ANSC 512 Urinary System - Kidney and Glomerular Filtration
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
2 kidneys, 2 ureters, urainry bladder, urethra
What does the urinary system consist of?
metabolic waste (useless substance produced by body), nitrogenous waste (toxic, 50% urea, uric acid, creatinine)
What is a waste product?
blood urea nitrogen - measures how well kindeys are functioning (too high = lower function)
What is BUN?
A WET BED
What is the acronym for functions of the kidney?
A - acid-base balance
W - water balance
E - electrolyte balance
T - toxin removal
B - blood pressure control
E - makes erythropoetin
D - vitamin D metabolism
What does A WET BED stand for?
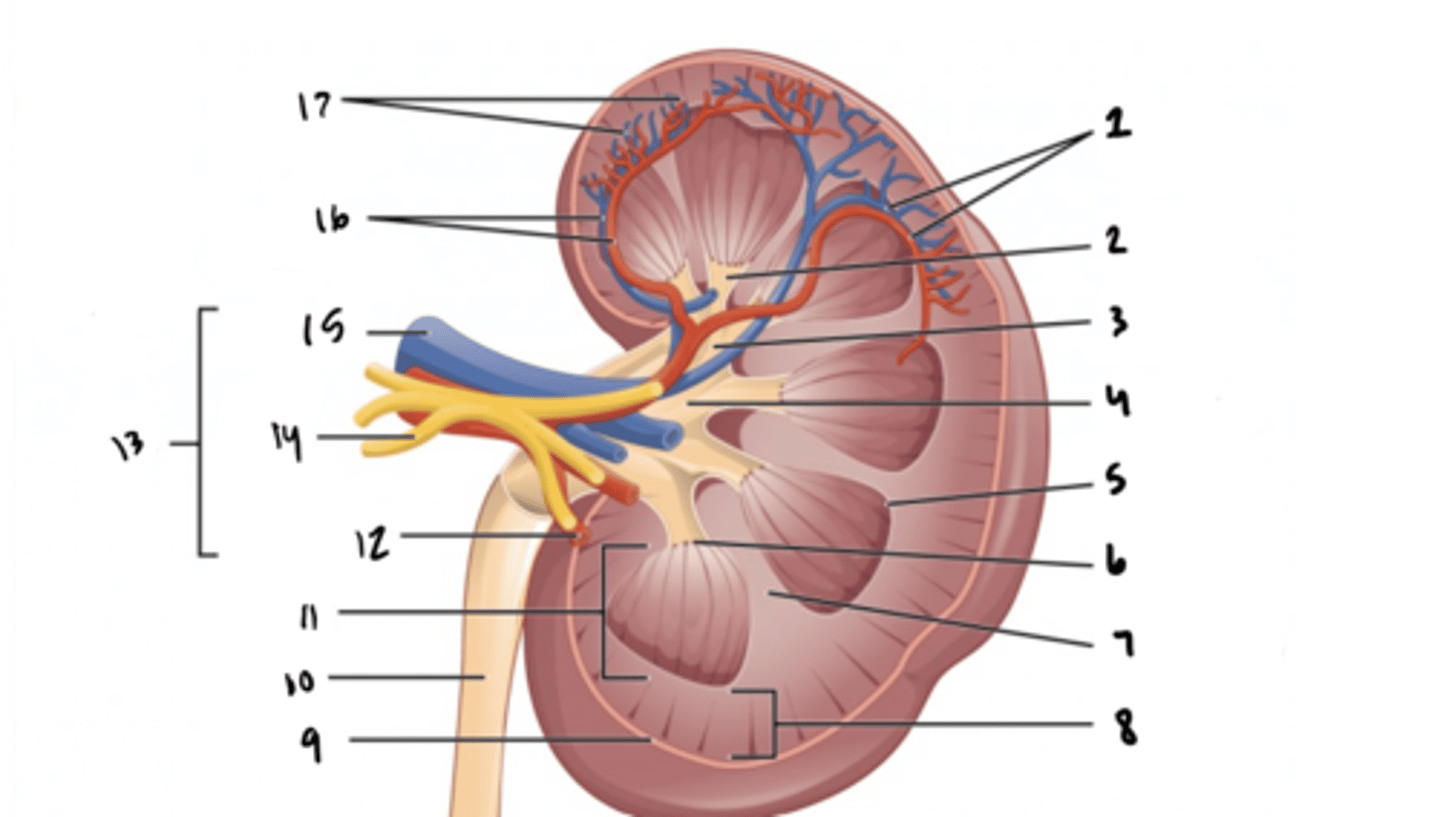
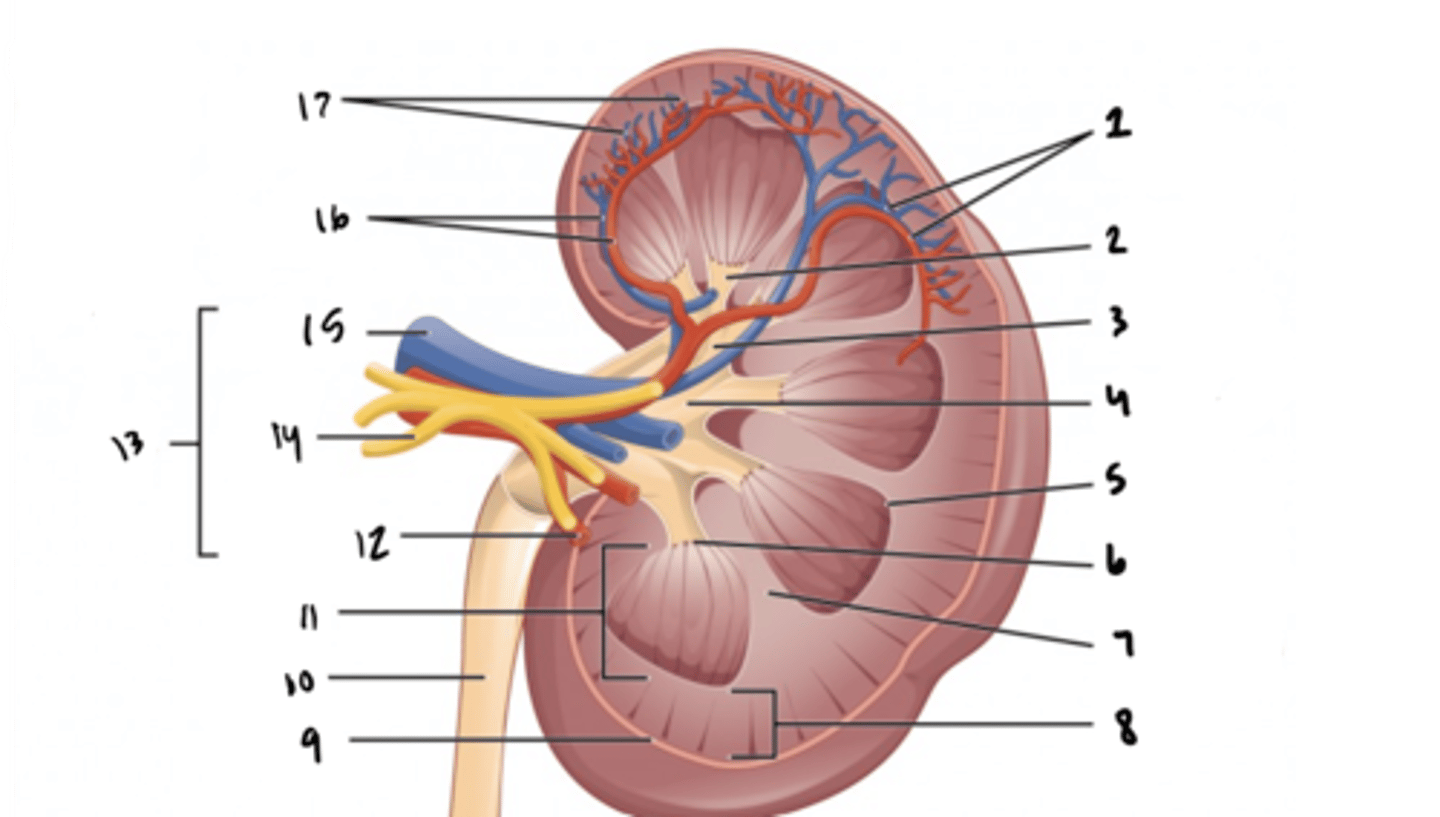
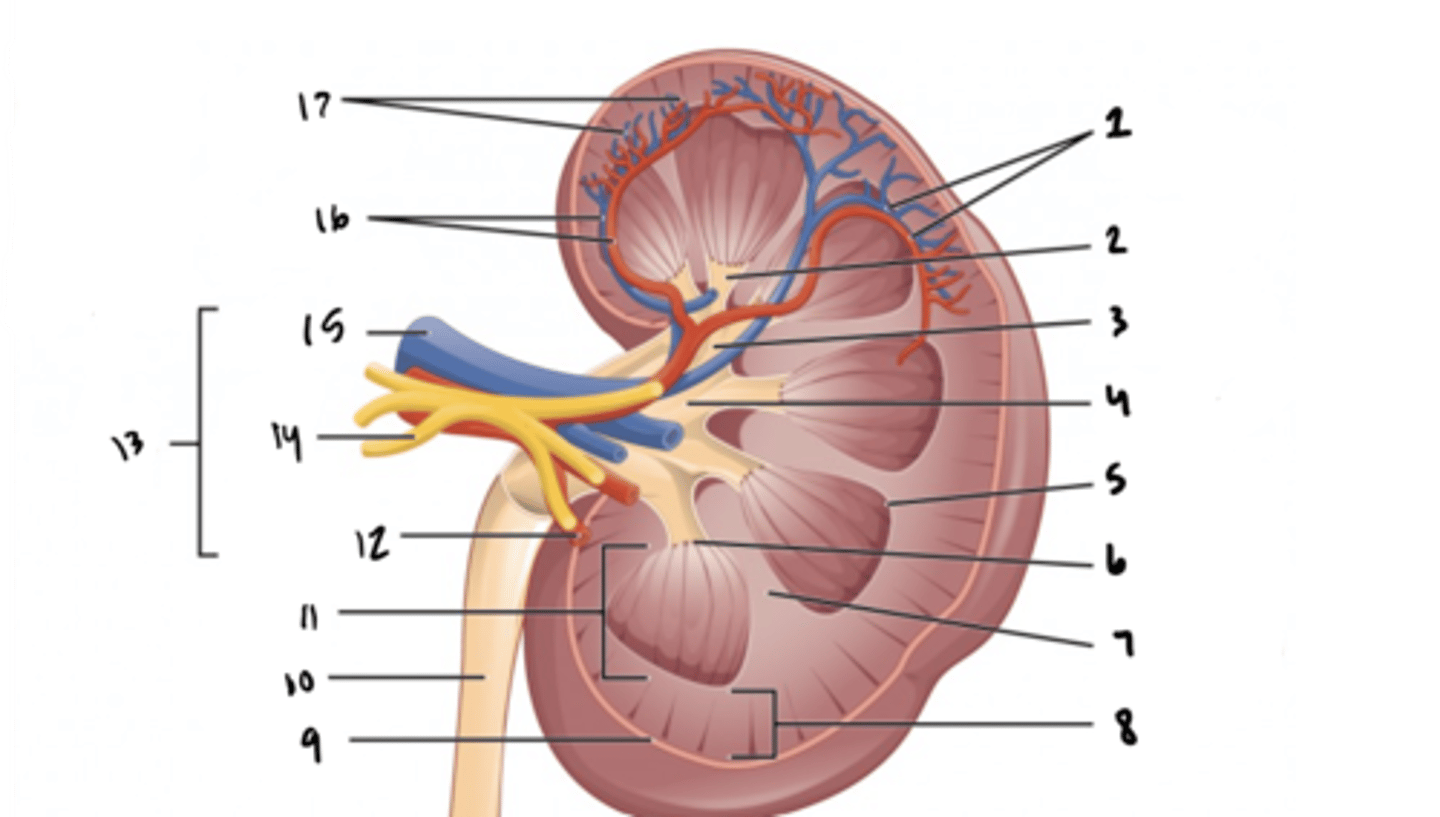
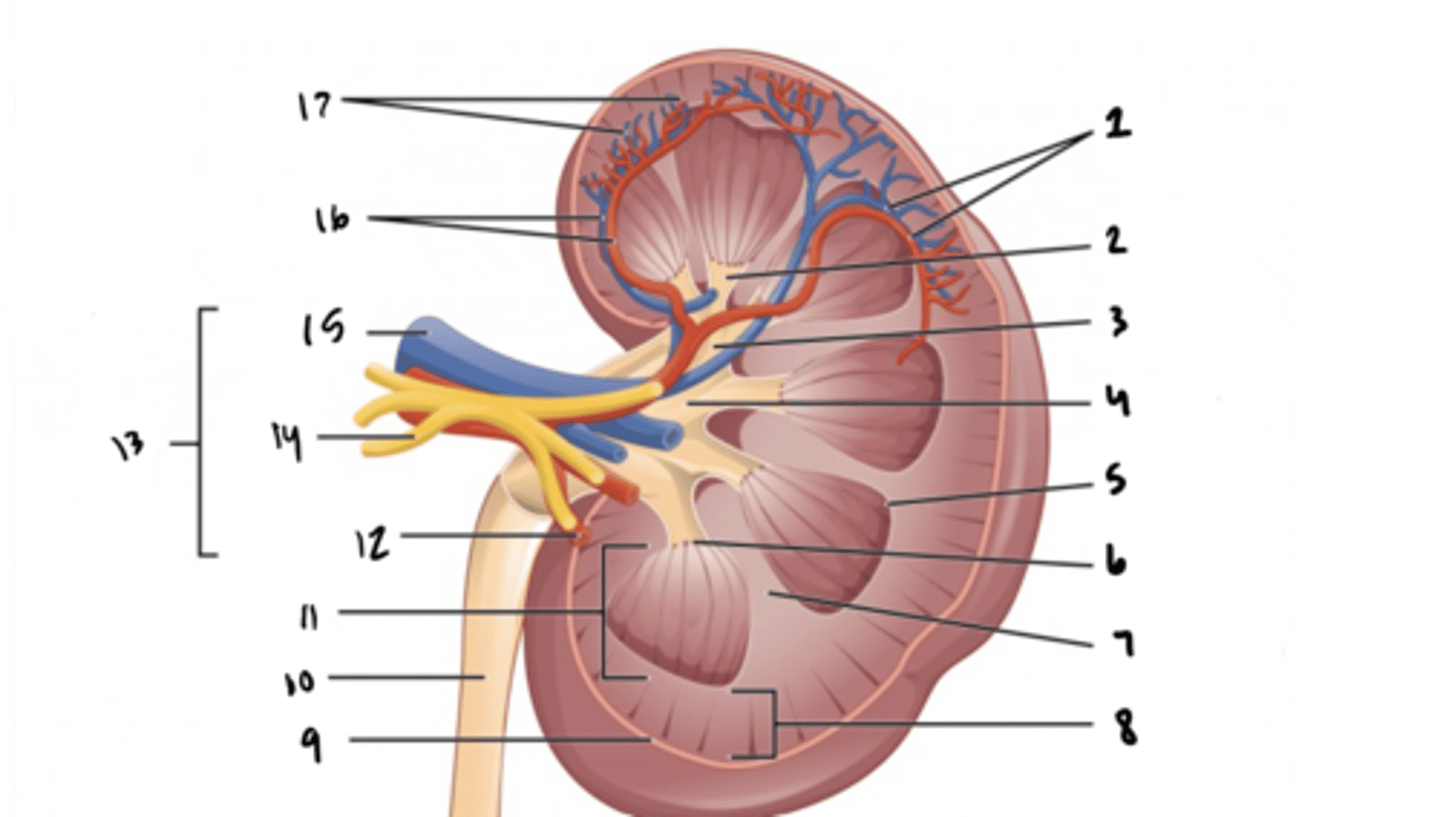
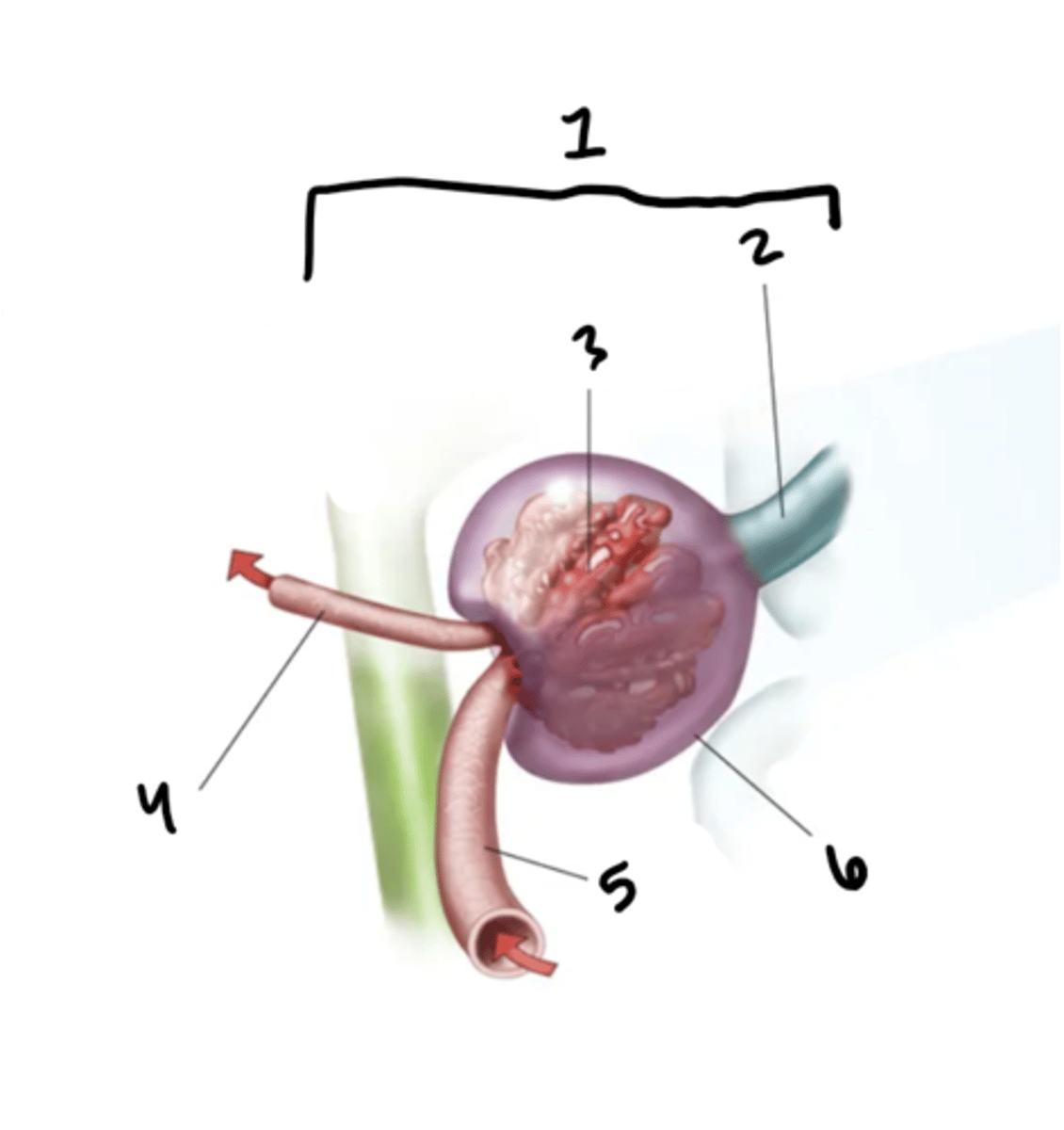
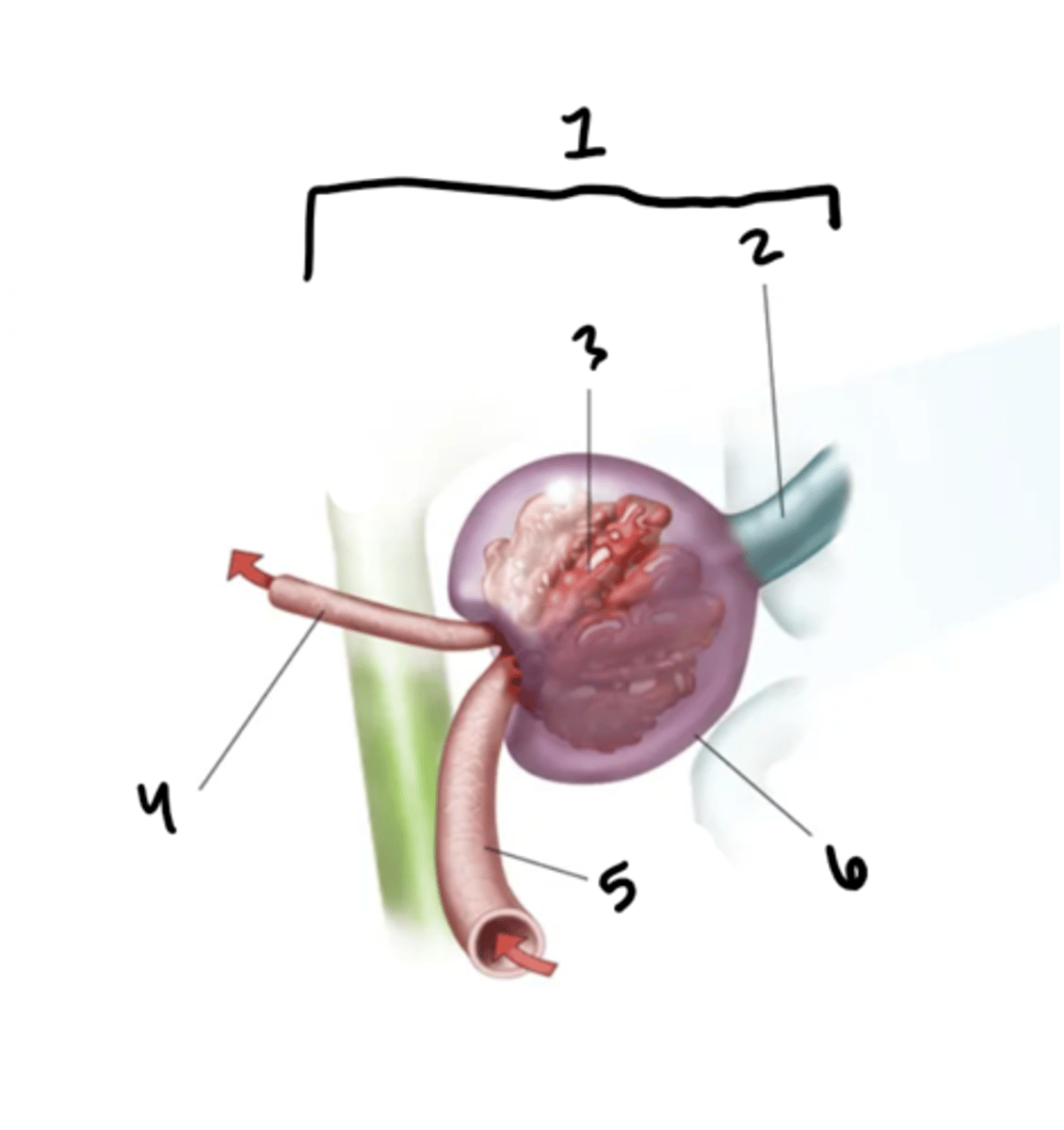
arcuate vessels
What is structure 1?
minor calyx
What is structure 2?
major calyx
What is structure 3?
renal pelvis
What is structure 4?
renal pyramid
What is structure 5?
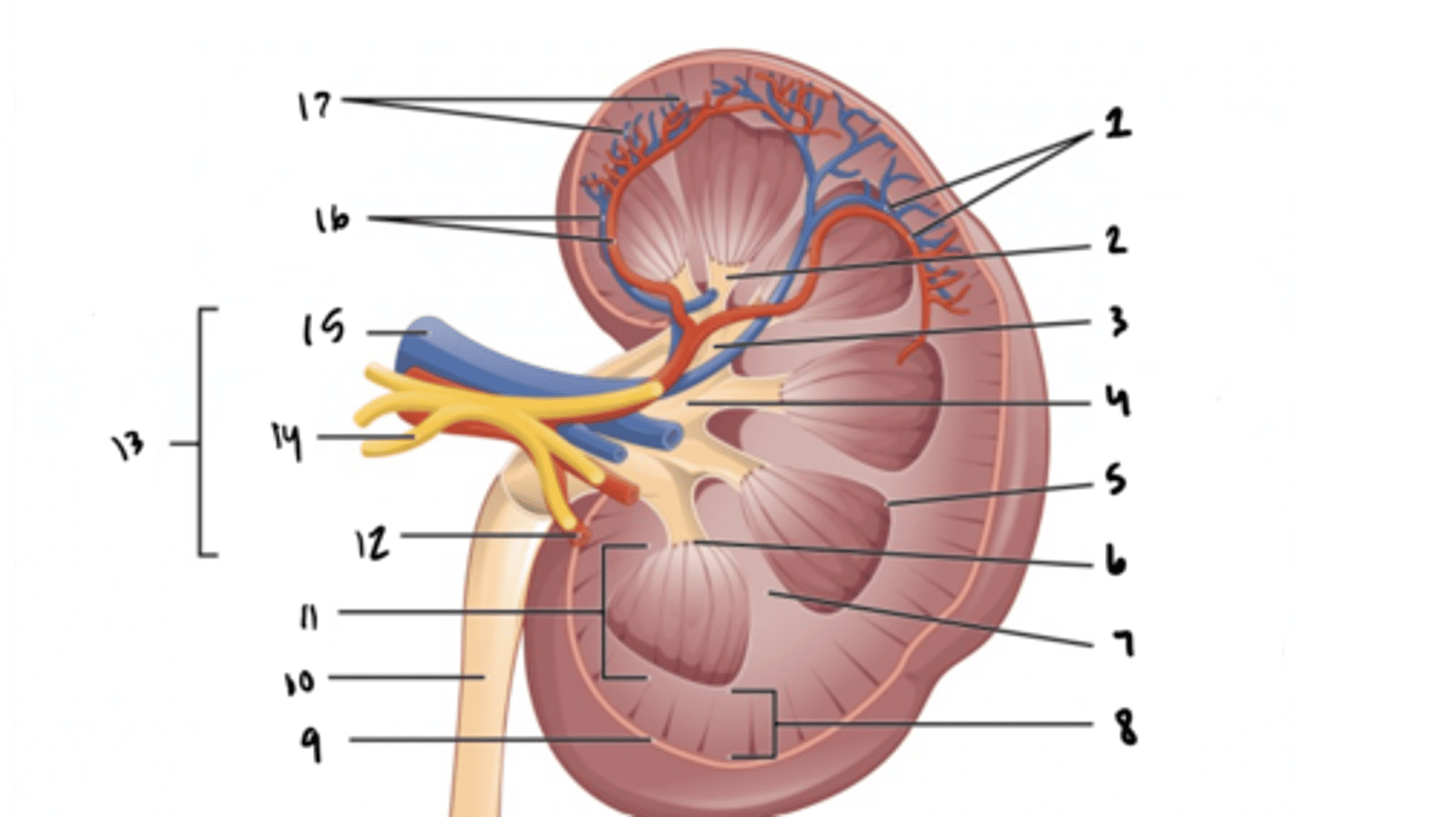
renal papilla
What is structure 6?
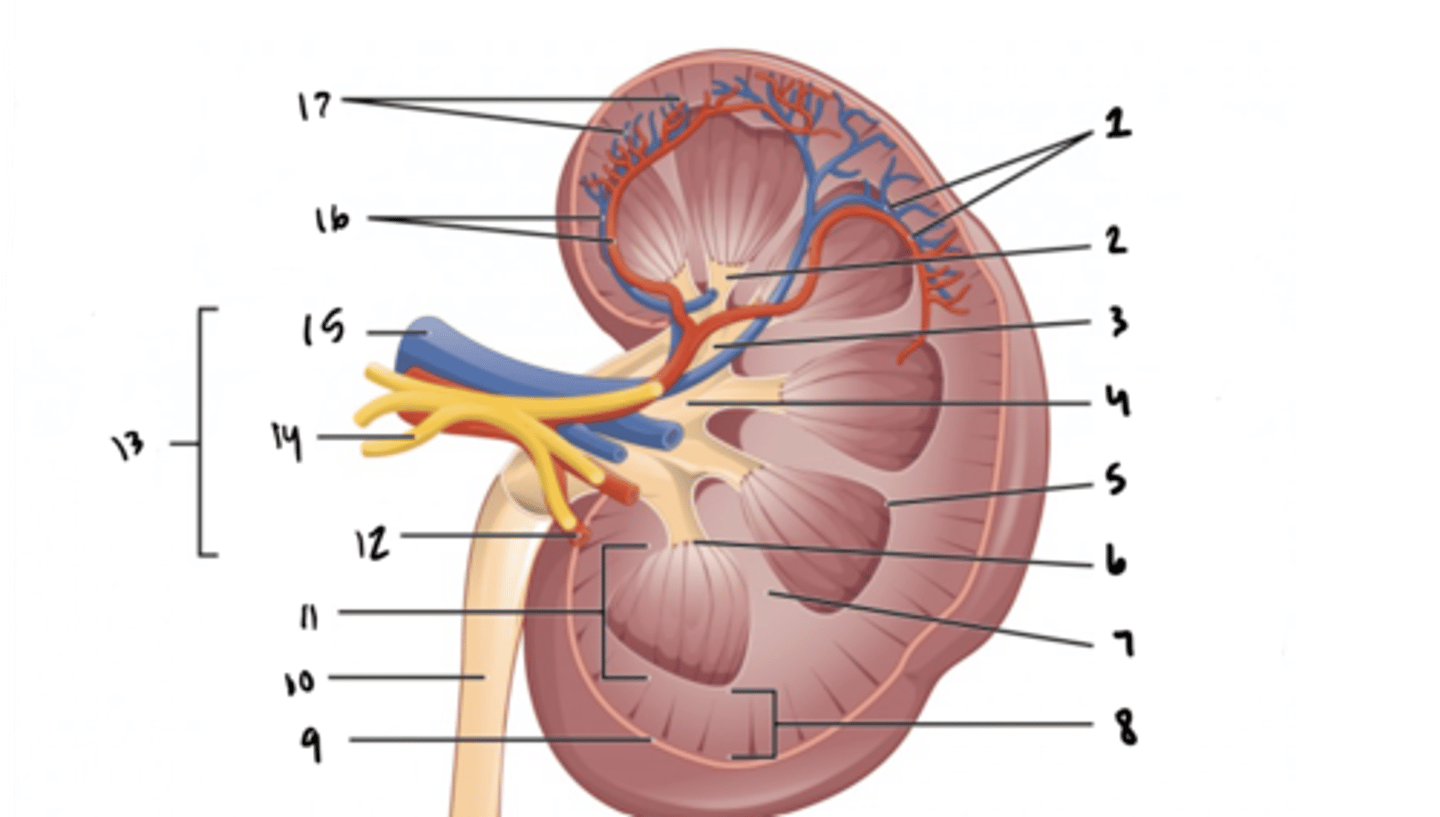
renal column
What is structure 7?
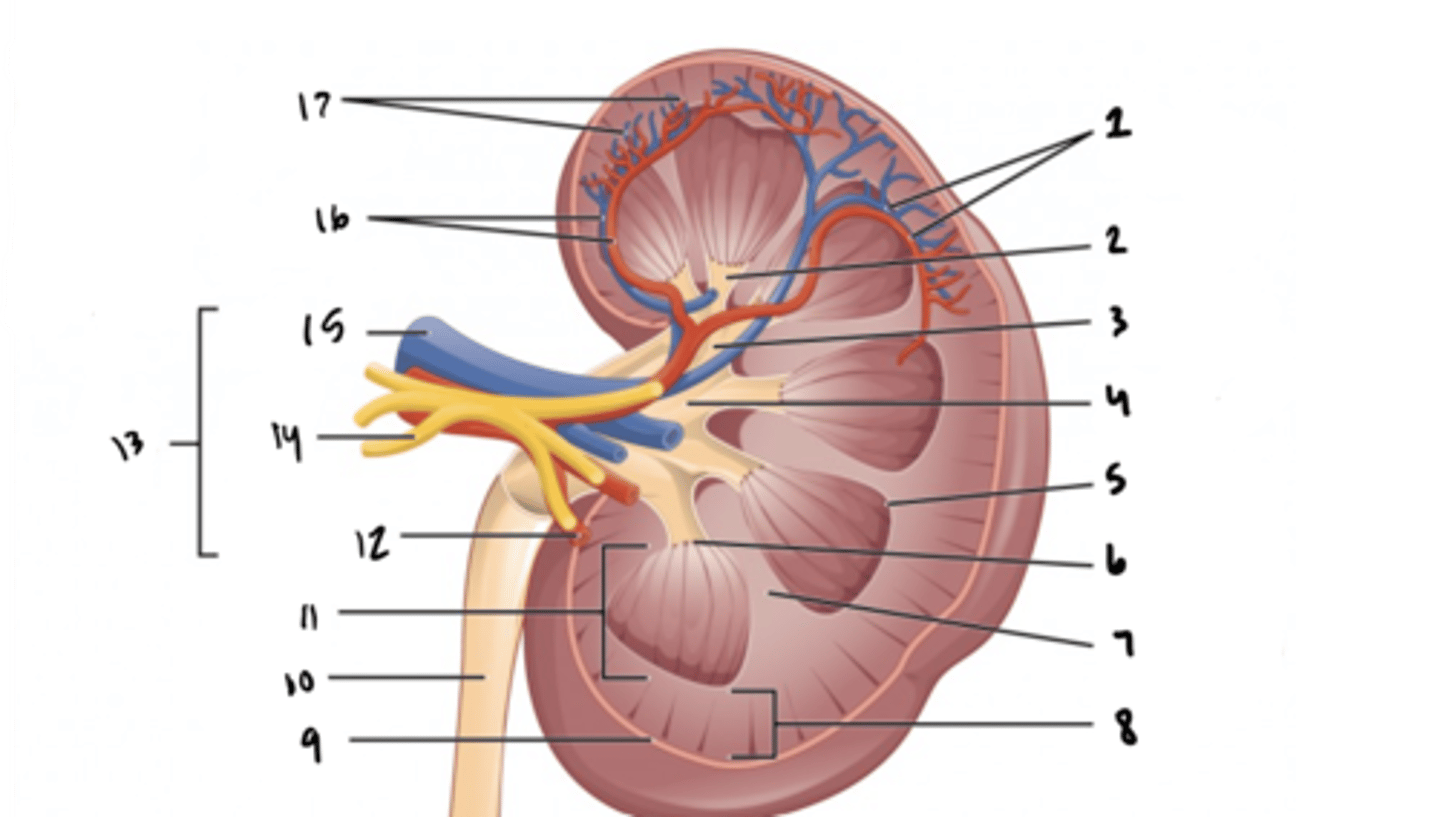
renal cortex
What is structure 8?
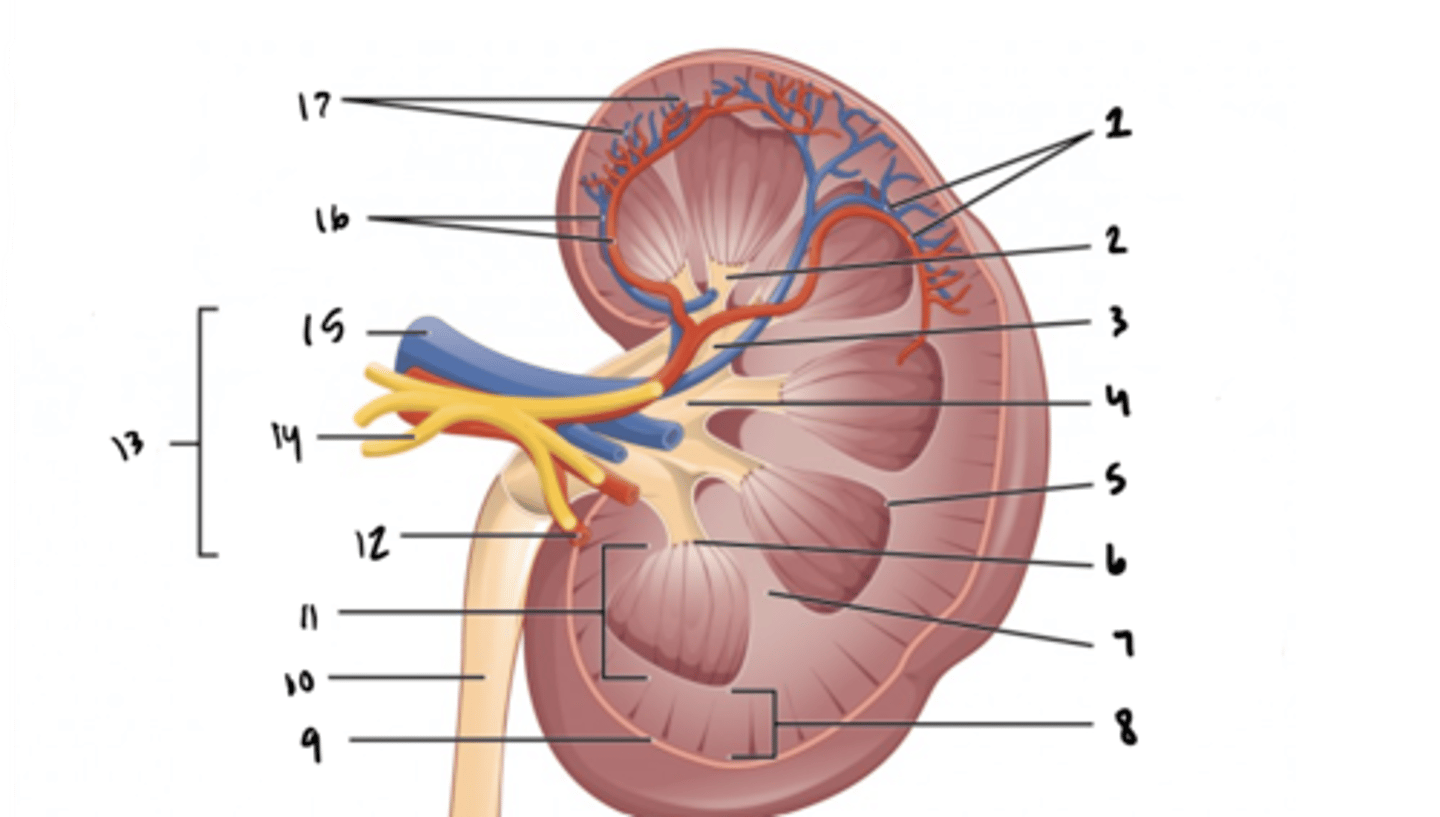
renal capsule
What is structure 9?
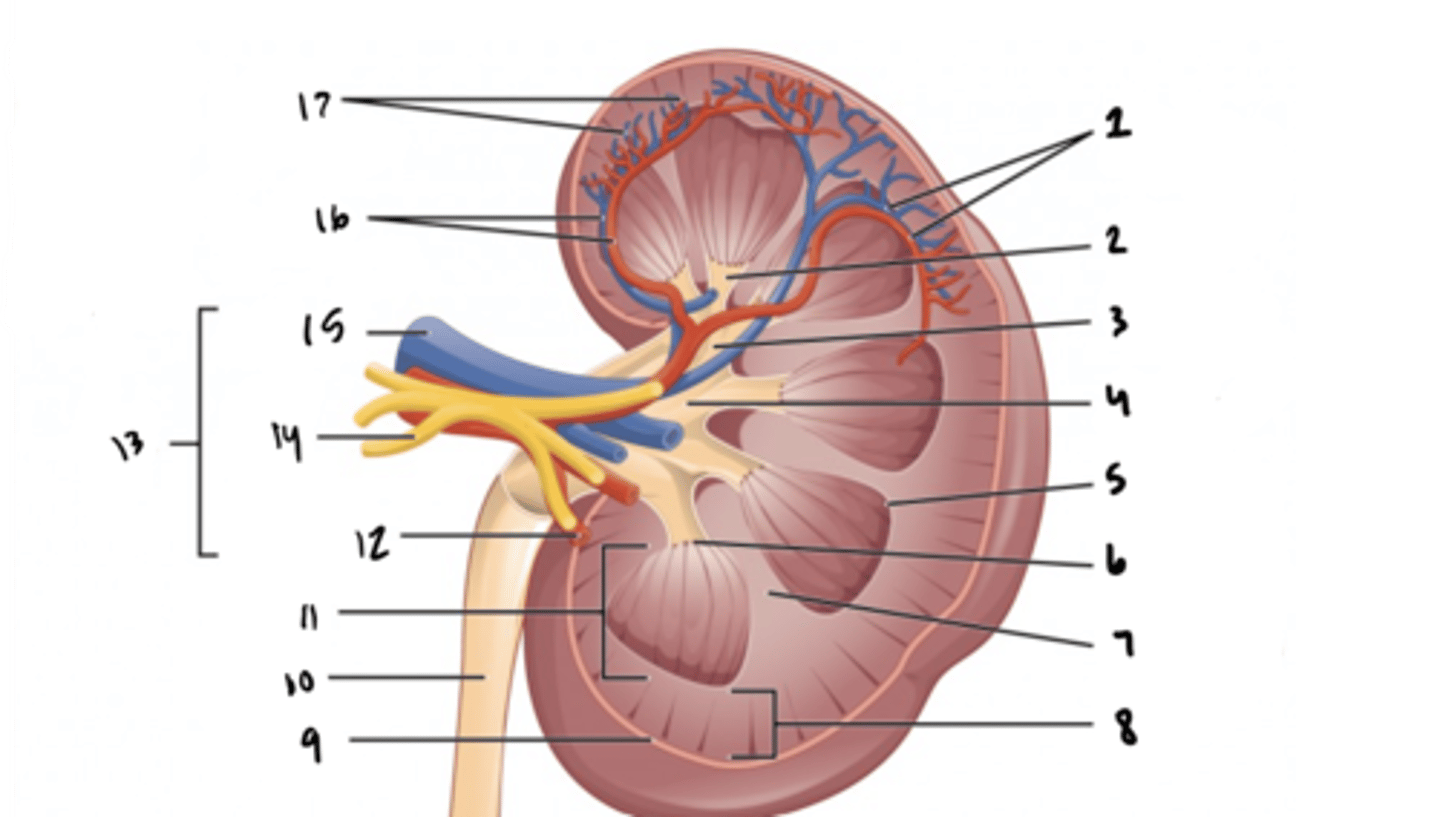
ureter
What is structure 10?
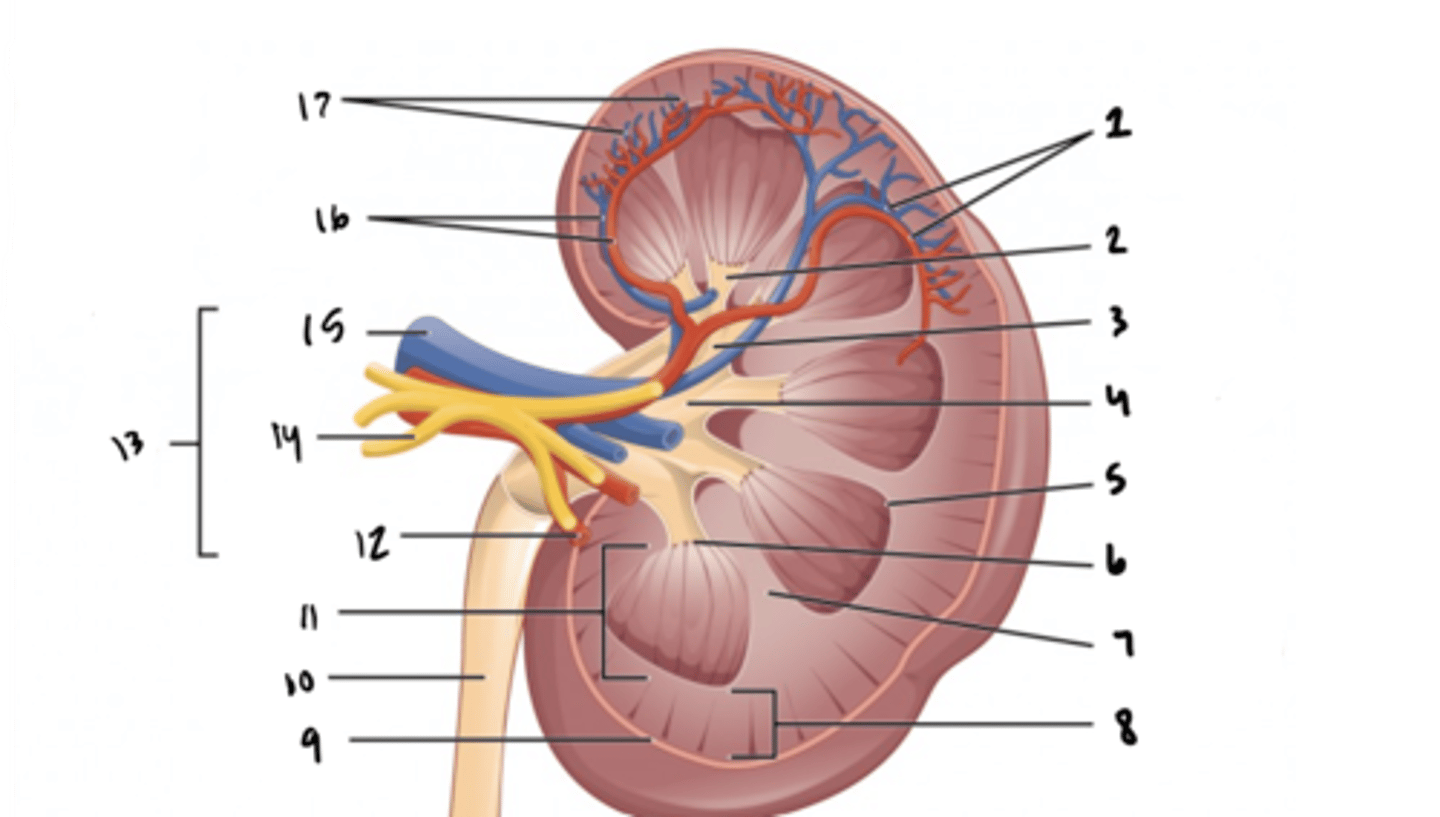
renal medulla
What is structure 11?
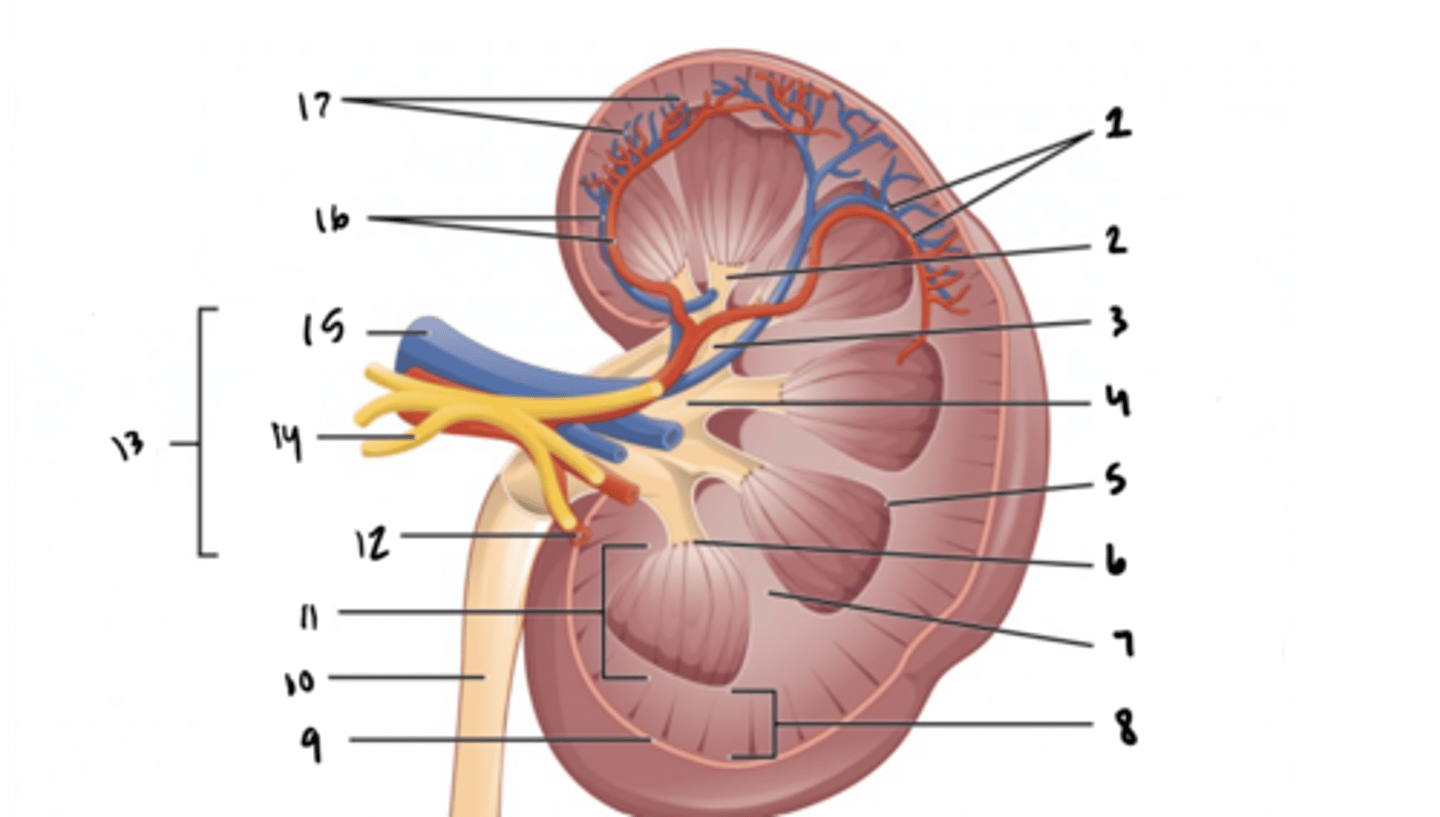
renal artery
What is structure 12?
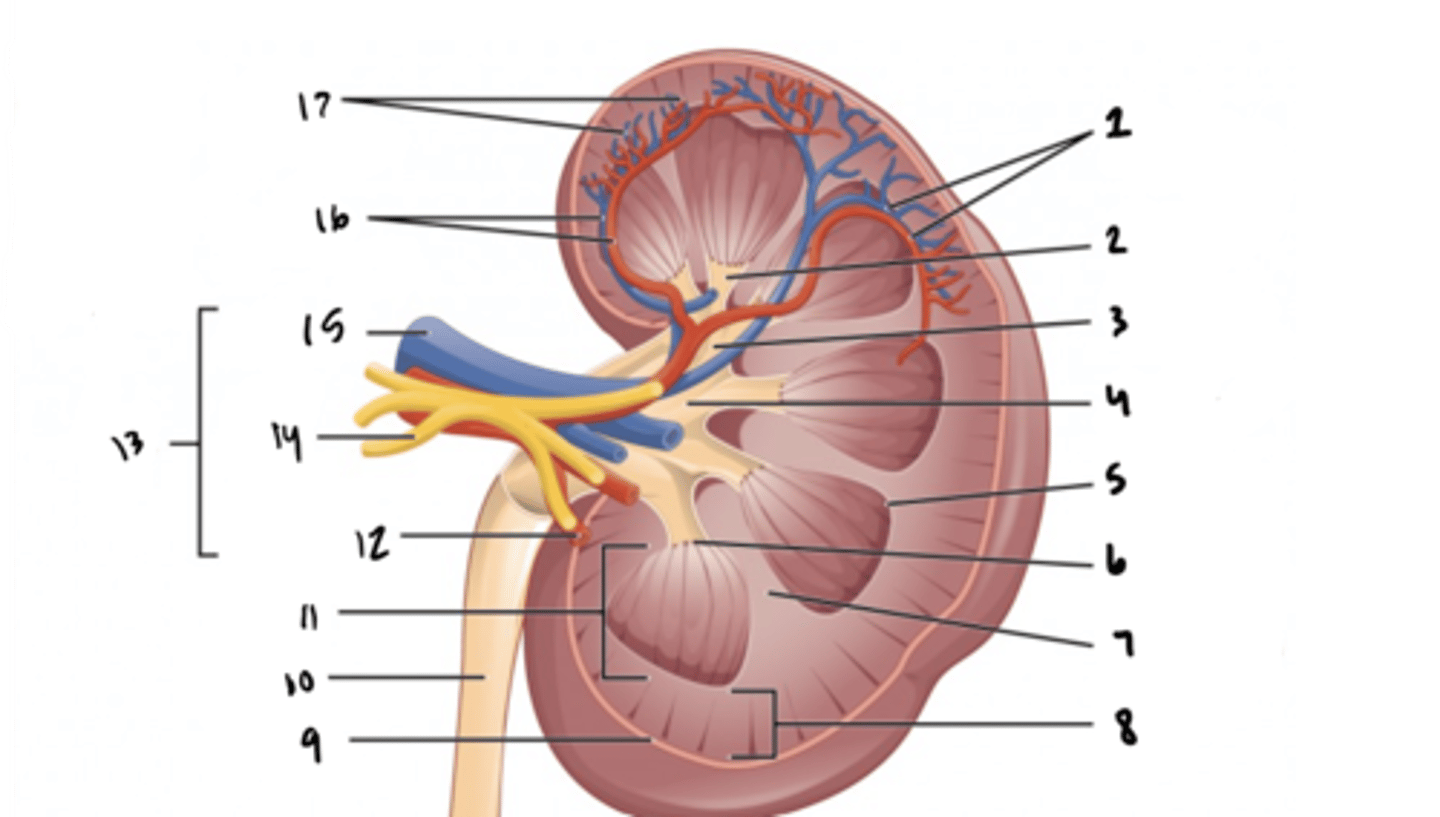
renal hilum
What is structure 13?
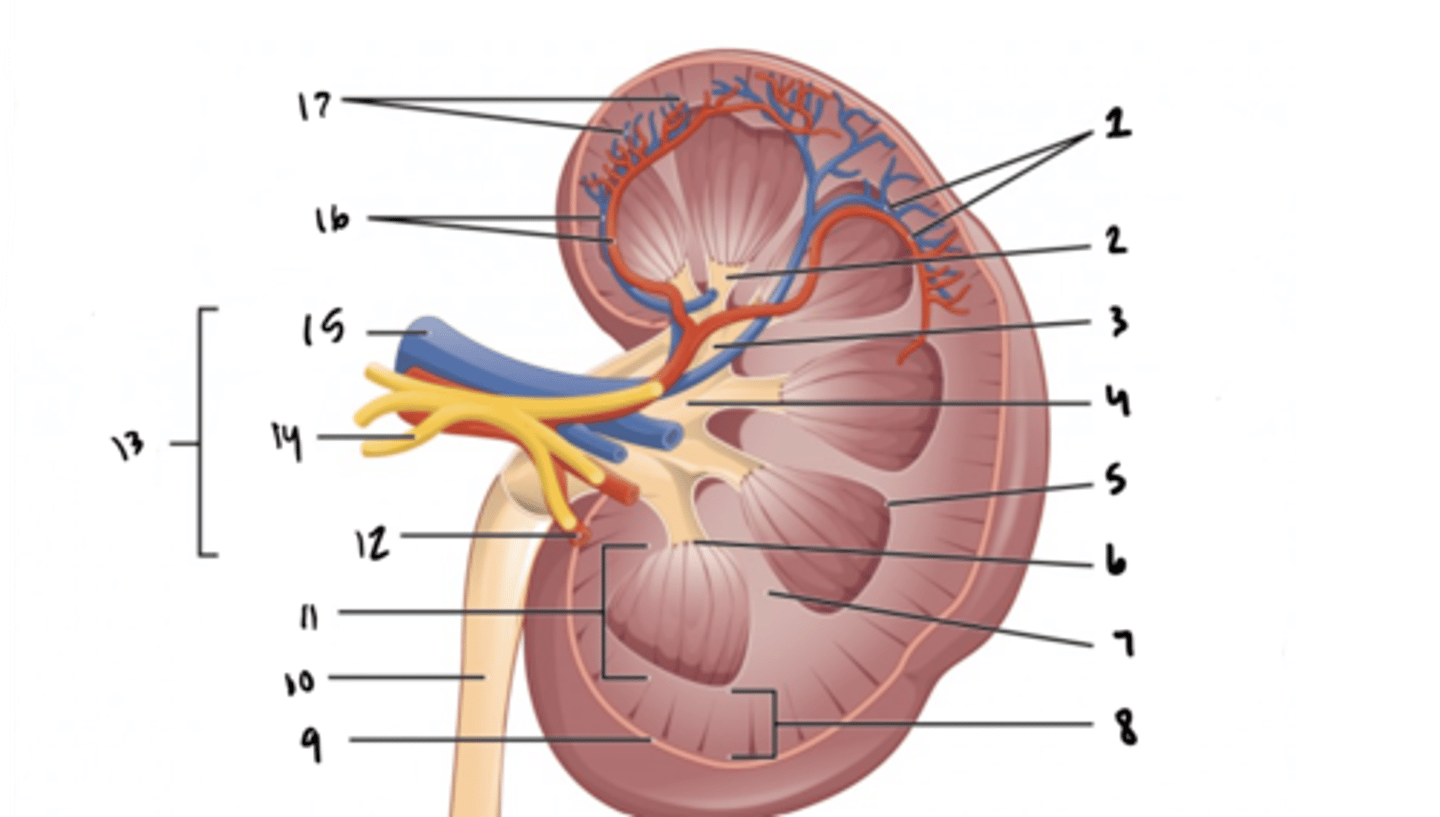
renal nerve
What is structure 14?
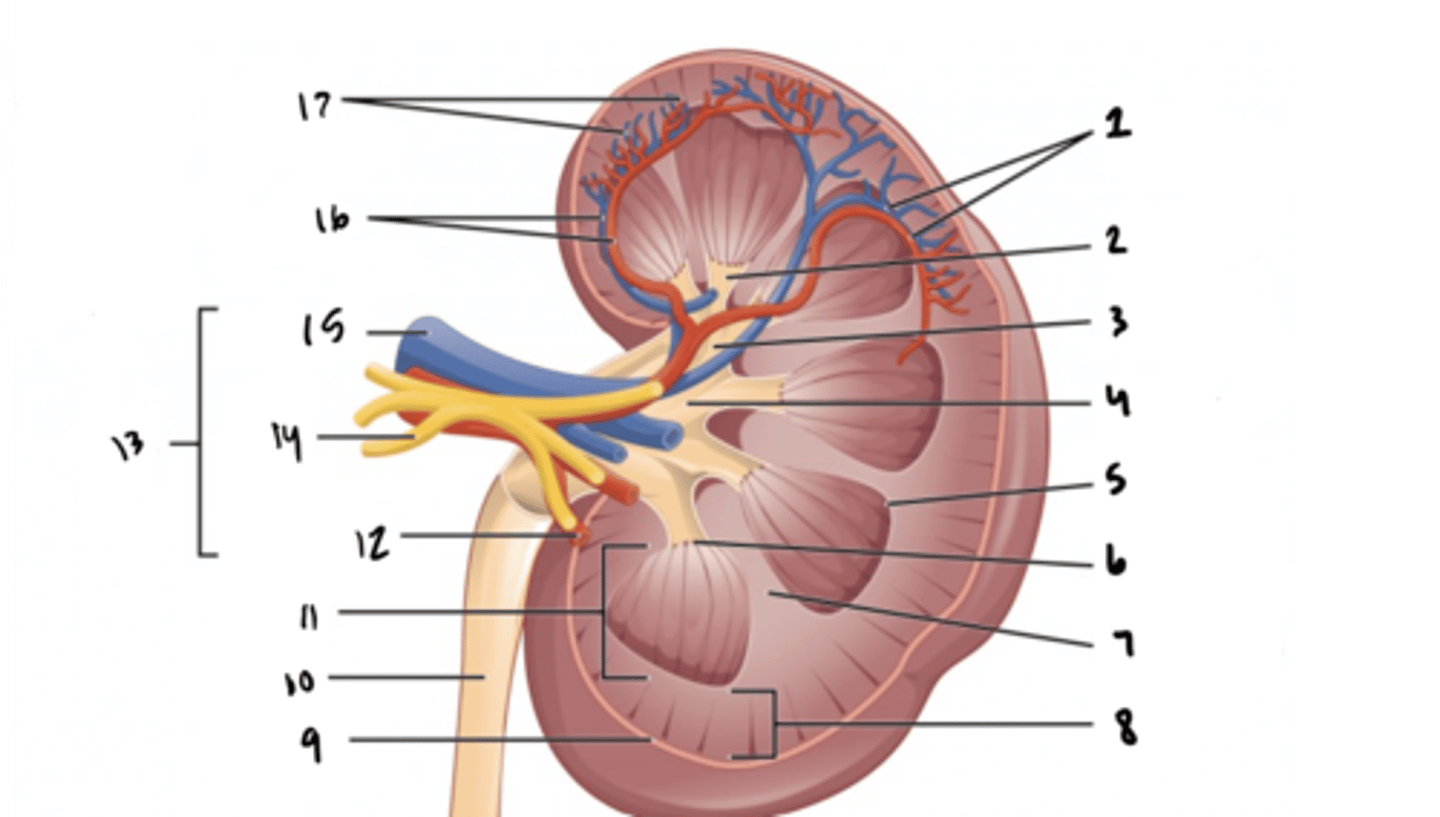
renal vein
What is structure 15?
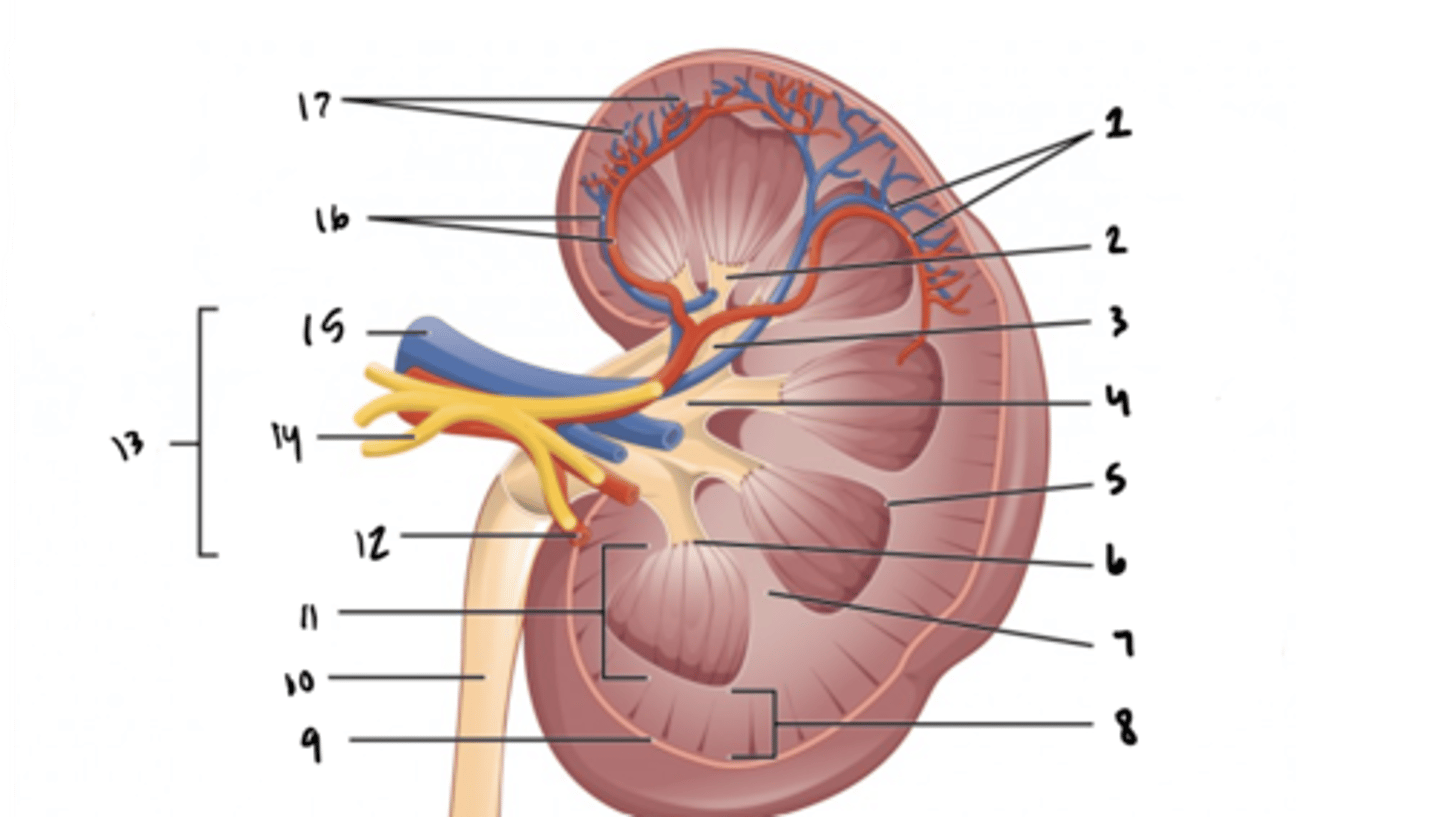
interlobar vessels
What is structure 16?
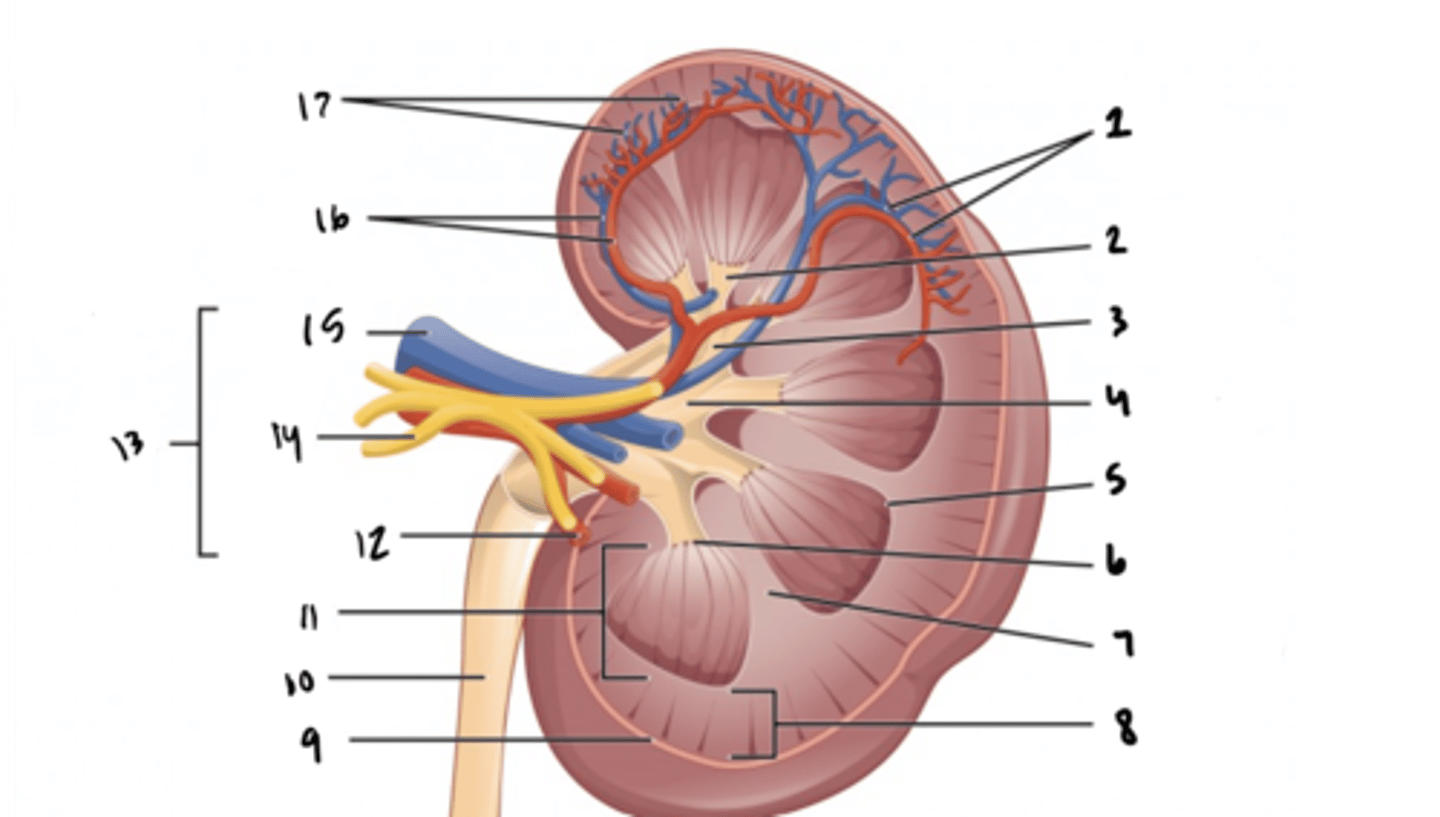
cortical vessels
What is structure 17?

nephron
What is the fuctional unit of the kidney?
renal cortex and medulla
Where are nephrons found?
system of tubes associated with system of blood vessels
What are nephrons?
renal corpuscle
What is structure 1?
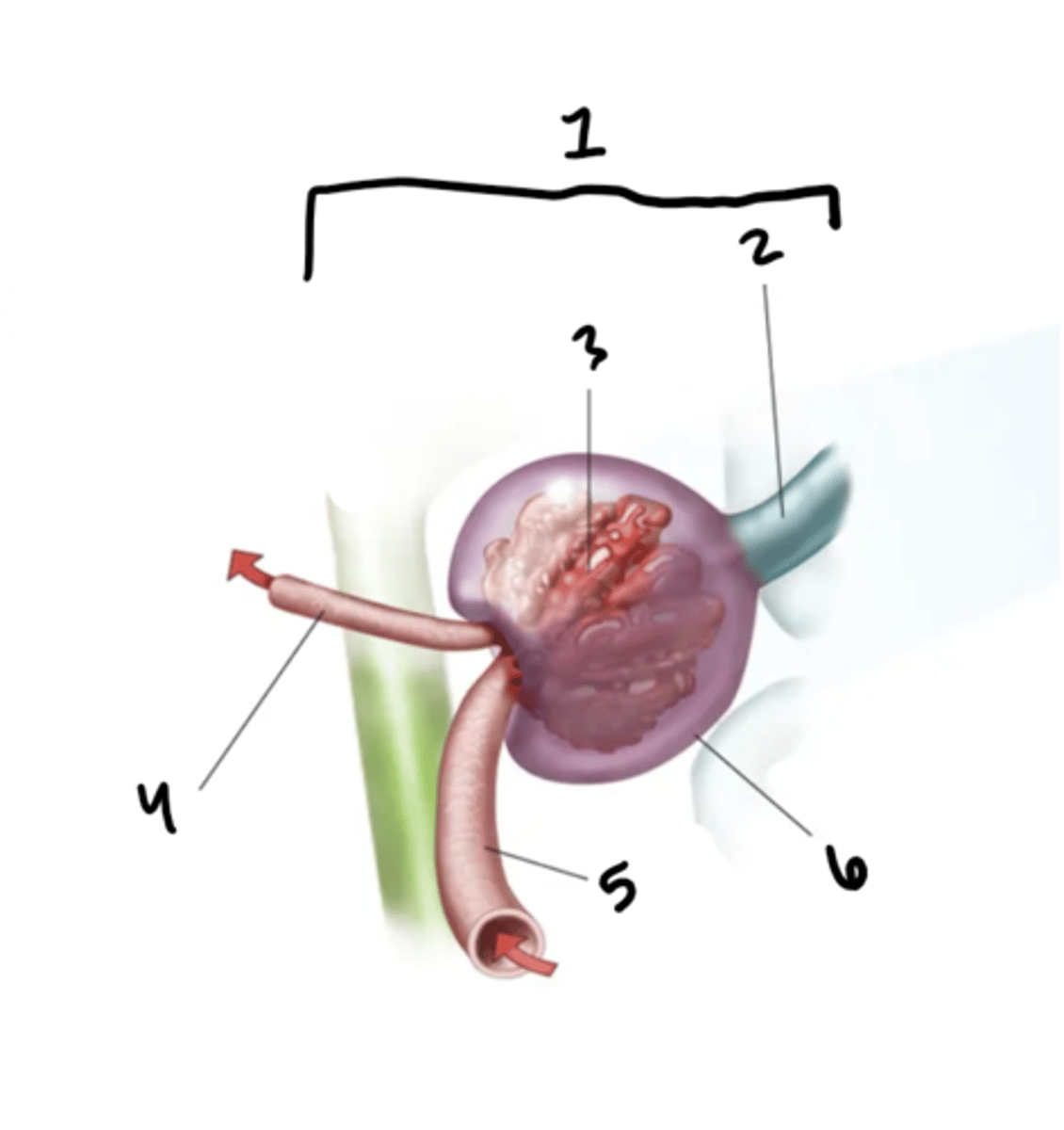
proximal convoluted tube
What is structure 2?
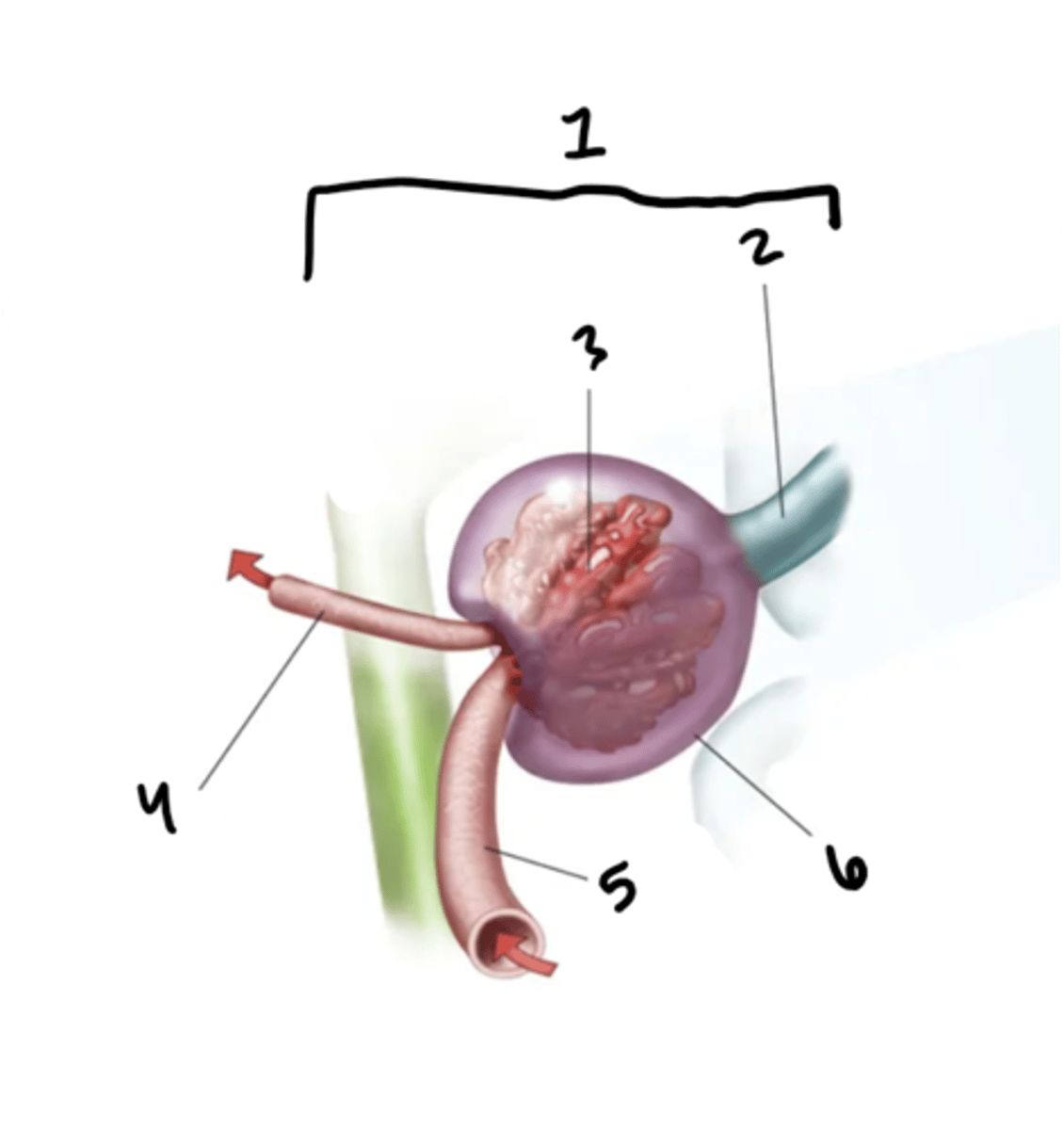
glomerulus
What is structure 3?
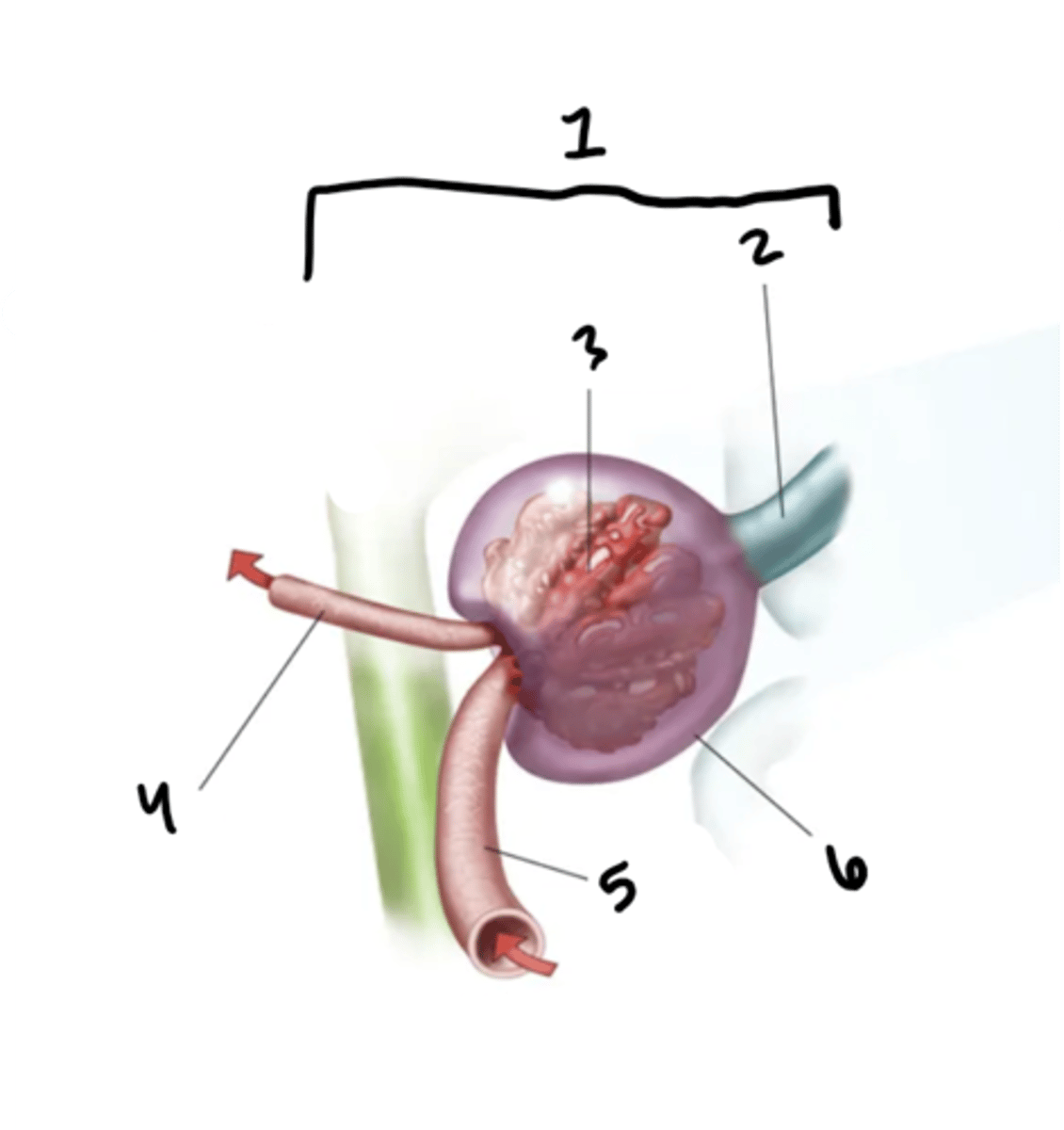
efferent arteriole
What is structure 4?
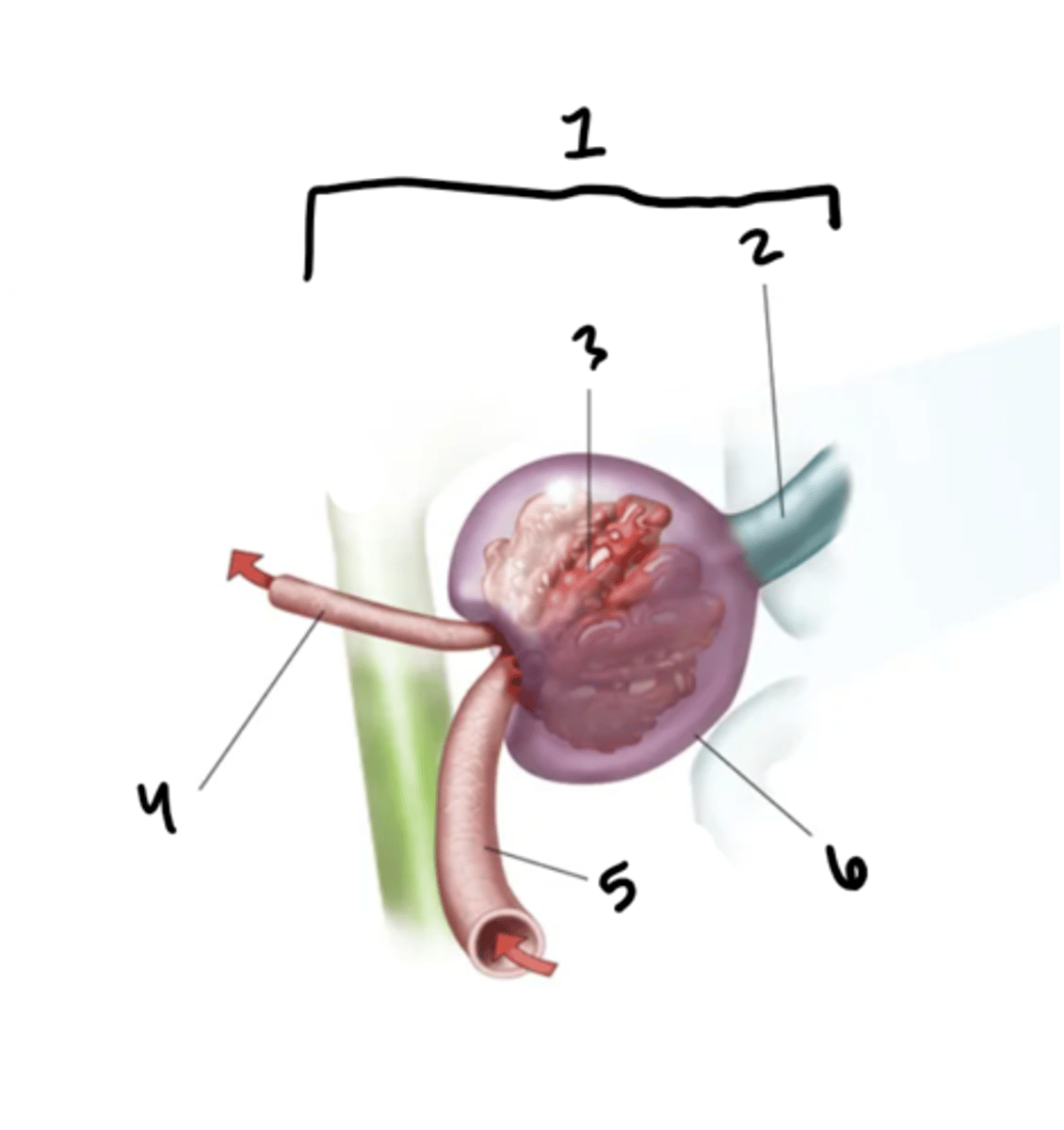
afferent arteriole
What is structure 5?
Bowman's capsule
What is structure 6?
glomerulus, proximal convluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct
What is the flow of fluid through the nephron?
hydrostatic pressure (fluid on walls of tube) and colloid oncotic pressure (proteins in blood)
What are the two pressures at play with glomerular filtration?
if there is more fluid, there is going to be a higher pressure gradient, pushing more material through the membrane (always greater inside than outside)
How does hydrostatic pressure impact glomerular filtration?
proteins cannot move across membrane so they exert great force on the venule side making the pressure greater in the blood than the tissues
How does colloid oncotic pressure impact glomerular filtration?
the use of ATP to move material against a concentration gradient via enzymes, carriers, pumps
What is active transport?
movement reliant on concentration gradients (always high to low)
What is passive transport?
fenestrated endothelium of arteriole, basement membrane with (-) glycocalyx gel, filtration slits between foot processes of podocytes, and then urinary space
What layers must fluid move through from blood to filtrate in the glomerulus?
can: water, electrolytes, small positive ions, nitrogenous waste
cannot: proteins, vitamins, negatively charged dissolved particles, blood cells
What can move into urinary space and what cannot?
rate at which the glomerulus filters blood
What is the glomerular filtration rate?
blood and capsular fluid pressure, hydrostatic pressure
What impacts glomerular filtration rate?
no - proteins cannot move across barrier into tubule
Is there colloid oncotic pressure in the glomerulus?
high hydrostatic pressure in afferent arteriole
What drives fluid into the tubule?
too much filtration occurs which can result in dehydration and electrolute depletion
What happens if the GFR is too high?
too much reabsorption happens and toxic material stays in body
What happens if the GFR is too low?
sympathetic control, renal autoregulation, hormonal control (epinephrine)
How is the GFR controlled?