Breeding and Selection Part 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Phenotype
the observable characteristics of an individual.
Genotype
the genetic constitution of an individual.
Locus/Loci
where on a chromosome a particular gene/genetic marker can be found.
Chromosome
thread-like structure made up of DNA which contain genes.
Gene
the basic unit of heredity which can pass from parent to offspring.
Gamete
reproductive cell; female = ova/egg cells, male = sperm cells (haploid cells).
Progeny
another word for offspring.
Animal Breeding
the process of selective mating of animals with desirable traits to maintain or enhance these traits in future generations.
Qualitative Traits
traits that can be classified into categories and are controlled by a single or a small number of genes.
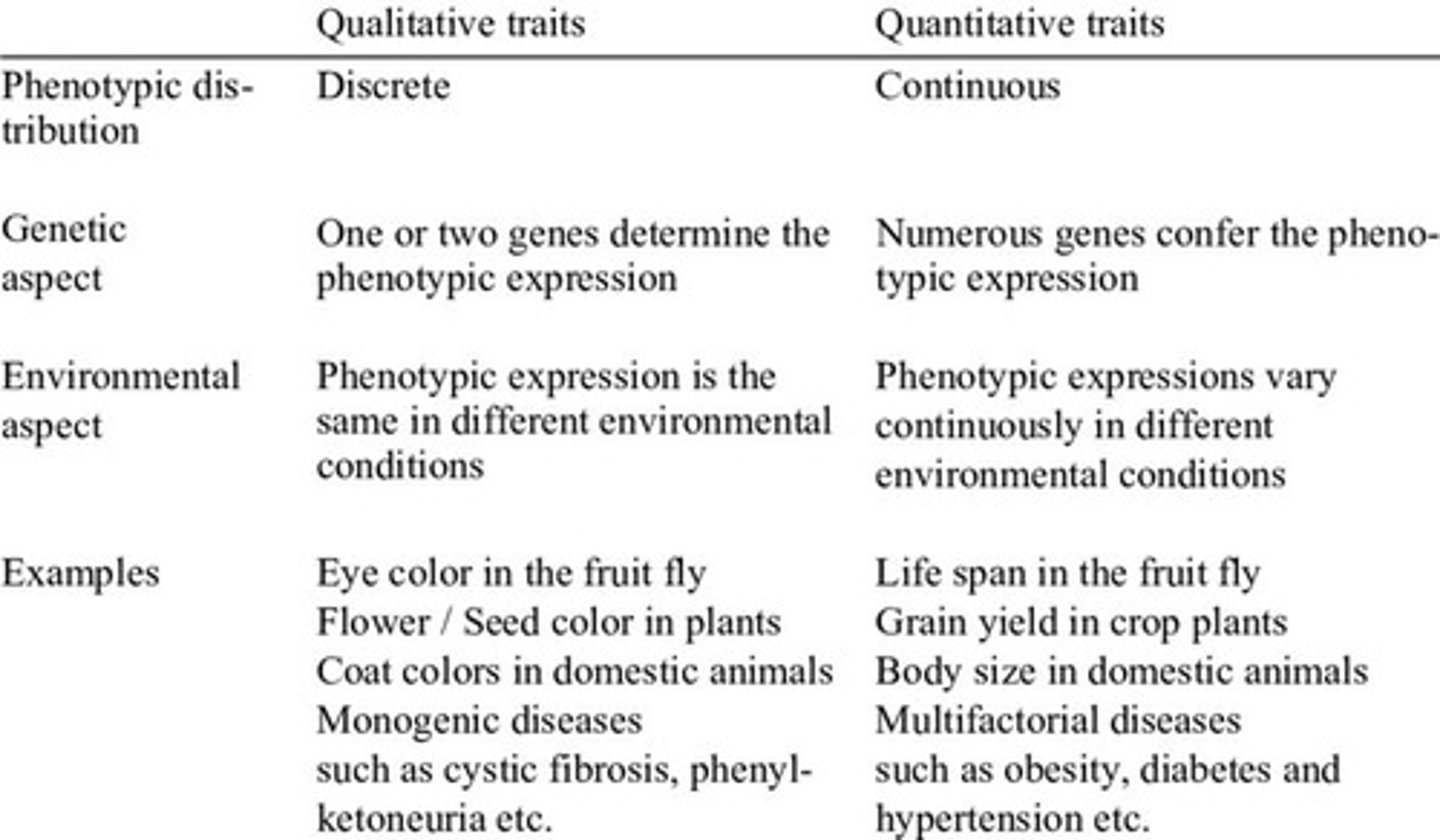
Quantitative Traits
traits that cannot be classified into category and are controlled by a larger number of genes (polygenic) and can be affected by the environment.
Mendelian Inheritance
inheritance patterns following laws of segregation and independent assortment.
Fisher's Infinitesimal Model
variation in quantitative traits influenced by an infinitely large number of genes, each making an infinitely small contribution to the phenotype.
Breeding Programmes
function to increase production, productivity, product quality and cost efficiency.
Genetic Diversity
the variety of genetic characteristics within a species.
Animal Welfare
the well-being of animals, considering their physical and psychological needs.
Sustainable Systems
practices that maintain the health of the environment while meeting human needs.
Heritability
the proportion of observed variation in a trait that can be attributed to inherited genetic factors.
Breeding Value
an estimate of the genetic value of an individual as a parent.
Crossbreeding
the practice of breeding animals from different breeds to produce offspring with desirable traits.
Selection
the process of choosing individuals with desirable traits for breeding.
Production Efficiency
the ability to produce more output with the same or fewer inputs.
Product Quality
the characteristics of a product that meet the needs and expectations of consumers.
Single Locus/Qualitative Traits
Traits determined by a single gene, with distinct phenotypes.
Genotype RR
Phenotype RED.
Genotype rr
Phenotype WHITE.
Genotype Rr
Phenotype ROAN (white and another colour).
Examples of Single Locus Traits
Coat colour and polled vs. horned cattle.
Epistatic interactions
Action of one gene on another; one gene can mask another.
Albinism
Complete lack of melanin producing cells.

Leucism
Lack of some melanin producing cells.
Melanism
Excessive production of melanin in cells.
Complex Vertebral Malformation (CVM)
Mutation in SLC35A3 Gene.
Three Genotypes and two phenotypes in CVM
+ and + (normal), + and CVM (normal), CVM and CVM (affected).
Law of Segregation
Members of a gene pair separate into the gametes, such that half carry one member of the gene pair and half carry the other.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes controlling separate traits segregate independently.
Polygenic/Quantitative Traits
Phenotypes are measured on a continuous scale and affected by the environment.
Breeding Value
Predicts progeny phenotype based on parental alleles.
Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (BLUP)
Method of estimating random effects.
Heritability (h2)
Proportion of the superiority in performance of the parents in a trait that is passed onto their offspring.
Pleiotrophy
Some genes influence more than one trait.
Antagonistic corrections
Negative links that can slow down genetic progress.
Negative correlation between milk yield and fat percentage
Selecting for milk yield could decline fat percentage.
Quantitative Traits; Heritability - Type/Conformation
High; 0.4-0.5.
Quantitative Traits; Heritability - Quality
Moderate; 0.2-0.35.
Quantitative Traits; Heritability - Production
Low; 0.05-0.15.