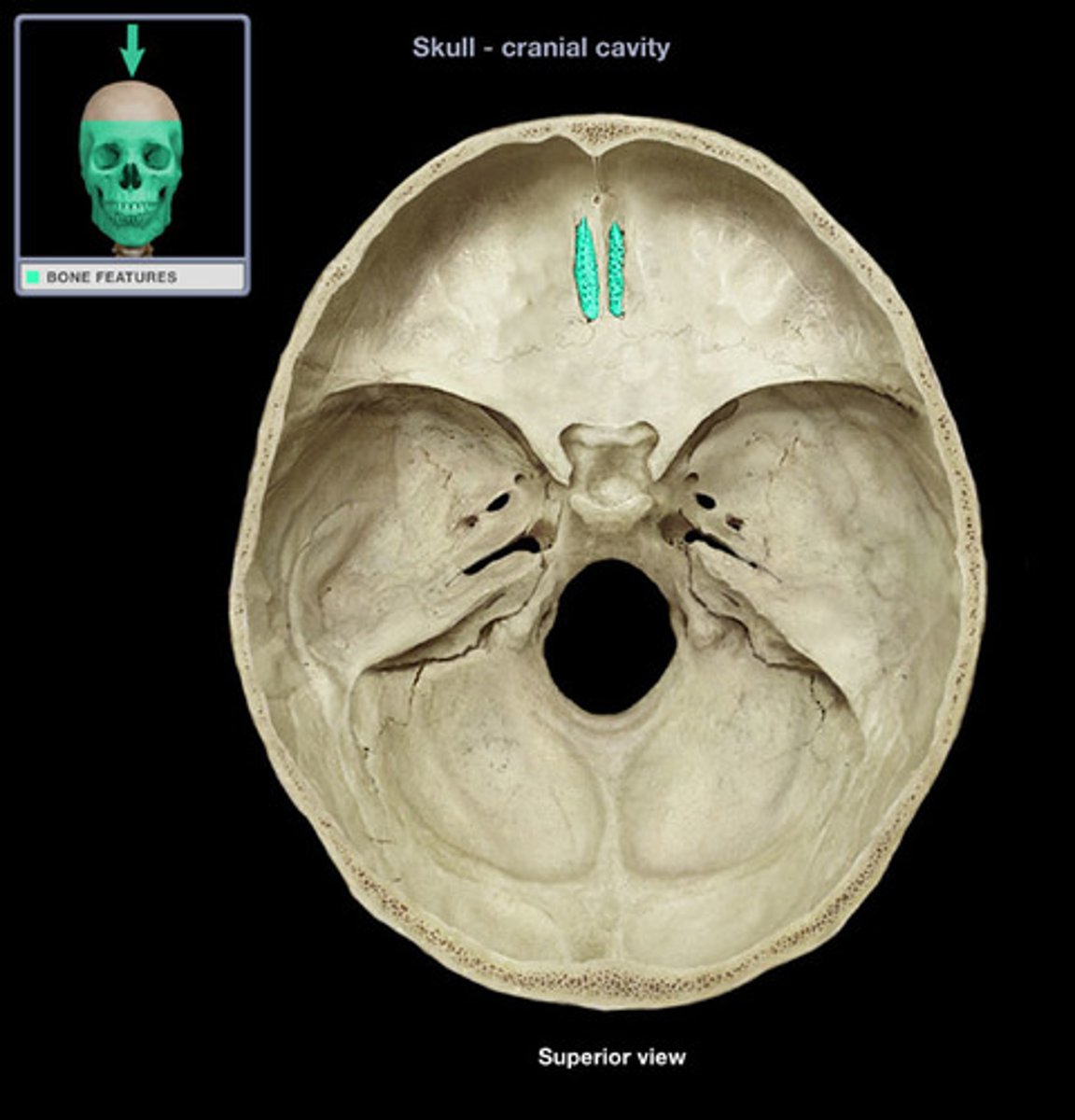
cribriform plate
The horizontal plate of the ethmoid bone separating the cranial cavity from the nasal cavity.
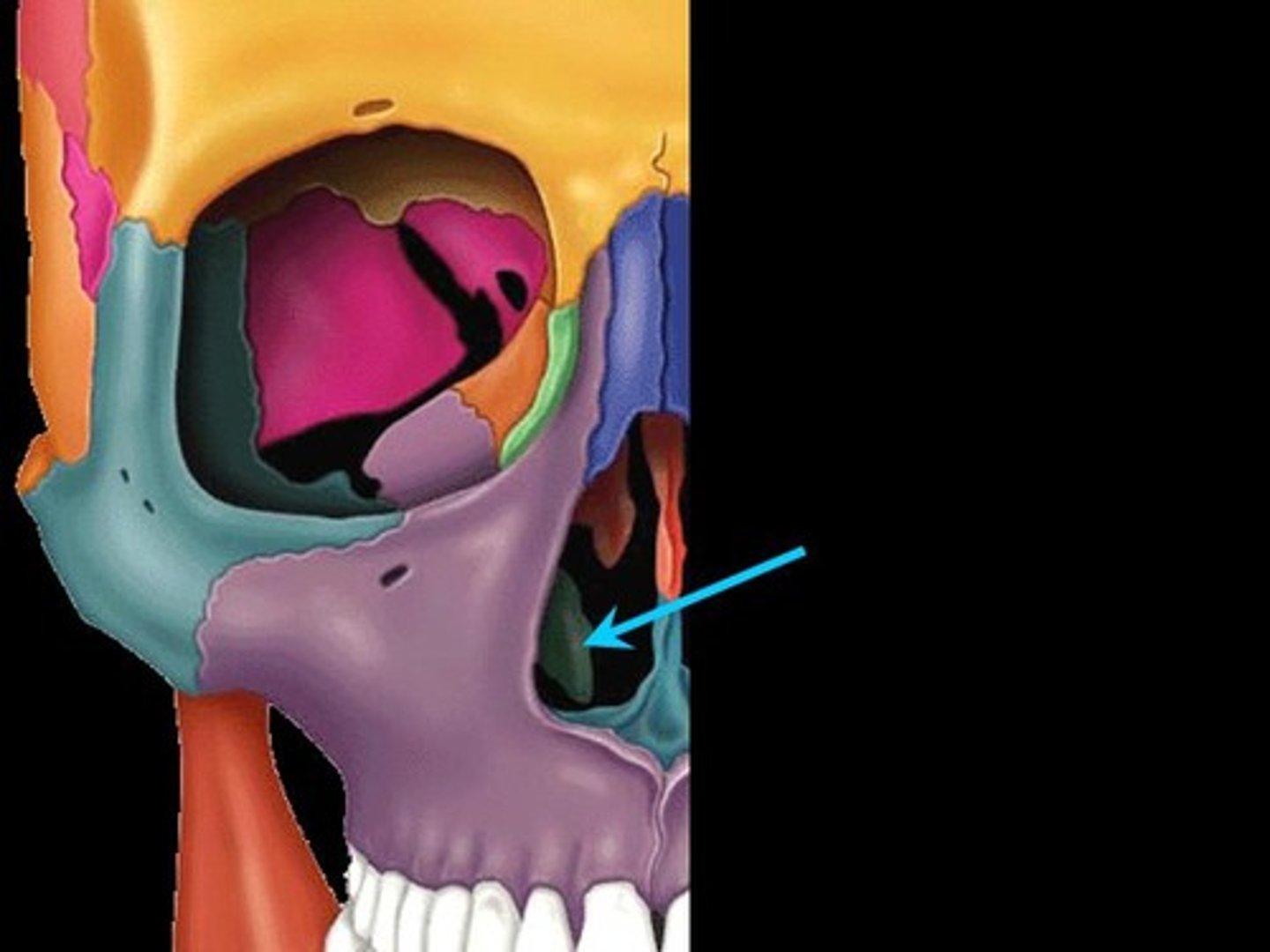
inferior nasal conchae
The lowermost scroll-shaped bones on the sidewalls of the nasal cavity.
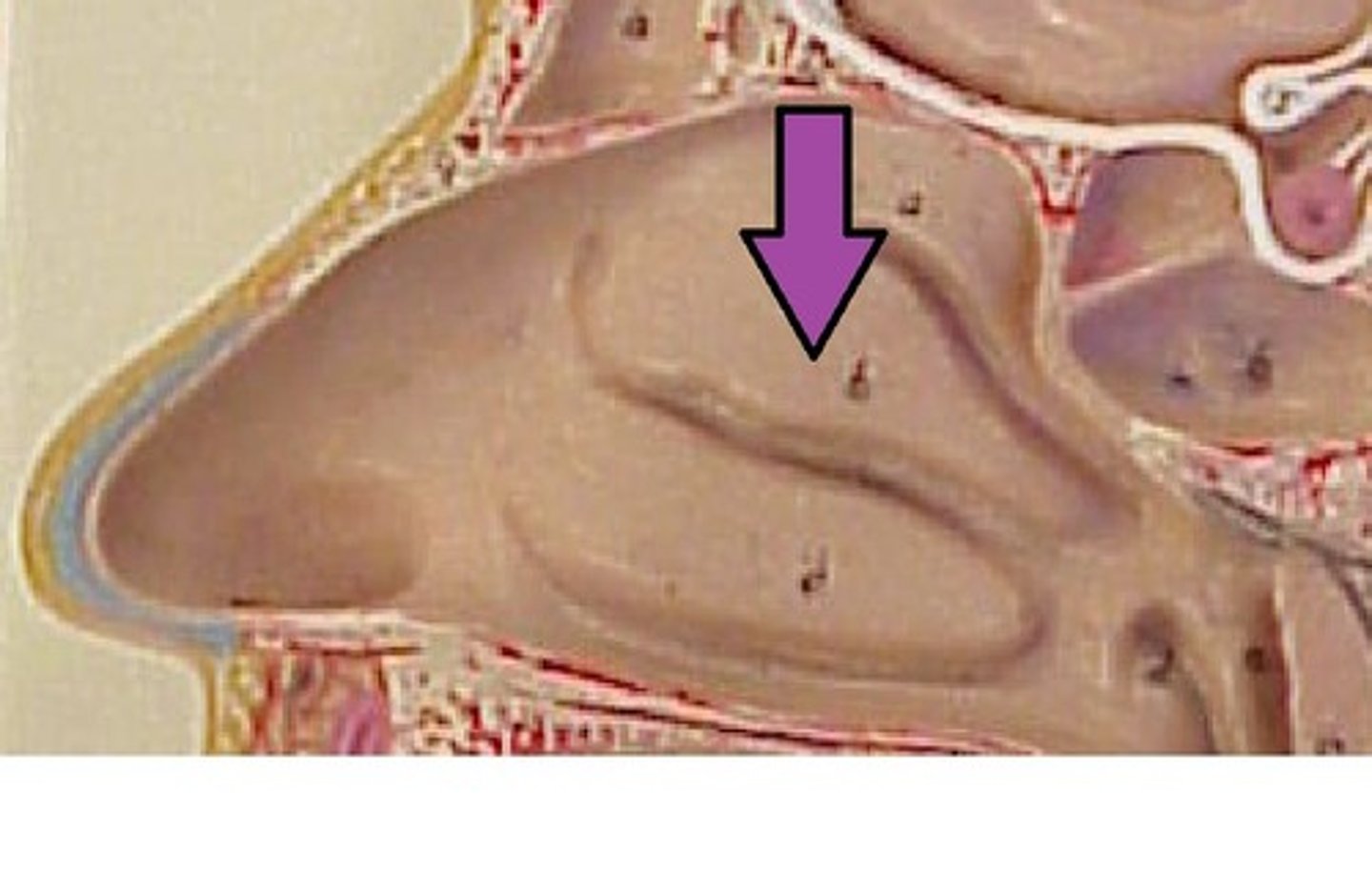
middle nasal conchae
scroll-like projections on each lateral wall of nasal cavity
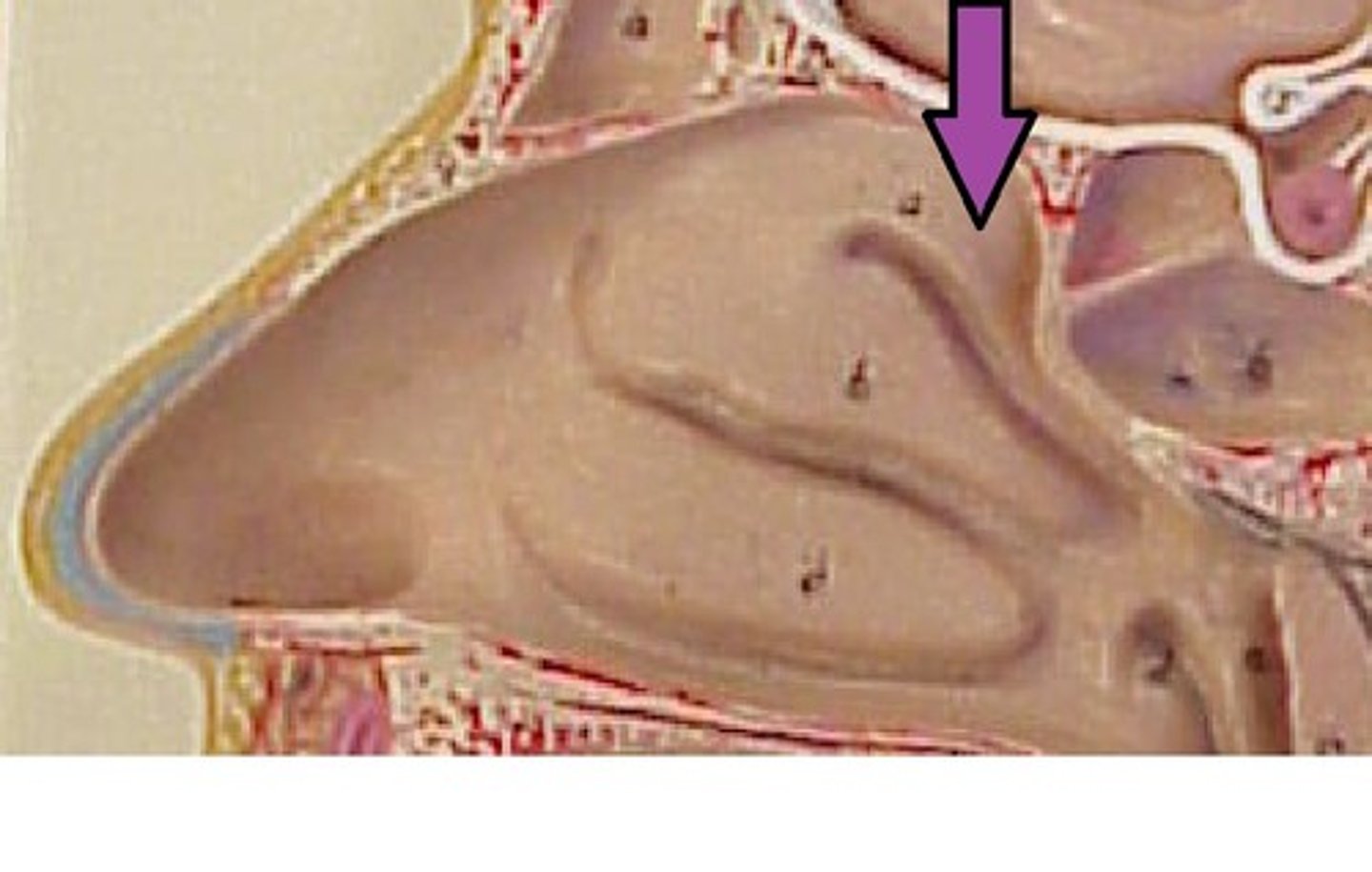
superior nasal conchae
scroll-like projections on each lateral wall of nasal cavity
nasal meatuses
irregularly shaped pockets or air spaces in the nasal cavity
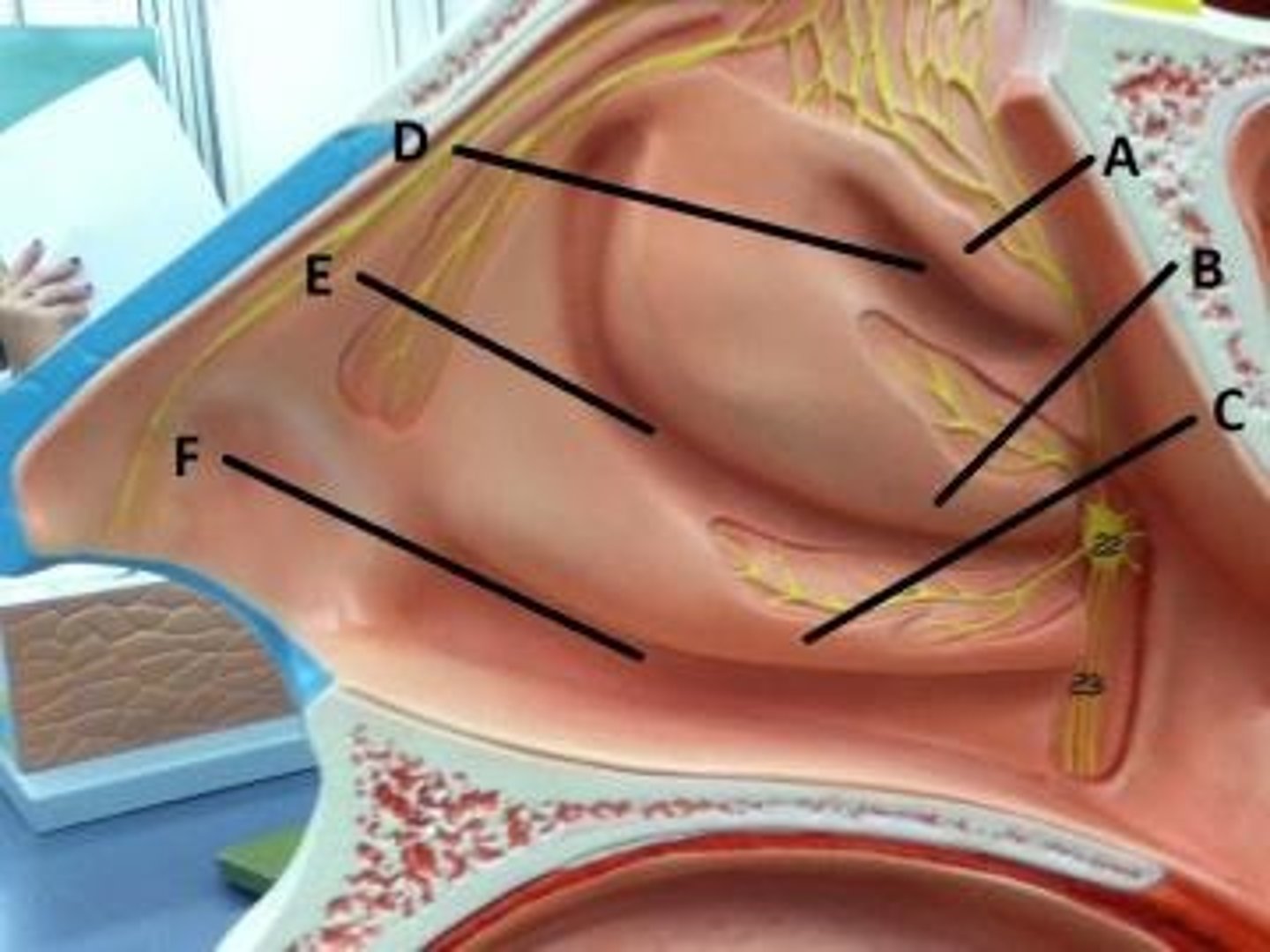
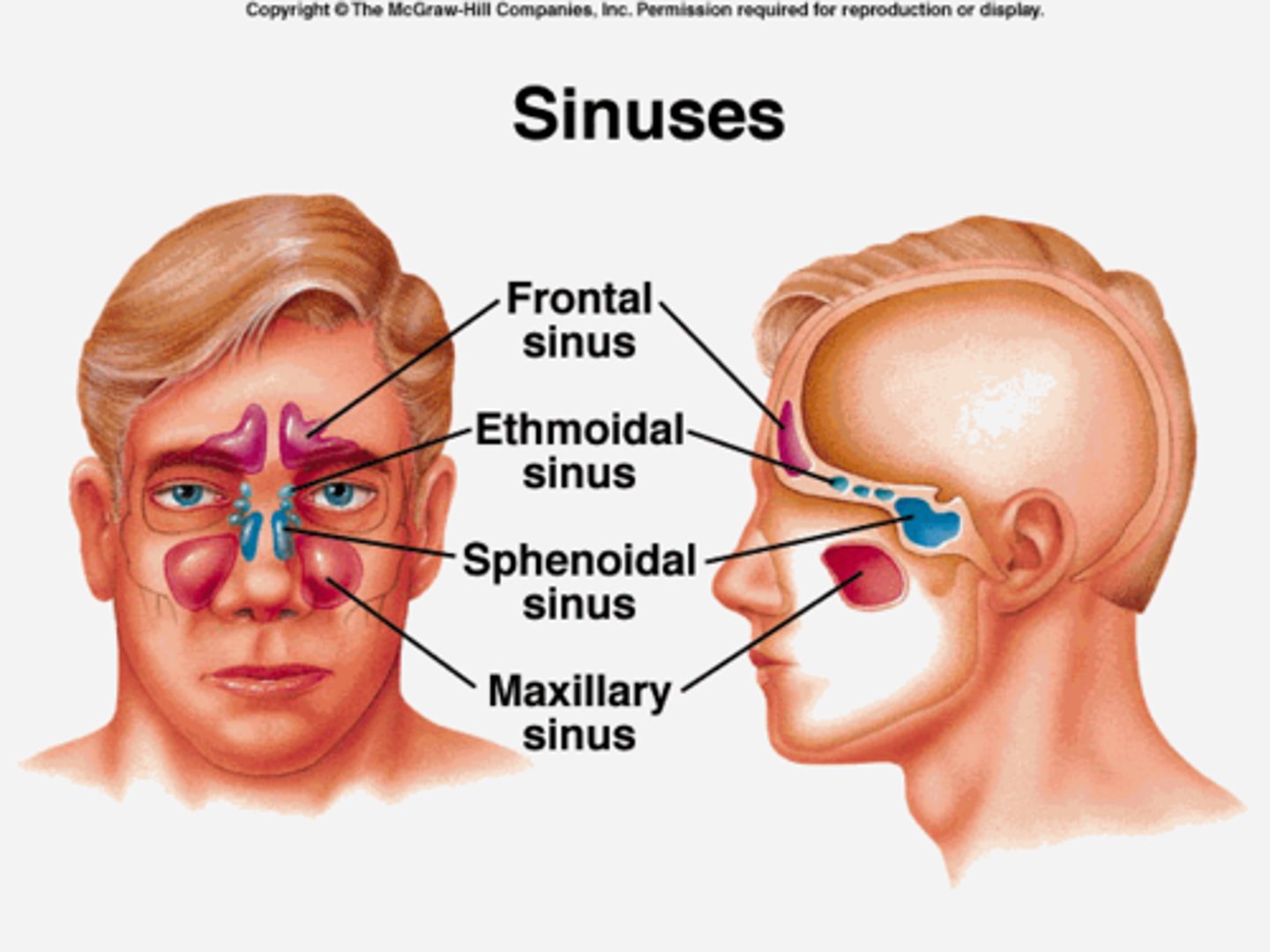
para nasal sinuses
air-filled cavities lined with mucous membrane, located in the bones of the skull
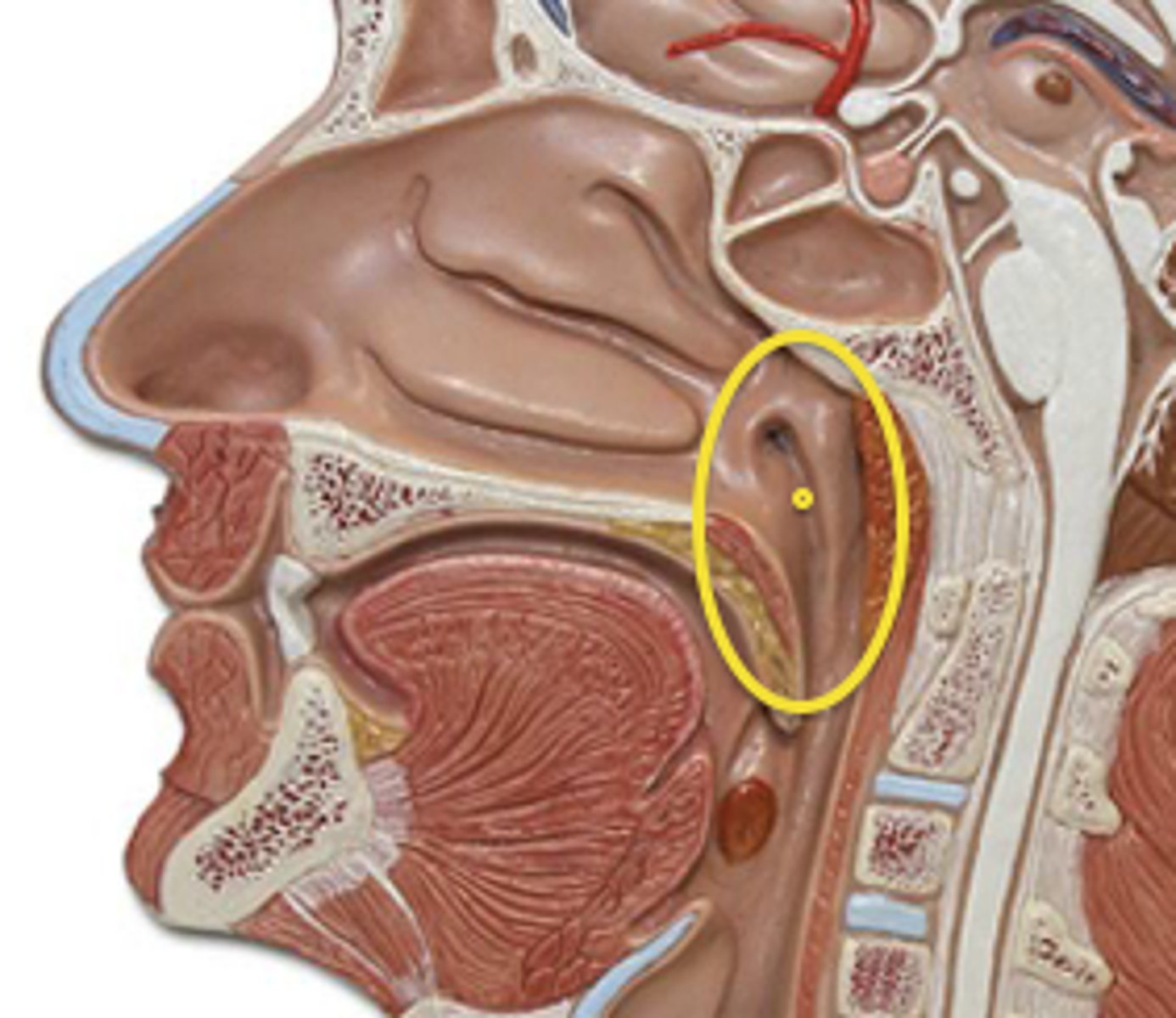
nasopharynx
region of the pharynx at the back of the nose and above the soft palate
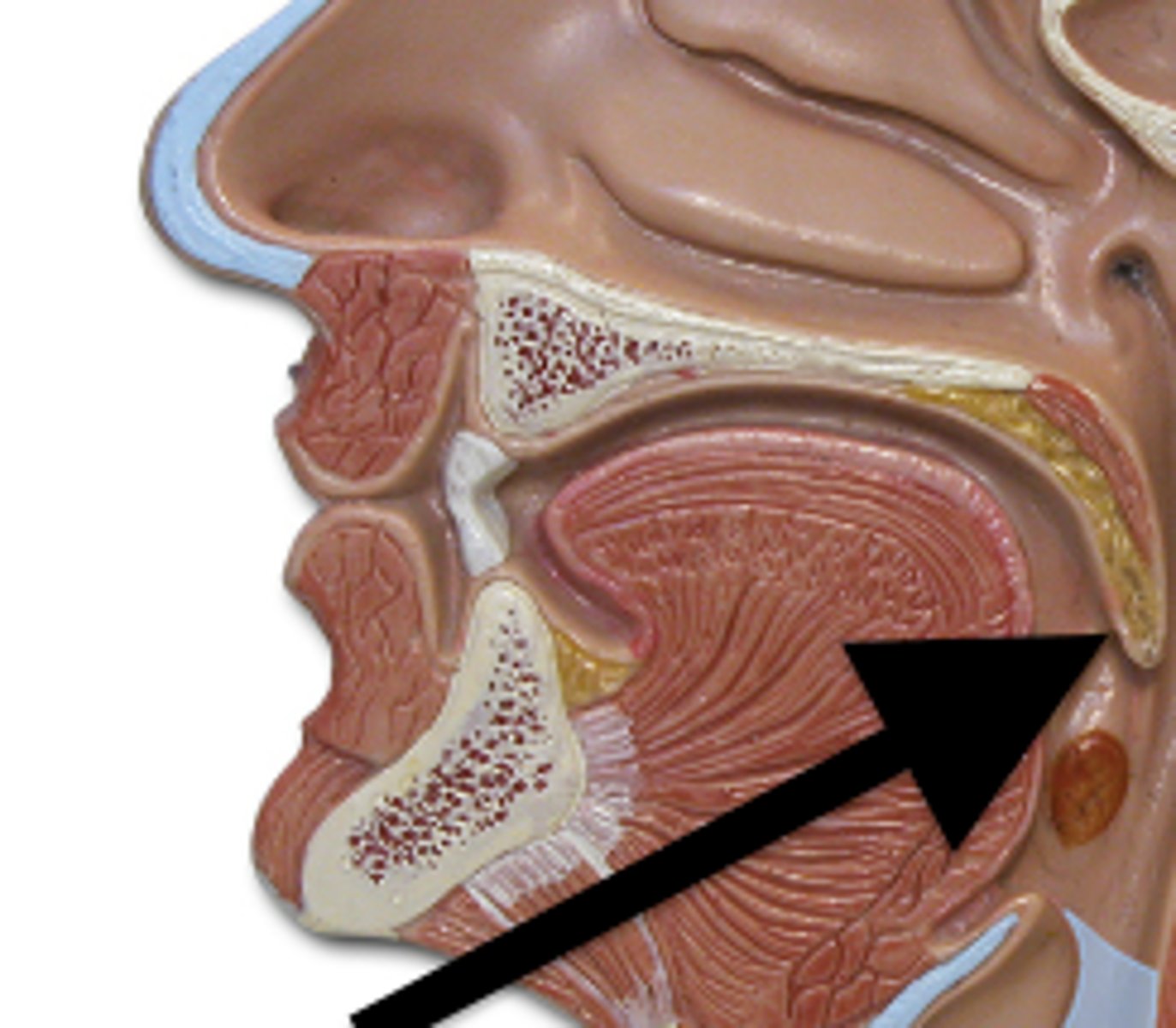
uvula
soft tissue hanging from the middle of the soft palate
pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
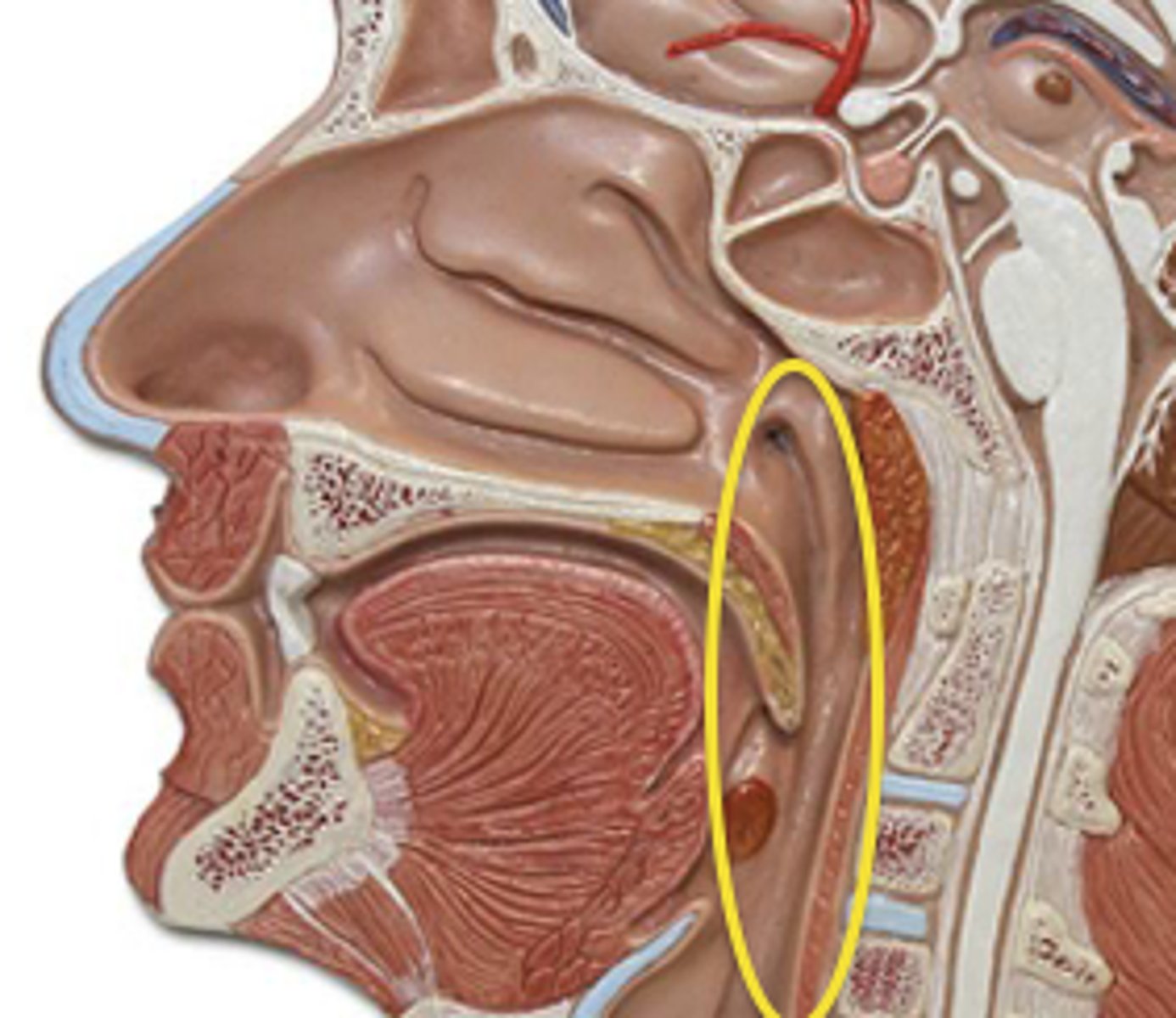
epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
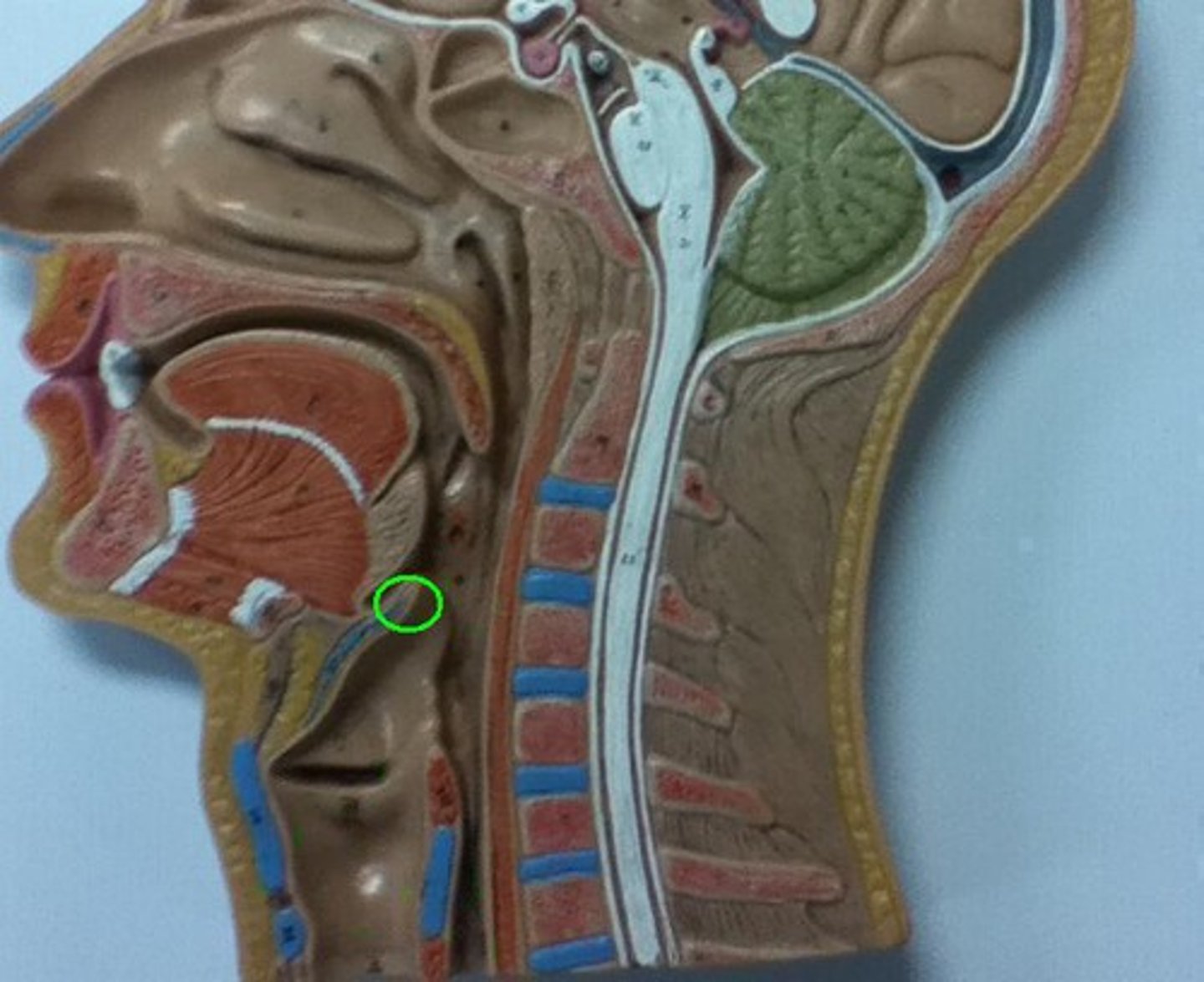
circoid cartilage
inferior to thyroid cartilage, ring of hyaline cartilage that attached larynx to trachea. reinforces wall of larynx
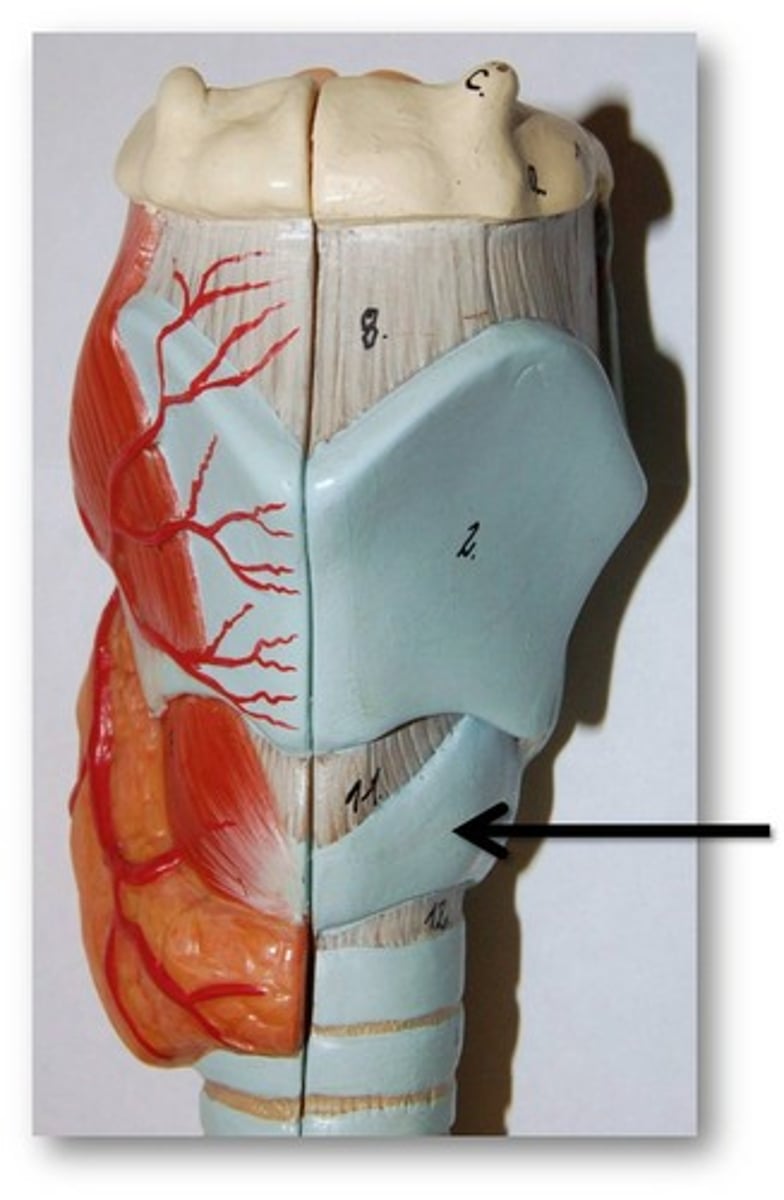
larynx
voice box
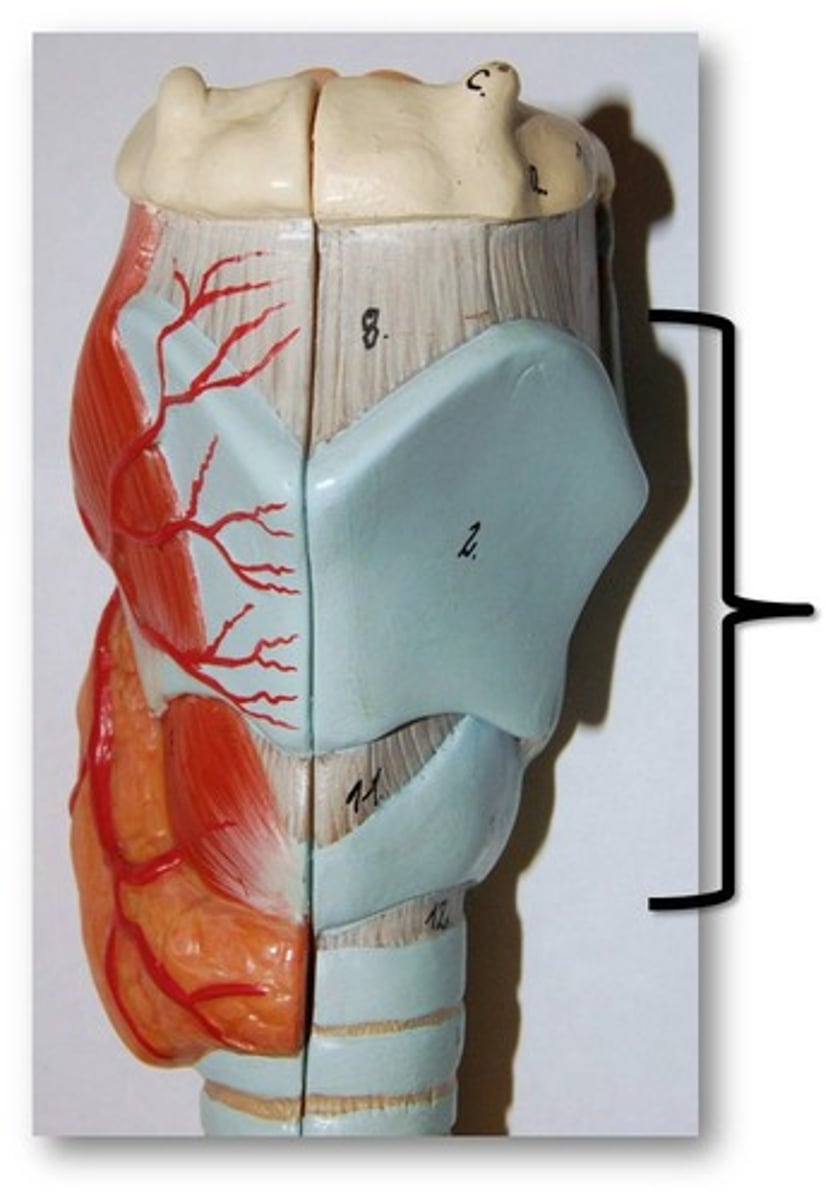
trachea
windpipe
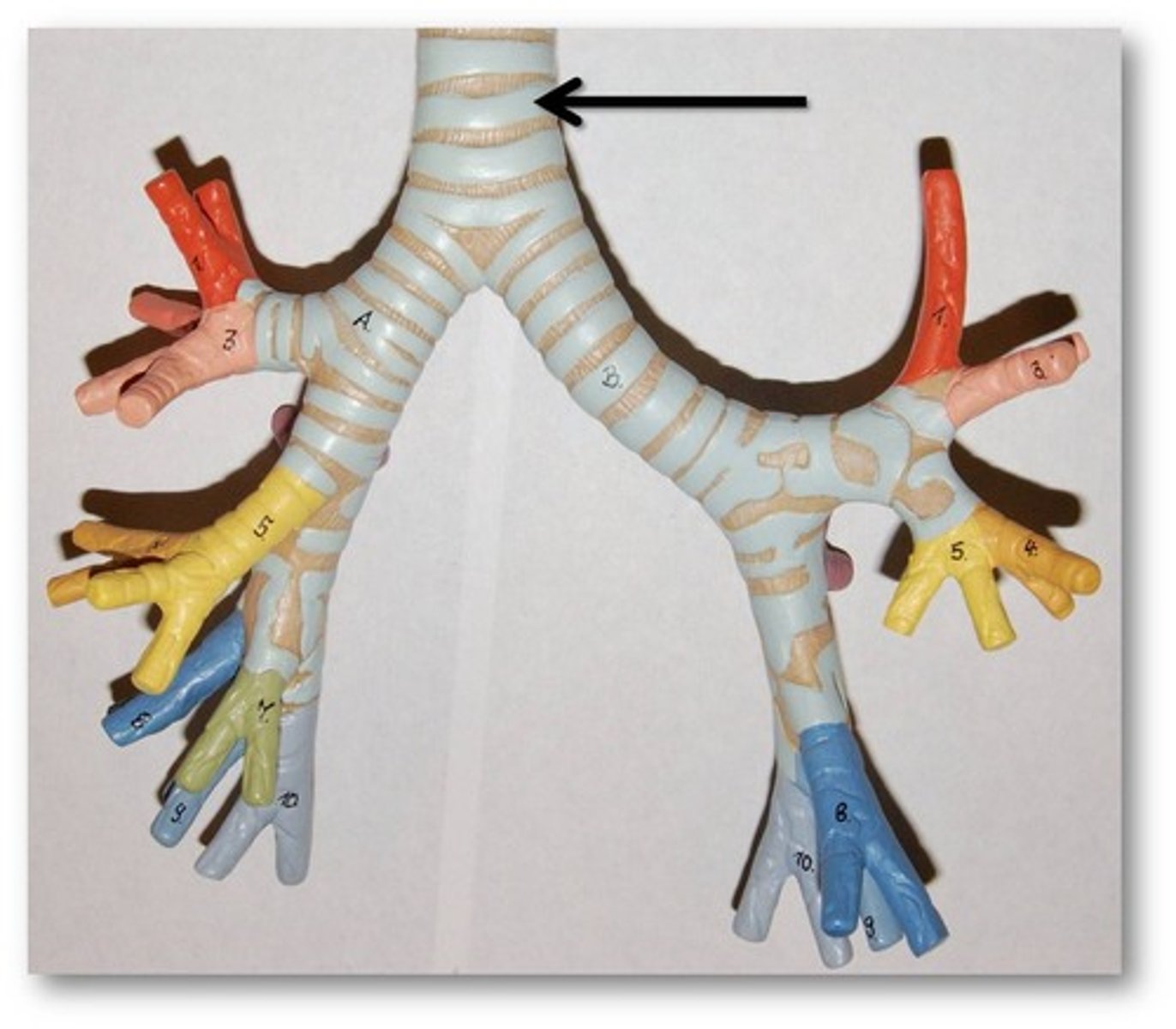
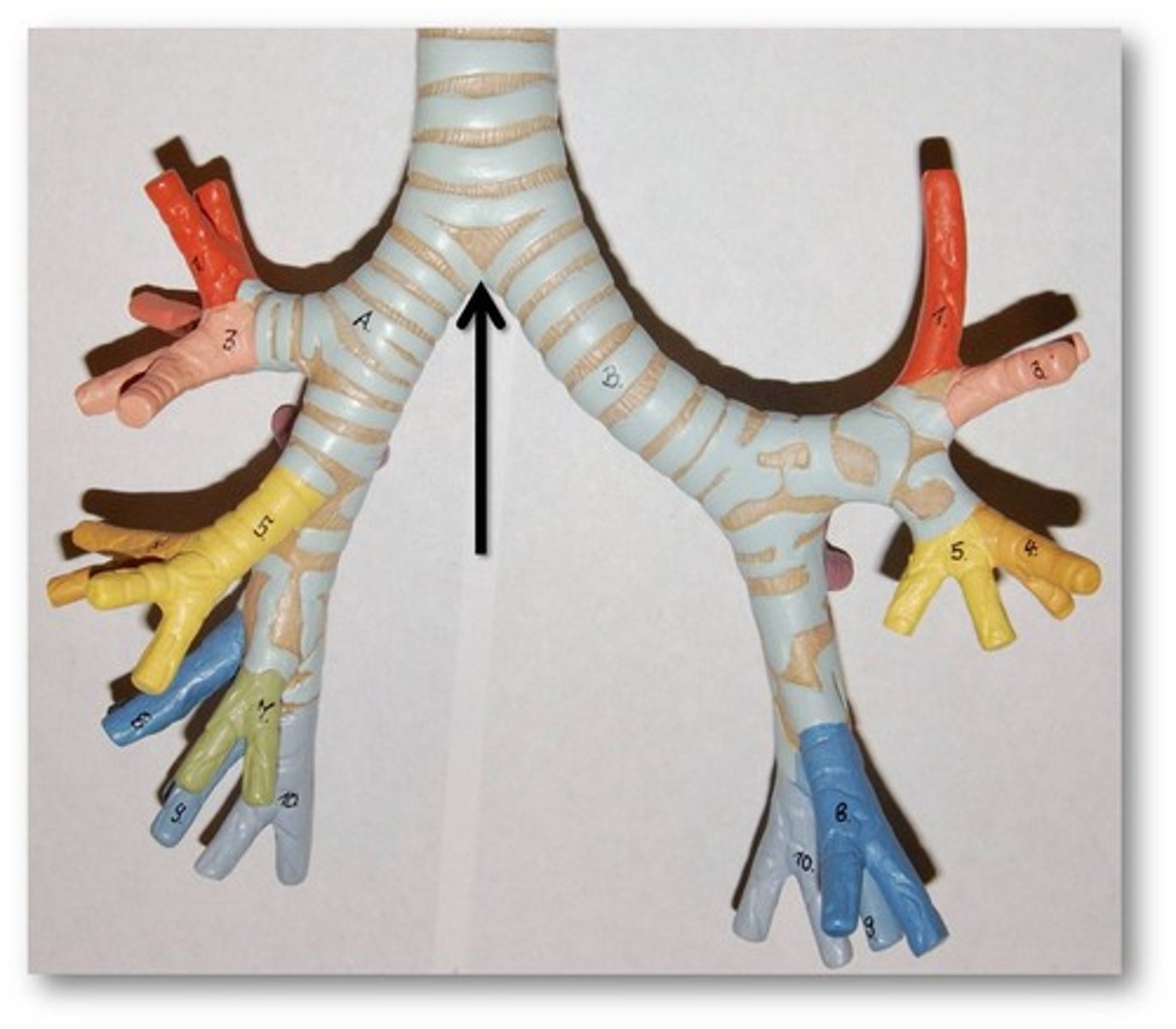
carina of trachea
Point at which the trachea divides into bronchi
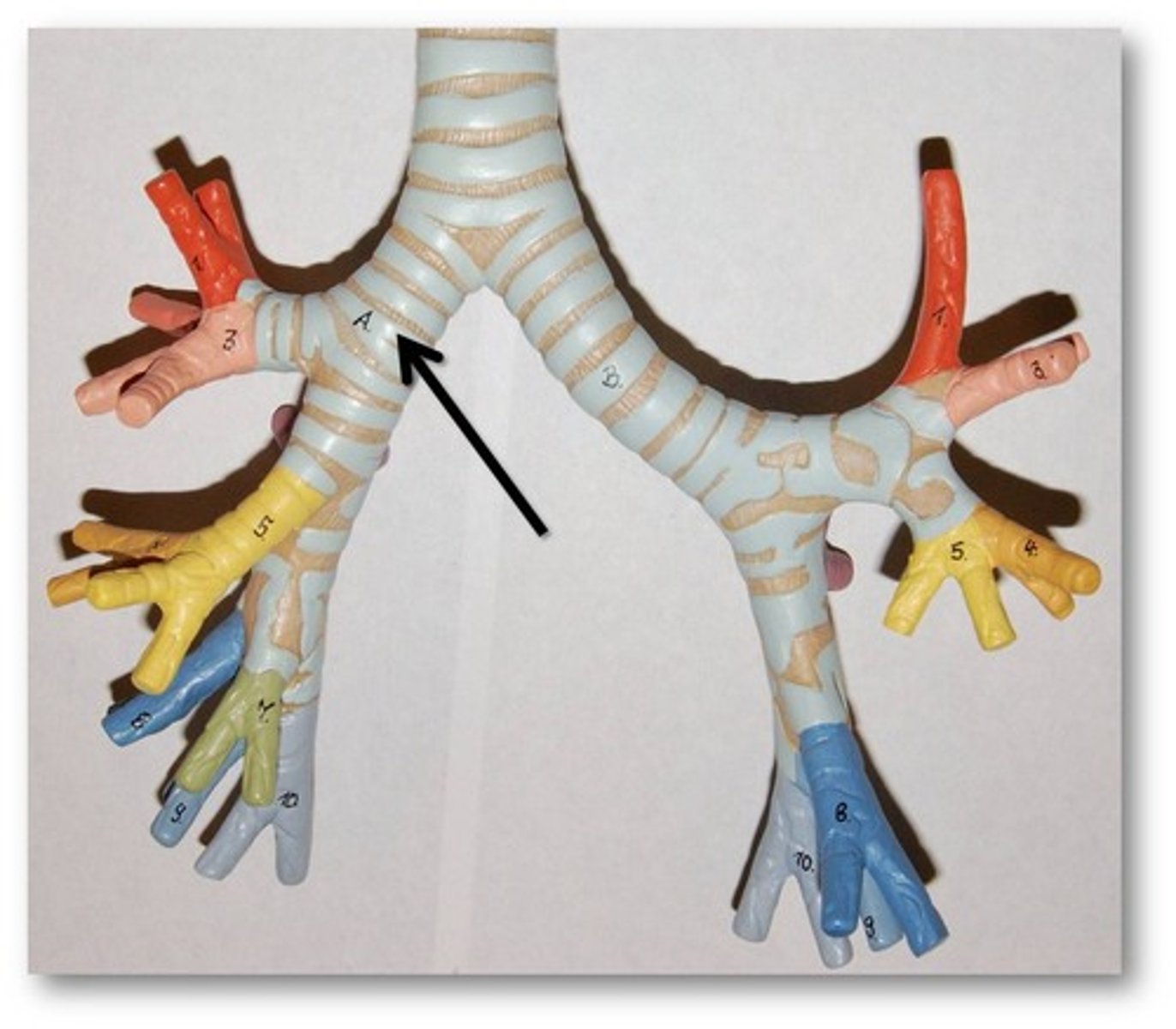
primary bronchi
The first branches of the trachea. There are two primary bronchi, one for each lung.
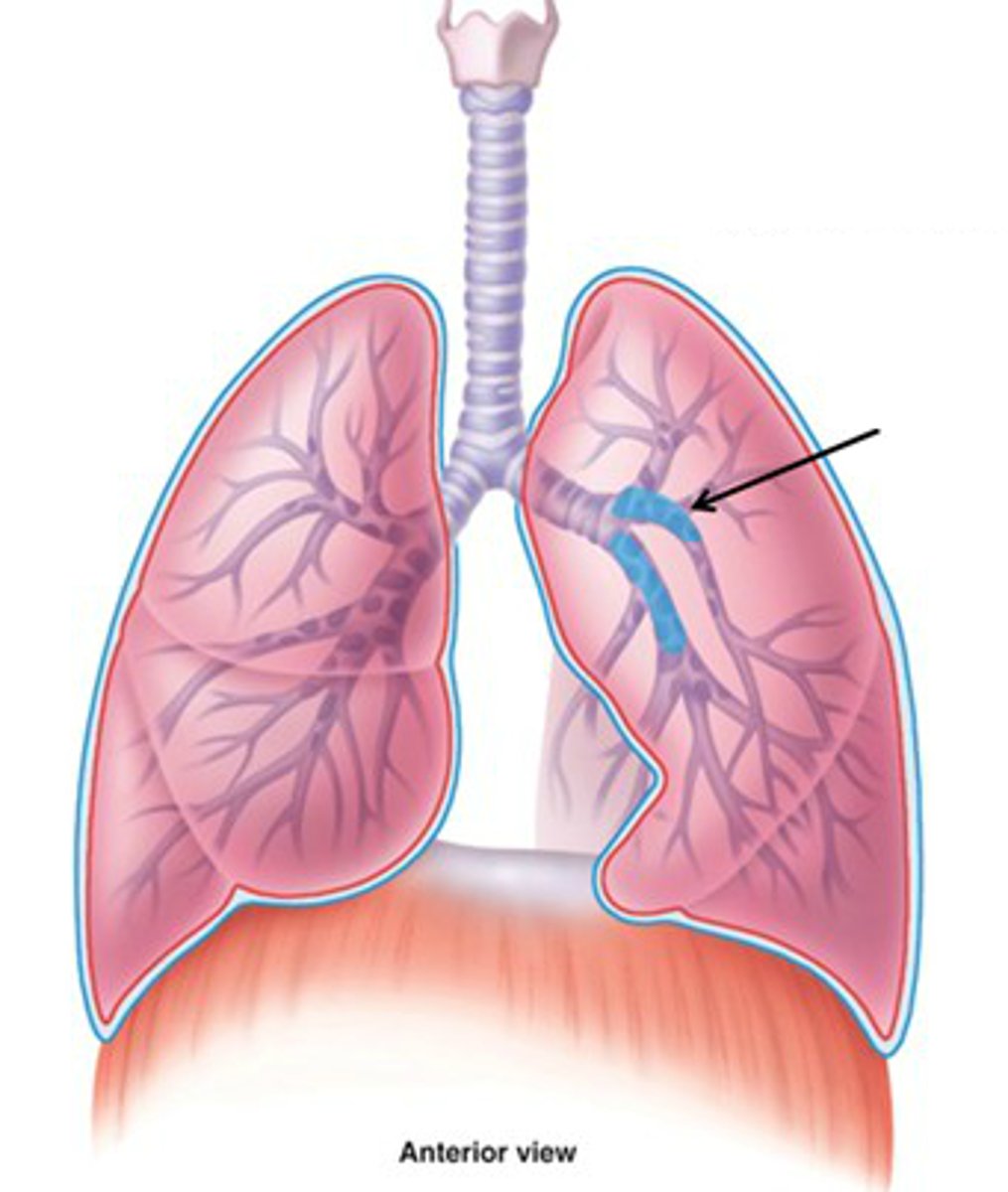
lobar bronchi
bronchial passageways connecting the mainstem bronchi with individual lobes of the lungs
segmental bronchi
Airways leading into specific lung segments.
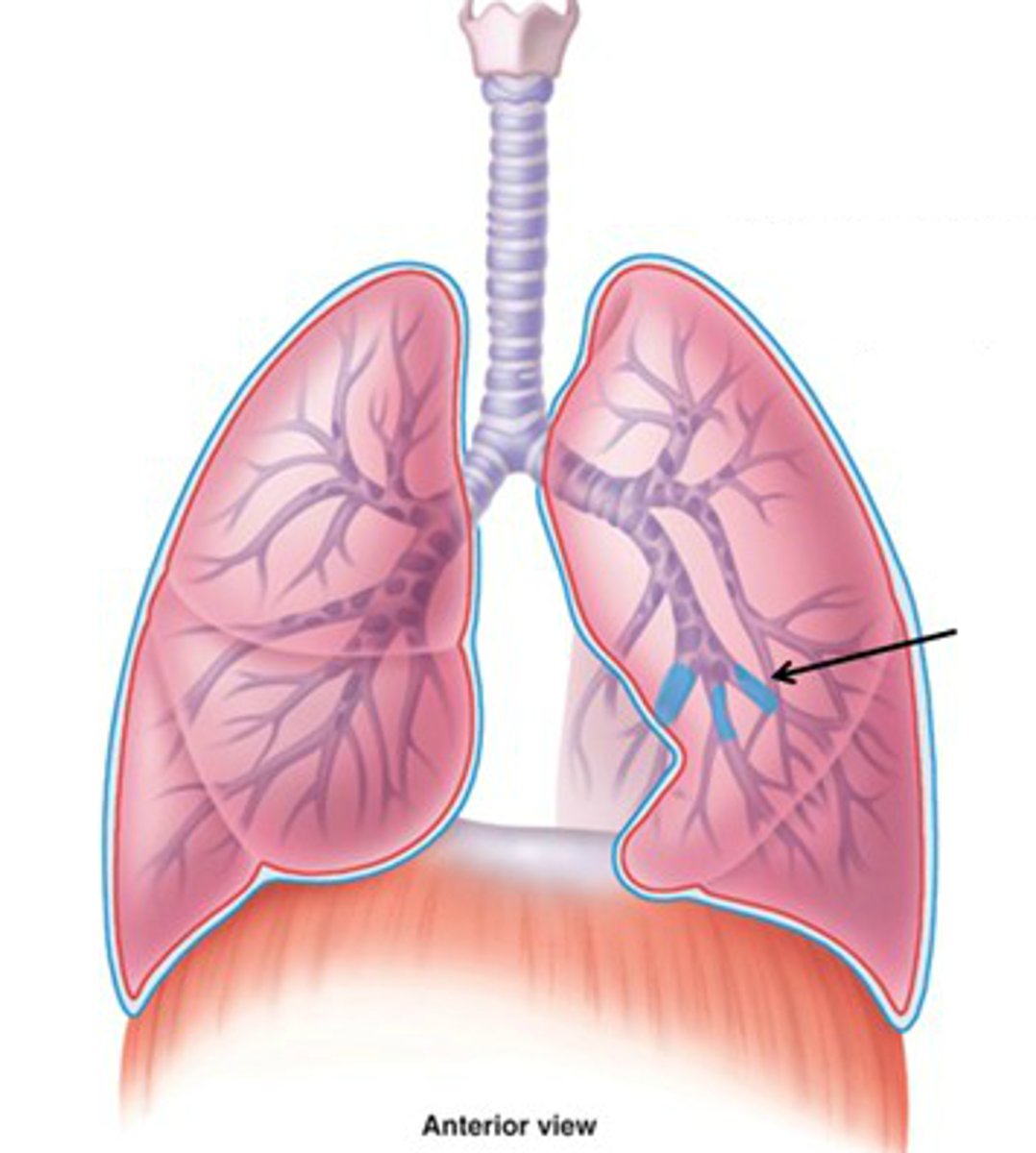
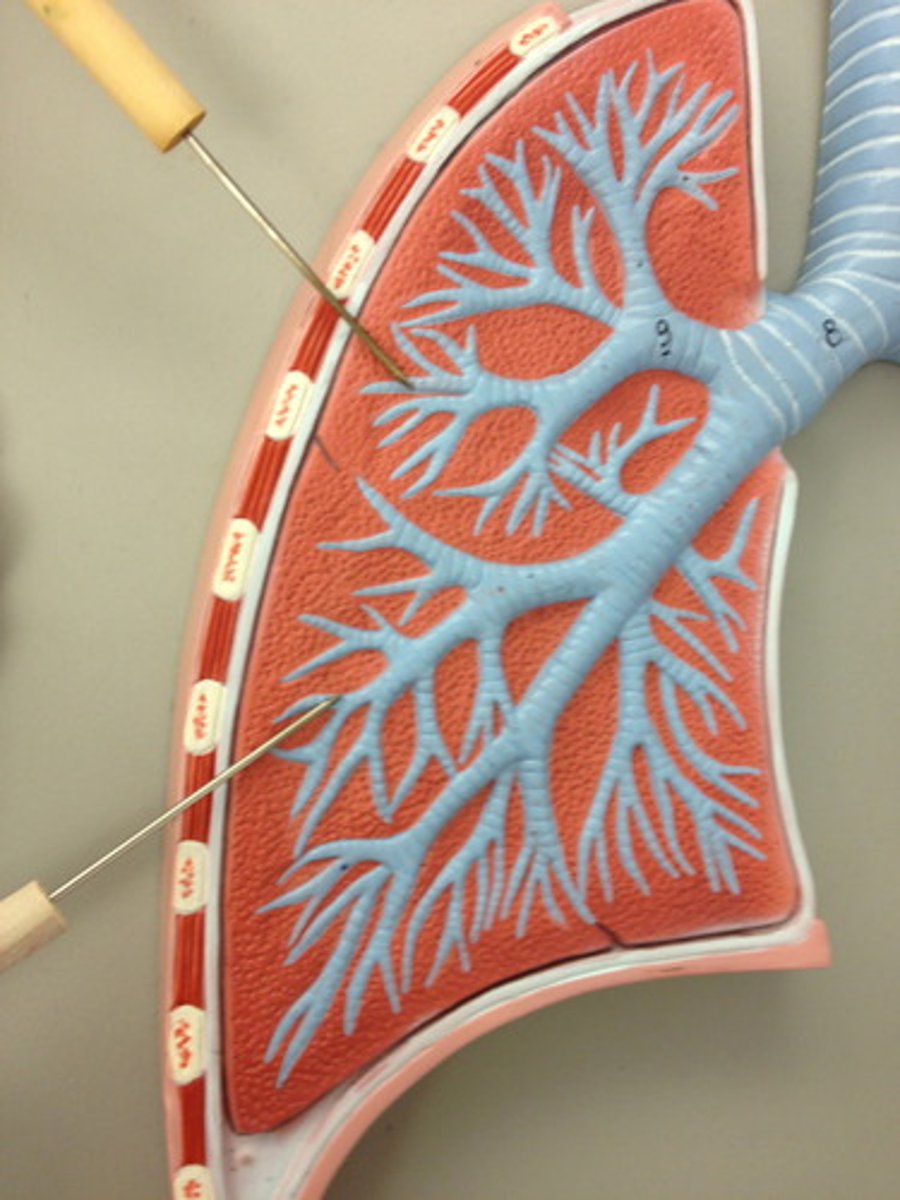
bronchioles
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
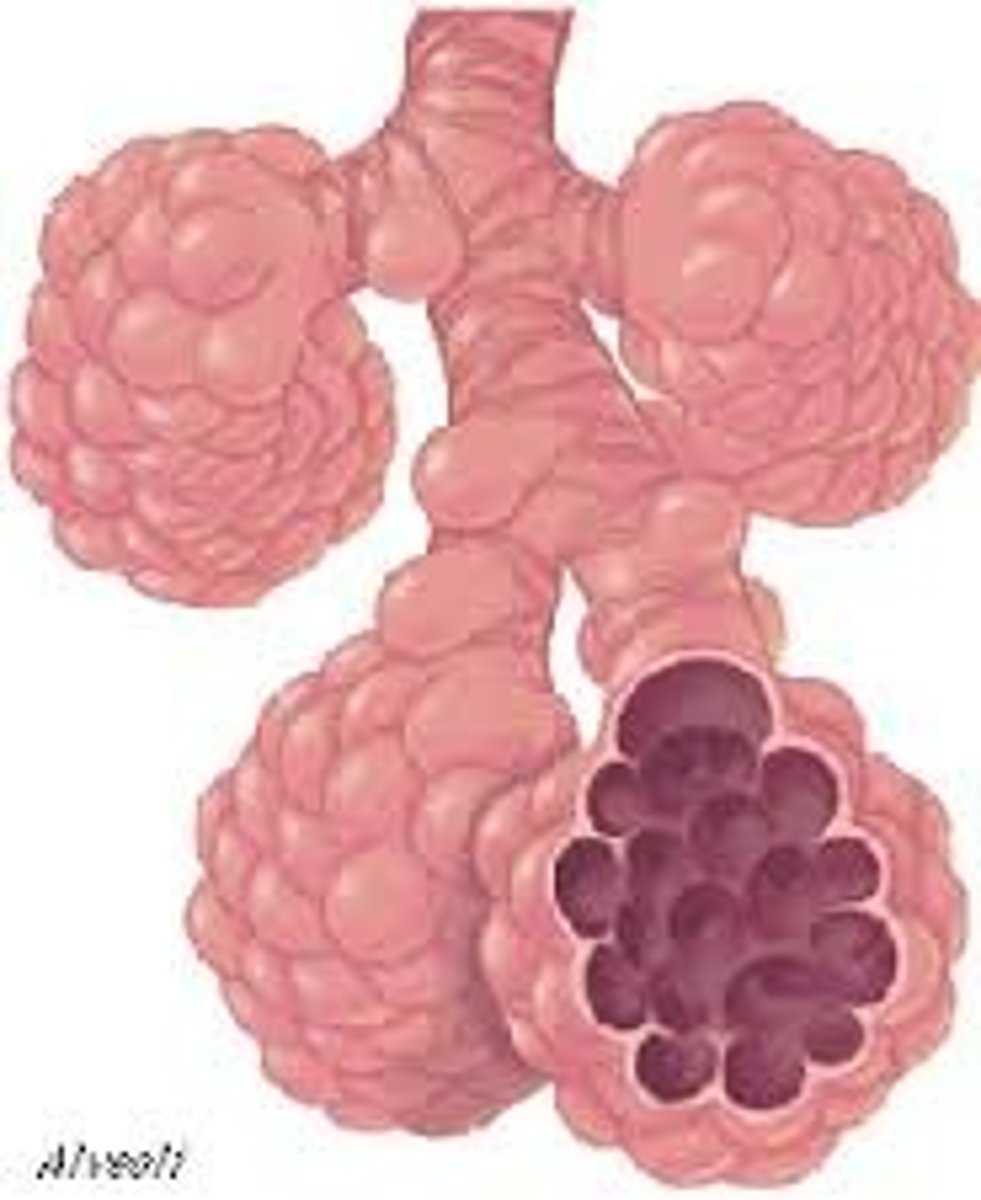
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
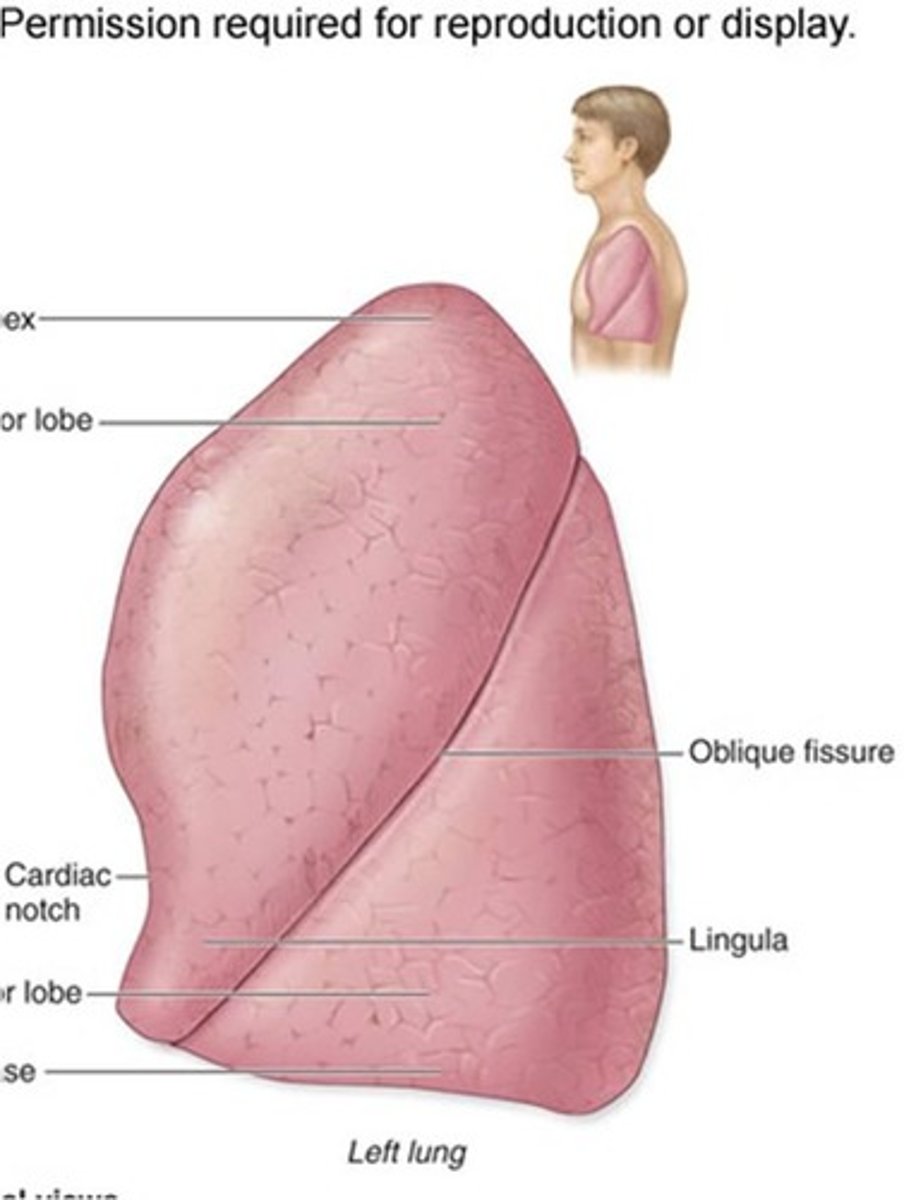
lobes of the left lung
superior and inferior
lobes of the right lung
superior, middle, inferior
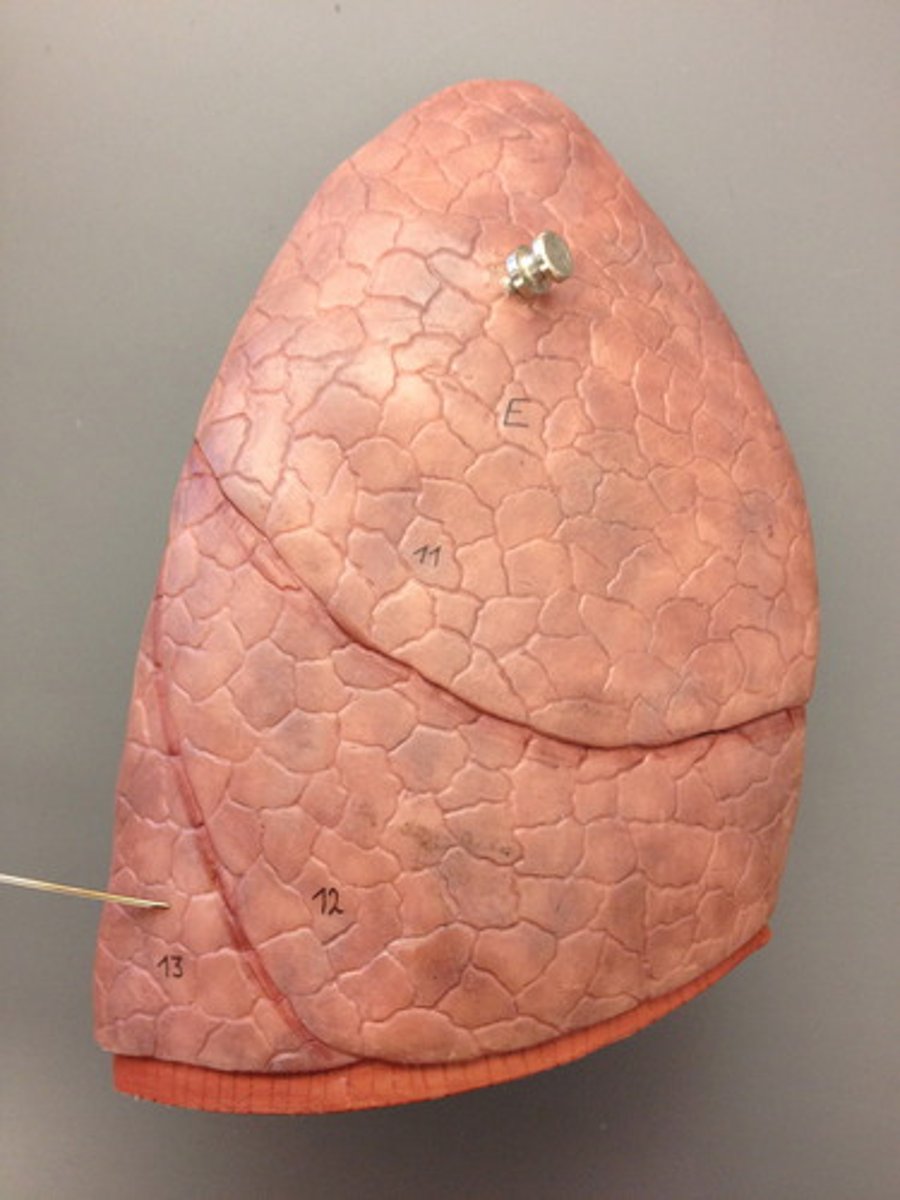
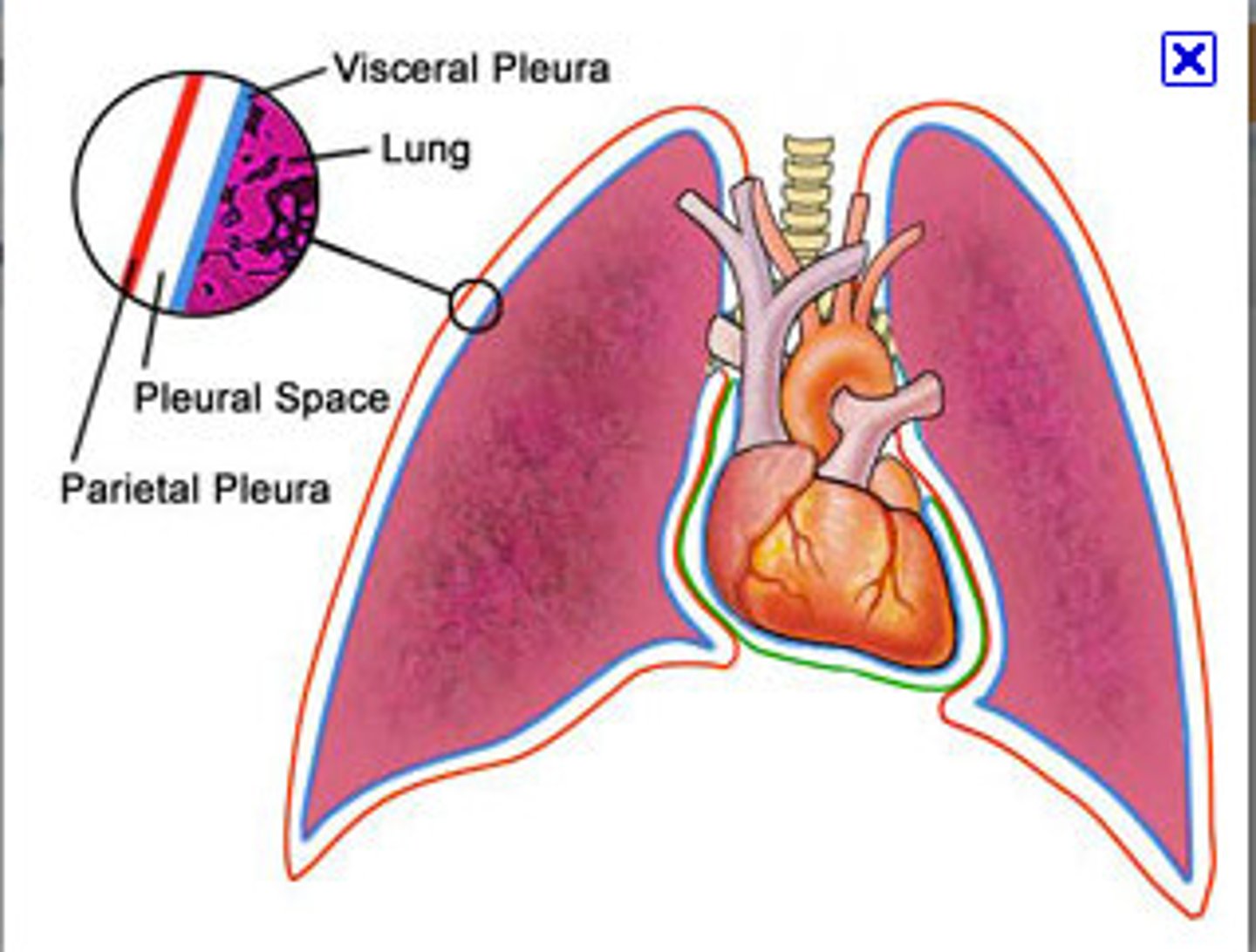
lungs parietal pleura
most superficial layer; lines thoracic wall
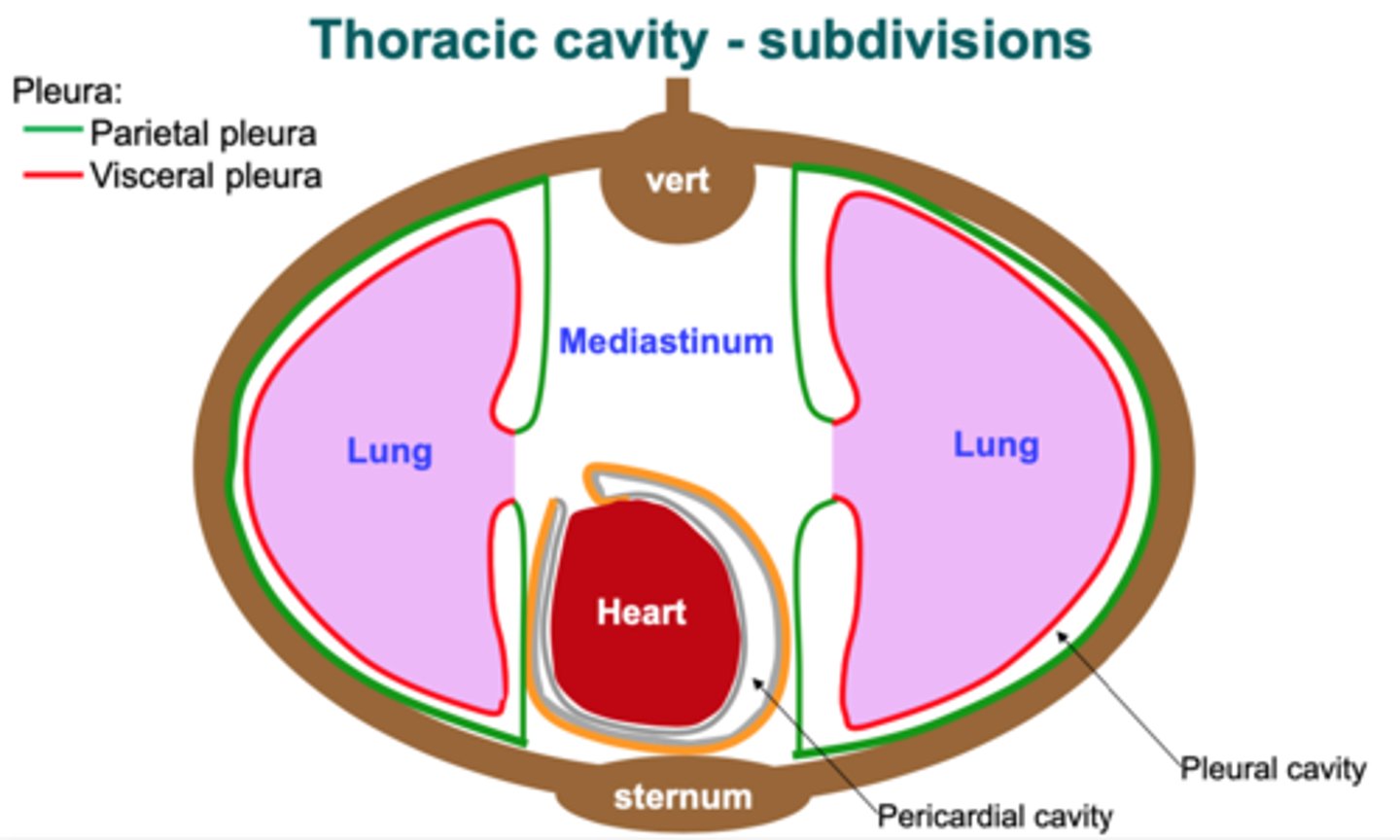
visceral pleura
inner layer of pleura lying closer to the lung tissue
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
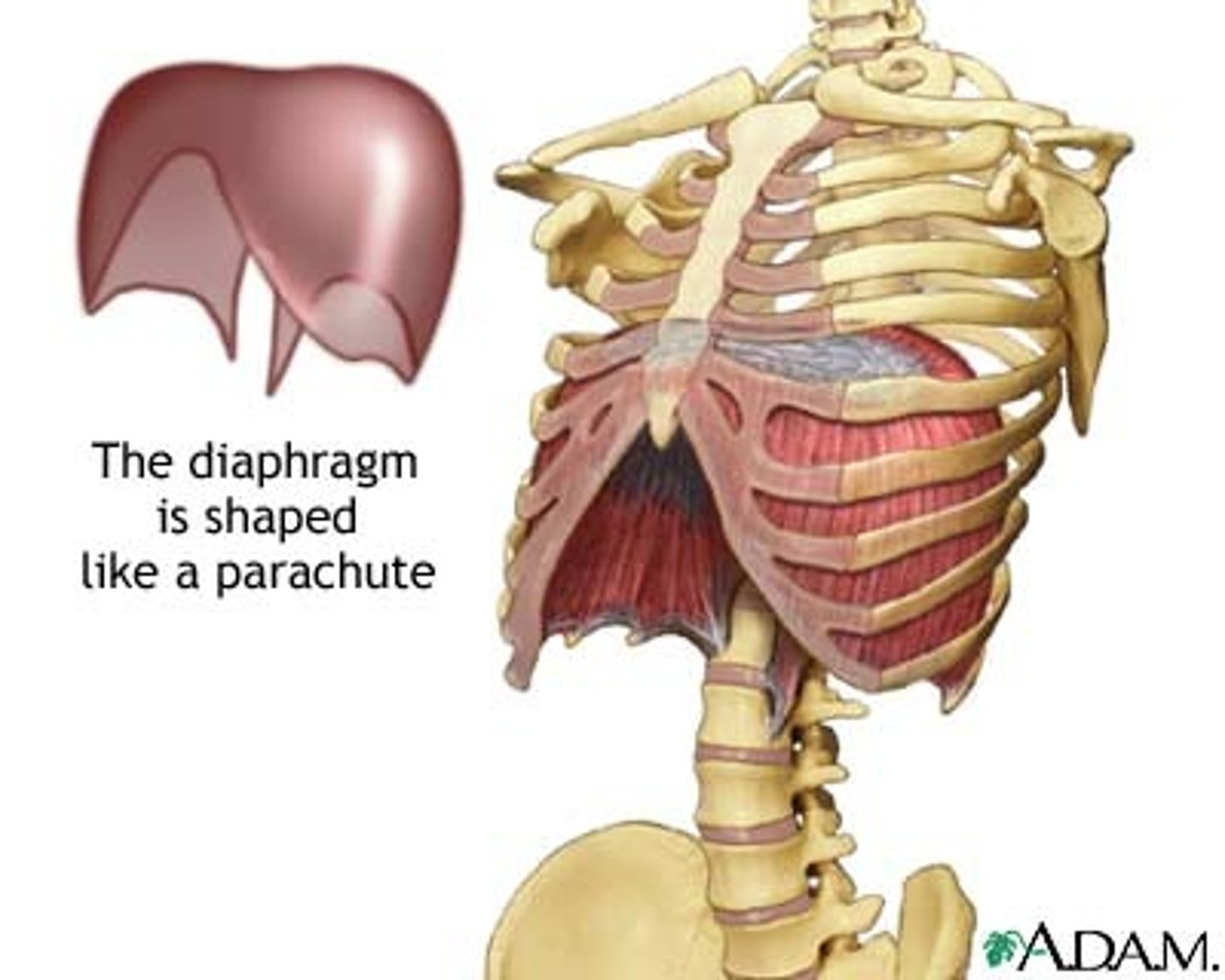
diaphragm origin
xiphoid process of sternum, lower 6 costal cartilages, first 3 lumbar vertebrae, medial and lateral arcuate ligaments
diaphragm insertion
central tendon
diaphragm action
contraction expands thoracic cavity, inhalation
relaxation leads to exhalation
diaphragm innervation
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
eupnea
normal breathing
apnea
dypnea
difficulty breathing
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, lung Dz commonly seen in smokers
surfactant
chemical produced in the lungs to maintain the surface tension of the alveoli and keep them from collapsing
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
pneumothorax
air in the pleural cavity
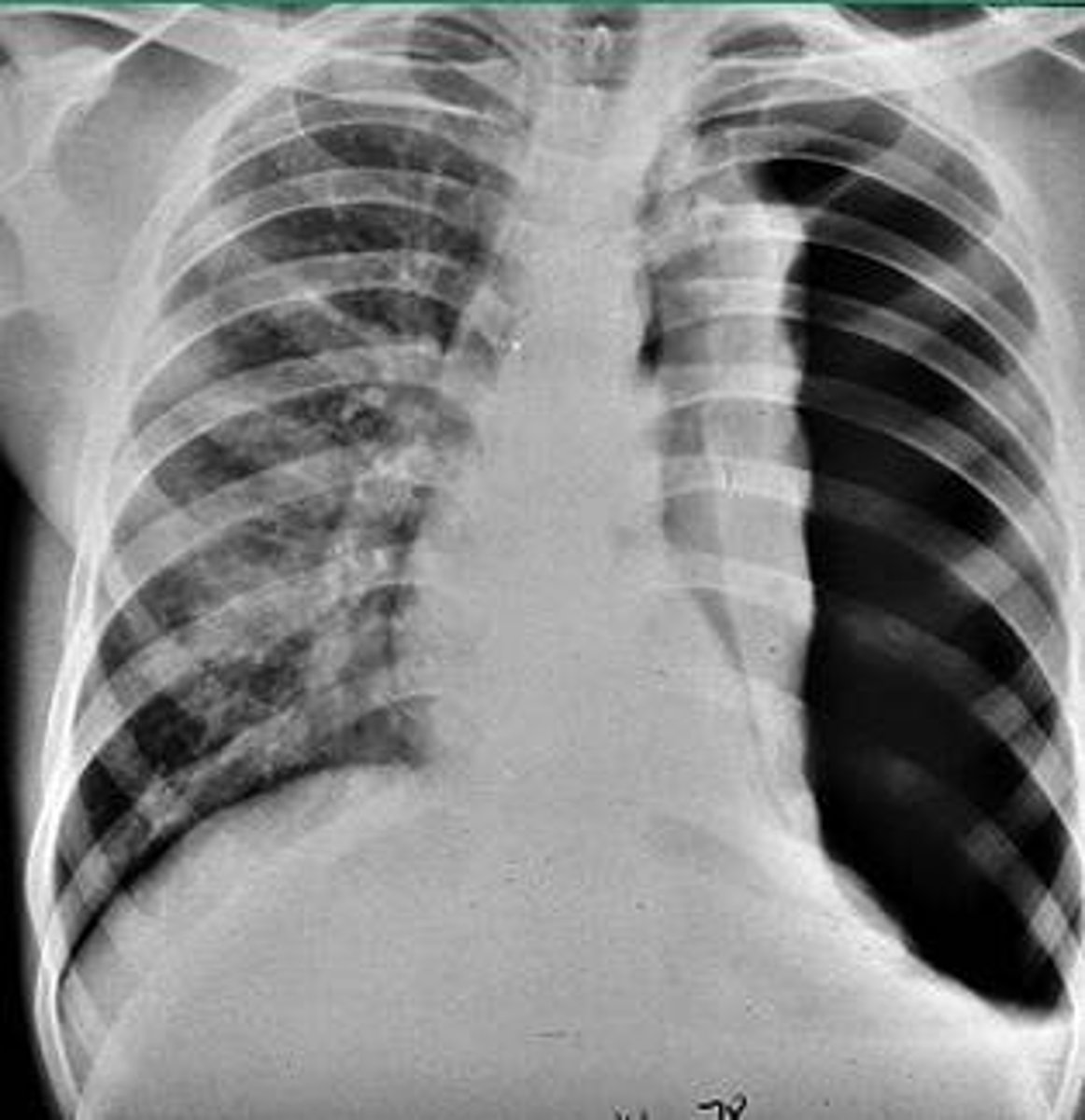
atelectasis
collapsed lung
air between pleural layers can cause
Pneumothorax, collapsed lung