Radiology Exam 4
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
What is interpretation?
An explanation of what is viewed in a dental image
Image interpretation plays a vital role in the detection of what?
Allows the dental professional to gather information about diseases, lesions, and conditions of teeth that cannot be identified clinically
Who interprets images?
Any dental professional with training in interpretation. DDS or RD (DAs may or may not be adequately trained)
Interpreting dental images involves identification of what?
Normal Anatomy
Dental restorations, materials, and foreign objects
Dental Caries
Periodontal Disease
Trauma, pulpal lesions, and perlapical lesions
Lesions of bone and bone anomalies
Common artifacts and errors
What is the identification of disease by examination or analysis?
Diagnosis
Final interpretation & diagnosis are the responsibilities of who?
the dentist
Dental hygienists and dental assistants are restricted by LAW from rendering a __________.
diagnosis
What is the sequence for interpreting images?
#1-16, #17-32, BWX
Interpretation must be documented and include what?
Date of exposure
Number/type of images
Evaluation of diagnostic quality
List of limiting factors, retakes, or additional images needed
Description of teeth
Images are what?
An educational tool that can point out areas for the patient to be aware. This makes them more likely to be open to routine radiographs.
When should dental images be reviewed?
Immediately after exposure as this is the roadmap for the appointment
What is descriptive terminology?
Terms used to describe a lesion's appearance, location, and size.
Why use descriptive terminology?
It allows dental professionals to describe & discuss what is seen on a dental image
Descriptive terminology eliminates the chance for ________________, and is essential for __________ purposes.
miscommunication
legal
Descriptive terminology allows the dental hygienist to describe what is seen on an image without doing what?
Implying a diagnosis
What is the portion of processed image that is dark or black?
radiolucent
_________ are less dense that surrounding structures, due to passage of x-ray beam.
Caries
What is the portion of processed image that appears light or white?
radiopaque
____________ restorations are very dense & absorb radiation.
Metallic
What are some terms used to describe radiolucent lesions?
unilocular, multilocular, "moth-eaten", widened PDL space, and multifocal radiolucency
What description is used for a lesion that tends to be small & nonexpansile? (not likely to expand or grow larger)
unilocular
A unilocular lesion with ___________ borders exhibits a thin, well-demarcated radiopaque rim of one at the periphery (outline).
corticated
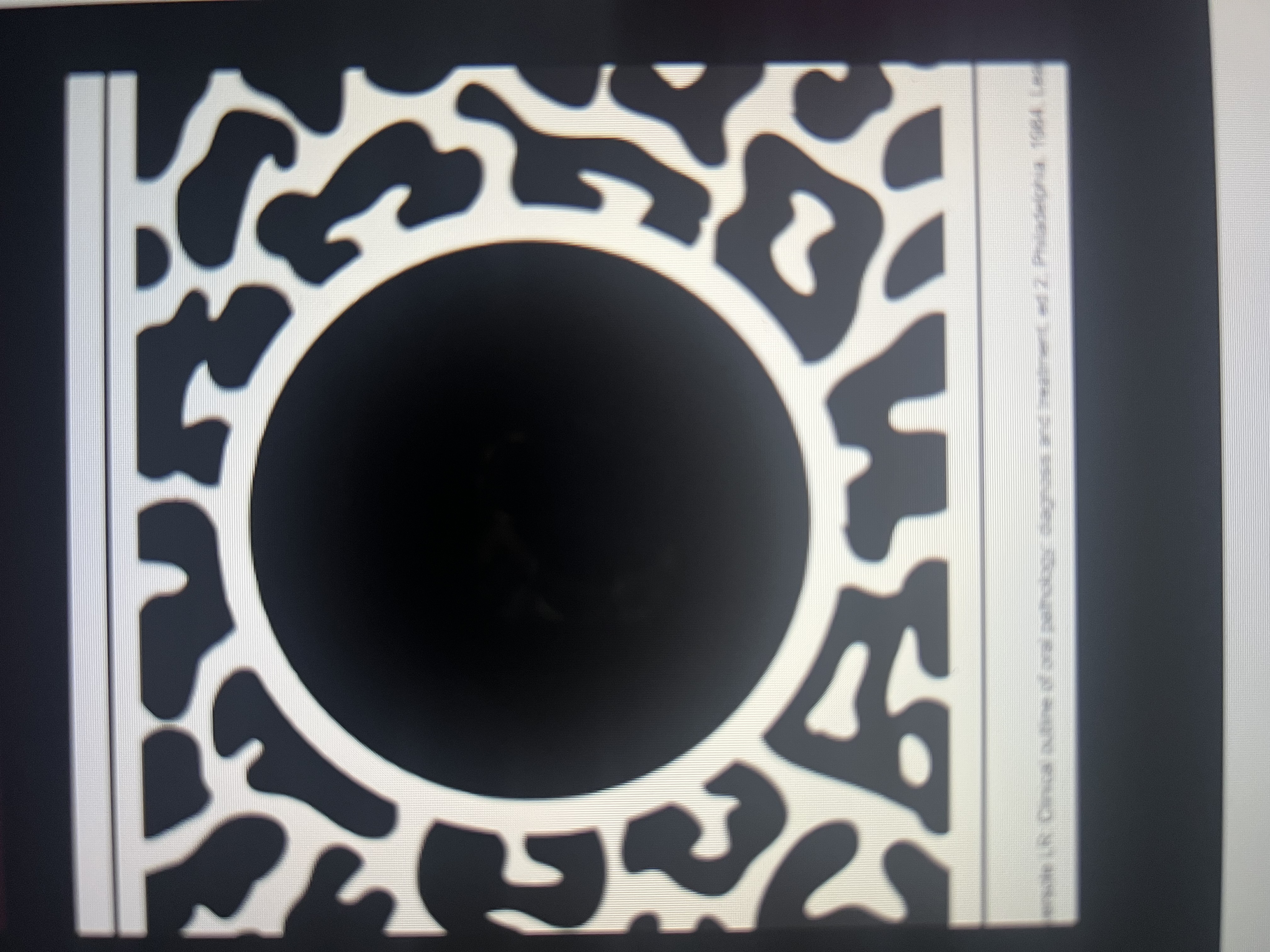

A unilocular lesion with ____________ borders does NOT exhibit a thin radiopaque rim of bone, the periphery (outline) actually appears fuzzy or poorly defined.
noncorticated
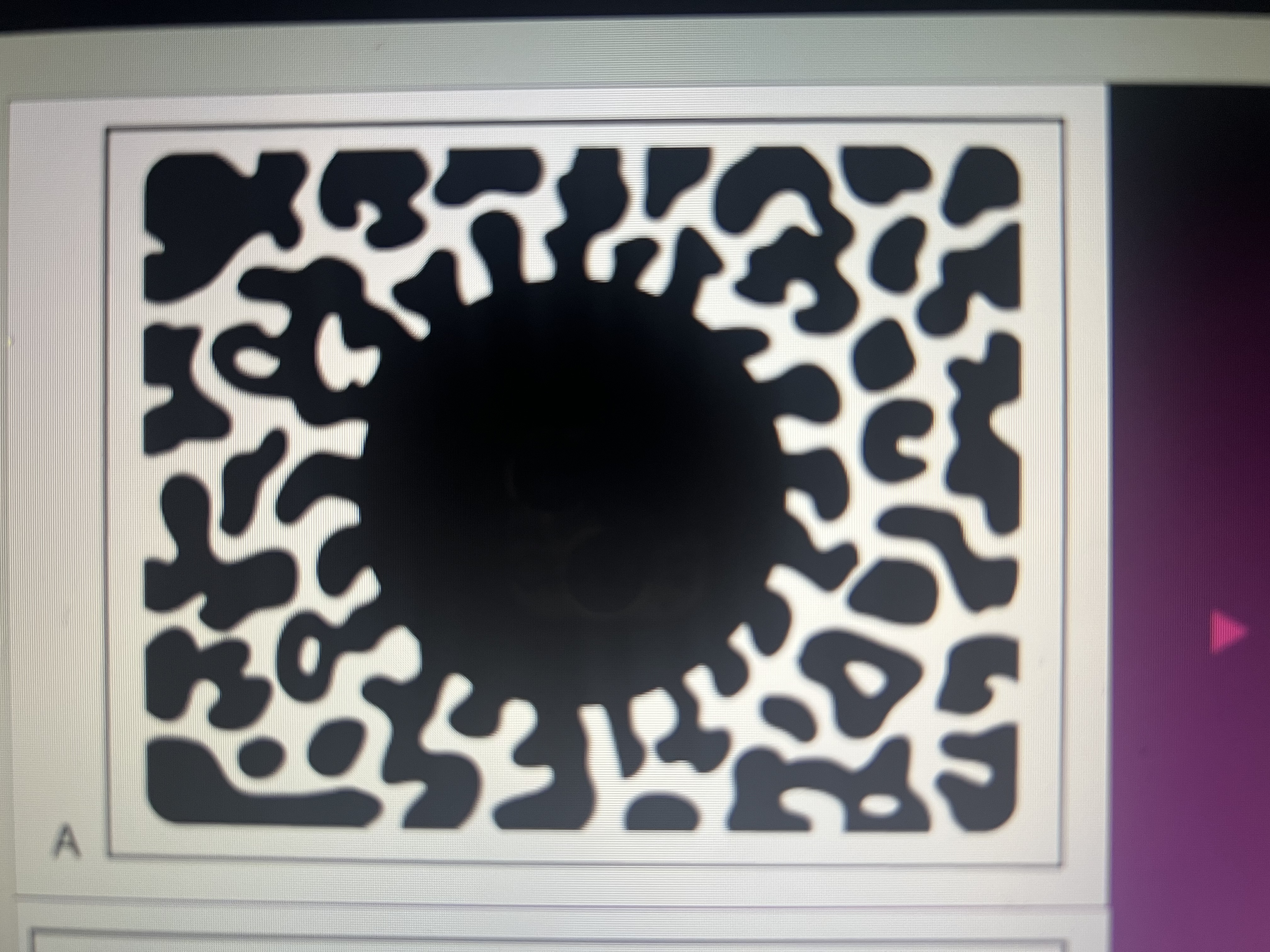

What radiolucent lesion exhibits multiple radiolucent compartments?
multilocular
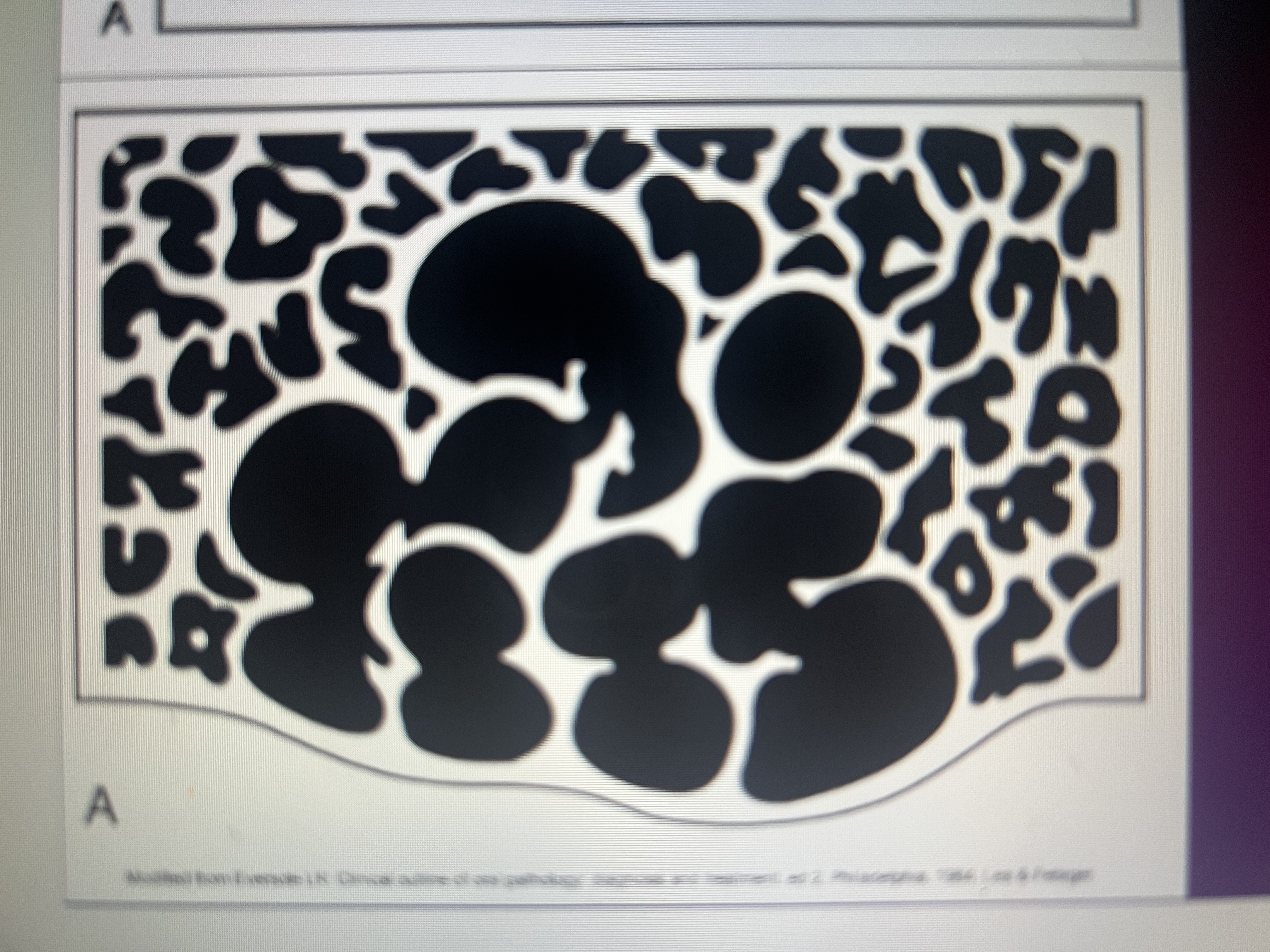

How does a multilocular lesion appear?
soap bubles

What is the growth of a multilocular radiolucent lesion?
benign with aggressive growth potential
What 3 things does descriptive terminology use to describe?
appearance, location, and size
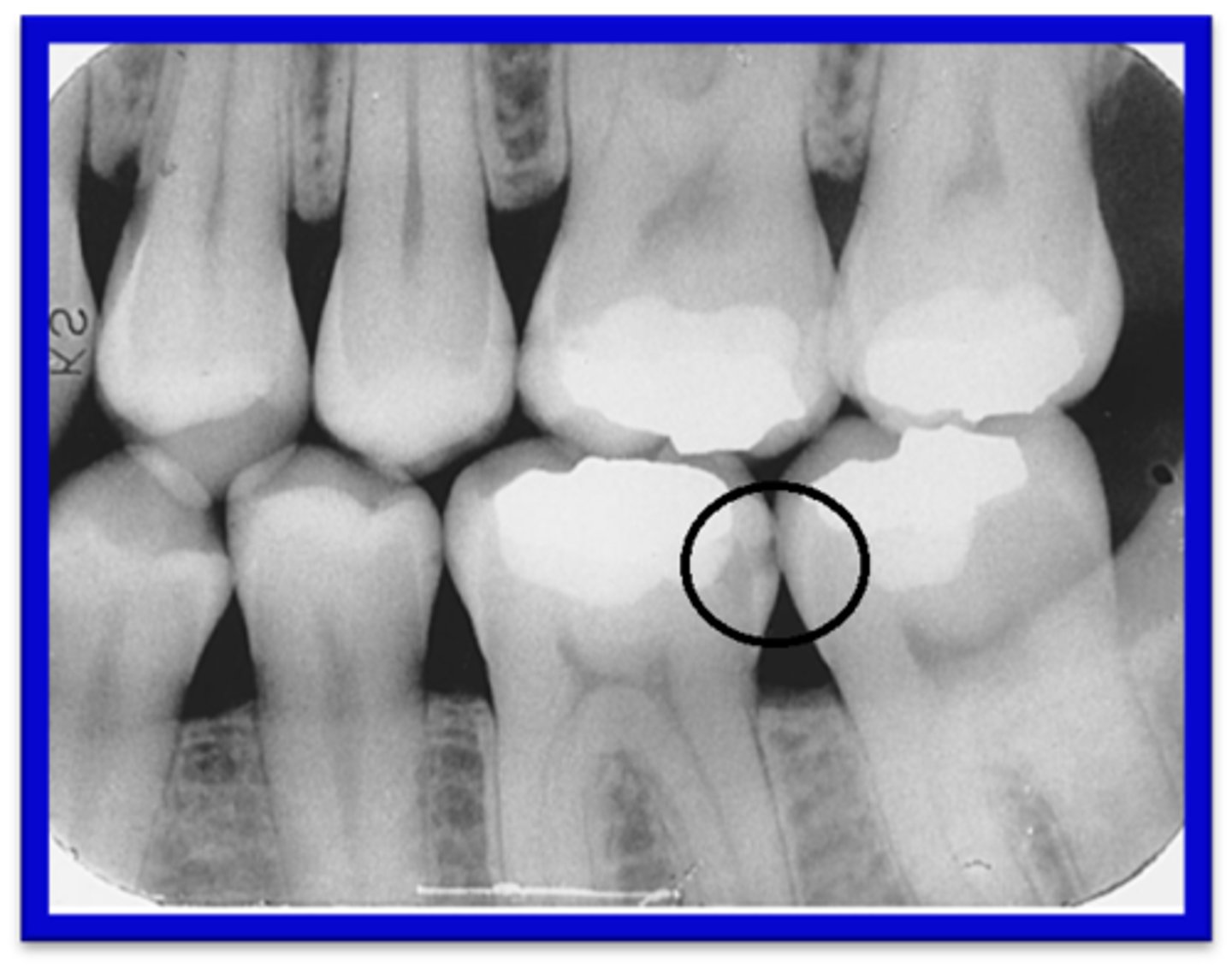
What lesion does periapical describe?
A lesion located around the apex of a tooth.
What lesion does interradicular describe?
A lesion located between the roots of adjacent teeth.
What is a lesion located in an area without teeth?
edentulous
What is lesion does pericoronal describe?
A lesion located between the roots of adjacent teeth.
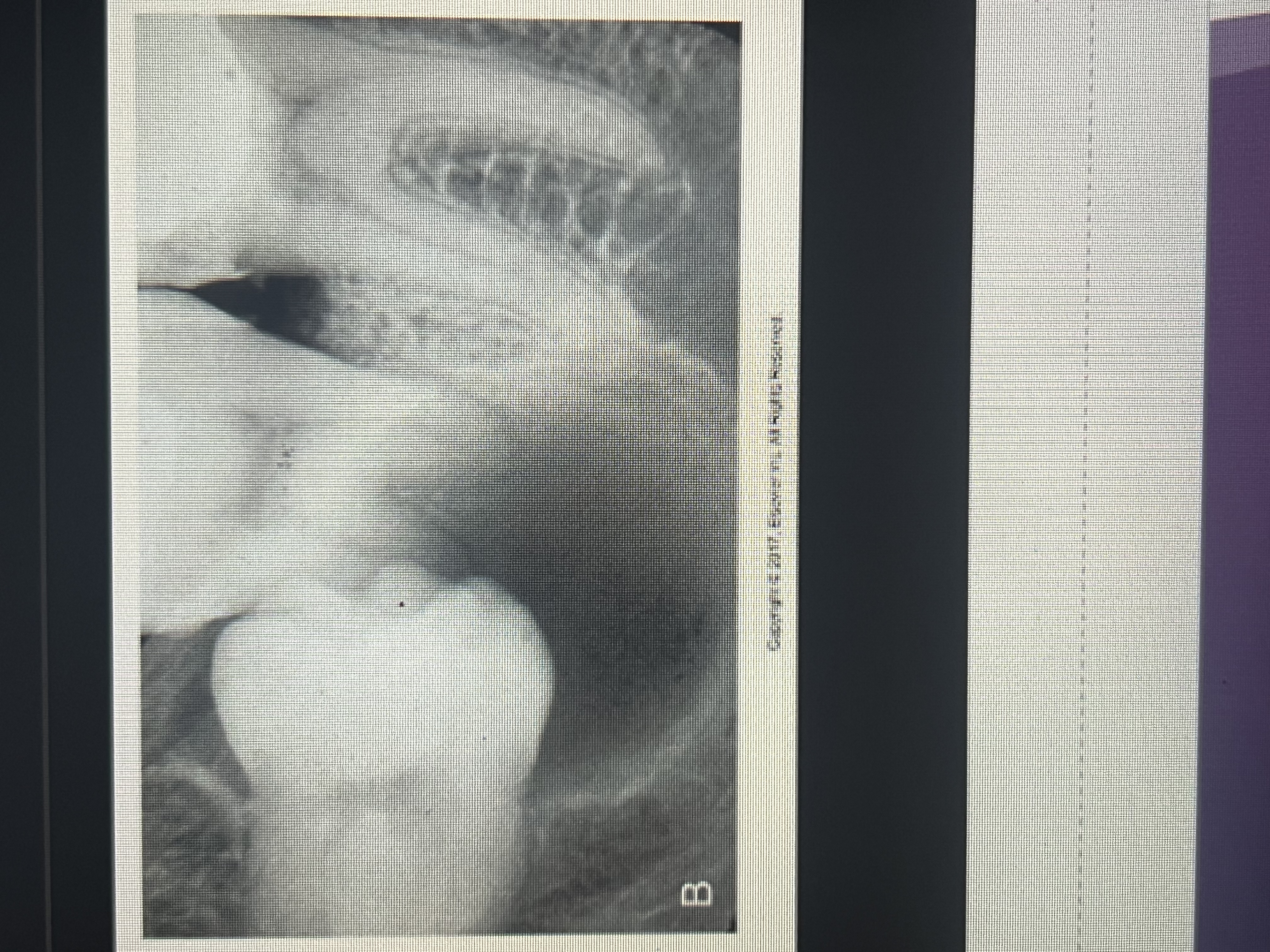
What is alveolar bone loss?
Loss of bone in the maxillar or mandible that surrounds & supports teeth.
How does alveolar bone loss appear?
radiolucent
T or F: Radiopaque lesions only appear in bone
False. They appear in soft tissue as well.
What is a well-defined, localized radiopaque lesion on an image?
Focal opacity
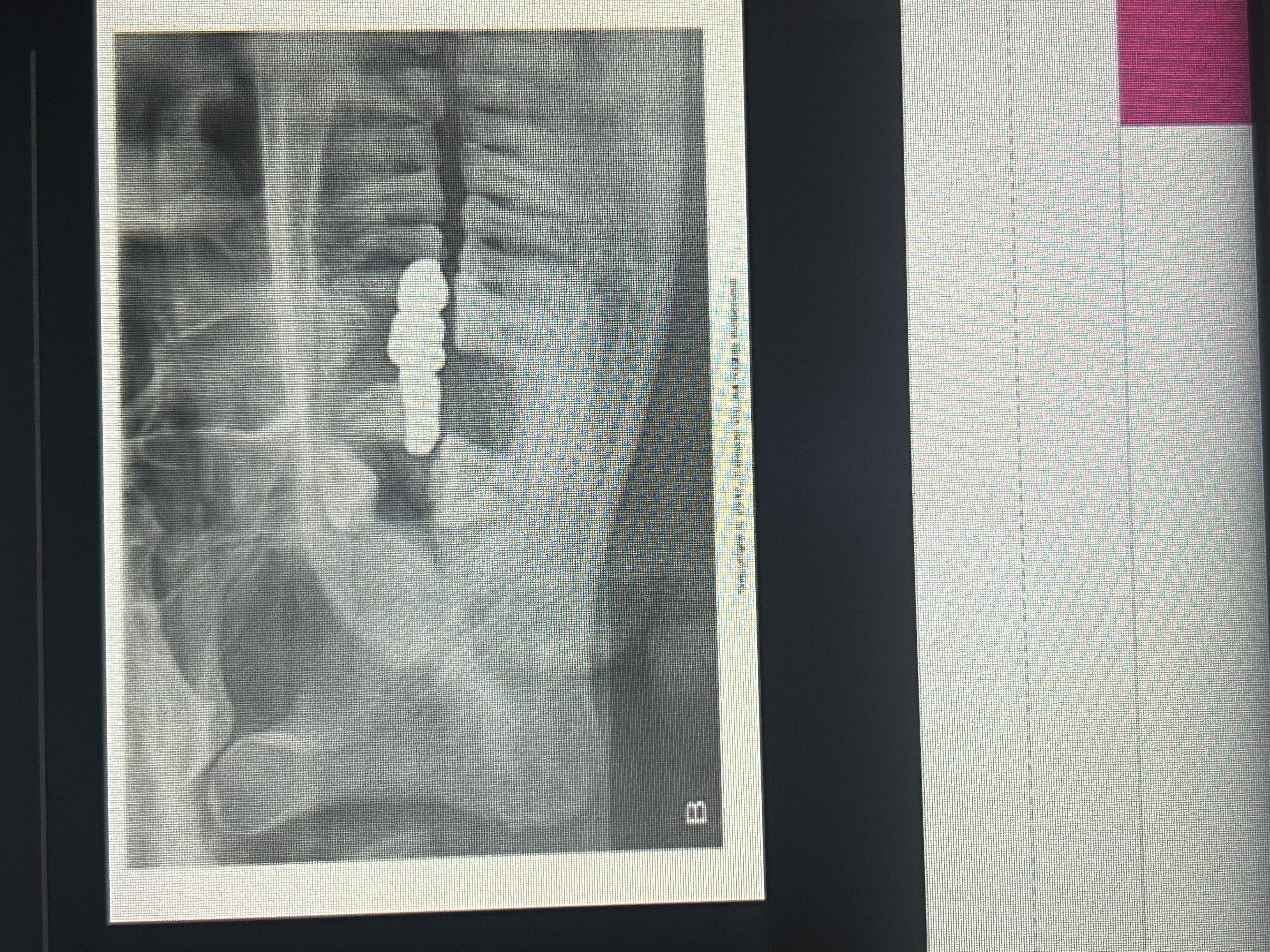
What is a well-defined, localized radiopaque area surrounded by a uniform radiolucent halo?
Target lesion
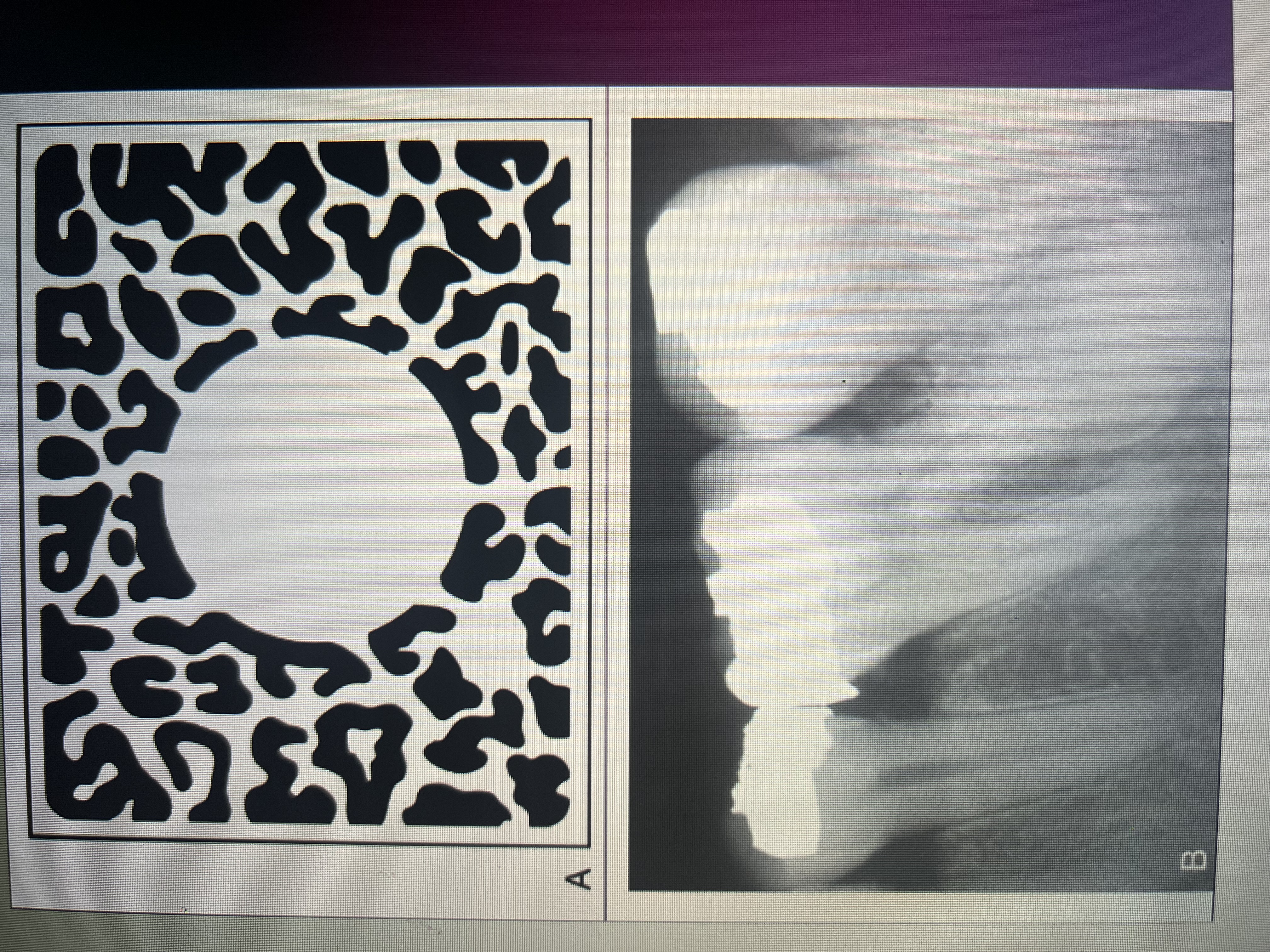
What describes multiple radiopacities that appear to overlap or flow together?
Multifocal confluent pattern
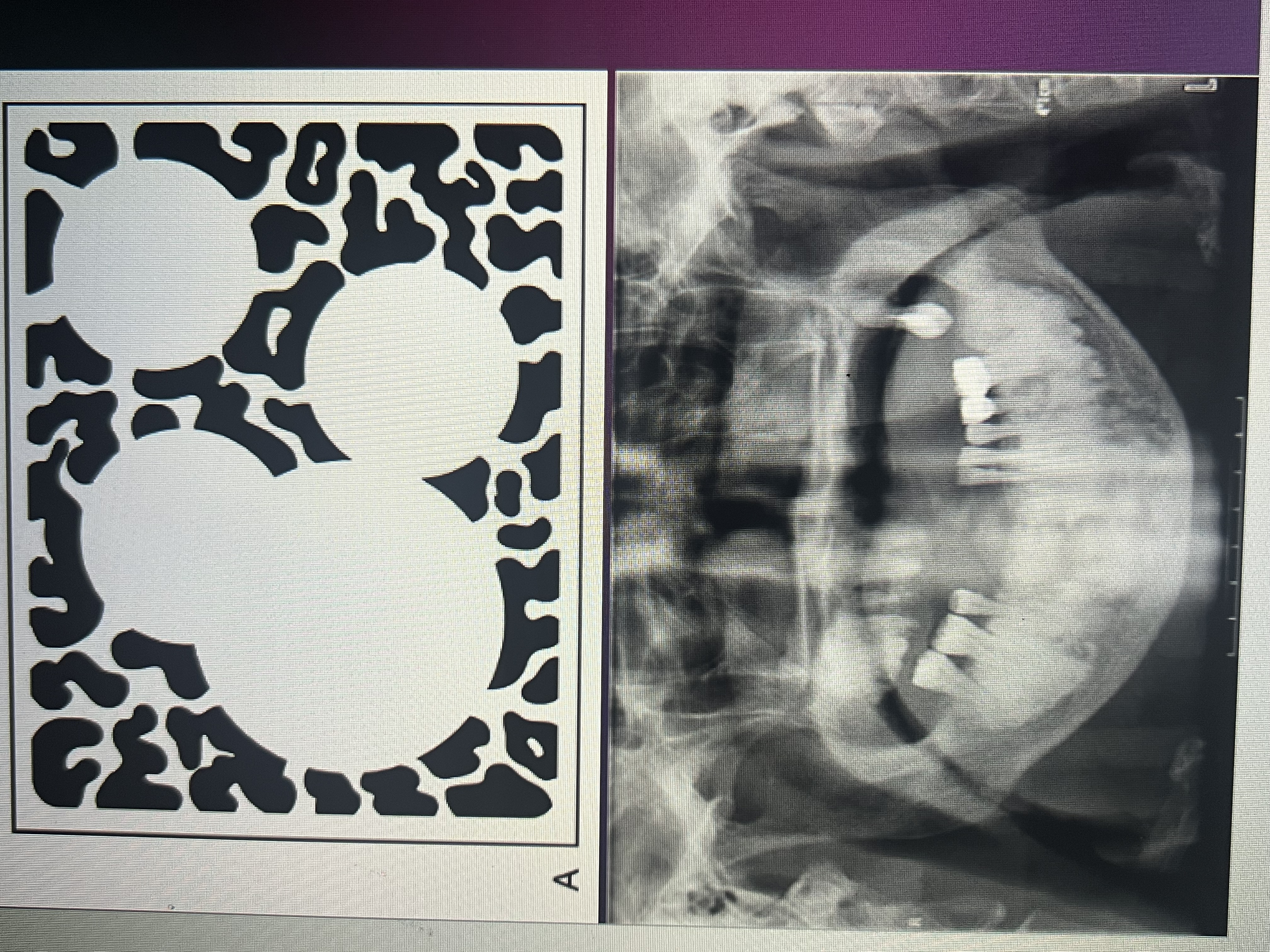
What is a radiopacity that may exhibit an irregular, poorly defined pattern?
Irregular/Ill-defined opacity
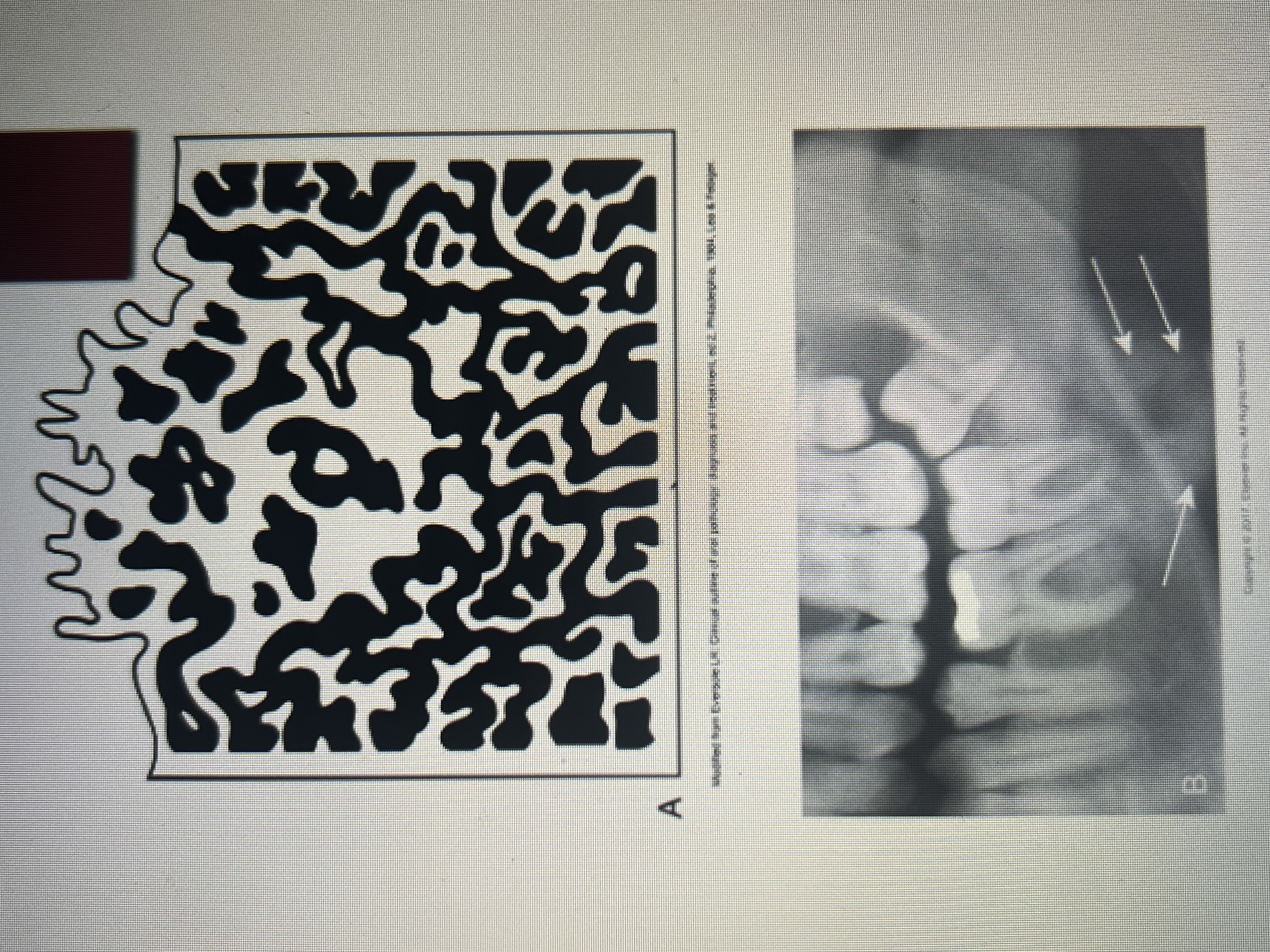
An irregular poorly defined radiopacity may represent a ____________ condition.
malignant
What is a granular or pebbled radiopacity that resembles pulverized glass?
radiopaque/ground glass opacity
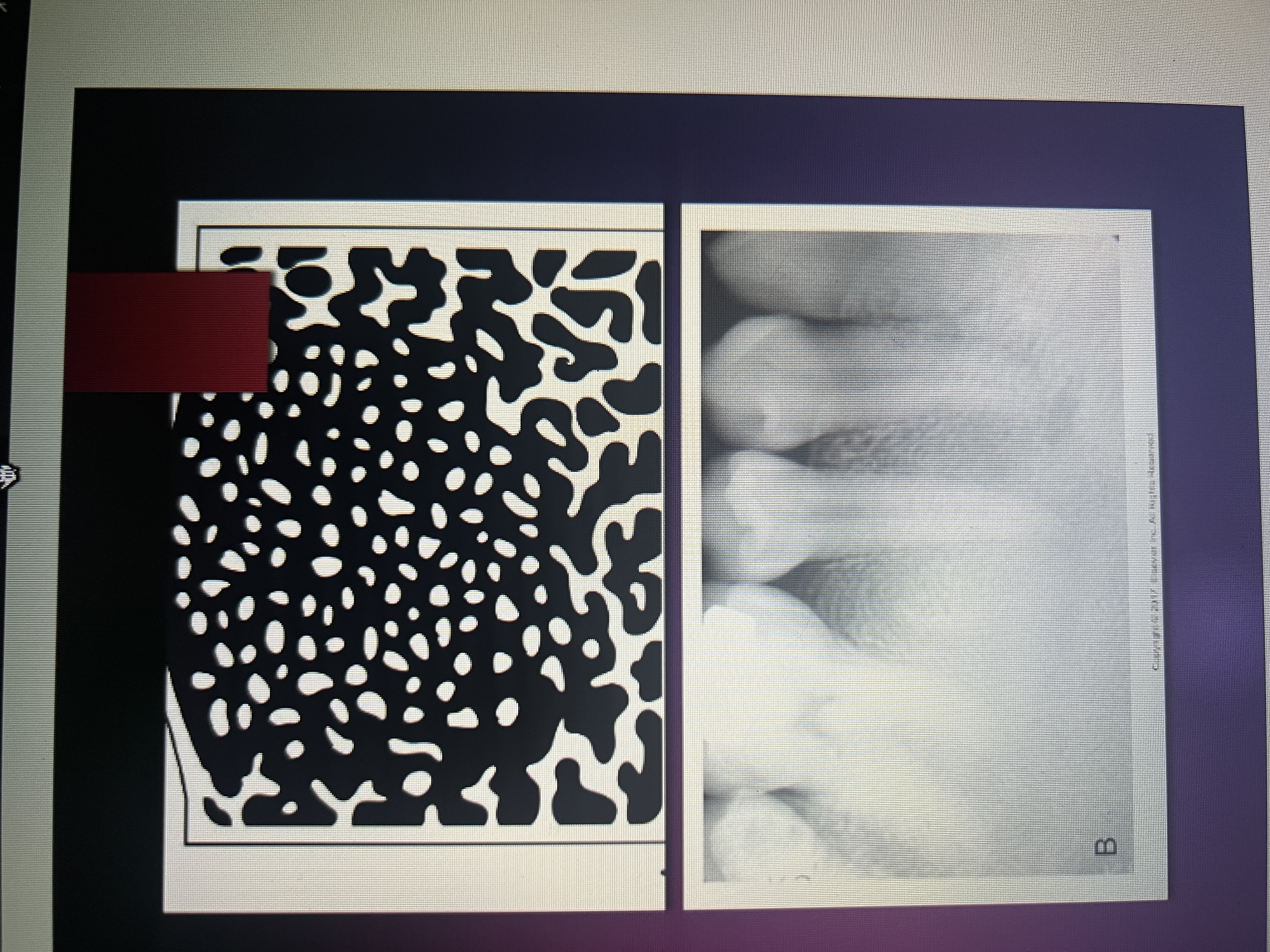
What lesion exhibits both a radiopaque and a radiolucent component?
Mixed lucent-opaque lesion
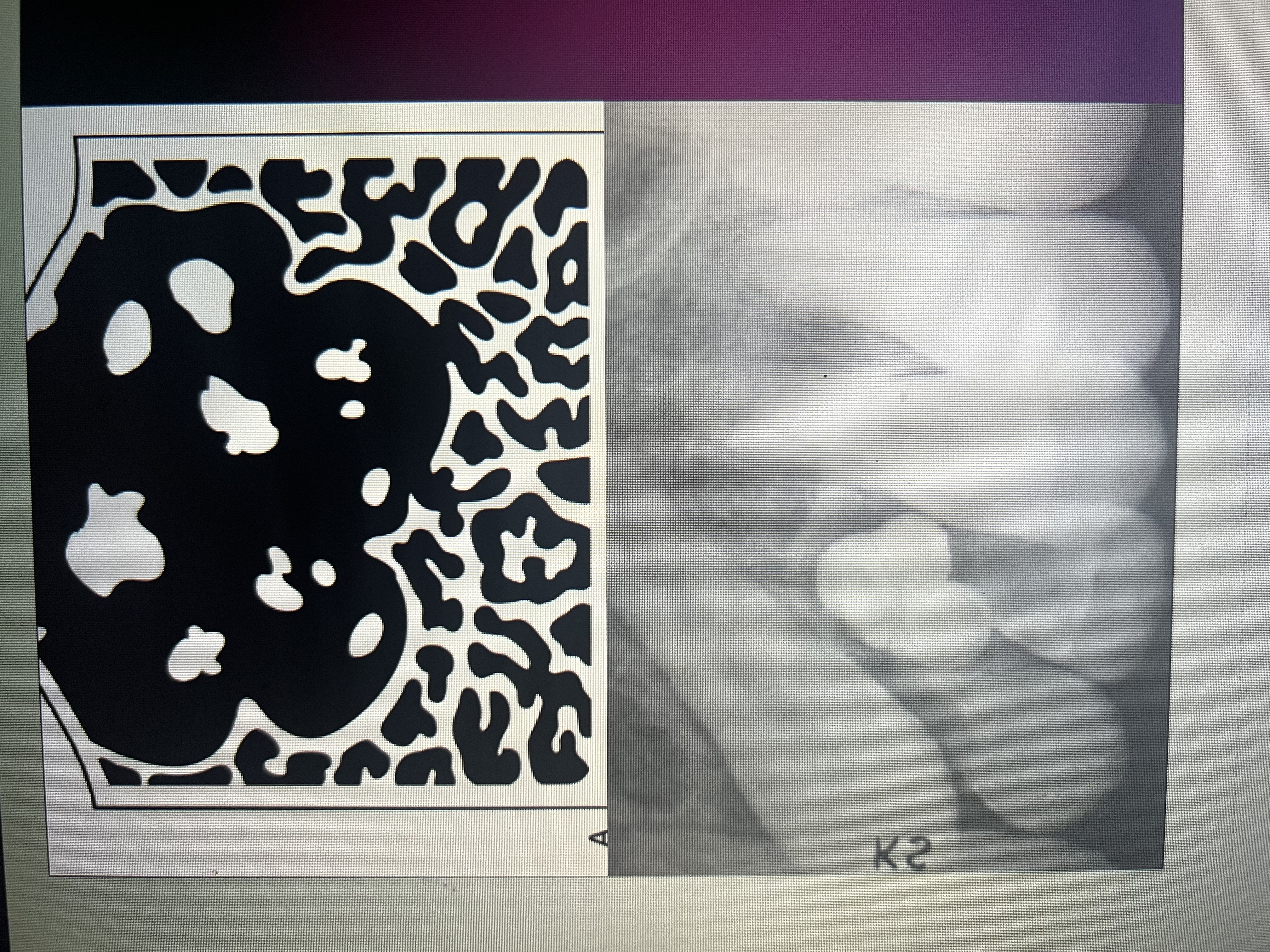
What does a soft tissue opacity appear as?
Well defined radiopaque area located in soft tissue.
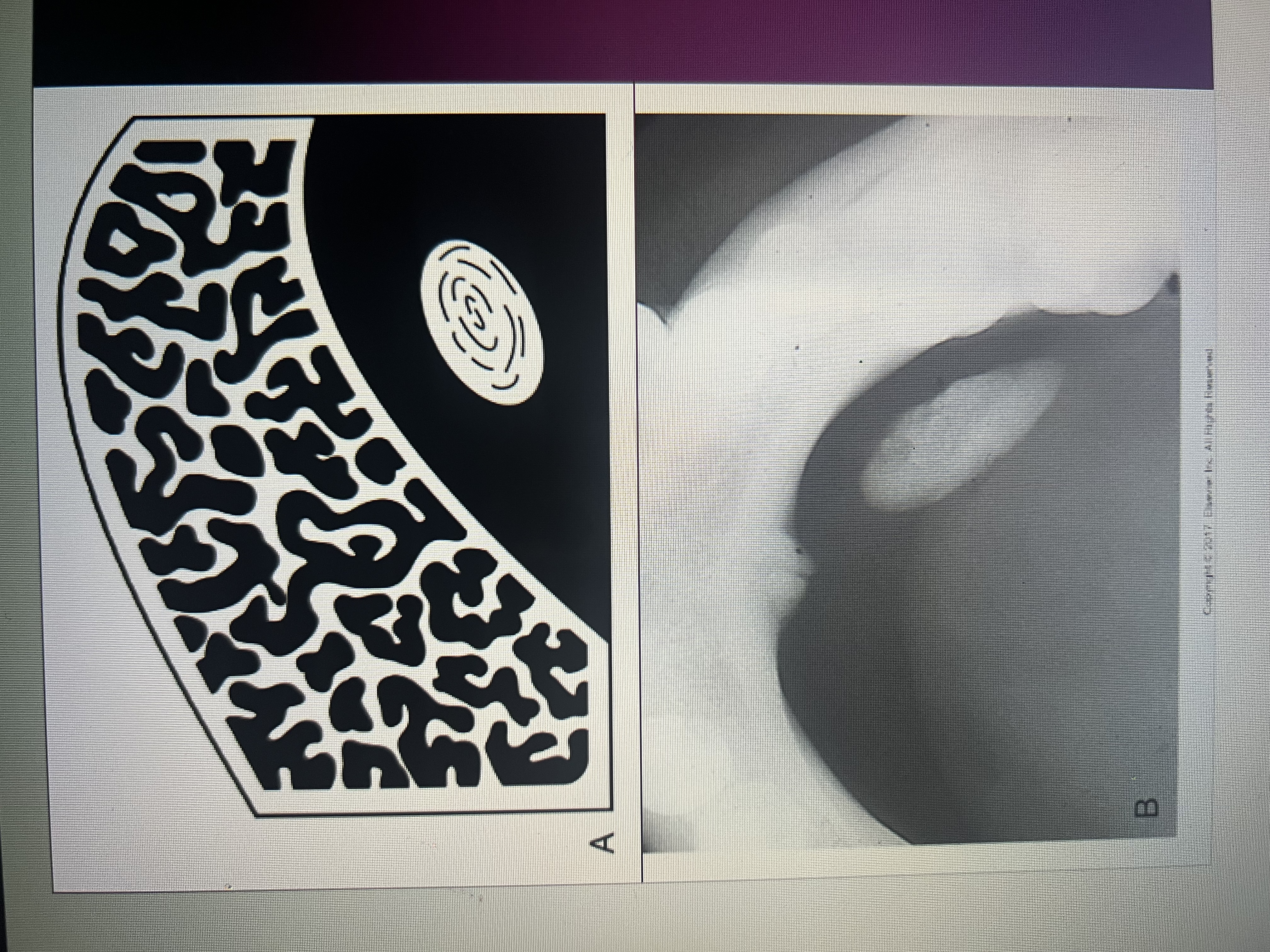
Radiopaque lesions may appear in the same places as ___________ lesions. In what locations?
Radiolucent.
Periapical, inter-readicular, edentulous, pericoronal or soft tissue.
How do metallic restorations appear?
Absorb x-rays, and very little (if any) radiation comes in contact with the receptor
What are examples of metallic restorations?
Amalgam and gold
How do metallic restorations appear on a dental image?
completely radiopaque
Nonmetallic restorations examples?
porcelain and composite
How do nonmetallic restorations appear?
Vary in appearance from radiolucent to slightly radiopaque, depending on the density
What is the most dense and least radiolucent nonmetallic restoration?
Porcelain
What is the least dense and most radiolucent nonmetallic restoration?
Acrylic
What is the most common restorative material used in dentistry?
Amalgam
How does amalgam appear on a dental image?
Completely radiopaque
How do one surface amalgam restorations appear on a dental image?
Distinct, small, round, or ovoid radiopacities with IRREGULAR borders
Where can one surface amalgams be seen?
buccal, lingual, occlusal surfaces
How can two surface and multi surface amalgams be characterized?
By their irregular outlines or borders on any tooth surfaces
What is an amalgam overhang?
Extensions of amalgam seen beyond the crown portion of a tooth in the interproximal region.
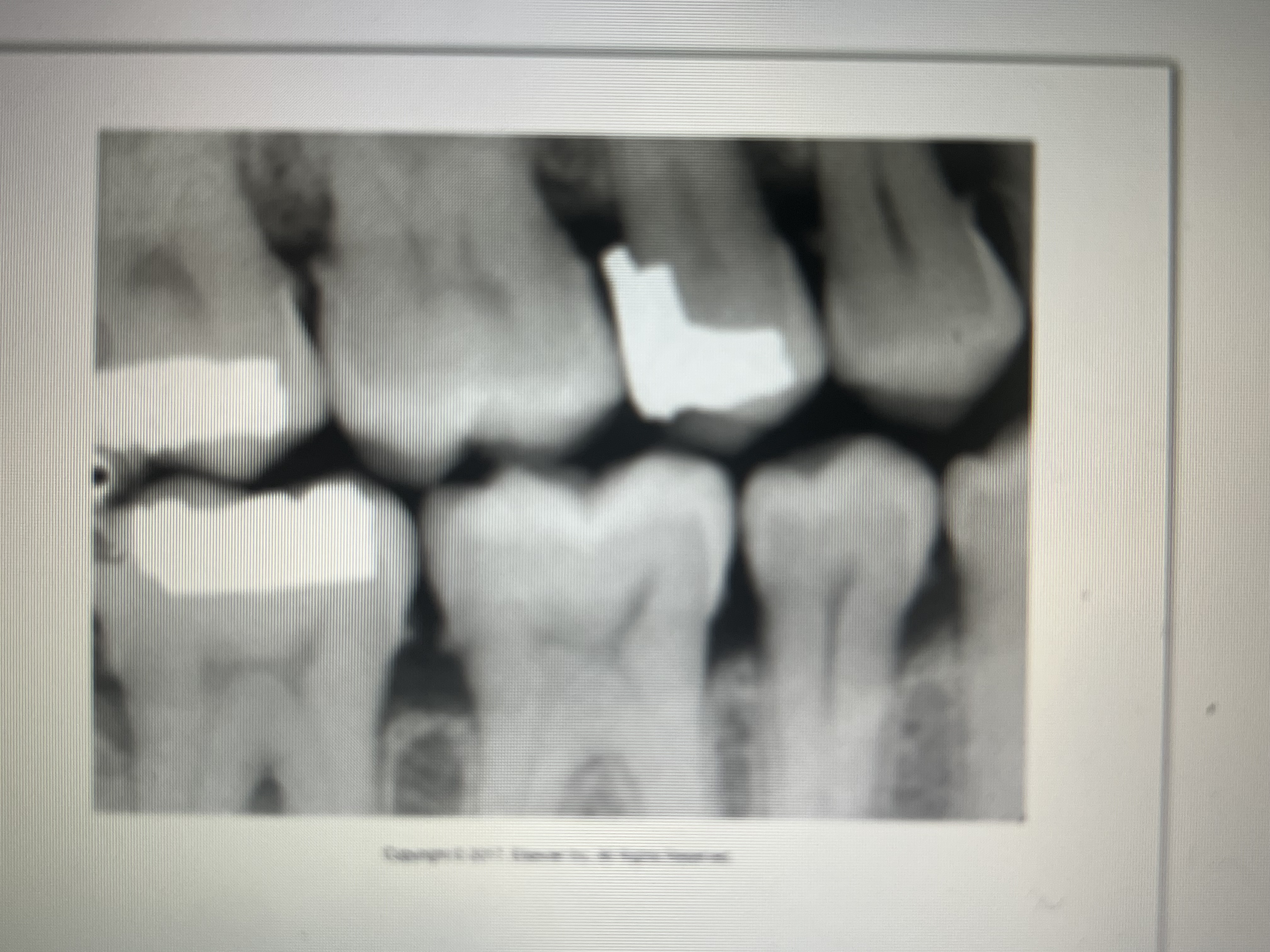
What are amalgam fragments?
Fragments of amalgam embedded in adjacent soft tissue during restoration of a tooth.
What do amalgam fragments look like on a dental image?
As dense radiopacities with irregular borders.
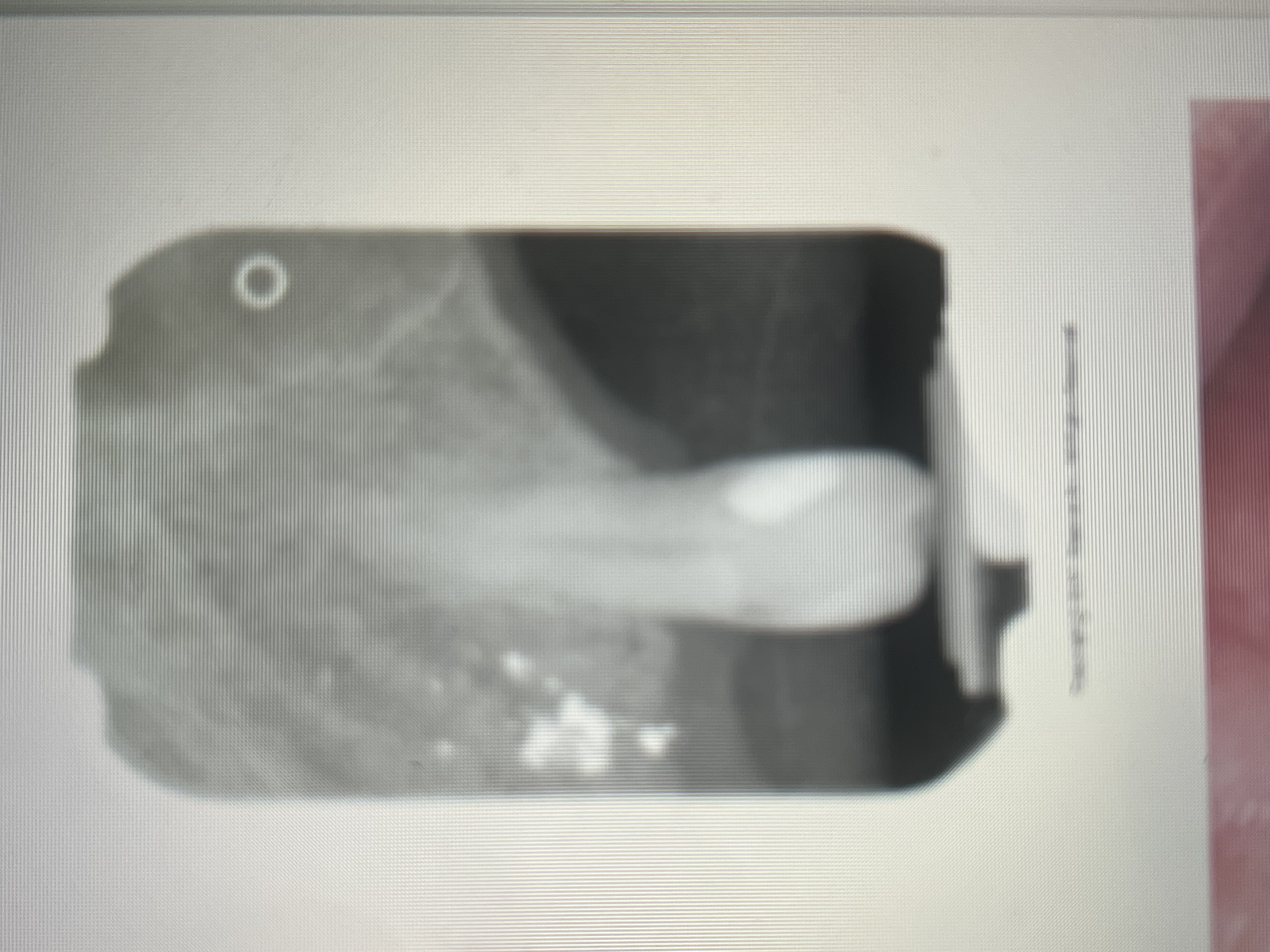
Amalgam fragments displaced in soft tissue during an extraction of a tooth with an amalgam restoration preset are called what?
An amalgam tattoo.
What does a gold restoration look like on a dental image?
A large radiopaque restoration with SMOOTH borders.
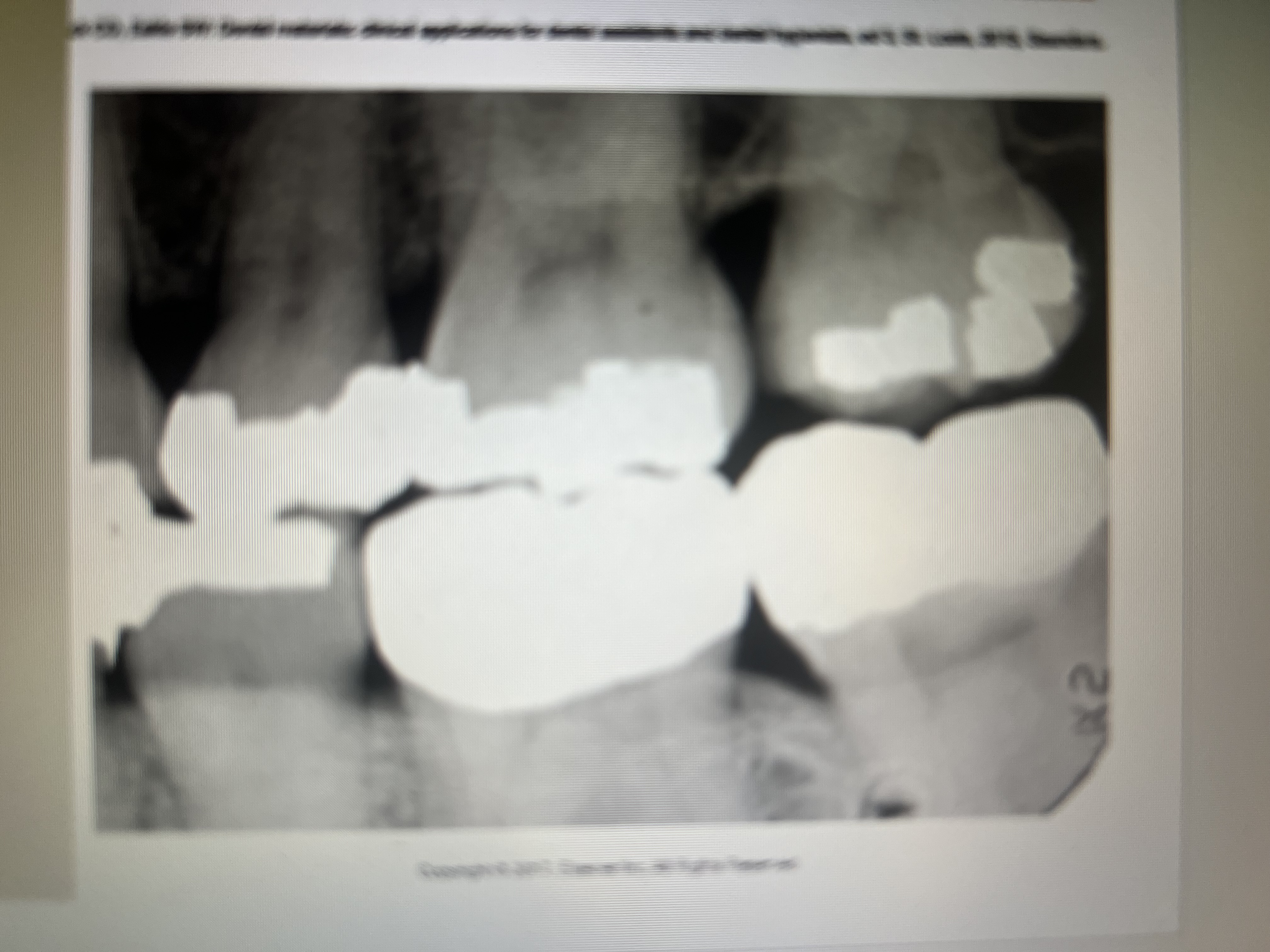
How can you determine a gold restoration from an amalgam restoration?
Good has a smooth marginal outline and amalgam does not, to be sure look in the patients mouth
How do gold crowns and bridges appear?
Large radiopaque restorations with smooth contours and regular borders. #18 and 19.
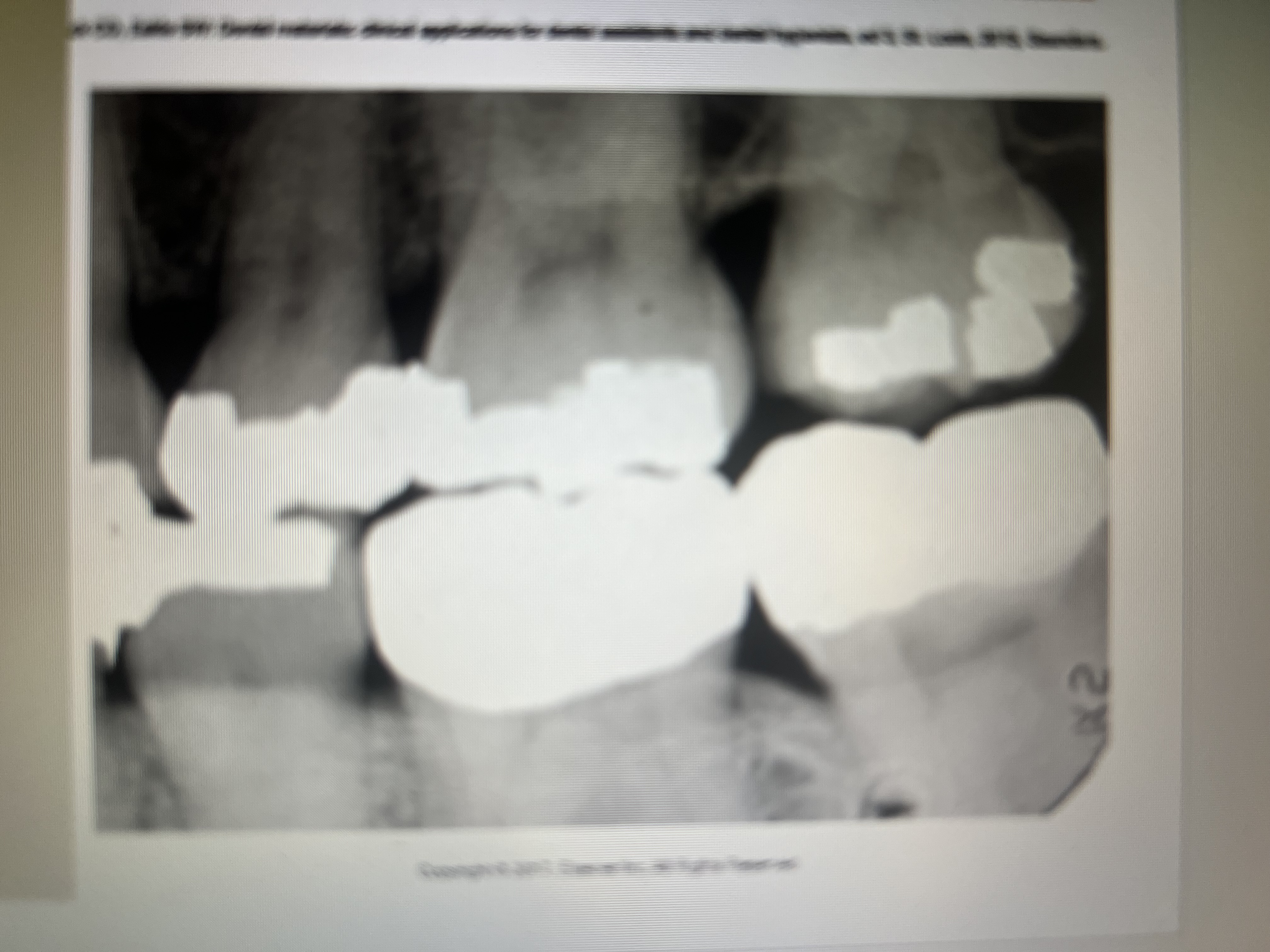
How do one surface gold foil restorations appear?
Small, round, radiopacities indistinguishable from amalgam
How do stainless steel and chrome crowns appear?
Radiopaque with smooth and regular margins. Appear see through
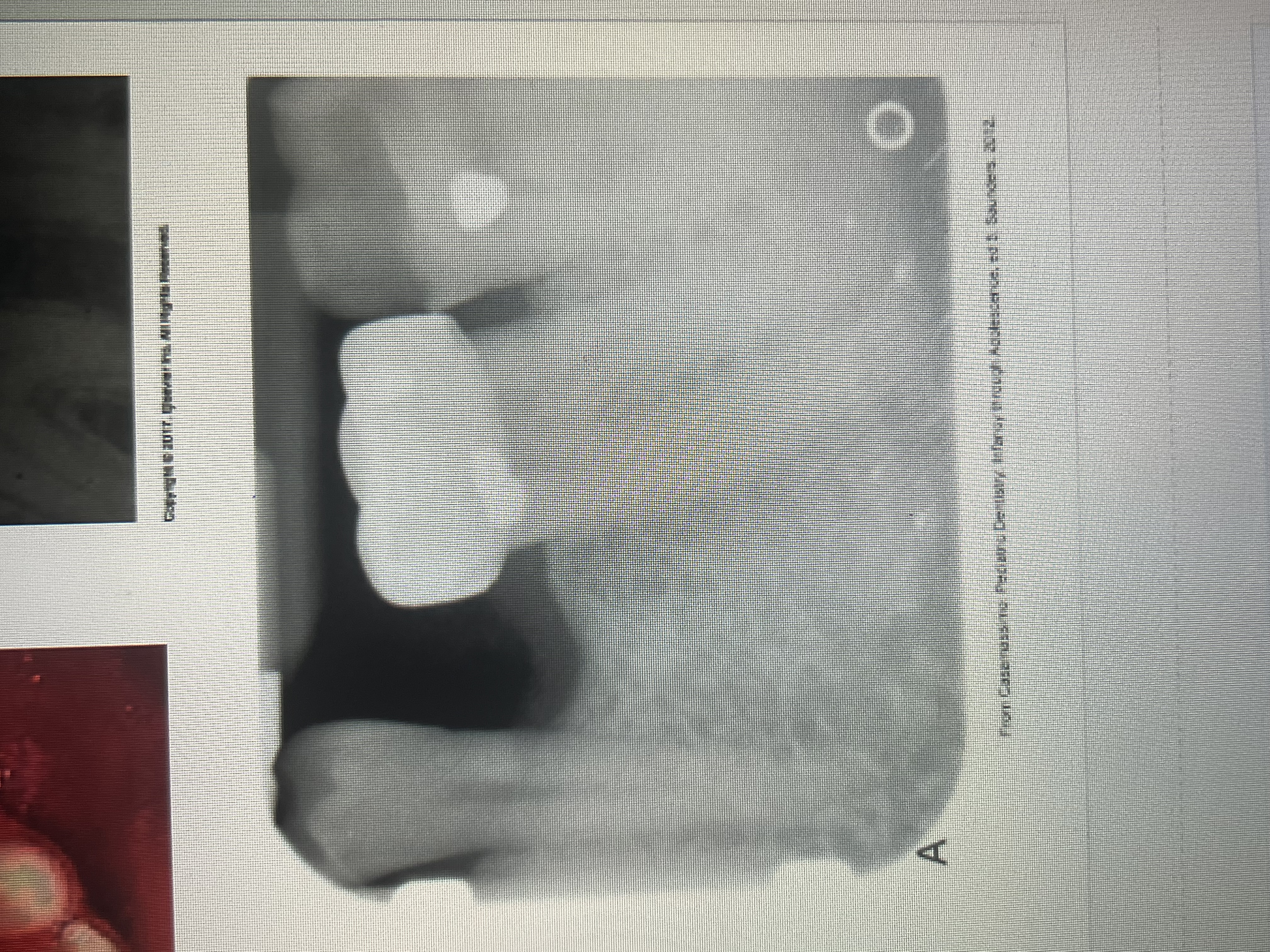
What restorations are not contoured properly to the cervical portion of the tooth and may cause periodontal problems?
stainless steel and chrome crowns
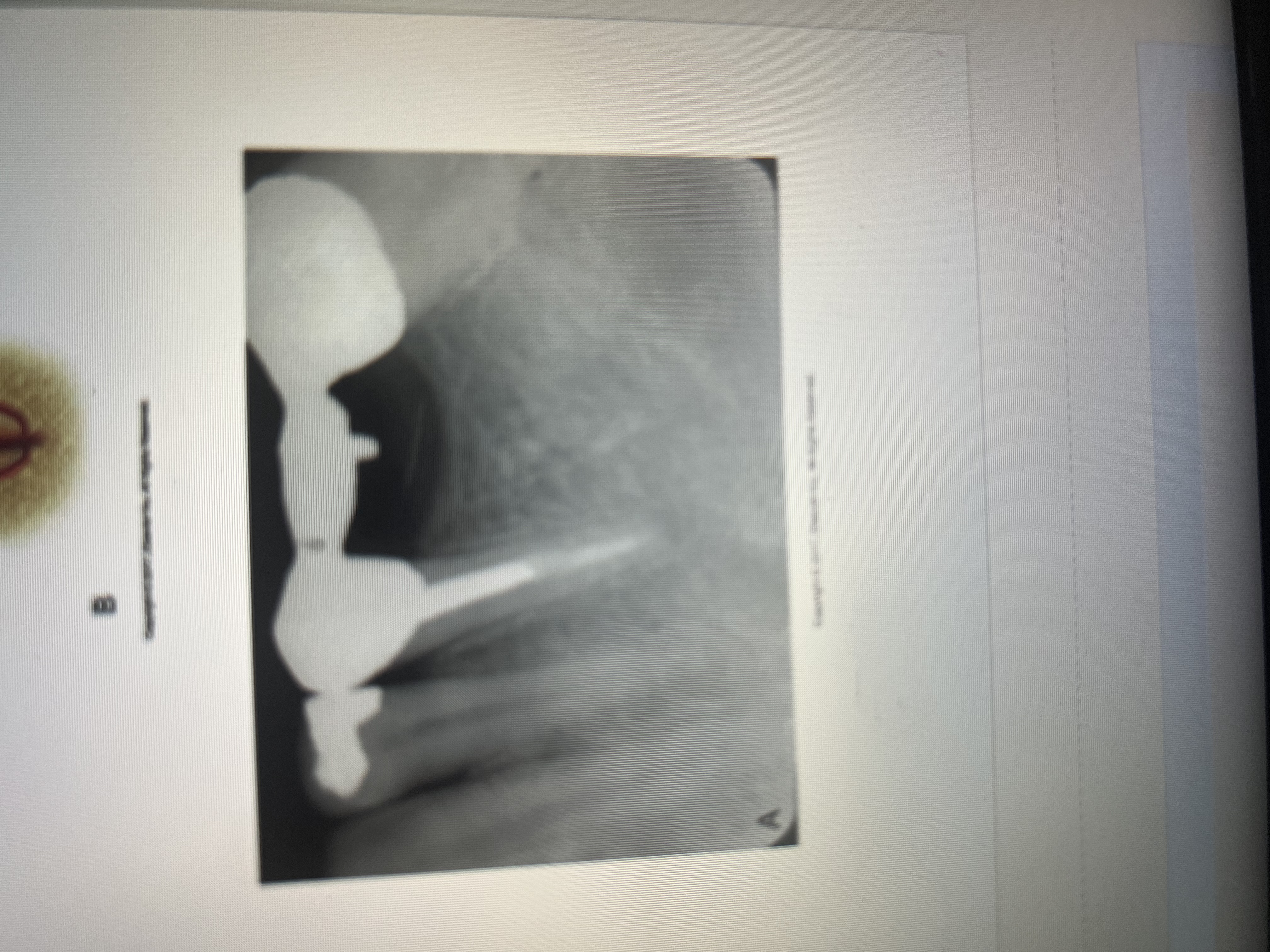
Post and core restorations can be seen in teeth treated with?
Endodontic therapy
How does post and core look like?
Radiopaque in the crown with the pot potion extending into the canal
How does a porcelain restoration appear?
Slightly radiopaque and resemble the radiodensity of dentin
How do all porcelain crowns appear on a dental image?
Slightly radiopaque, with a thin outline of the prepared tooth may be evident

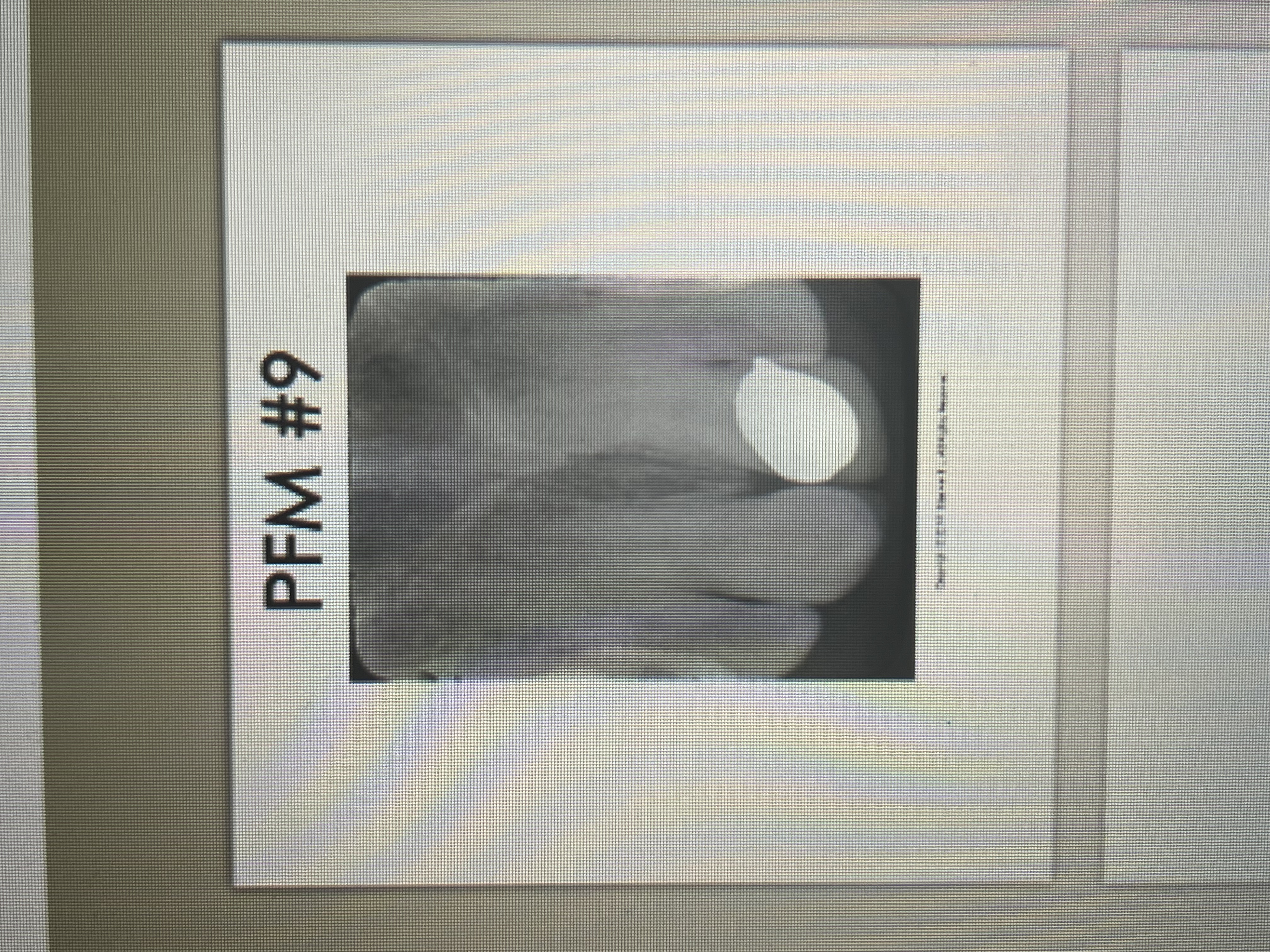
What does a PFM look like on a dental image?
metal component: completely radiopaque
porcelain component: slight radiopaque
What does a composite look like on a dental image?
Varies from radiolucent to slightly radiopaque, depending on the composition.
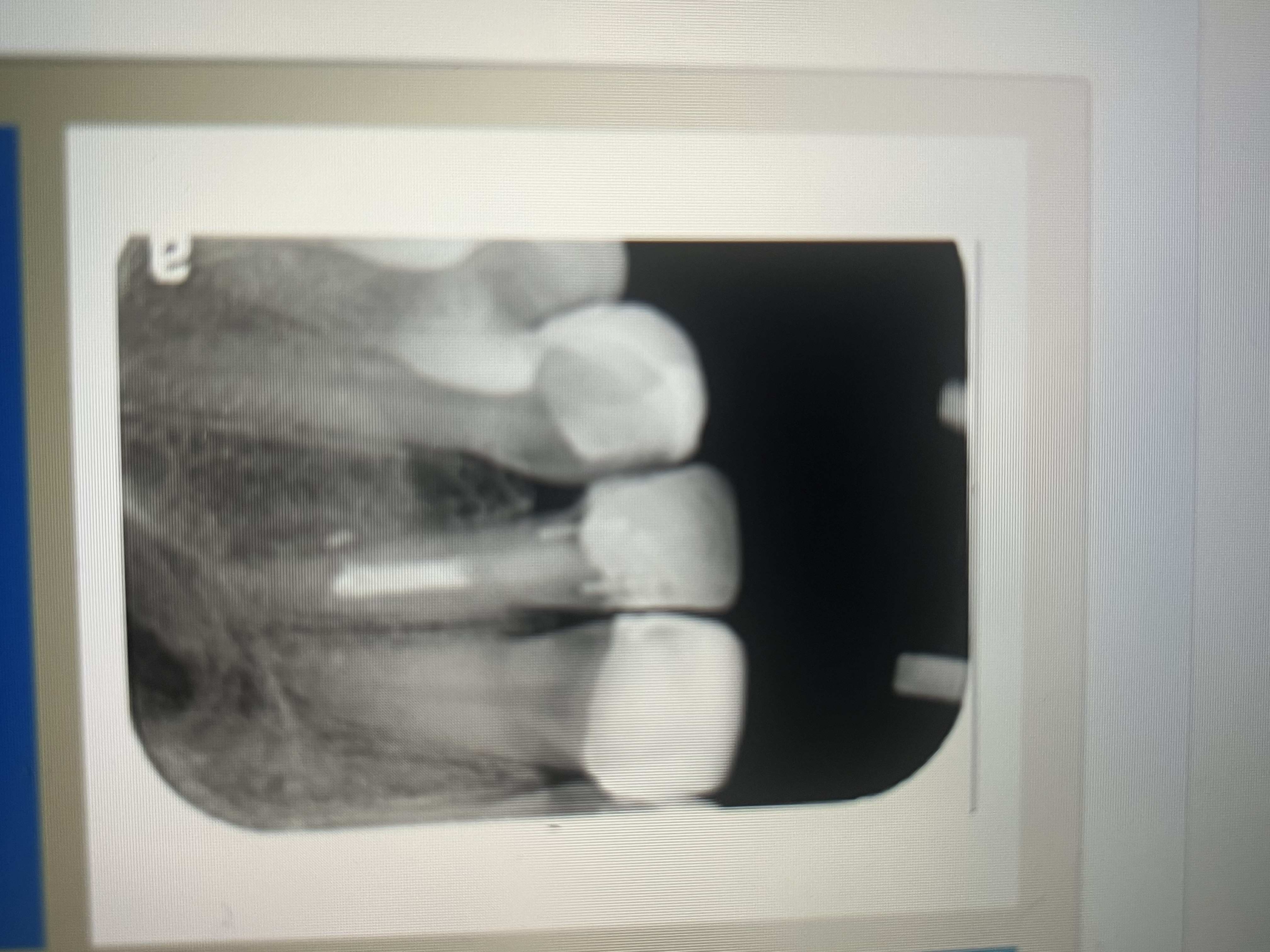
When there is confusion between composite and dental caries, what should you do?
A careful visual and digital examination of the tooth in question
How does acrylic appear on a dental image?
Radiolucent or barely visible
How does base material appear on a dental image?
Less radiopaque than restoration placed over it.
What are Metallic pins used for?
To enhance the retention of amalgam or composite.
How do metallic pins appear on a dental image?
As cylindrical or screw-shaped radiopacities.
What is Gutta percha?
Claylike material used in endo to fill the canals. Radiopaque.
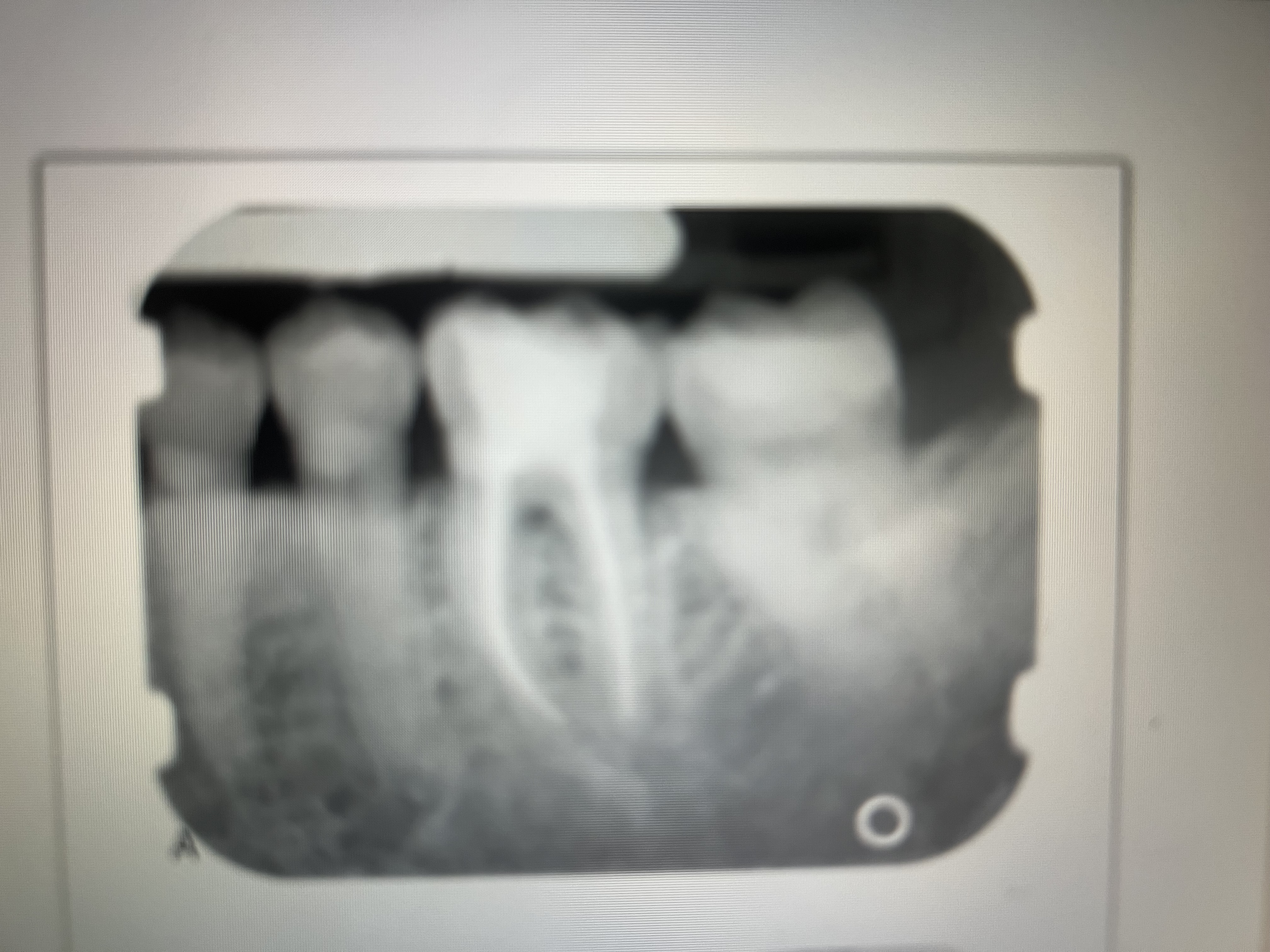
When compared with metallic restorations, gutta percha appears what?
Less radiodense
How do silver points appear on a dental image?
Highly radiopaque
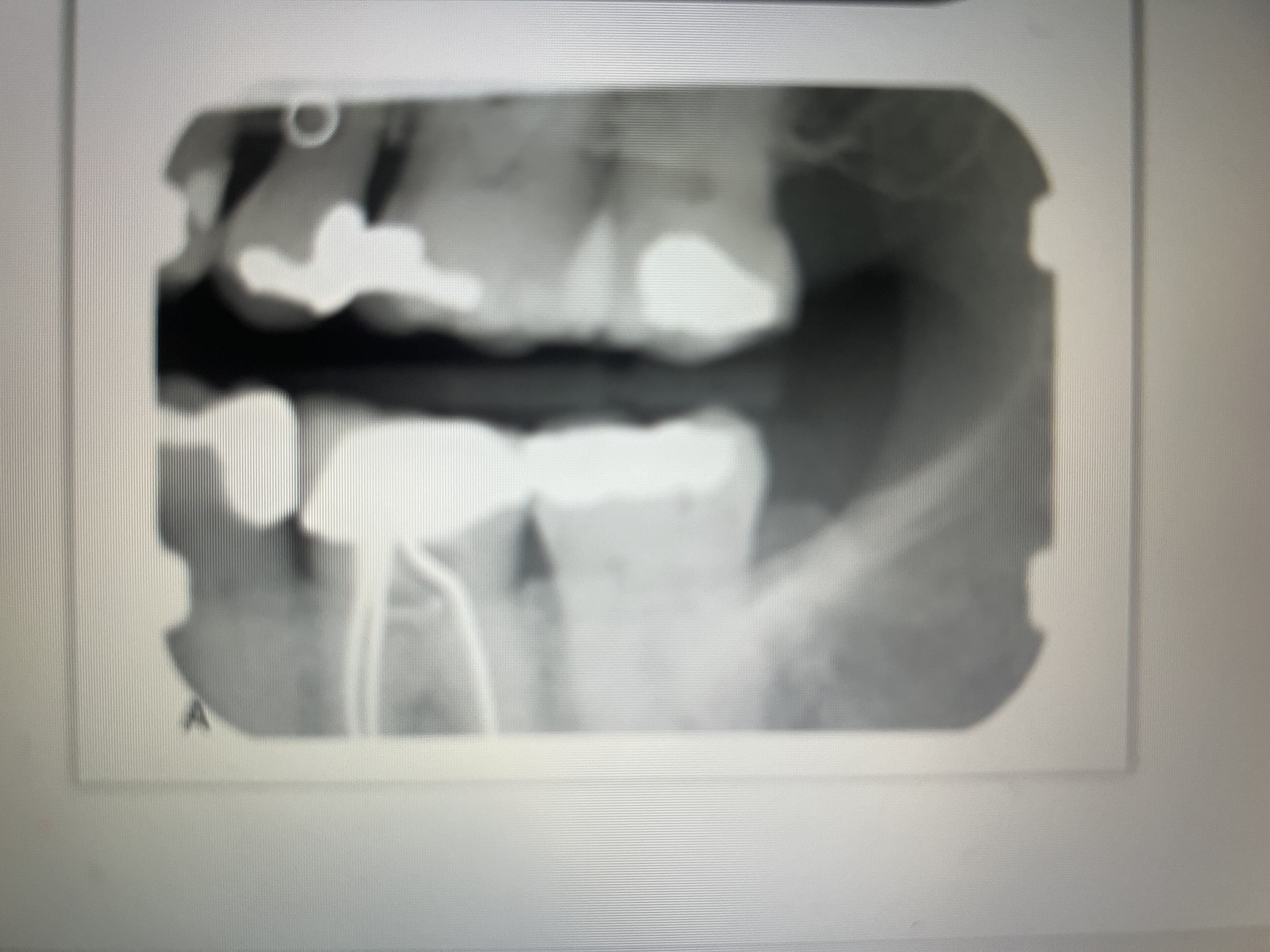
Silver points appear more ___________________ than does gutta percha
radiodense
Complete and removable partial dentures appear how?
Varies depending on the materials used
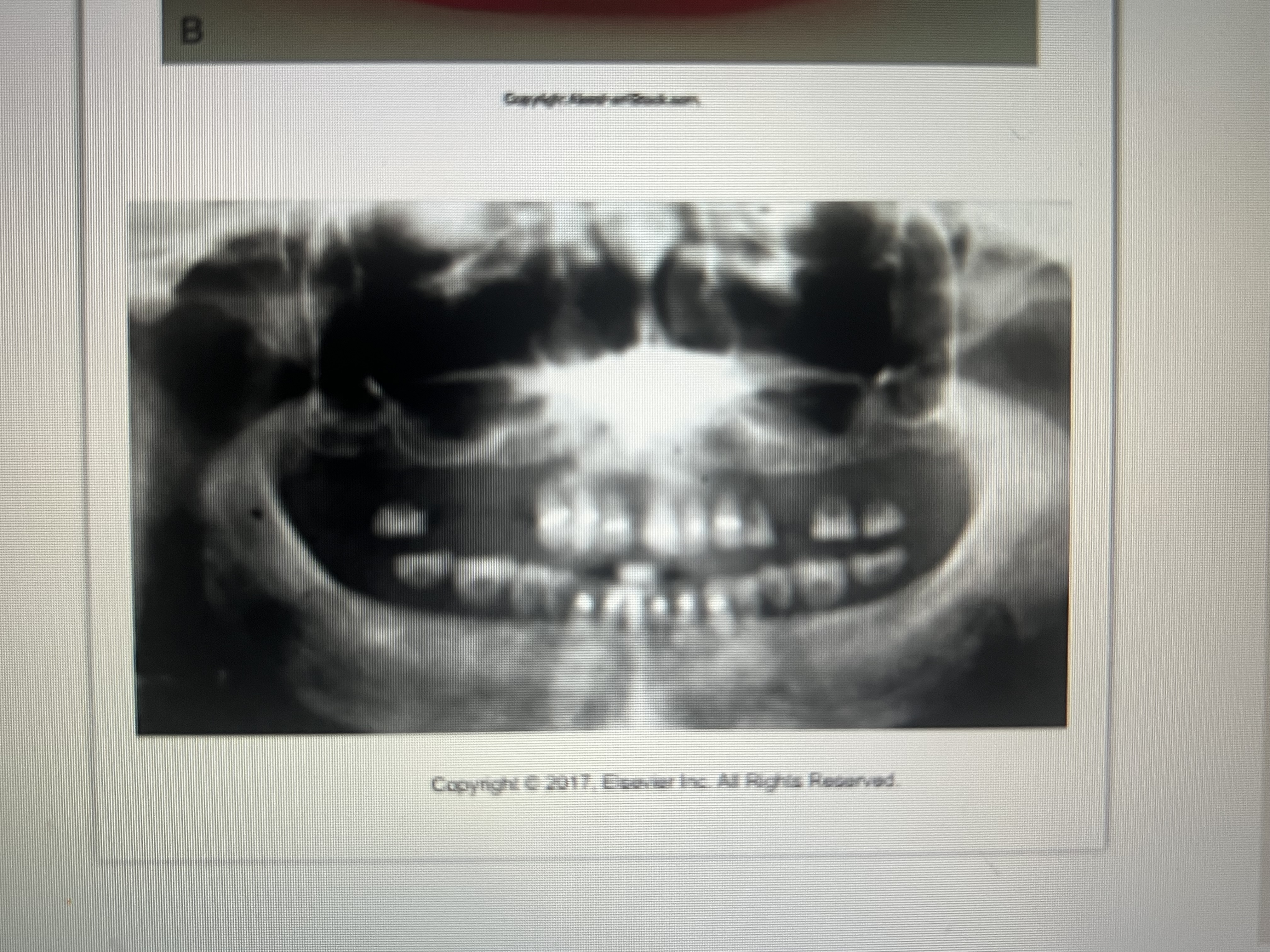
What two component parts do complete dentures consist of?
A base material and denture teeth
What does a denture base material appear like on a dental image?
It’s composed of acrylic and appears as a very faint radiopacity or not seen at all
Denture teeth appear how on a dental image?
May be composed of porcelain or acrylic
Acrylic lacks density and appear faintly radiopaque or radiolucent
Partial denture with a metal framework appear how?
Large radiopacities
What are diatorics?
Metal retention pins on anterior porcelain denture teeth.
Hoe do diatorics appear on a dental image?
Tiny, dense, radiopacities superimposed over the radiopaque porcelain denture teeth
If a complete denture is not removed before exposure, what will it look like on the image?
"rootless" or "floating"
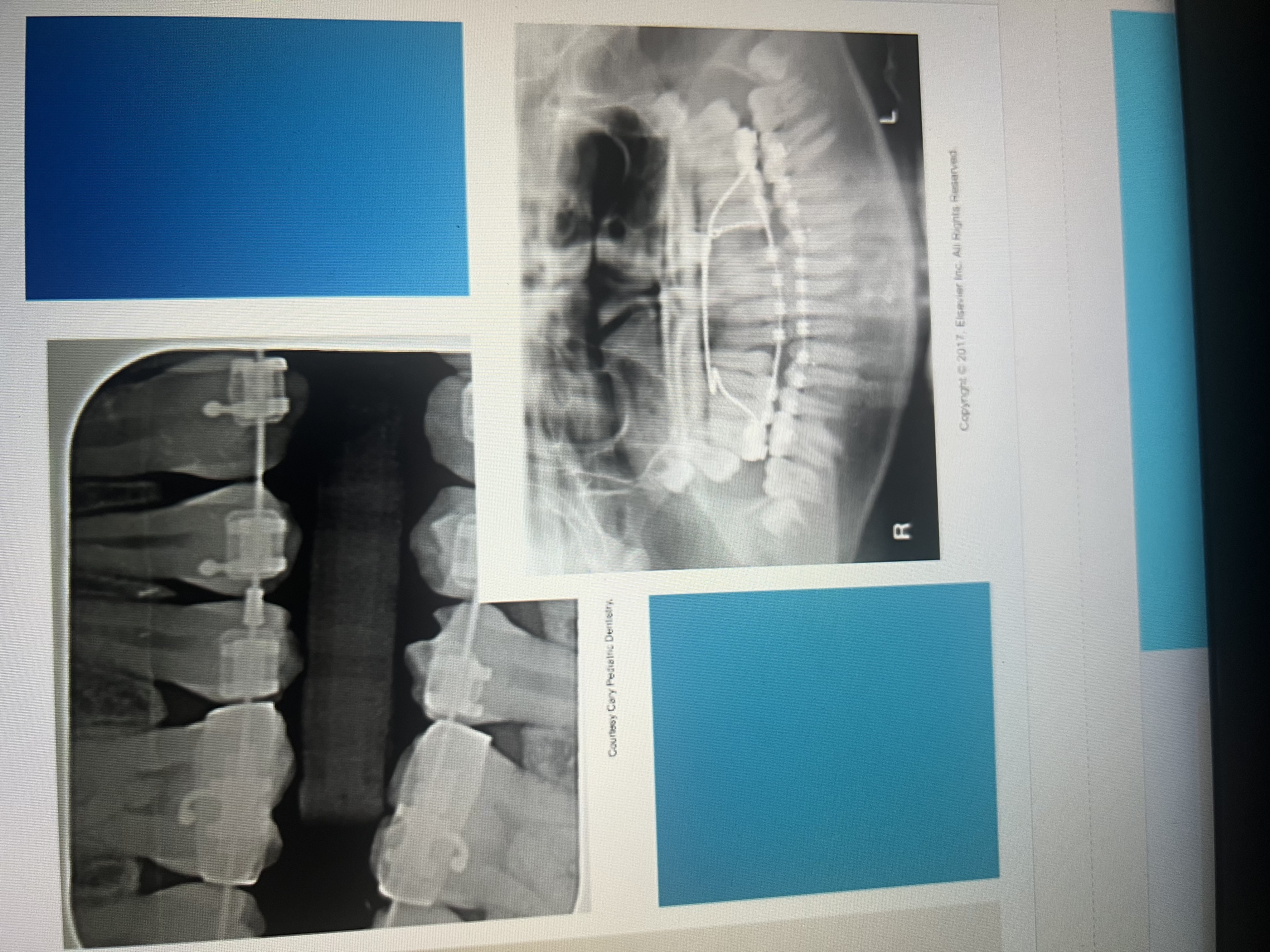
How do orthodontic bands, brackets, and wires appear on dental images?
White radiopaque
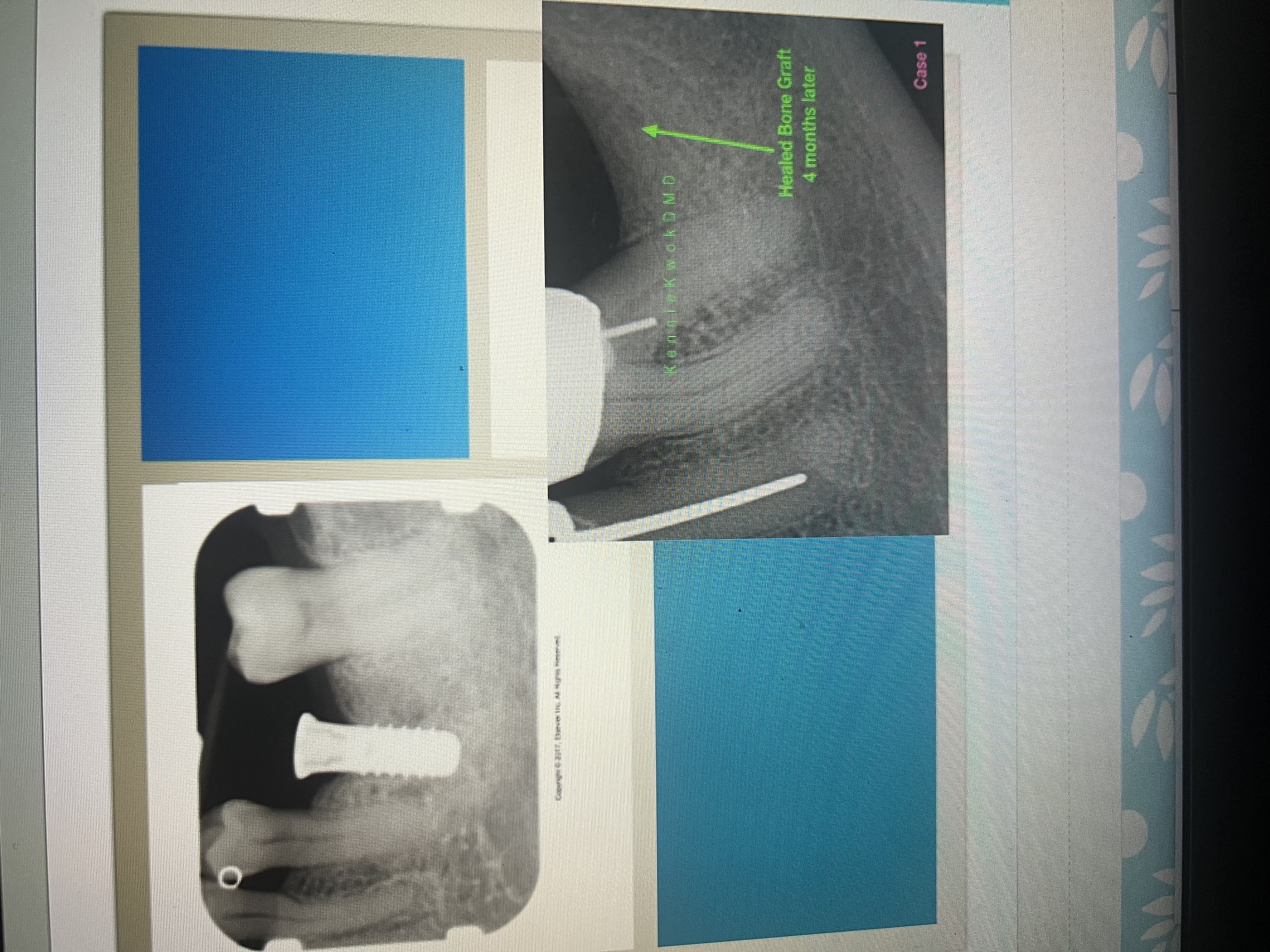
How does an endosteal implant appear on a dental image?
Radiopaque
How do suture wires appear?
As thin radiopaque lines
What should patients be instructed to remove before an intraoral image?
Eyeglasses, nose jewerly and any removable appliances in the mouth
What do radiodense objects like metallic earrings, cause on an extraoral image?
ghost image
What are Caries (tooth decay)?
The localized destruction of teeth by microorganisms
What are necessary to detect caries?
A clinical examination and dental images. Interproximal are reliant on dental images
A carious are appears radiolucent because...
Decreased density allows for greater penetration in the carious area
How do Interproximal Caries apppear?
Between 2 adjacent surfaces; typically seen at/just below the contact point. Triangular pattern begins at enamel.

What are Incipient Interproximal Caries?
Extends less than halfway through the thickness of enamel. Class I
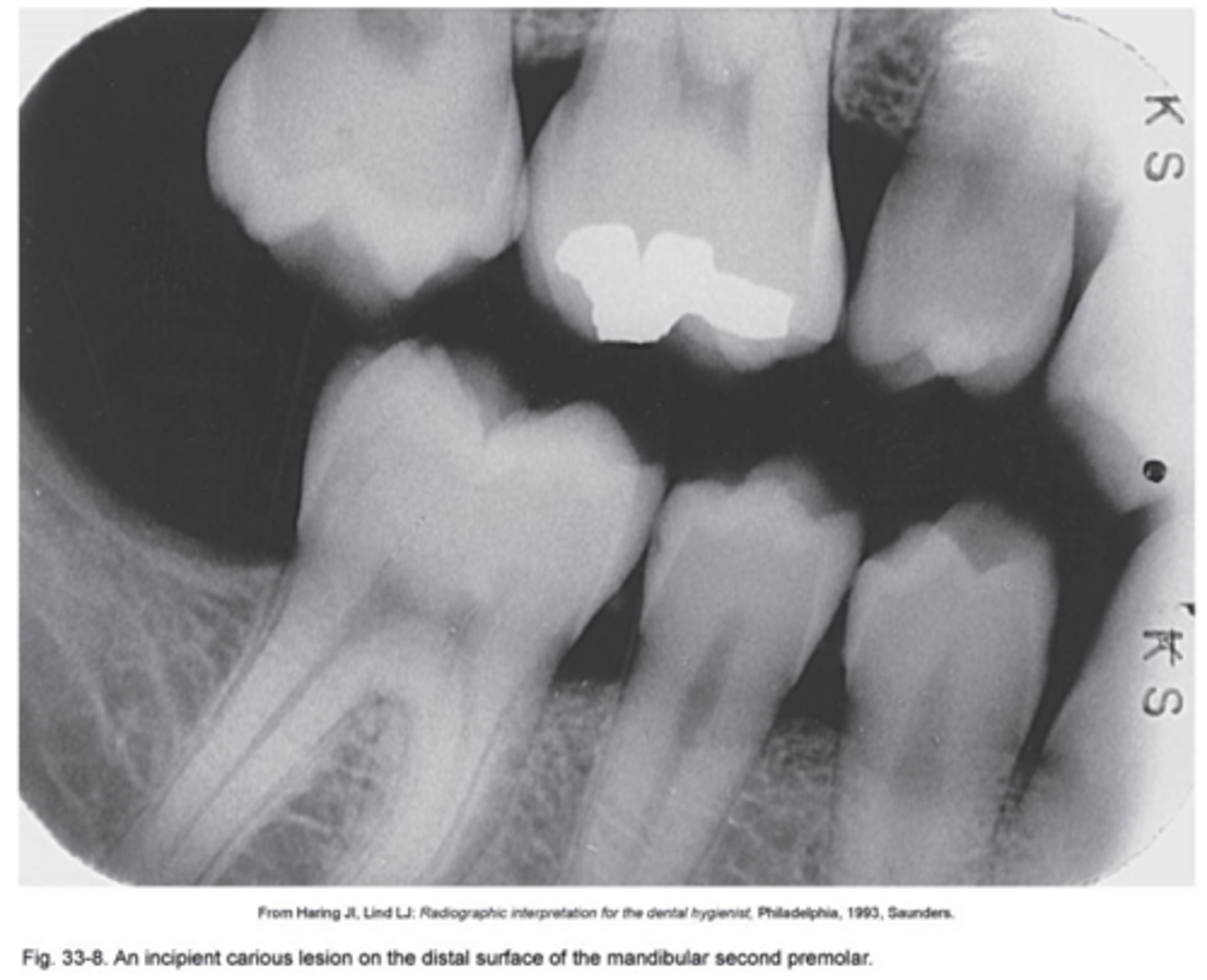
What are Moderate Incipient Caries?
Extends more than halfway through enamel but does not involve the DEJ. Class II
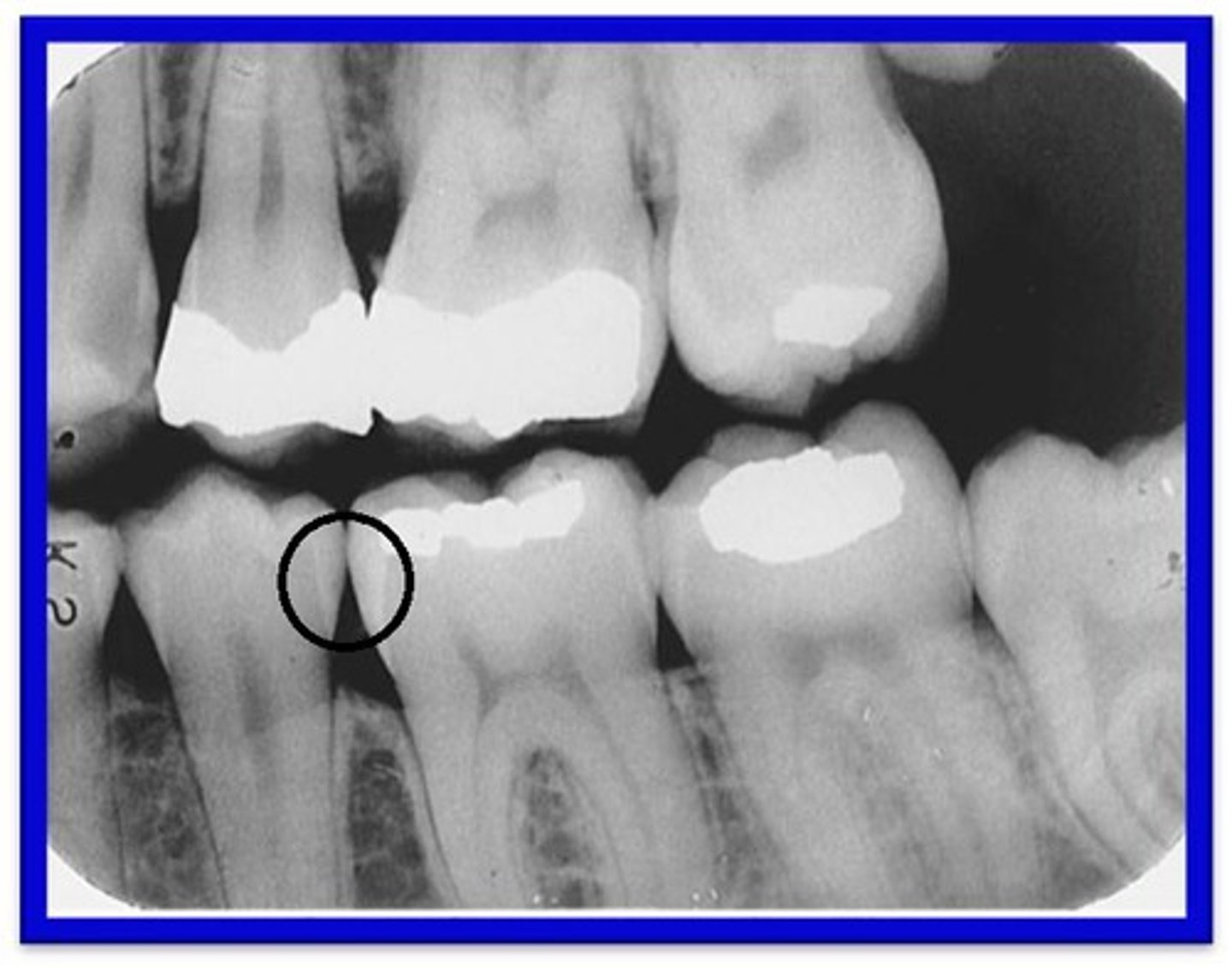
What are Advanced Incipient Caries?
Extends to or through the DEJ and into dentin but does not extend into dentin more than half the distance toward the pulp. Enamel and Dentin. Class III