FULL SET
1/773
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
774 Terms
what are some key words for muscles of the trunk
unilateral - one side
bilateral - both sides
concentric - muscles shorten under tension
eccentric - muscles length under tension
isometric - muscles says the same length under tension
intrinsic - muscles contained within a region
extrinsic - muscles partially contained within a region
what is some information about intrinsic back muscles
proximally attached to (originate from) back
distal attachment on the arm/shoulder blade
what is the thoracolumbar fascia
a connective tissue that overlies intrinsic back muscles
a common point of attachment for extrinsic back muscles
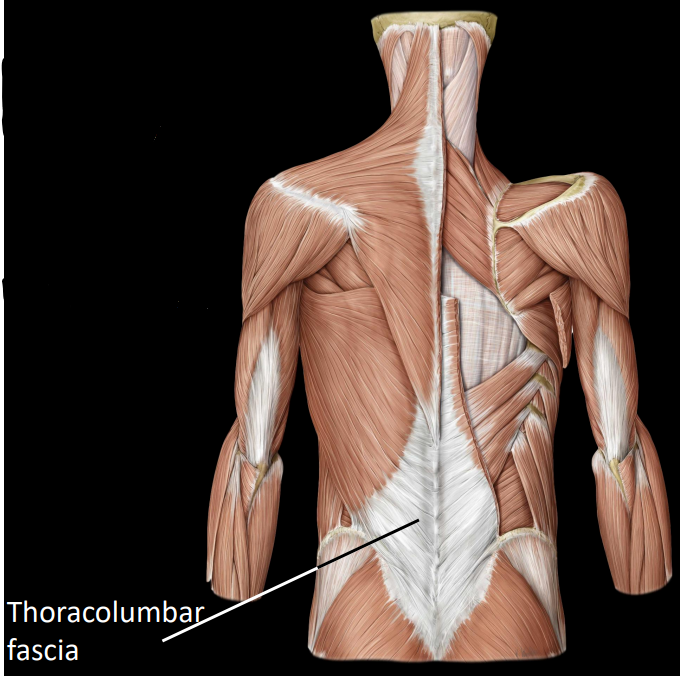
what is some information about intrinsic back muscles
span from one vertebrae to another, can also attach to:
ileum, ribs, skull base
what are the functions of intrinsic back muscles
act upon vertebrae column:
fine postural adjustments
rotation
forceful extension, lateral flexion
arranged in 3 layers
what is the orientation of superficial layer of intrinsic back muscles
fiber orientation = inferomedial → superolateral
bilaterally extend the spine
what are some muscles of the superficial layer
splenius:
only in head & neck
bilateral contraction = extends head & neck
unilateral contraction = laterally flexes head & neck
erector spinae (3 muscles):
spinalis - spinous process to spinous process
longissimus - longest muscle in body
iliocostalis - iliac crest to ribs
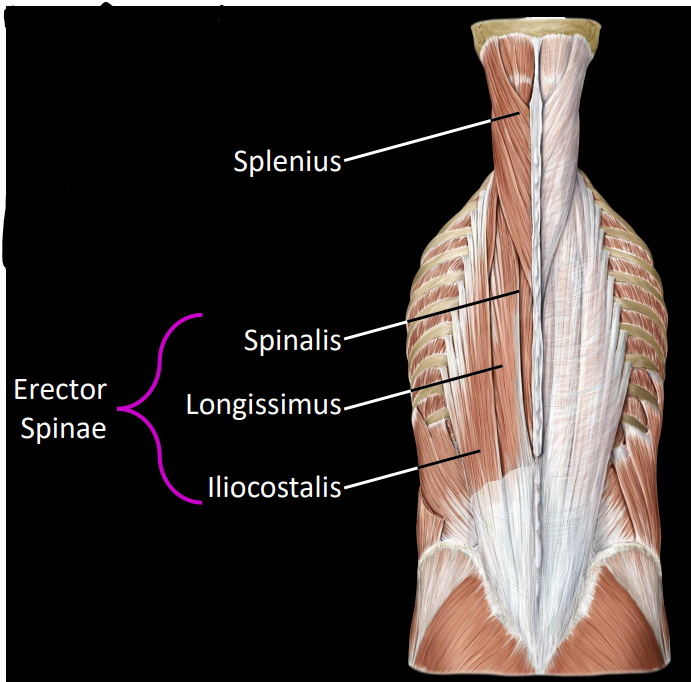
what is the movement pattern of the erector spinae
bilateral contraction = extension of the spine
unilateral contraction = lateral flexion
what is the orientation of transversospinales layer of intrinsic back muscles
fiber orientation = inferolateral → superomedial
from transverse processes → spinous processes
differing number of spanned segments
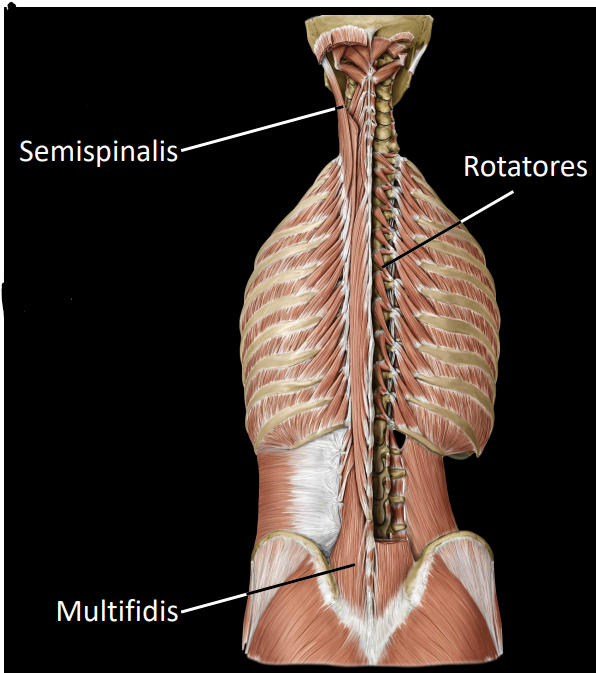
what are some muscles of the transversospinales layer
semispinalis:
spans 4-6 vertebrae segments
maintaining posterior
extension/lateral flexion of the head & neck
Multifidis:
spans 3-4 vertebrae segments
important core stabilisator of thoracolumbar vertebrae
allows erector spinae to act on VC as one unit
Rotatores:
spans 1-2 vertebrae segments
dynamic stabiliser of rotation movement
what are proprioceptors
sensory nerve endings that provide input on body movement and muscle tension
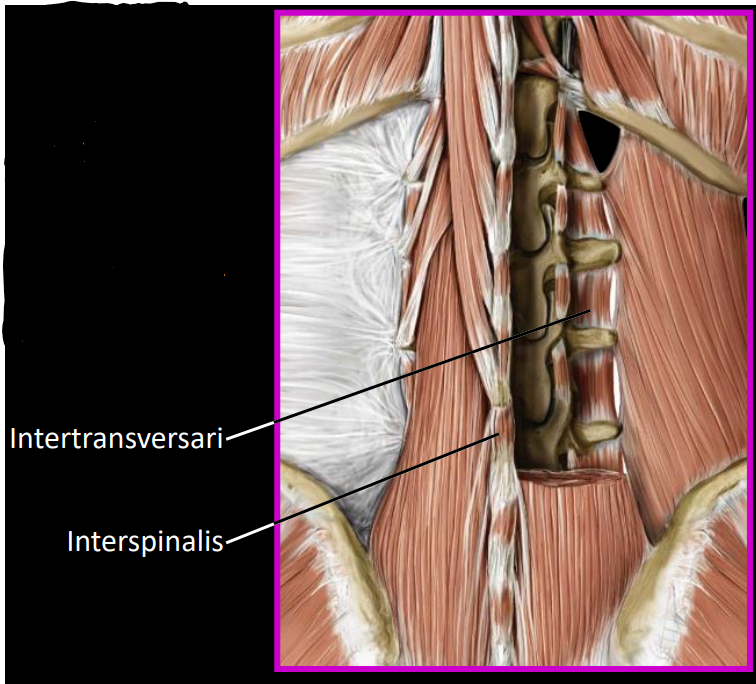
what is the fiber orientation of the deep layer
vertical, spans between adjacent vertebrae spinous processes (segmentals)
what are some muscles of the deep layer
interspinalis:
muscles between adjacent spinous processes
intertransversarii:
muscles between adjacent transverse processes
responsible for postural adjustments to the vertebrae
what are intercostal muscles
muscles that are located between the ribs
arranged into 3 perpendicular layers (external, internal, innermost)
what are the external intercostals
fibers that run obliquely down towards midline
superolateral to inferomedial
act to elevate ribs during inhalation (expand the thorax)
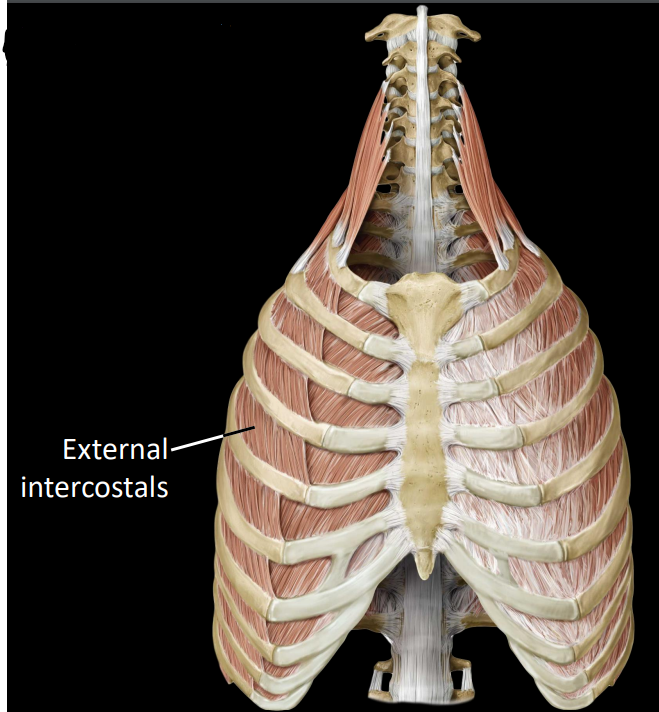
what are the internal intercostals
fibers that run inferolateral to superomedial
depresses rib during forced exhalation (compress/contract thorax)
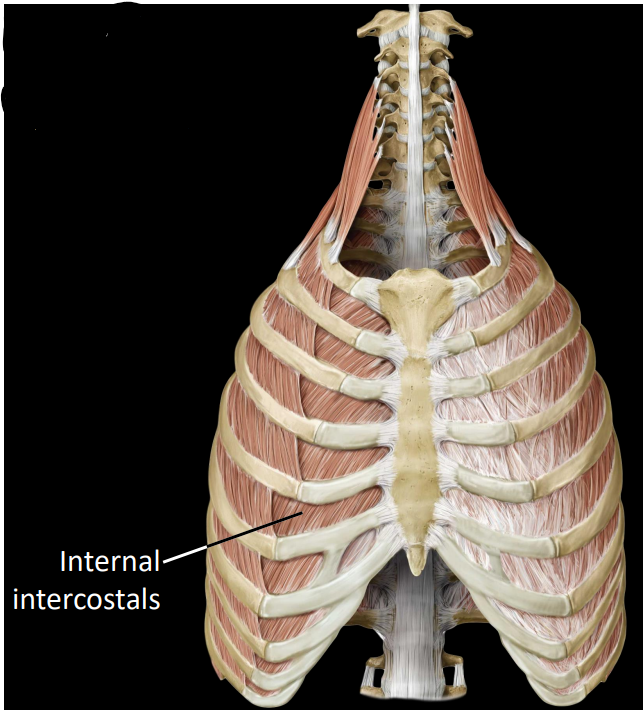
what are the innermost intercostals
fibers that run inferolateral to superomedial
depresses rib during forced exhalation (compress thorax)
only spans 1 intercostal space
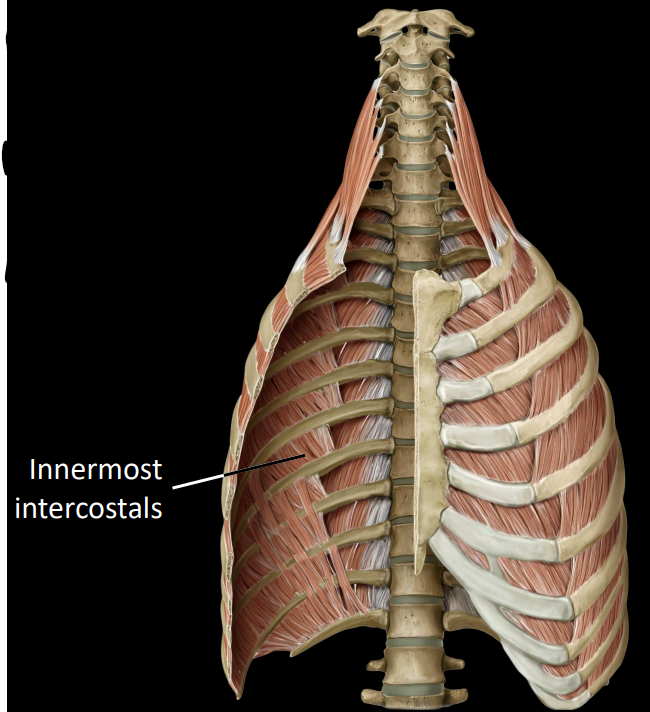
what are subcostal muscles
only present on posterior thoracic wall
fibers can span 2-3 intercostal spaces
depress ribs during forced exhalation
superolateral to inferomedial
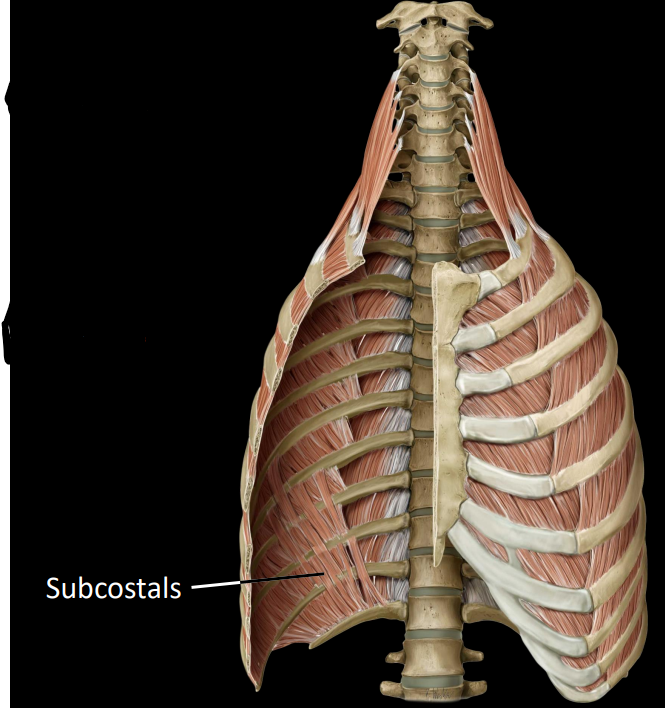
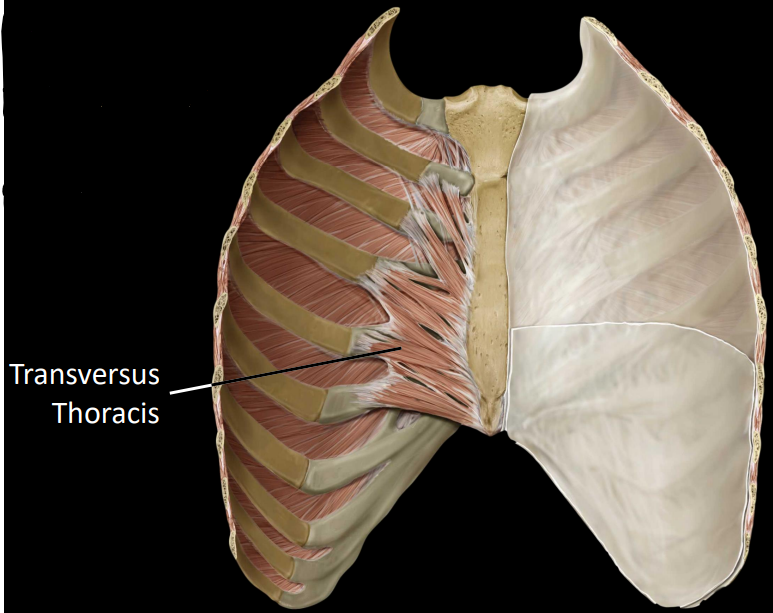
what are the transversus thoracis
fibers that project laterally from the internal aspect of the sternum
breastplate
depress ribs during forced exhalation
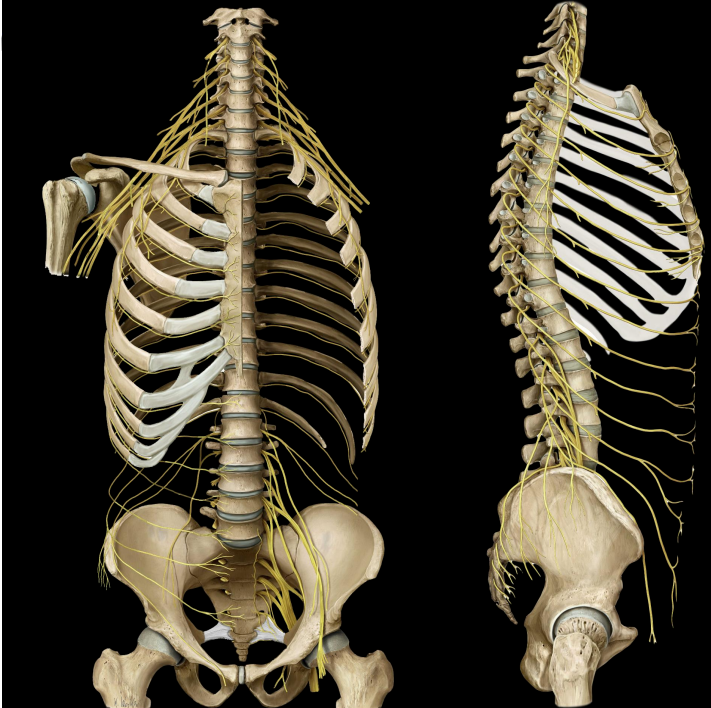
what is the intercostal neurovasculature
intercostal spaces are shared by:
veins, arteries, nerves (superior to inferior
runs along costal groove between internal & innermost intercostals
what are the intercostal nerves
11 intercostal nerves
ventral rami of the thoracic nerves
12th nerves = subcostal nerve (beneath rib)
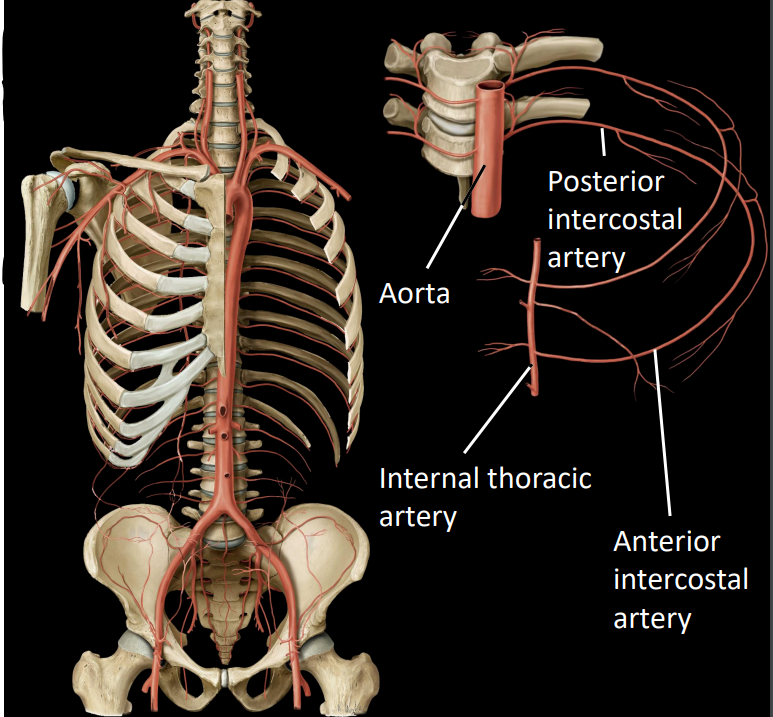
what are the intercostal arteries
2 sets of intercostal arteries:
anterior intercostal arteries - arises from internal thoracic artery (lateral of sternum)
posterior intercostal arteries - arises from the aorta
anterior & posterior intercostal arteries with anastomose (connect) with each other at the most lateral part of the trunk wall
what are the intercostal veins
2 sets of intercostal veins:
anterior intercostal veins - drains to internal thoracic veins (2)
posterior intercostal veins - drains to azygous & hemiazygous veins
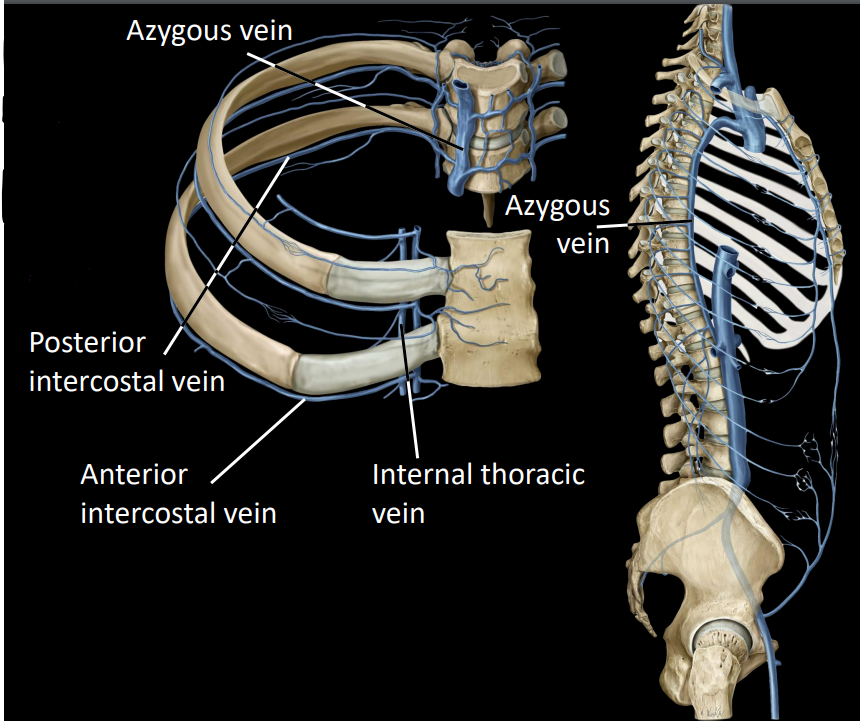
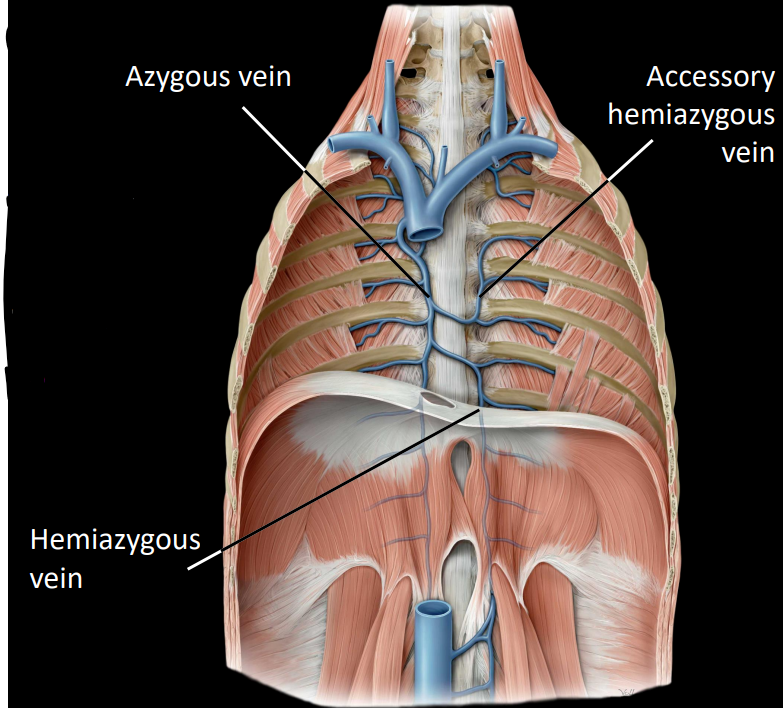
what is the azygous system
azygous:
located on the right side of the midline
receives right posterior intercostal veins
hemiazygous & accessory hemiazygous:
receives left posterior intercostal veins
this ultimately drains into the azygous
what is some information on the abdominal wall muscles
encloses the abdominal cavity
anterolateral & posterior groups
involved in actions that increased intraabdominal pressure (coughing, laughing, vomiting)
retains abdominal viscera (protects from injury)
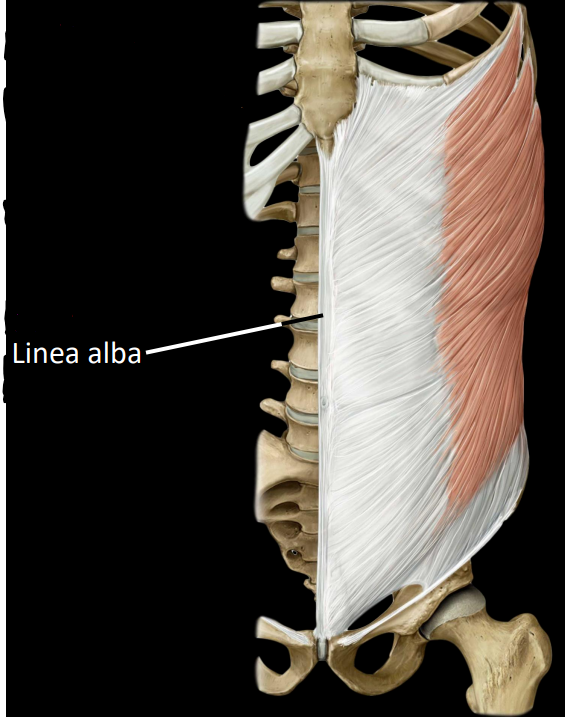
what is some information on the anterolateral abdominal wall muscles
attached anteriorly via aponeuroses
tendon sheets
muscles may insert on Linea alba
midline tendonous seam
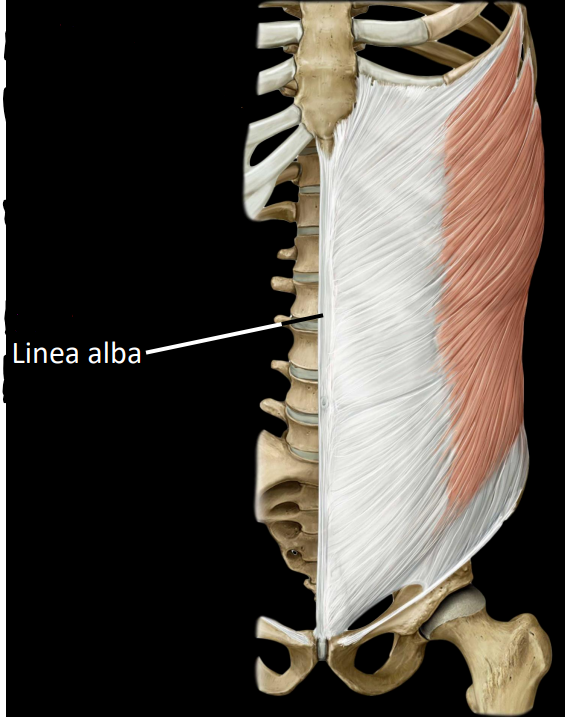
what are the external oblique muscles
largest, most superficial muscles
rotates torse towards contralateral (opposite) side
laterally flex trunk
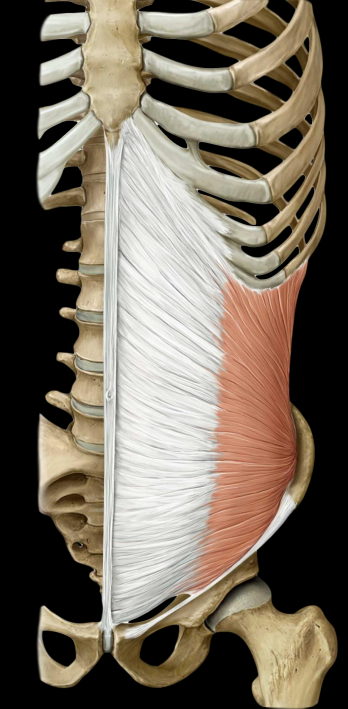
what are the internal oblique muscles
deep to external, smaller and thinner
rotates torso to ipsilateral (same) side
laterally flex trunk
what are the transverse abdominis
deepest, transverse fiber orientation
stabilizes lumbar spine & pelvis
attaches posteriorly to lumbar vertebrae
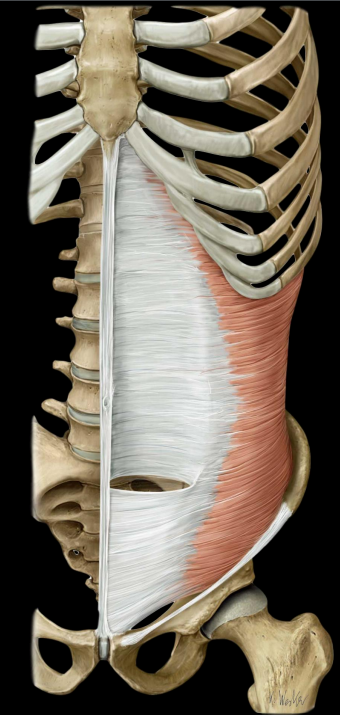
what is the rectus abdominius
flexes lumbar spine
Linea semilunaris at lateral border
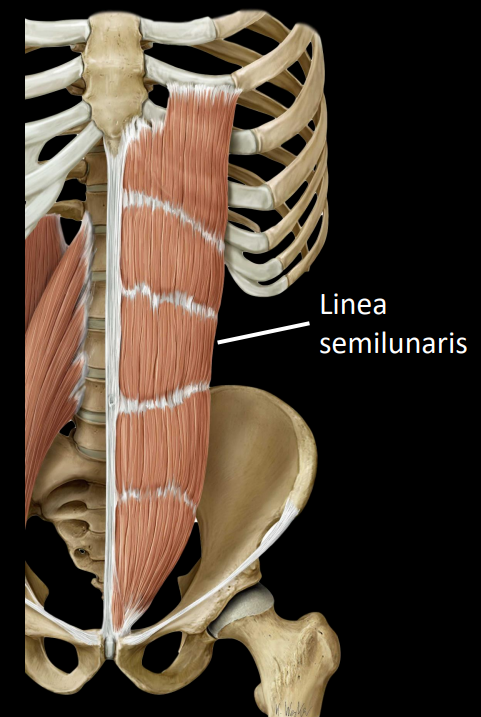
what is the rectus sheath
rectus abdominis enveloped by aponeuroses of:
external & internal obliques
transversus abdominis
these envelopes are the rectus sheath
aponeurotic relationship changes at the arcuate line
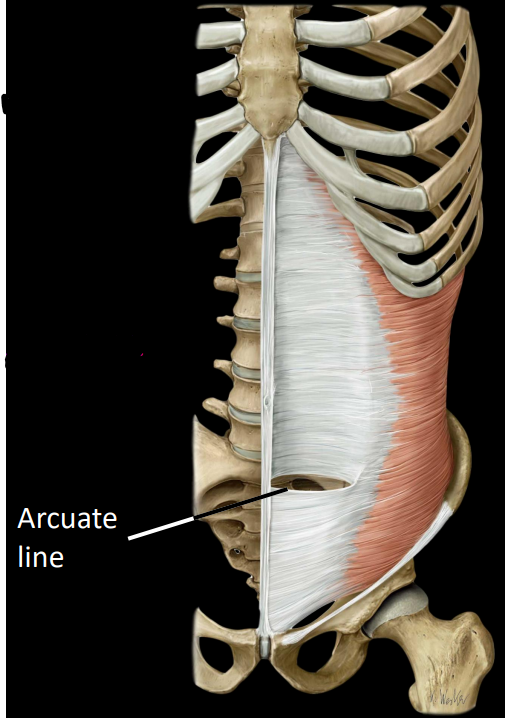
what is some information about the section superior to the arcuate line
Aponeuroses evenly distributed anterior and posterior to rectus abdominis
Transversus abdominis aponeurosis courses posterior to rectus
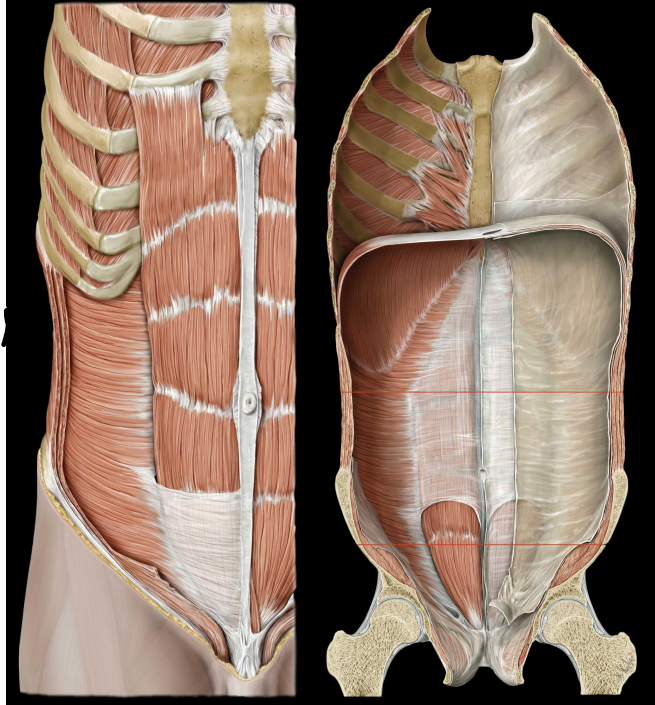
what is some information about the section inferior to the arcuate line
All aponeuroses course anterior to rectus abdominis
Strengthens lower abdominal wall
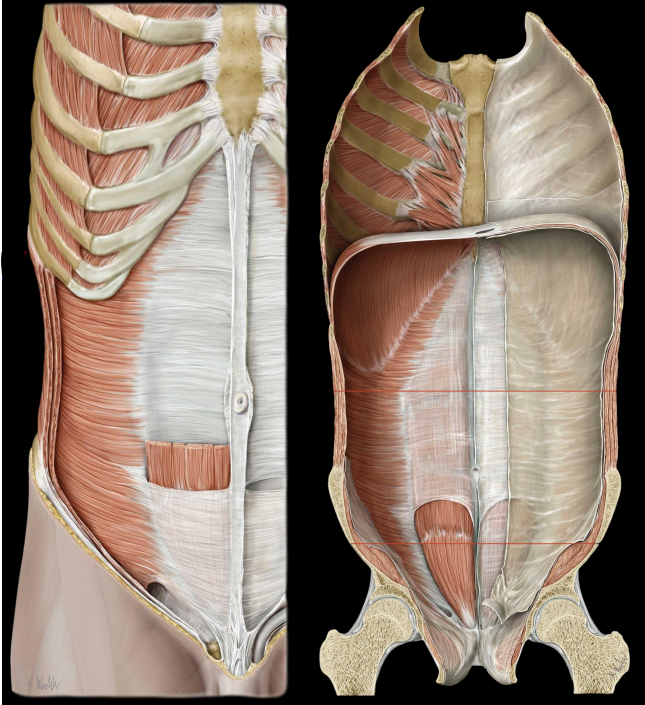
what is diastasis recti
separation of the abdominis rectus
caused by chronic increase intra-abdominal pressure
can lead to umbilical hernia (part of small intestine pokes through belly button)
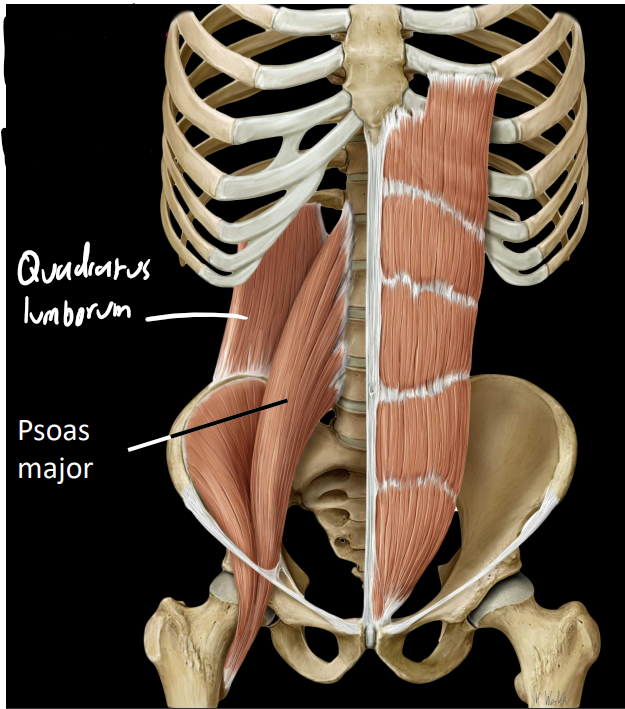
what are some structures of the posterior abdominal wall muscles
psoas major:
attaches laterally to lumbar spine
flexes hip
important postural muscle
Quadratus lumborum:
lateral to psoas major
attaches to 12th rib & iliac crest
what is some information on the pelvic floor
formed by 4 muscles
retains pelvic & abdominal viscera within pelvis
perforated (pierced) by 2-3 apertures
what are the main 2 apertures of the pelvic floor
urogenital hiatus
rectal hiatus
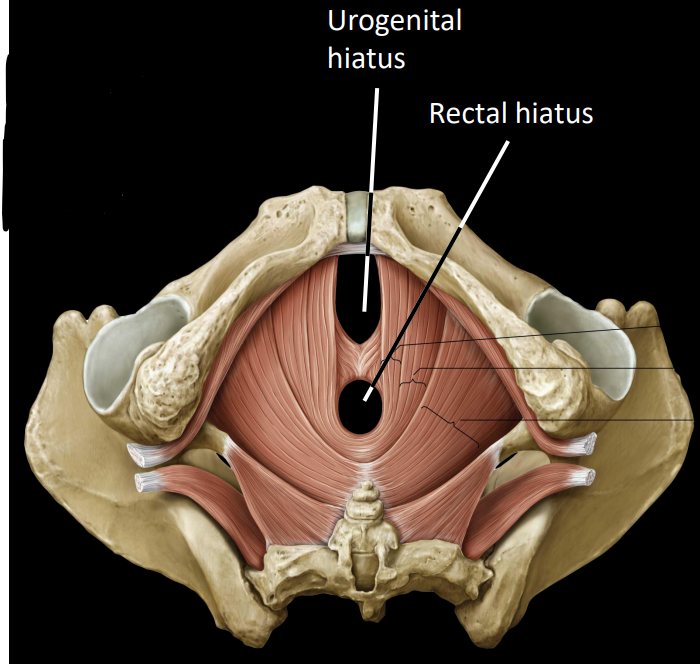
what is some information on the pelvic floor muscles
support abdominopelvic viscera through tonic contraction (always contracting) important for expelling waste
resists intra-abdominal pressure
what are the levator ani
3 of the 4 pelvic muscles that act to elevate the anus
Puborectalis
Pubococcygeus
Iliococcygeus
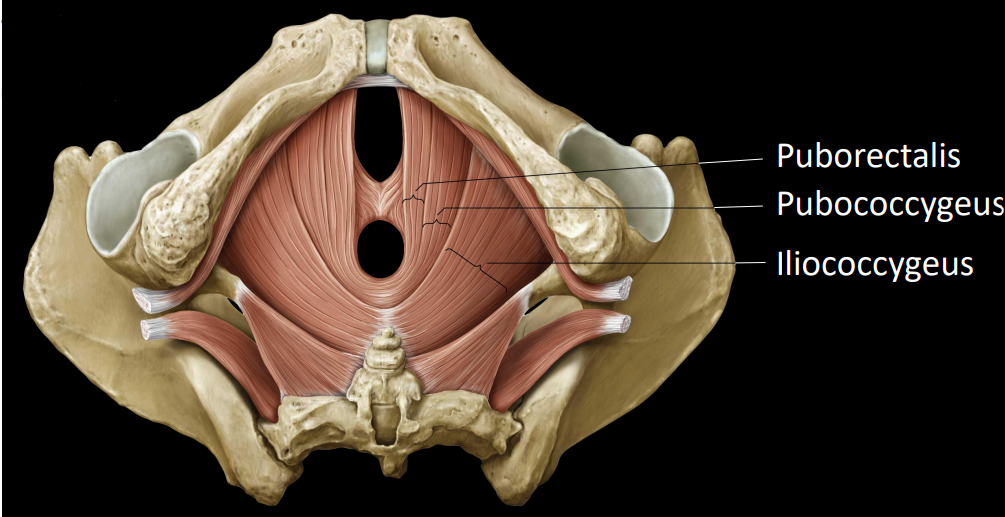
what is the coccygeus
last pelvic floor muscle
support pelvic viscera & weakly flexes coccyx
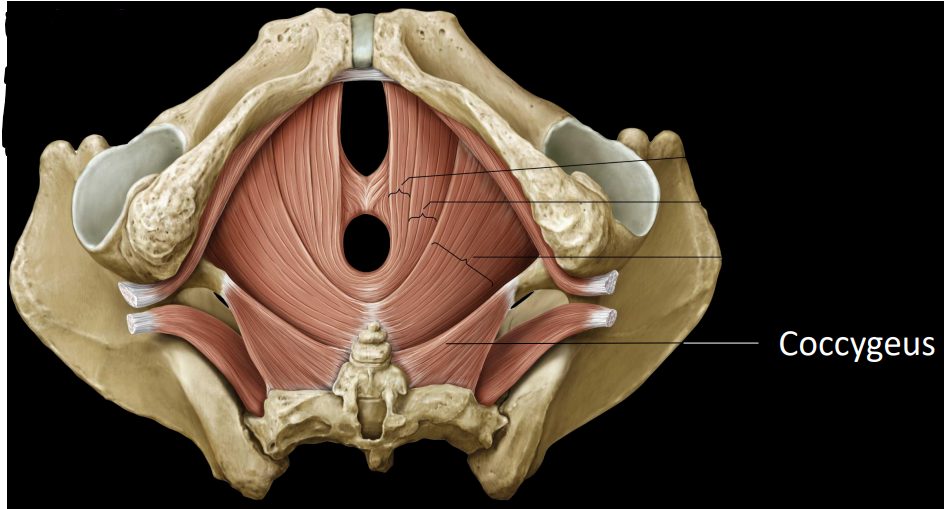
what is some information on the quadratus lumborum
vertically arranged
arises from lumber vertebrae
arises from ribs (partly)
what is some information on the psoas major
flexes the hip
arises from lumber vertebrae
what are some Latin terms for the spine
foramen/foramina - ‘hole’
inter - ‘between’
intra - ‘within’
articulation - ‘joint’
vertebrae - ‘turning’
what is the difference between flexion & extension
flexion - ‘bending’ (front)
extension - ‘straightening’/’stretch out’
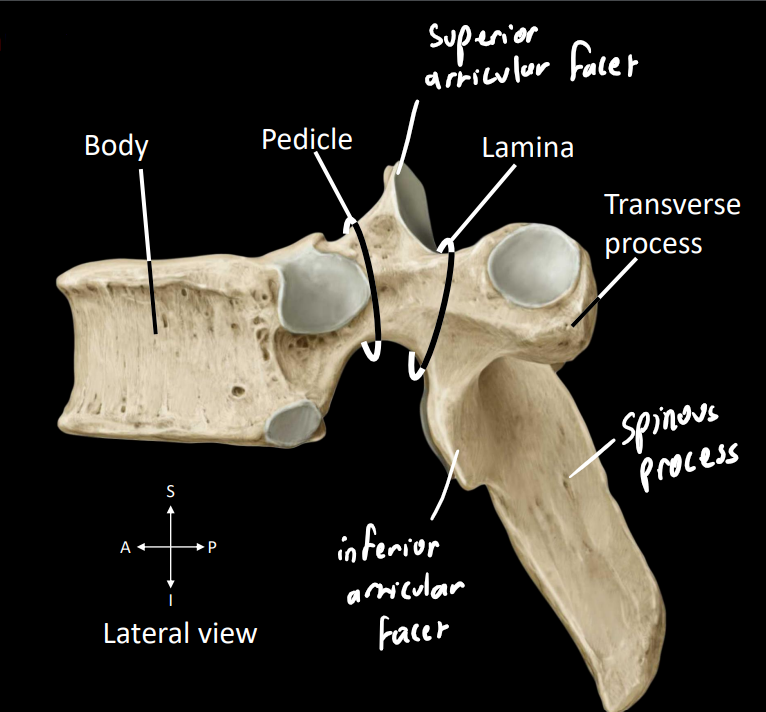
what are some of the components of the spinal cord
body - dense part that supports the weight of the body
pedicle - posterior projection
lamina/laminae - flat sheet
spinal/vertebral foramen - single unit of the spinal canal, encloses the spinal cord
spinous process - posterior projection (spinal palpate [can feel over skin])
transverse process - lateral projection
![<p><strong>body</strong> - dense part that supports the weight of the body</p><p><strong>pedicle</strong> - posterior projection</p><p><strong>lamina/laminae</strong> - flat sheet</p><p><strong>spinal/vertebral foramen</strong> - single unit of the spinal canal, encloses the spinal cord</p><p><strong>spinous process</strong> - posterior projection (spinal palpate [can feel over skin])</p><p><strong>transverse process</strong> - lateral projection</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/58cf754a-8049-4726-a8e7-3d1a93a7eaa6.png)
what is a neural arch
combination of the pedicle & lamina
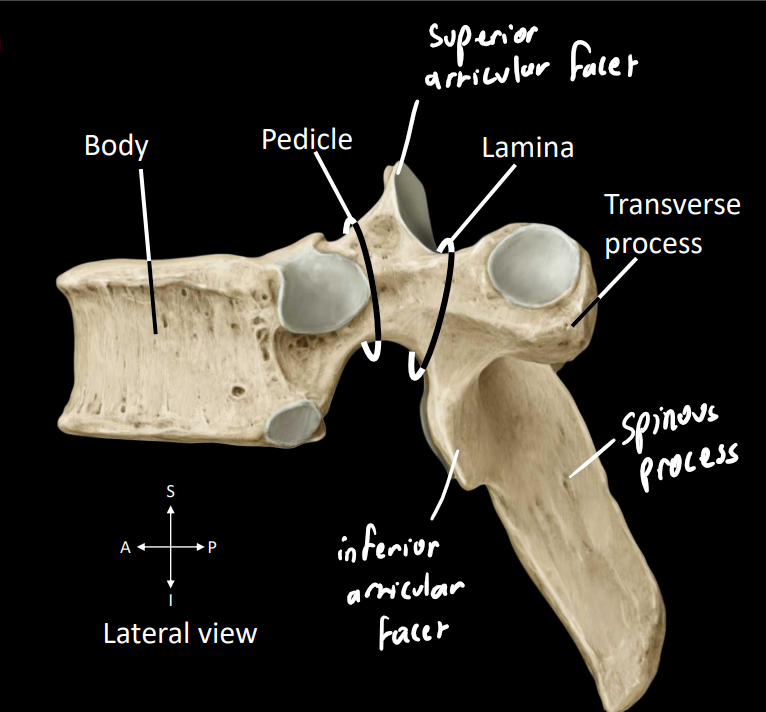
what are key structures in this image
superior articular facet - forms synovial (fluid-filled) joint with vertebrae above
inferior articular facet - forms synovial (fluid-filled) joint with vertebrae below
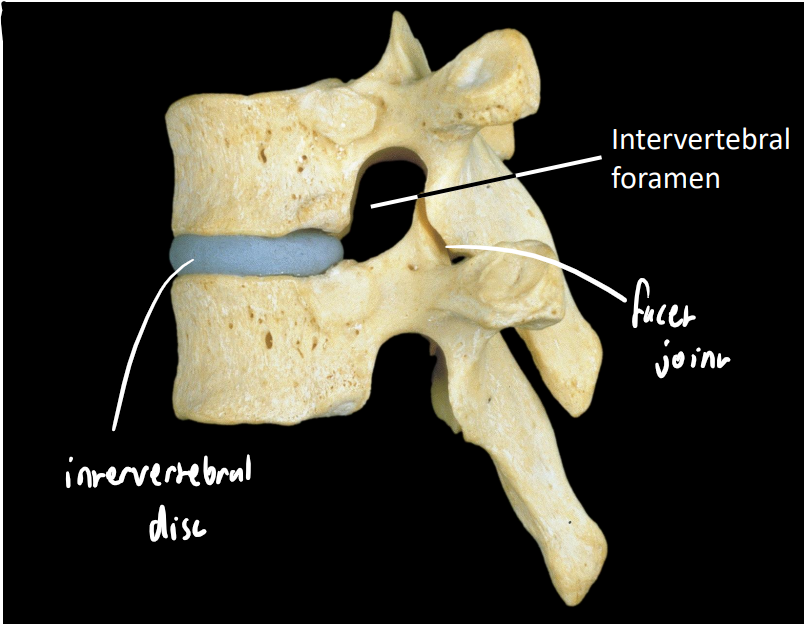
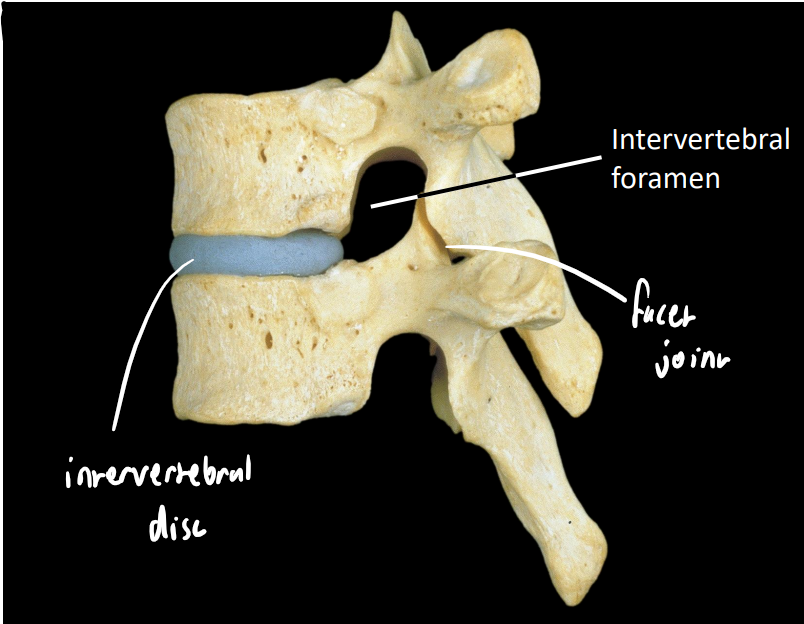
what are some key structures in this image
intervertebral disc
facet/zygapophyseal joint - synovial
orientation changes rotationally (impacts regional movement)
intervertebral foramen - conveys spinal nerves
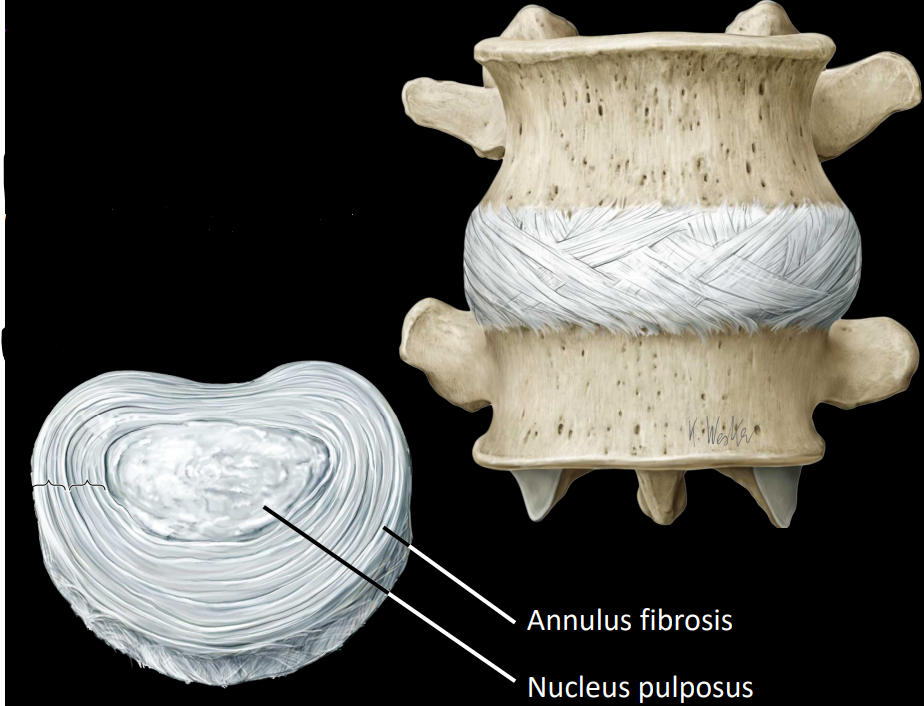
what are intervertebral discs
fibrocartilage between adjacent vertebrae
remains of the notochord
example of symphysis - type of cartilaginous joint
what are some structures of the intervertebral discs
annulus fibrosis - ring of fibrosis tissue
nucleus pulposus - core of gel-like substance
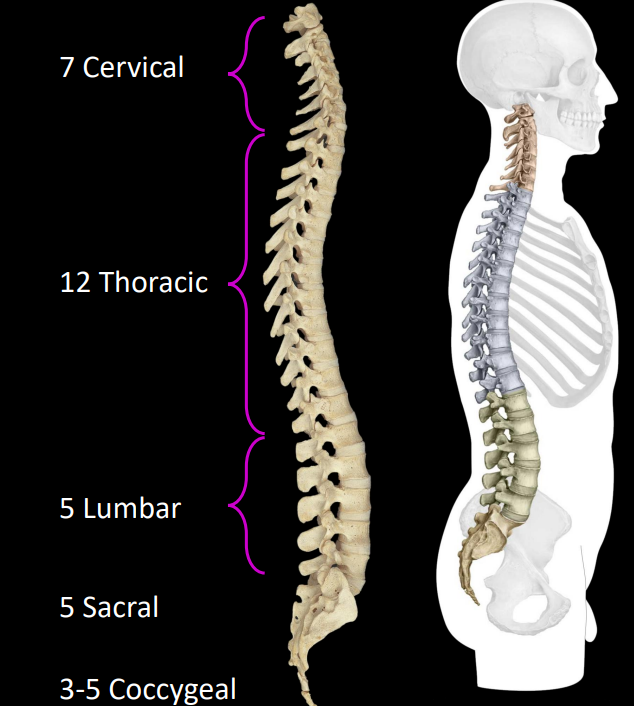
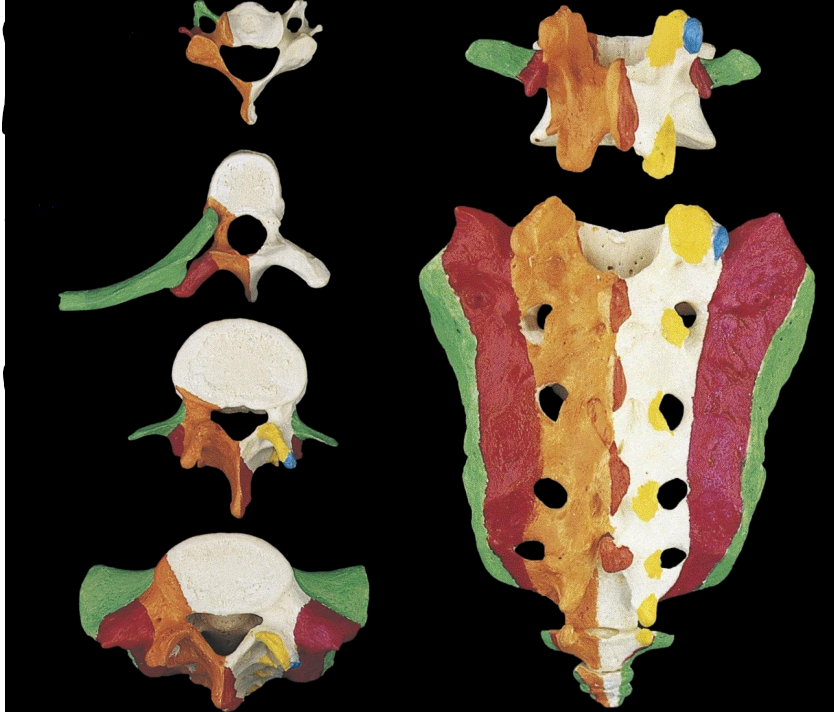
what are the different segments of the spine
cervical - 7
thoracic - 12
lumbar - 5
sacral - 5 (fused)
coccygeal - 3 (fused)
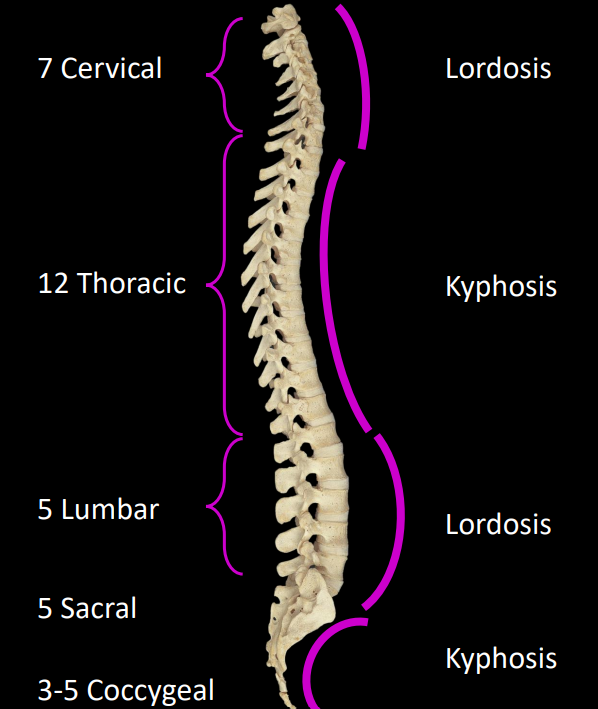
what are the different curves of the spine called
lordosis - convex anteriorly
cervical, lumbar
kyphosis - concave anteriorly
thoracic, sacral/coccygeal
what is a common pattern for the vertebrae as we move inferiorly
increase in the size of the vertebrae body, supports more body mass
what is scoliosis
exaggerated lateral curvature of the spinal cord
what is some information of the cervical region
obliquely transverse (slanted) facet joints, allows for:
flexion/extension
lateral flexion
rotation
triangular spinal foramen - larger as spinal cord is thickest here
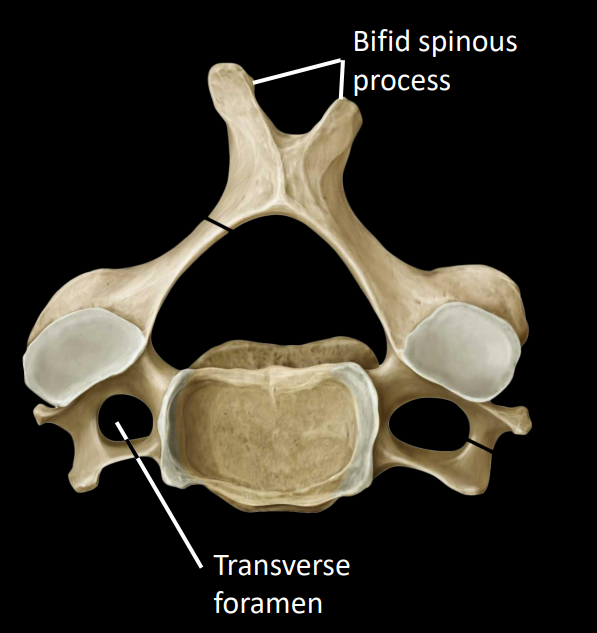
bifid spinous process
transverse foramen - houses the vertebral artery, supplies blood to brain stem
what is a vertebral artery dissection
damage of each form to the vertebral artery
most cases are fatal
may result in locked-in syndrome
lose of all voluntary movement except eye-control
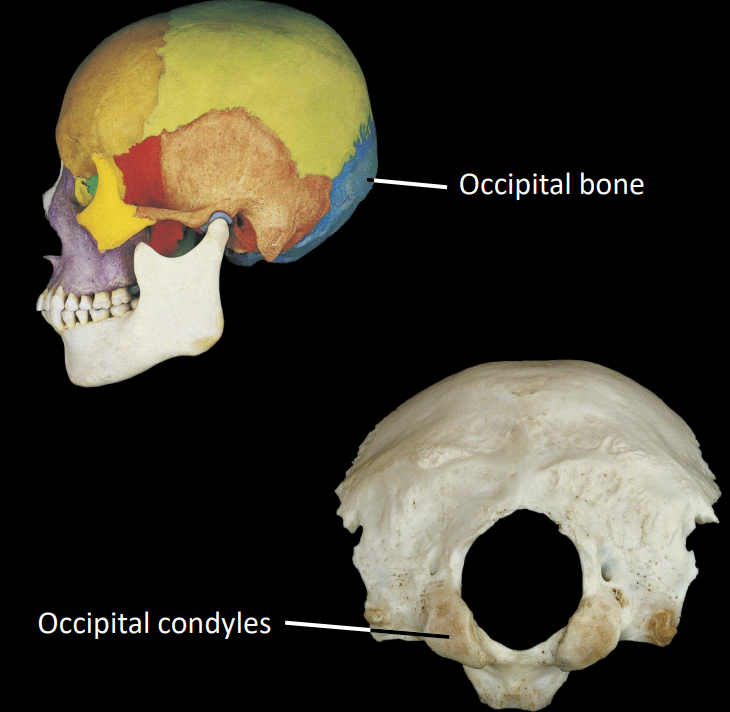
what is a key structure on the occipital bone
occipital condyles, articulates with C1
what are the a-typical members of the cervical region
C1 (atlas)
C2 (axis) - important rotational joint
C7 (vertebra prominens) - uppermost palpable spinous process
what are some structures of the C1 vertebrae (atlas)
no spinal body
anterior/posterior tubercle
large lateral mass (each side) to support occipital condyles
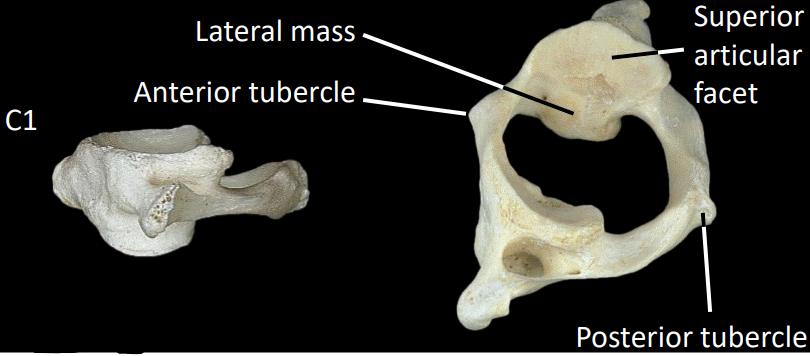
what is the atlanto-occipital joint
C1 superior articular facets to occipital condyle
provides flexion/extension
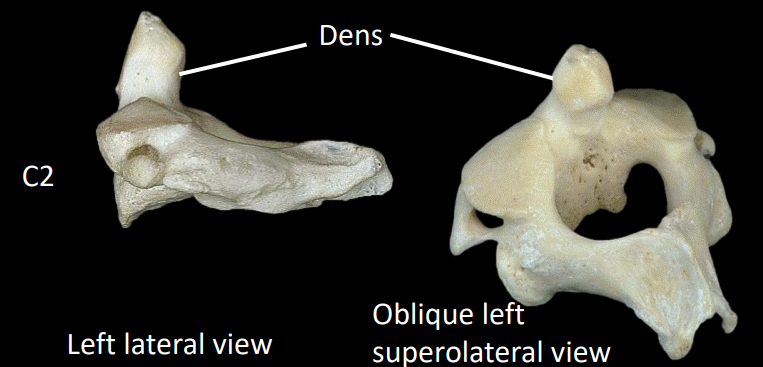
what are some structures of the C2 vertebrae (axis)
dens/odontoid process - “stolen” body of C1
forms the atlantoaxial joint that allows for rotation of the head
what is some information on the thoracic region
facilitates rotation
restricts flexion/extension
facets join in coronal plane
what are some features of the thoracic vertebrae
Articulation with ribs:
demifacets
transverse facet
elongated spinous processes
small, heart-shaped bodies
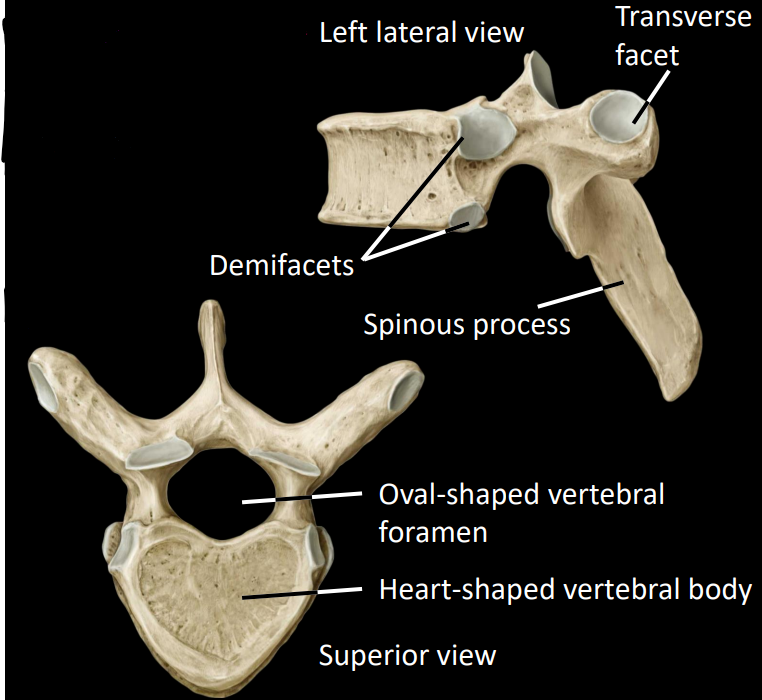
what is some information about the lumbar region
facets join in sagittal place
facilitates flexion/extension
limits rotation
what is the only a-typical member of the lumbar region
L5, due to articulation with the sacral region
what are some structures of the lumbar vertebrae
large, cylindrical body
small, triangular spinal foramen
costal (transverse) process
mamillary process
thick, short spinous process
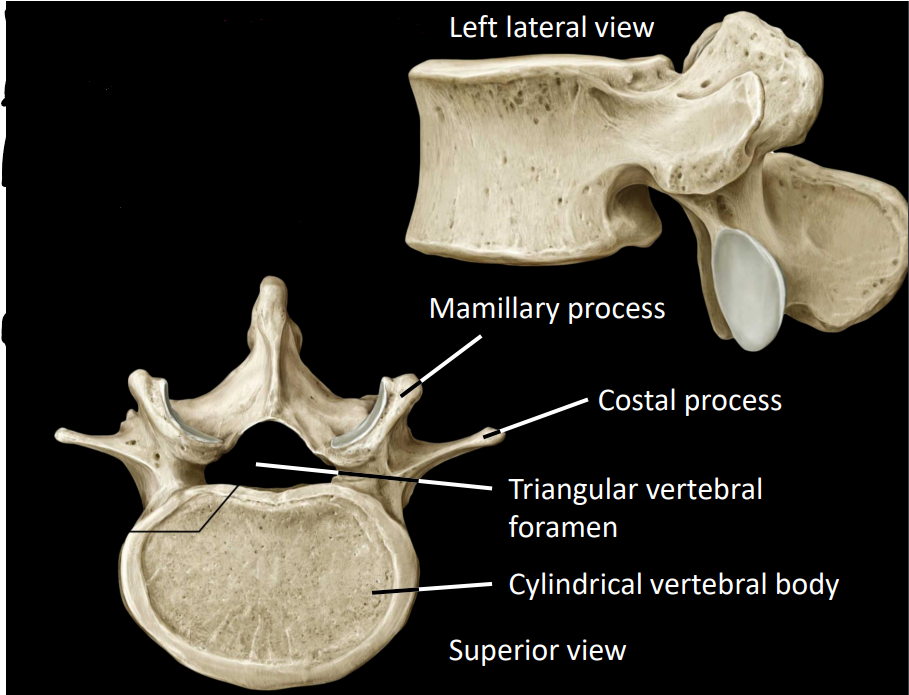
what is some information about the sacrum region
consists of 5 fused segments (may fuse with coccyx)
what are some anterior structures of the sacral region
auricular surface - articulates with pelvis
enlarged lateral part
superior part = sacral ala
promontory - articulates and supports L5
anterior sacral foramina - convey ventral rami for sacral nerves
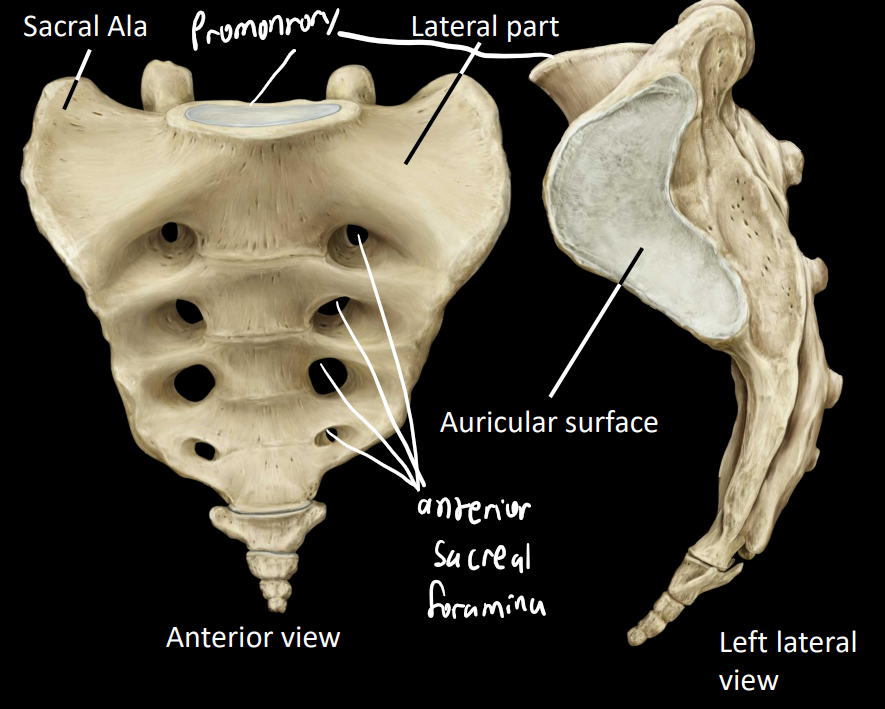
what are some posterior structures of the sacral region
posterior sacral foramina - conveys dorsal rami of sacral nerves
sacral canal - houses caudal nerves of spinal cord
medial sacral crest - similar to spinous process
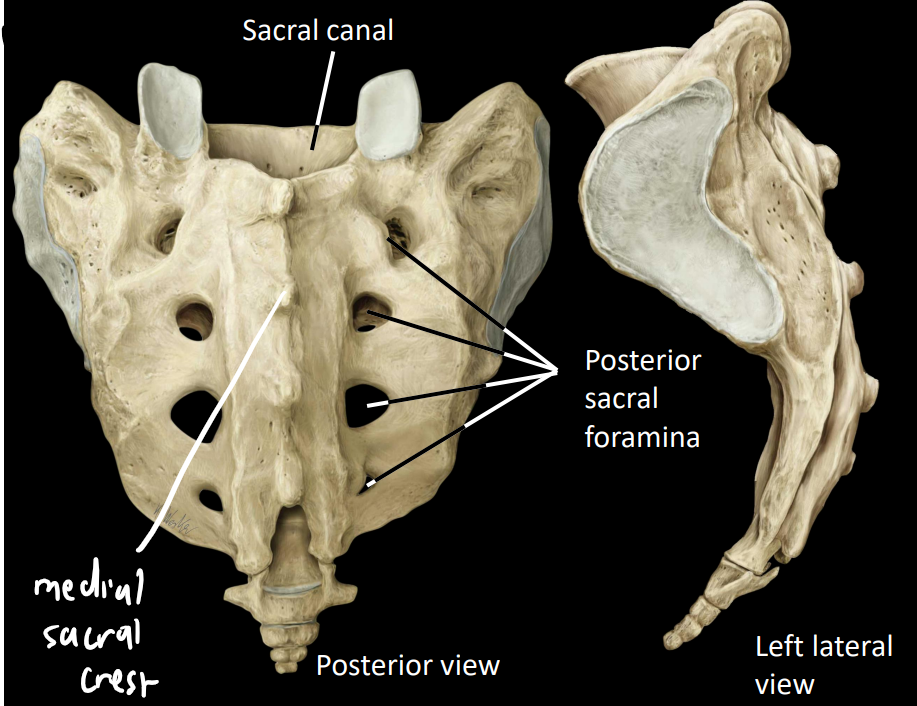
what is transitional lumbosacral vertebrae are what are the 2 types
a spinal abnormality where L5 is not fully connected to the sacrum
lumbarisation of S1 - S1 incorrectly incorporated into sacral block
sacralisation of L5 - L5 incorrectly incorporated into sacral block
what is some information about the coccyx
consists of 3-5 fused segments
represents vestigial tail
what are some root terms for the ribs
costal - '“rib”
chondral - “cartilage”
what are the 3 regions of the sternum
manubrium
body
xiphoid
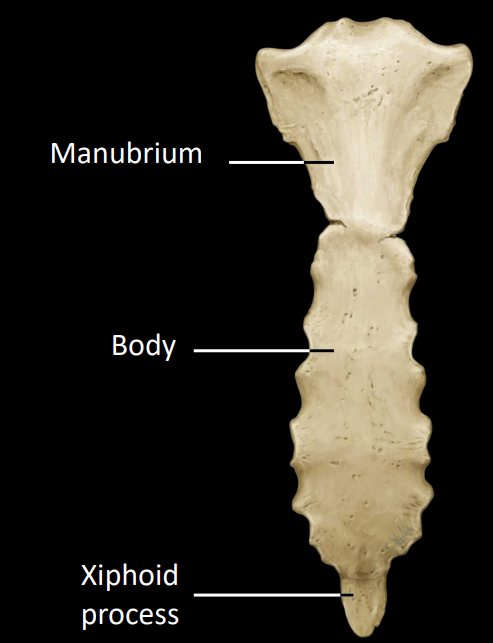
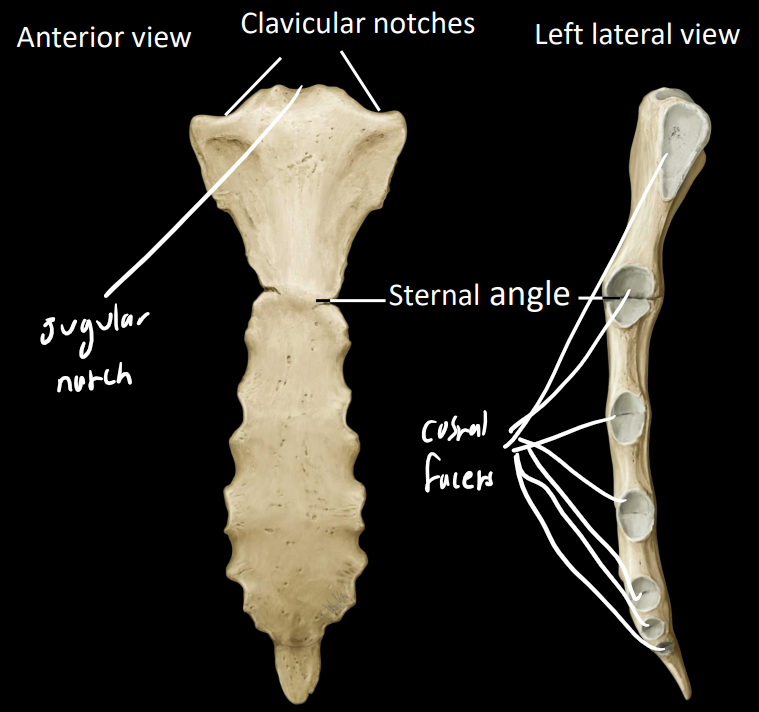
what are some of the other features of the sternum
sternal angle - at manubriosternal joint
clavicular notches - sternoclavicular joint
jugular notch - palpable depression
7 costal facets - articulation with the ribs
what is some information on the ribs
set of 12 (usually)
protect the thorax
articulate posteriorly with thoracic vertebrae
terminate anteriorly as costal cartilage
how are the ribs classified
2 different classifications:
true, false, floating
typical, atypical
what ribs are classified as what
True: 1-7 (cartilage directly attach to sternum)
False: 8-10 (cartilage attaches indirectly via 7th rib cartilage)
Floating: 11-12 (don’t attach to sternum)
how do ribs connect to the sternum
attach to sternum via cartilaginous intervals, thus there exists 2 joint types:
costochondral (rib-cartilage)
sternochondral (sternum-cartilage)
what are interchondral joints
joints between cartilage of ribs, the connection between ribs 8-10 and the 7th rib
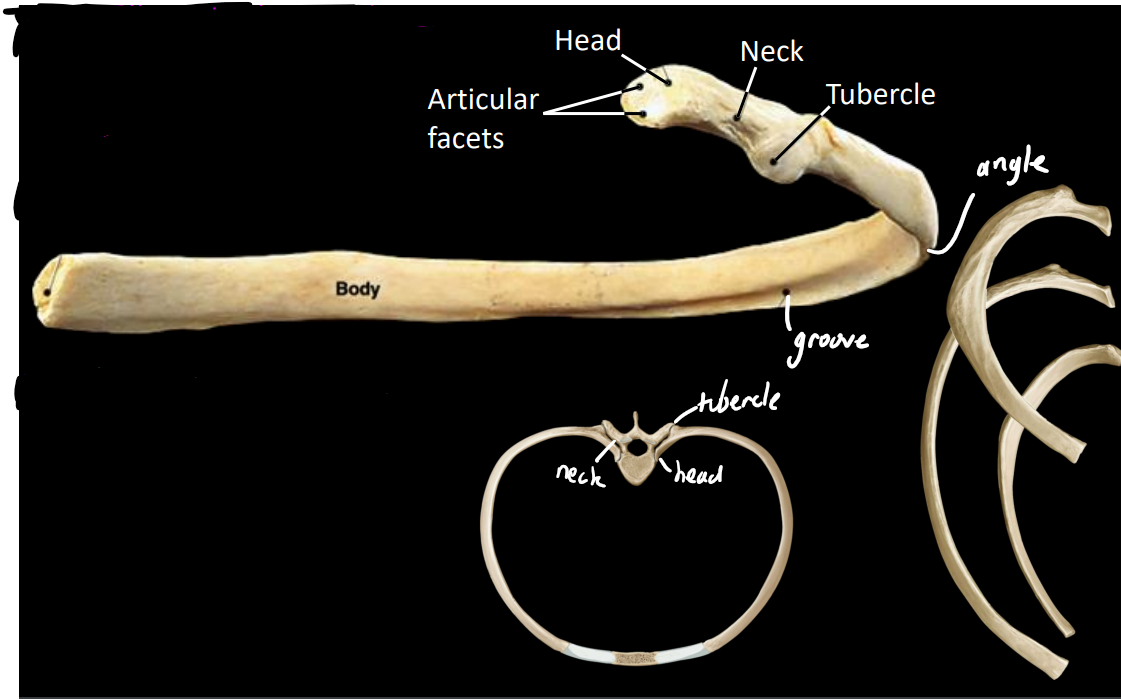
what are some anatomical features of a rib
head
articular facets
attaches to vertebral bodies
neck
tubercle
attaches to transverse process
distal to neck
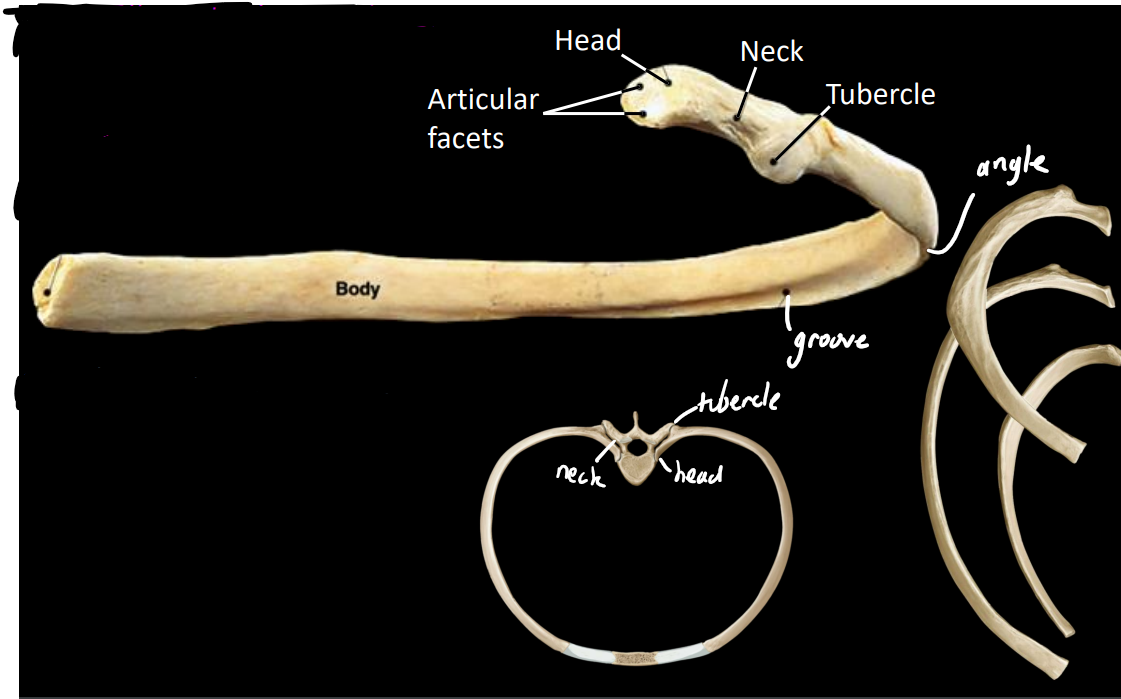
what are some typical features of the ribs
body (shaft)
costal groove - conduit for intercostal neurovascular structures (nerves, arteries, veins)
angle
flat laterally & anteriorly
what are some atypical structures of the ribs
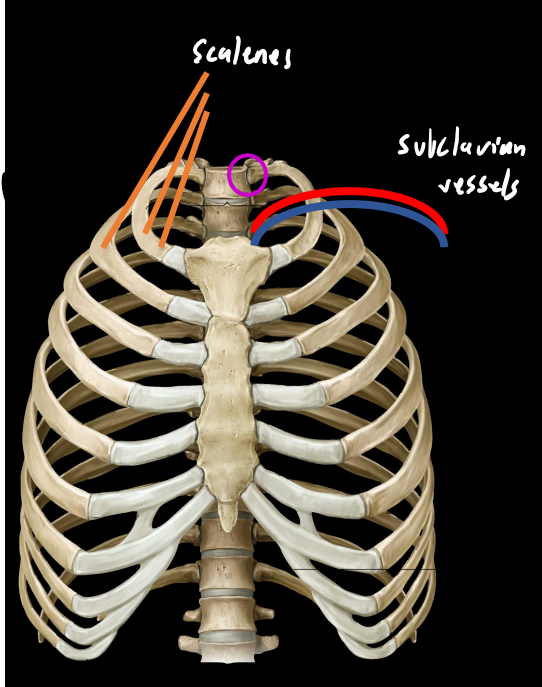
ribs 1&2:
shorter/wider than most ribs
head of rib 1 only attaches to body of 1 vertebrae (T1)
marked by grooves:
subclavian vessels (rib 1)
scalenes (rib 1&2)
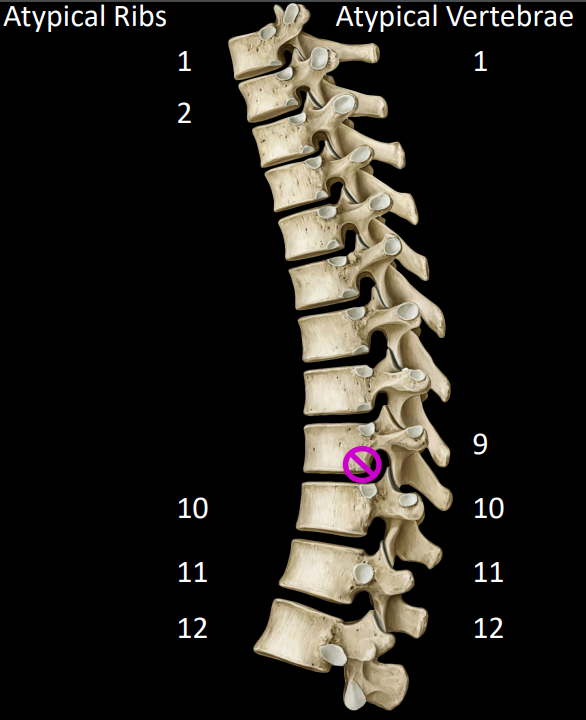
how are ribs 10, 11 & 12 atypical
rib 10 only attaches to 1 vertebral body
rib 11 & 12 are floating (don’t attach to transverse process)
why is vertebrae 9 atypical
ribs normally articulate with the body of 2 ribs
in the case of rib 10, it only articulate with the body of vertebrae 10, thus making both rib 10 and vertebrae 9 atypical
in summary, what are the atypical ribs & vertebrae
ribs: 1, 2, 10, 11, 12
vertebrae: 1, 9, 10, 11, 12
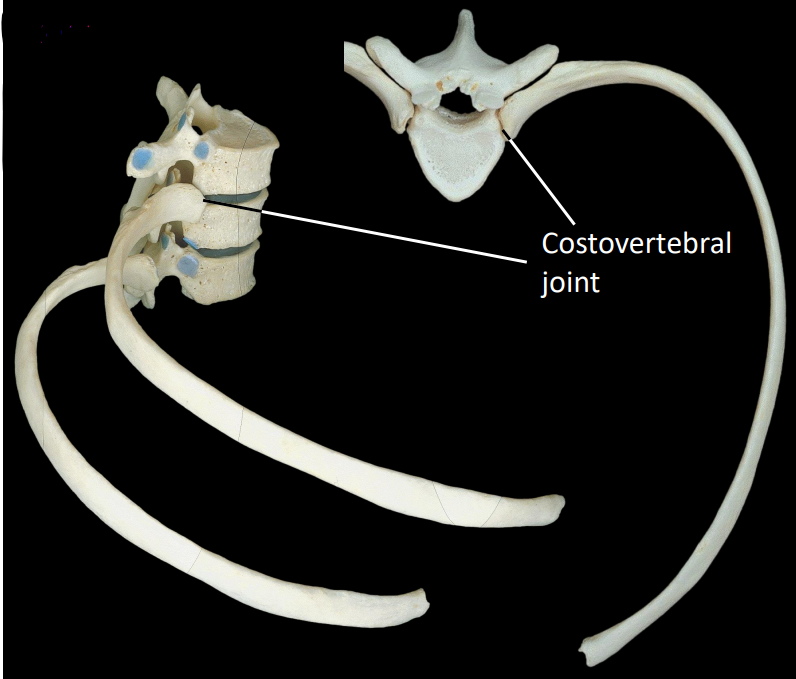
what is some information about the costovertebral joint
articulation between rib & vertebrae
spans 2 thoracic vertebrae & intervertebral disc
demifacets facilitate this joint
what is the costotransverse joint
articulation between the costal tubercle & transverse facet
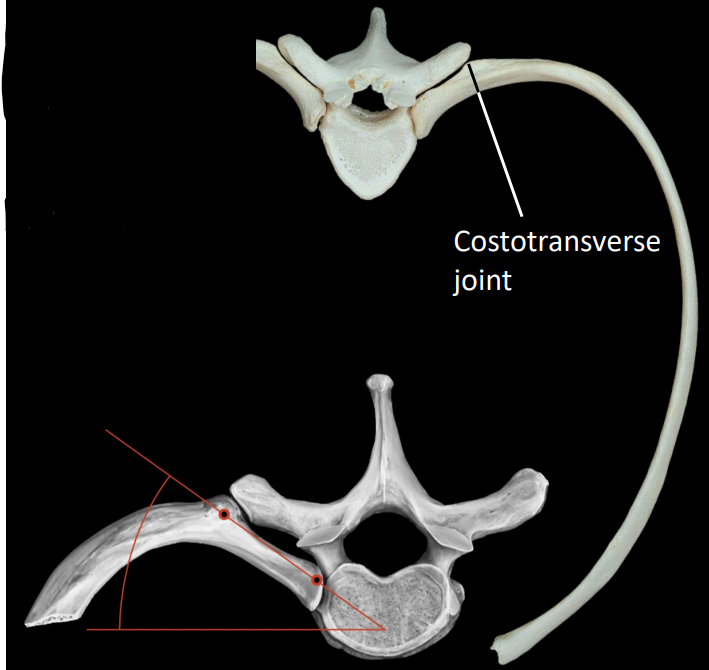
what do the costovertebral & costotransverse joint allow for
function together to facilitate rotation
how do the ribs move during breathing
increases width of thorax
increase anteroposterior depth of thorax
why can ribs grow in other vertebrae regions abnormally
there is a costal (rib) derivative region in each spinal region which can lead to the development of a rib under abnormal circumstances.
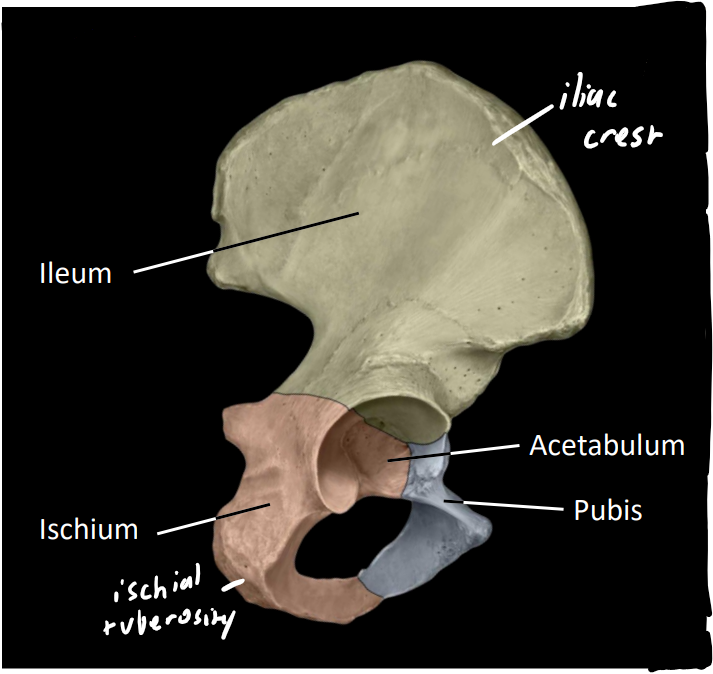
what are the three main bones of the pelvis
ileum, pubis, ischium
all meet at acetabulum (hip socket)
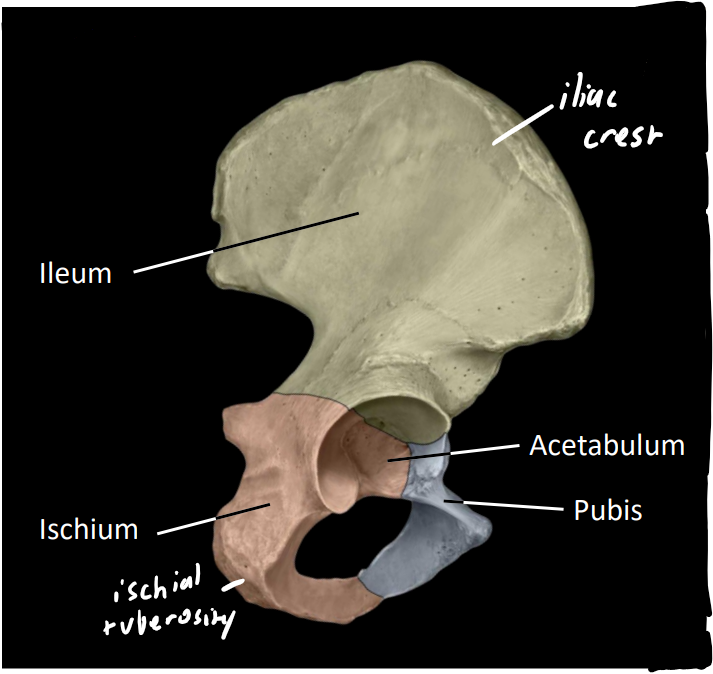
what are some other features of the pelvis
iliac crest
bony ridge
felt as hips/waist
ischial tuberosity
‘sit'‘ bone
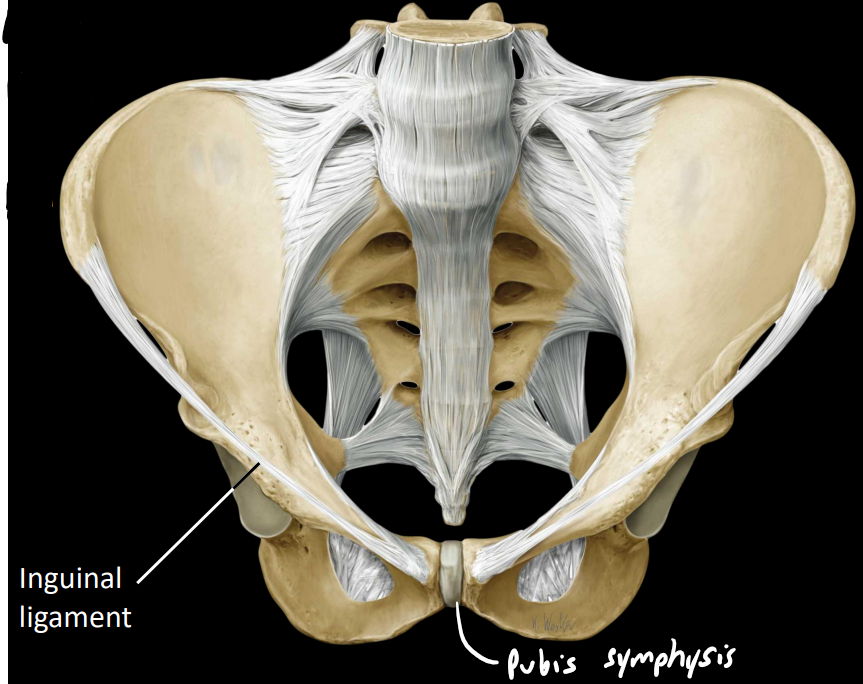
what are some other features of the pelvis
pubic symphysis
fibrocartilage joint (medial caudal part of pelvis)
inguinal ligament
connective tissue band from ileum to pubis
attachment of abdominal wall muscles
what rib meets the the sternum at the manubriosternal joint
rib 2
what are some common greek terms for embryotic anatomy
epi - upon
hypo - below
blast - build
clast - broken (in pieces)
what is the bilaminar embryonic disc
The bilaminar embryonic disc is a flat structure formed during early embryonic development, consisting of two layers: the epiblast and the hypoblast. It gives rise to the three germ layers.
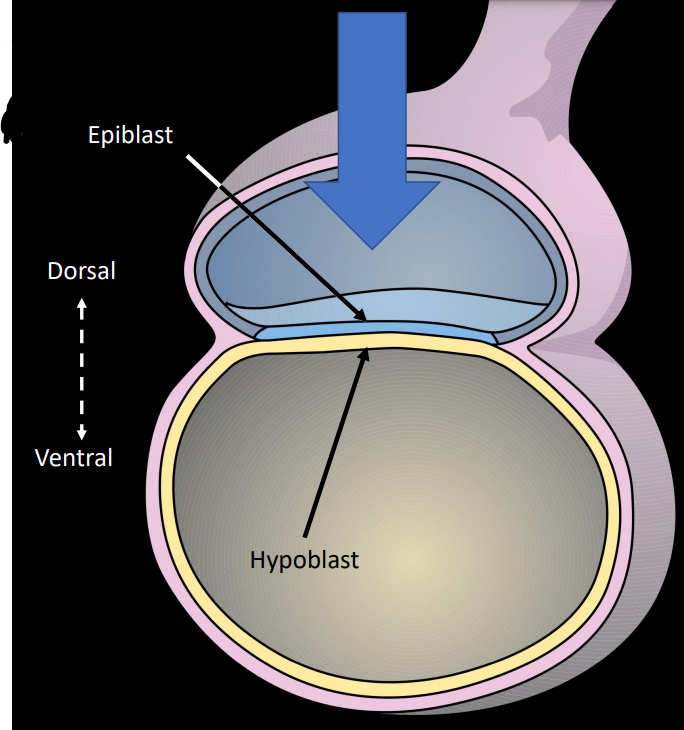
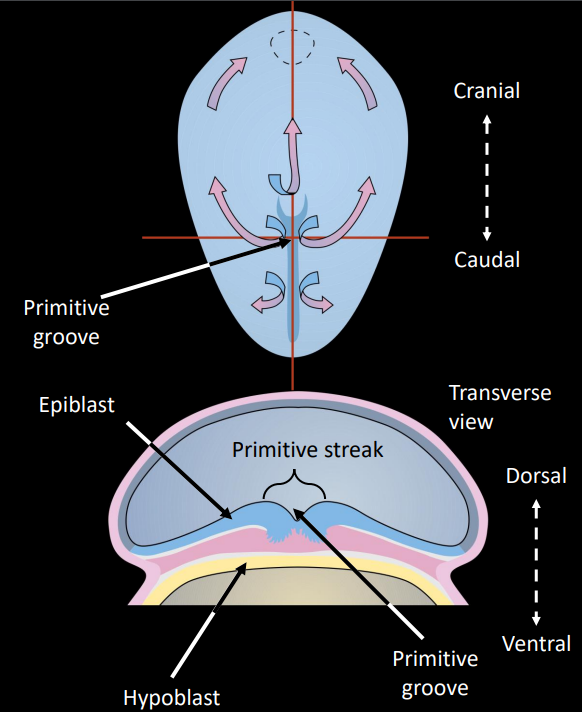
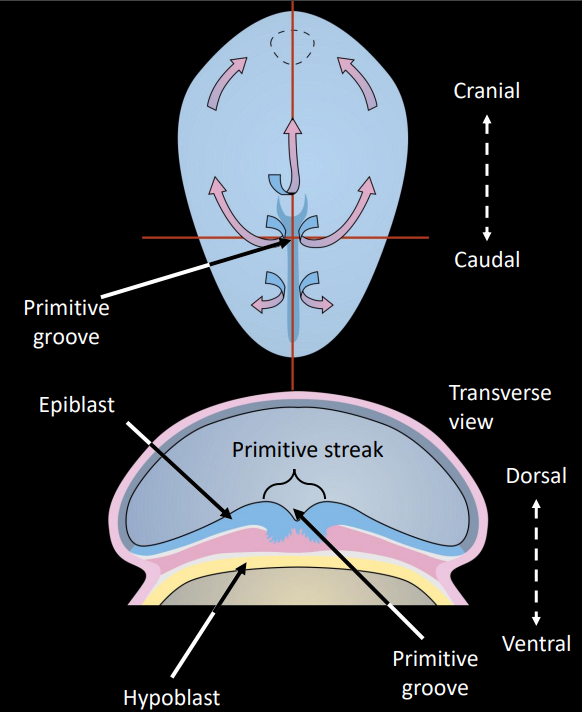
describe some of the labelled structures
primitive streak: thick layer of epiblast cells that migrate caudal to cranial
primitive groove: indentation caused by the primitive streaks, forms as cells migrate during gastrulation
primitive node: cranial from primitive streak, indented by primitive pit
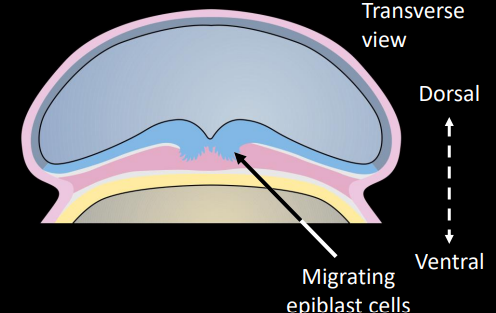
what is the process of ingression
process by which dorsal epiblast cells migrate into the primitive pit and groove to form the mesoderm
what are the new names of the blast cells are ingression (primary germ layers)
hypoblast becomes endoderm
migrating epiblasts becomes mesoderm
remaining epiblasts becomes ectoderm
what do ectoderm cells form
brain & spinal cord
nerves
nails, hair & skin