Exam 2 - Physiology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Biological Functions of Larynx
builds up pressure in respiratory tract during effortful activity, cough reflex to remove food, prevents aspiration during swallowing
Larynx change as infant
Downward migration of larynx
Larynx change as elder
Females drop in fundamental frequency, males rise in fundamental frequency
Bernoulli Effect
Air moving through a point of constriction will increase in velocity and decrease in pressure
Stages of phonatory cycle (Myoelastic Aerodynamic Theory)
subglottal pressure opens vocal folds from the bottom
vocal folds serve as point of constriction, create negative pressure
Bernoulli effect occurs, vocal folds close
elastic structure allows folds to move in specific vibratory patterns
Cover Body Model
Cover mass of vocal folds (epithelium and superficial lamina propria) move like waves from bottom to top (move differently than body mass), convergent airflow then divergent airflow
Modal/Chest vocal register
typical register, used during sustained phonation, most efficient for each individual
Pulse Register
low end of register, vocal fry at the very far end, low tracheal pressure
Falsetto/Loft Register
high end of register, high levels of longitudinal tension and tracheal pressure
Simultaneous/Usual Vocal Attack
respiration and adduction occur at the same time, any voiced phoneme, medium laryngeal opposing pressure
Breathy/Soft Vocal Attack
respiration occurs BEFORE adduction, breathy sound quality (/h/), low laryngeal opposing pressure
Hard/Glottal Vocal Attack
respiration occurs AFTER adduction, emphasis/increased loudness, strong medial compression, high laryngeal opposing pressure
Vocal Pitch
Psychological correlate to frequency, determined by mass and elasticity of vocal folds + longitudinal tension
Fundamental Frequency
Average rate of vibration for individuals (males 125, females 225, children 264-294)
Vocal Loudness
changed by adjustments of medial compression
Vocal Quality
changed by vocal registers and vocal attacks
Vocal Nodules
benign functional voice pathology, affects kids and adult women, caused by voice hyperfunction, lesions covered by fibrous tissue on vocal folds, voice production becomes harder because vocal folds don’t close
Hertz
phonatory cycles per second, measured with instruments
Abductor Muscles
open vocal folds (posterior cricoarytenoids)
Adductor Muscles
close vocal folds (everything intrinsic except for posterior cricoarytenoids, medial thyroarytenoids, and cricothyroids)
Paramedian Position
vocal folds during regular breathing
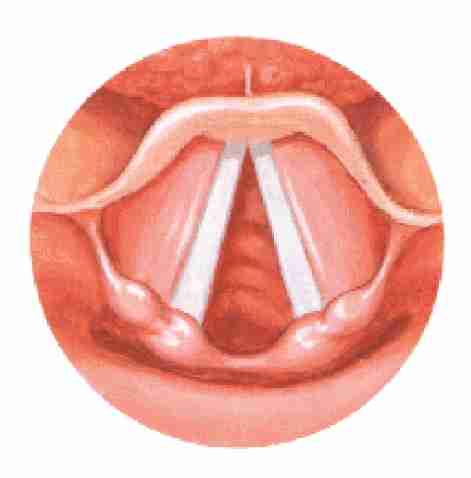
Adducted Position
vocal folds during speech
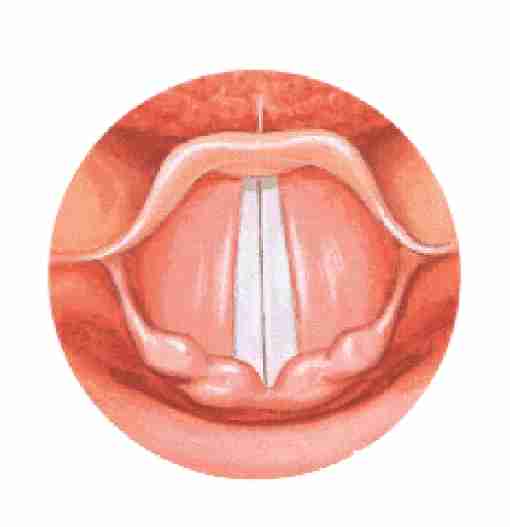
Medial Compression
Extent of force with which the vocal folds come together at midline
Longitudinal Tension
Degree of stretching on the vocal folds
Structural Differences and Vibratory Patterns
patterns of vocal vibration vary as a result of longitudinal tension (stretch) and medial compression (force of vocal folds)
Periodicity
equidistance between waves and equal height of waves (if aperiodic, voice has poor quality)