Fundamentals of Pharmacy Practice: Spring 2025 Overview
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Premium
Amount individuals pay for health insurance every month
Deductible
Out-of-pocket payment BEFORE insurance coverage
Copay
A fixed out-of-pocket payment after deductible is met
Formulary
List of drugs covered by insurance plan
Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs)
Companies that manage prescription drug benefits on behalf of health insurers, Medicare Part D, large employers, and other payers.
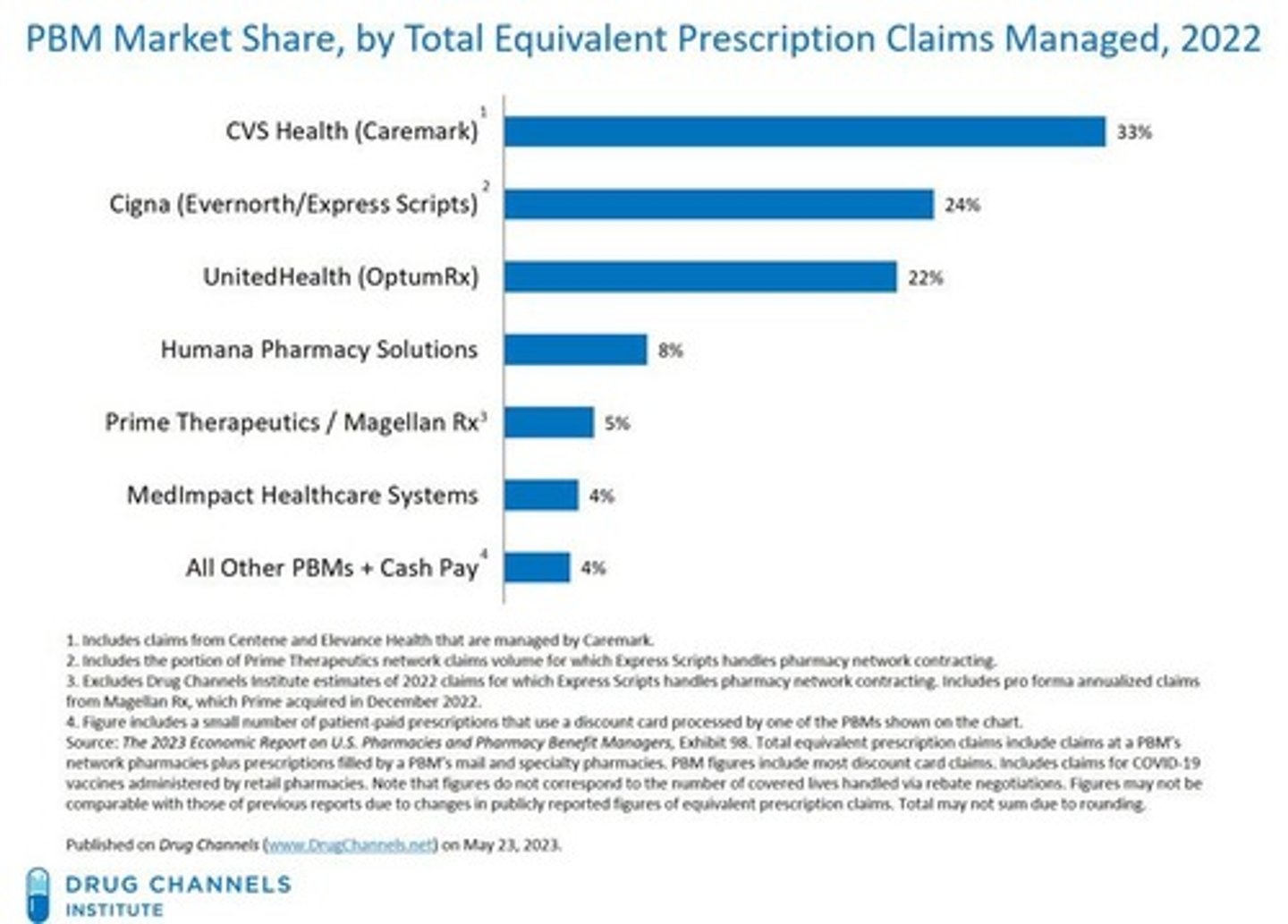
Examples of PBMs
CVS Caremark, Express Scripts, Prime therapeutics

Rx BIN
Bank Identification Number
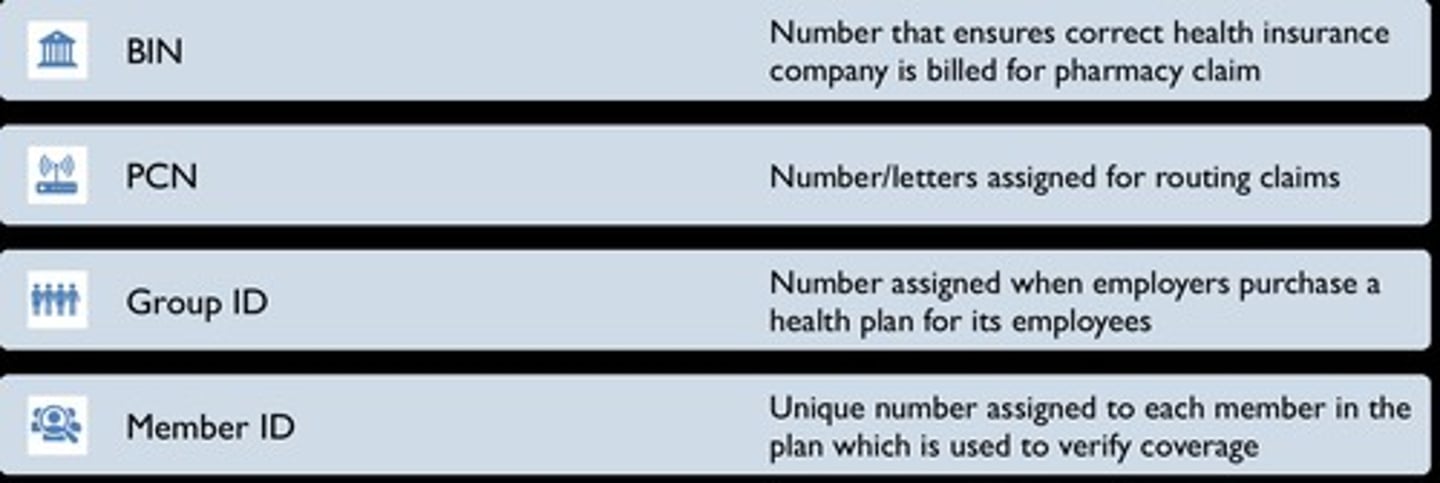
Rx PCN
Processor Control Number, Number/letters assigned for routing claims
Rx Group
Identify plan
ID number
Unique number assigned to each member in the plan, which is used to verify coverage

Person Code
01: card holder, 02: spouse, 03: child #1, 04: child #2
Mismatched Patient Information
Ensure correct information entered, Insurance expired? Patient's info, Double-check Full name and DOB, Correct person code?
Refill Too Soon
Calculate days from last fill, Inform patient when they can refill their medication
Drug Regimen Review (DRR)
Rejection related to MRPs or formulary substitutions
Prior Authorizations (PA)
Rejections from insurance companies to ensure that prescribed medications are medically necessary
Reasons for PA rejection
Lower cost associated with alternative therapy, Medication is high risk, Physician is prescribing medication for off-label use, Prescribed dose exceeds max daily limit
Prior Authorization Timeline
Not specified in the notes
Discount cards
Ask patient for discount cards info in Data Entry
Pharmacist's Role in Patient Safety
The role of the pharmacist is to dispense and offer expertise in safe use of prescriptions
Goal of Pharmacists
DO NO HARM!
Right patient
Ensuring the medication is given to the correct individual.
Right drug
Administering the correct medication as prescribed.
Right dose
Giving the appropriate amount of medication.
Right route
Administering the medication via the correct method (e.g., oral, intravenous).
Right time
Providing the medication at the correct scheduled time.
Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP)
An organization that advances patient safety through reporting adverse events, providing education, and advocating for change to prevent medication errors.
2006 Preventing Medication Errors report
A report from the Institute of Medicine (IOM) showing that 51.5 million errors per 3 billion prescriptions occur annually.
Patient Information
Key element for patient safety that includes health conditions and allergies.
Drug Information
Key element for patient safety that includes knowledge about drug-drug interactions.
Communication of Drug Orders/Information
The process of clearly conveying prescription details to avoid errors.
Drug Labeling, Packaging, and Nomenclature
Ensuring medications are clearly labeled to prevent confusion, including look-alike names and bottles.
Drug Standardization, Storage, and Distribution
The organization and management of medications to ensure safety and efficiency.
Medication Device Acquisition, Use, and Monitoring
The process of obtaining and properly using medical devices for medication administration.
Environmental Factors, Workflow, and Staffing
Elements that influence the safety and efficiency of medication administration.
Staff Competency and Education
Ensuring that healthcare staff are properly trained and knowledgeable about medication safety.
Patient Education
Informing patients about their medications to enhance safety and adherence.
Quality Processes and Risk Management
Strategies to minimize errors and maximize patient safety.
Corresponding Responsibility
The shared responsibility between the prescribing practitioner and the pharmacist for the proper prescribing and dispensing of controlled substances.
C-II Prescriptions Dispensed in Texas
Generally should be dispensed to an electronic prescription (ePrescribe) that meets DEA requirements.
Electronic prescribing
A method of prescribing that needs to meet DEA requirements for C-II prescriptions.
Texas Official Prescription Form
Must be written on the Texas Official Prescription Form
30 days of issuance
Must be filled within 30 days of issuance; Date written counts as Day 0 (zero)
No Refills
No refills are allowed
Official Prescription Form (C-II)
No Longer Valid; Valid (as of June 1, 2019); Triplicate; Issued by DPS; Really old
Official Form before Sep 1, 2016
Issued by DPS
Official Form after Sep 1, 2016
Issued by TSBP after Sep 1, 2016 but before Sep 1, 2018
New Official Form
Only New Official Form issued after Sept 1, 2018; Issued by TSBP
C-II Rx days
The physical C-II Rx days are numbers
Control Number
Unique number which gets submitted to PMP
Pantograph
Void appears several times if copied or scanned
Thermochromic Ink
New: Red Rx on front
Watermark
Seal of State of Texas printed on face of Rx; 2nd watermark embedded in Rx paper
Forms are not transferrable
Forms are not transferrable ... Just for that prescriber
One C-II med per form
One C-II med per form (prescription)
Non C-II meds
Not intended for other - Non C-II meds
Faxing prescriptions
Can only be faxed in rare cases
C-II Rxs & APRN or PA
Can only write for C-II if authorized to do so and working in hospital-based practice for patient of hospital (admitted or ER visit) or terminally-ill patient
Official Form requirements
Official Form must have name and DEA number of supervising physician in addition to APRN / PA's name and DEA number
C-II Partial Fills
If a RPh cannot issue full quantity of C-II, balance must be dispensed within 72 hours of first partial dispensing
RPh notes on Rx
RPh notes on face of Rx (or electronically if ePrescribed) the quantity supplied
After 72 hours
No further amounts can be dispensed; RPh must notify prescriber to get a new prescription
Exceptions for partial fills
Exceptions exist if patient is resident of LTCF or terminally-ill
Multiple C-II prescriptions
Practitioner can issue multiple C-II Rx on same day for a med if up to 90-day supply for all Rx's issued that day
Legitimate medical need
Practitioner must determine there is legitimate medical need
Earliest fill date
Writes on each prescription (after 1st), the earliest fill date
What RPh Can't Change
RPh cannot change the name of patient, name of drug, name of prescribing physician, or date the prescription was issued
What RPh Can Add or Clarify
RPh can add or clarify notification alone, notification and permission, dosage form, drug strength, drug quantity, directions for use, correct obvious issuance date errors, and add missing date of issuance
Modify earliest fill date
RPh can modify earliest fill date on multiple issuance prescriptions
Without notification
Without notification a RPh, at professional discretion, can correct patient name (misspelling) and add patient address to prescription
Electronic Controlled Substance Prescribing
Mandatory electronic prescribing of controlled substances (C-II to C-V) in effect as of Jan 1, 2021
Opioid Rx for Acute Pain
Opioid Rx (C-II to C-V) for Acute Pain limited to 10 days with no refills
Safe Disposal of Controlled Substance
Requires RPh dispensing C-II to provide written notice on safe disposal of CS to patient unless pharmacy is a take-back location or provides no-cost means of CS destruction to patient
Notice on safe disposal
Notice must include info on safe disposal locations, or a website specified by TSBP with searchable data of safe disposal locations
DEA 222 Form
Used to order C-II meds; also used to transfer C-II between registrants but 5% Rule applies
Signers of DEA 222 Form
Only signer of most recent DEA registration or those granted Power of Attorney may order or complete 222
Electronic orders
Electronic orders allowed since 2005; Pharmacist may now electronically sign the data entry attestation
DEA 222 Form
A form used for ordering controlled substances that requires only one medication per line and must be completed with specific details.
Zero Reporting
A requirement for pharmacies to notify TSBP if no controlled substances are dispensed for 7 consecutive days.
PMP Access & Use
Regulations regarding the access and use of the Prescription Monitoring Program by pharmacists and pharmacy technicians.
Mandatory PMP Look-up Start Date
The date, set to March 1, 2020, when it became mandatory to look up the PMP for all opioid prescriptions.
ePrescribing of Controlled Substances
The process of electronically prescribing controlled substances, which must comply with DEA requirements.
Authentication for Prescribers
Prescribers must obtain authentication or a digital signature from a private credential service to ePrescribe.
Prescriber Authentication Options
Prescribers must choose 2 from: something you have (e.g., hardware token), something you know (e.g., username & password), or something you are (e.g., biometrics).
Compliance Audits
Prescriber and pharmacy systems must be audited by a third party for compliance at least every 2 years.
Exceptions to Mandatory Electronic Prescribing
Situations where electronic prescribing is not required, such as written prescriptions by veterinarians or due to technological failures.
Prescriber Waivers for Electronic Prescribing
A process for prescribers to request a waiver from electronic prescribing requirements by demonstrating specific circumstances.
Waiver Duration
A waiver for electronic prescribing can be issued for a period of 1 year.
Permanent Ink Requirement
DEA 222 Form must be filled out in permanent ink or typewriter, with no erasures or alterations allowed.
Last Line Completed
A requirement on the DEA 222 Form to indicate the last line that was completed.
Controlled Substance Prescriptions
Prescriptions for drugs classified as C-III to C-V under DEA regulations.
Health and Safety Code 481.075
The section of the Health and Safety Code that was amended to include zero reporting of controlled substance dispensing.
Health and Safety Code 481.076
The section of the Health and Safety Code that was amended to address PMP access and use.
Pharmacy Technician Trainee
A pharmacy technician who is in training and may access PMP records under the direction of a registered pharmacist.
Public Health Emergency Prescriptions
Non-patient specific prescriptions that may be issued during a public health emergency.
Research Protocol Drugs
Drugs prescribed under a research protocol that may not follow standard electronic prescribing rules.
Economic Hardship Waiver
A waiver request that must demonstrate economic hardship as a circumstance for not complying with electronic prescribing.
Technologic Limitations Waiver
A waiver request that must demonstrate technological limitations not reasonably in control of the prescriber.
Exceptional Circumstances Waiver
A waiver request that must demonstrate other exceptional circumstances as determined by the prescriber.
TSBP Clarification 2021
Clarification from TSBP that mandatory PMP look-up only applies to outpatient prescriptions.
Class A Pharmacies
Pharmacies that are subject to specific DEA and TSBP rules regarding the issuing and dispensing of controlled substance prescriptions.