8.2 Light dependent reactions of photosynthesis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is light energy?
Is electromagnetic energy, composed of photon particles that travel as waves.
Can only see a fraction of this energy (visible range)
Also used by plants in this range
What do longer wavelengths mean?
When crests are farther apart and carry less energy than shorter wavelengths
How do we see long wavelengths?
As red or orange
What color are intermediate wavelengths?
Yellow or green
What color are short wavelengths?
Violet or blue
Light that is a mixture of all wavelengths are seen as…
White
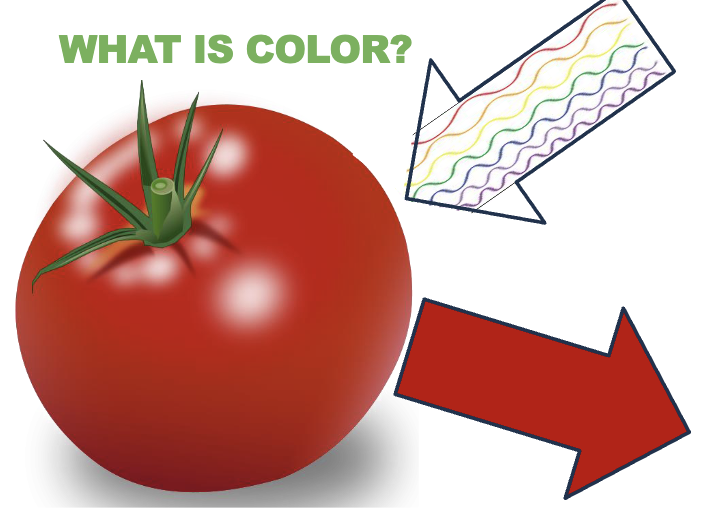
What happens when a wavelength hits the tomato?
White light of wavelength strikes the tomato
Only red wavelengths are reflected
All other wavelengths are absorbed by the pigments in the tomato
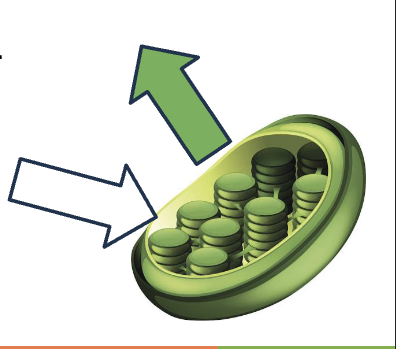
What happens when wavelengths hit the chloroplasts?
They’re absorbed by the pigments in chloroplasts providing energy for photosynthesis
How are wavelengths measured?
Are measured in nm
What wavelength has the most energy and is the shortest?
Violets
What wavelengths have less energy and are the longest?
Reds
Absorption of light
Pigments absorb specific wavelengths of light; each having a unique absorbance spectrum
What are the main pigments of thylakoid membranes?
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
β-carotene (c), a type of
carotenoid.
What color lights are least effective for photosynthesis?
Green and yellow light because they are reflected
What color lights are most effective for photosynthesis?
Blue and red light because their energy is able to be absorbed
What makes up the thylakoid membranes?
Photosystems II and I; sites of light absorption
Molecules that make up the ETC
Two enzyme complexes, NADP reductase and ATP synthase
What makes up the photosystems II and I?
a light harvesting complex and a reaction center
What happens in the light harvesting complex?
Pigments in the complex pass light energy through to two chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center
What happens in the reaction center?
The light excites an e- from the chlorophyll a pair, passing it to the first electron acceptor of the ETC. Is also a light driven redox reaction
How is the lost electron replaced in photosystem II
The e- comes from the splitting of water which releasees oxygen as a waste product
How is the electron replaced in photosystem I
The electron comes from the ETC
What is the first part of the ETC in the light reaction?
Electrons are transported from Photosystem II to I through;
Plastoquinone Qb
Cytochrome b6f
Plastocyanin
Hydrogen ions are transported into the lumen to form H+ gradient for synthesizing ATP
What happens in the second part of the ETC?
The second ETC transports e- from PS I to NADP reductase via ferredoxin
What is the final e- acceptor of the light reaction?
NADP+ which yields NADPH
How is an H+ gradient created?
When electrons move down the chain and H+ is pumped into the lumen space
What does ATP synthase do?
Uses the gradient to generate ATP (process of chemiosmosis)
Why is ATP and NADPH made?
Made in the stroma so it can be used in the Calvin Cycle
What wavelengths carry the most energy?
Short and tight waves
Where is chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b found?
In higher plant chloroplasts
What do carotenoids do in photosynthesis?
Helps protect photosystems by disposing excess energy.