Study Guide on Canvas
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
CNS
composed of brain and spinal cord
PNS
composed of cranial nerves and spinal nerves
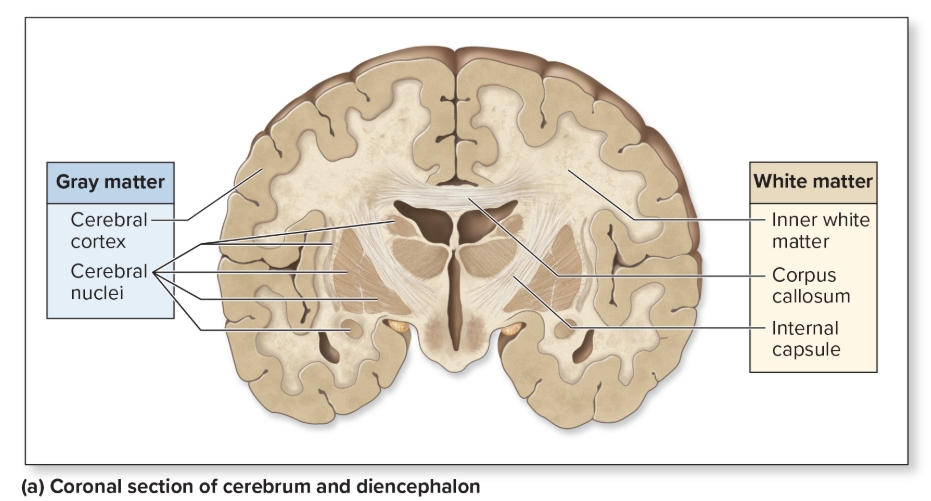
Gray Matter
composed of unmyelinated interneurons, dendrites and cell bodies
L: cortex (superficial layer), nucleus (cluster of neuron cell bodies)
F: integrating and processing area
White matter
myelinated axons
L: tracts, peduncles, funiculi
F: relay nerve signals
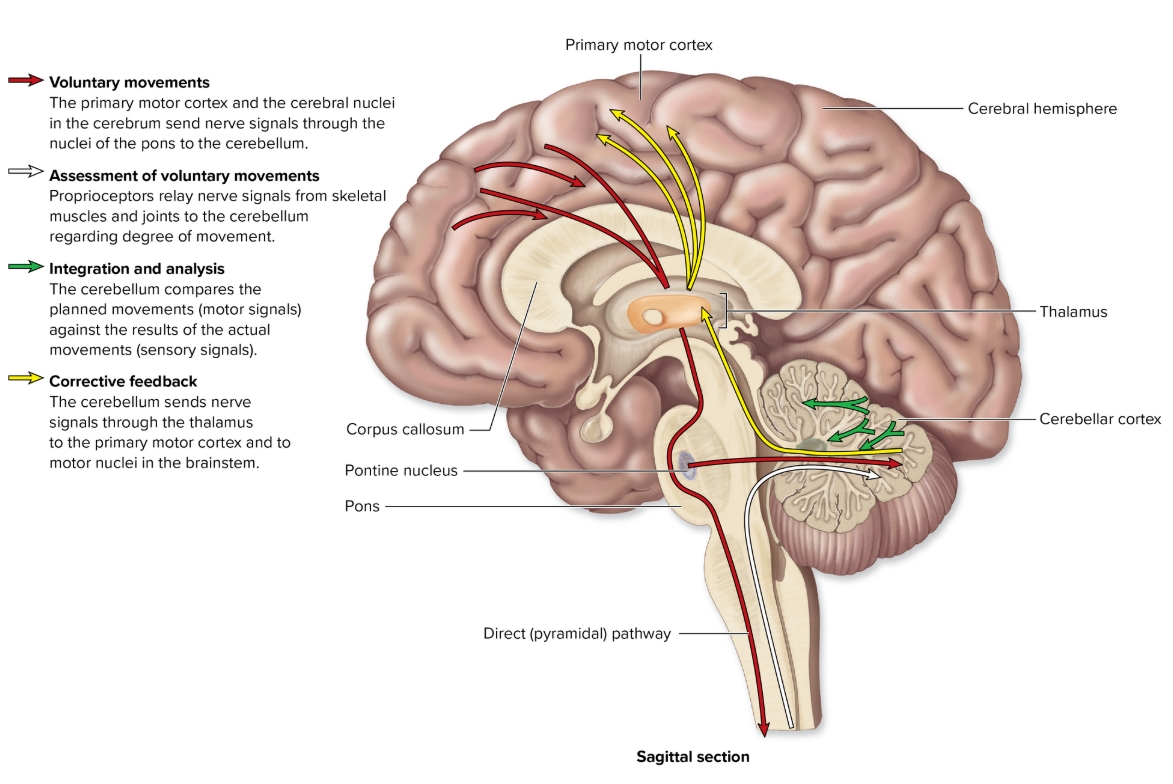
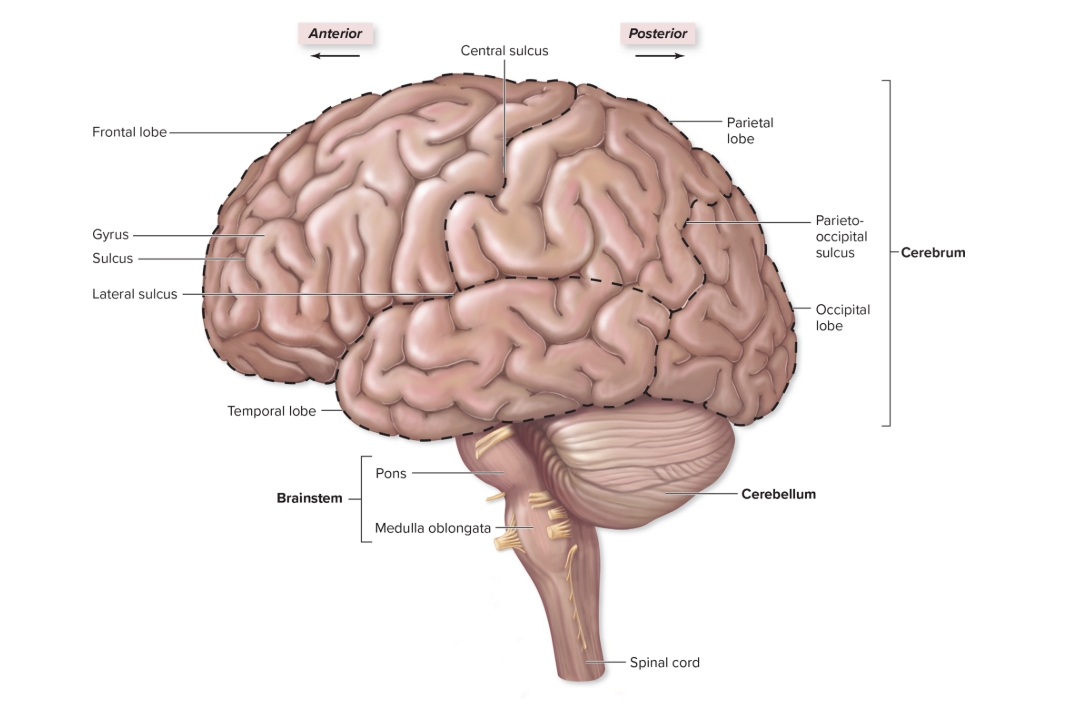
Cerebellum
L: inferior to cerebrum
F: coordinates/fine tunes skeletal muscles movements, ensures skm follow correct pattern = smooth, muscle memory
Brainstem
three regions: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata,
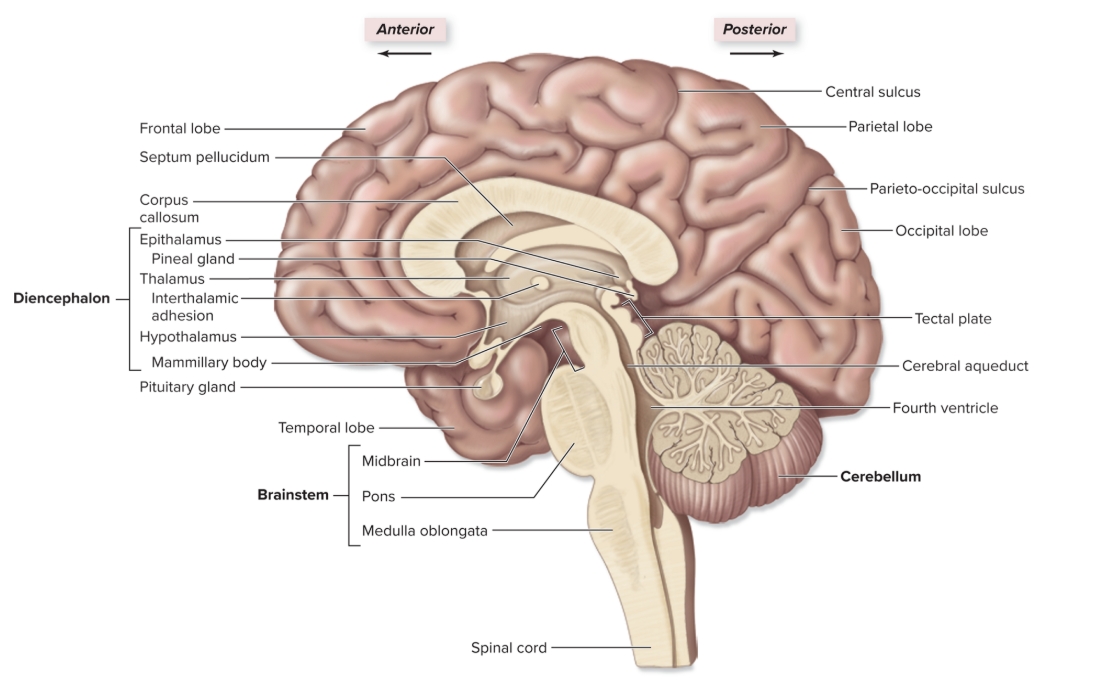
Diencephalon
epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
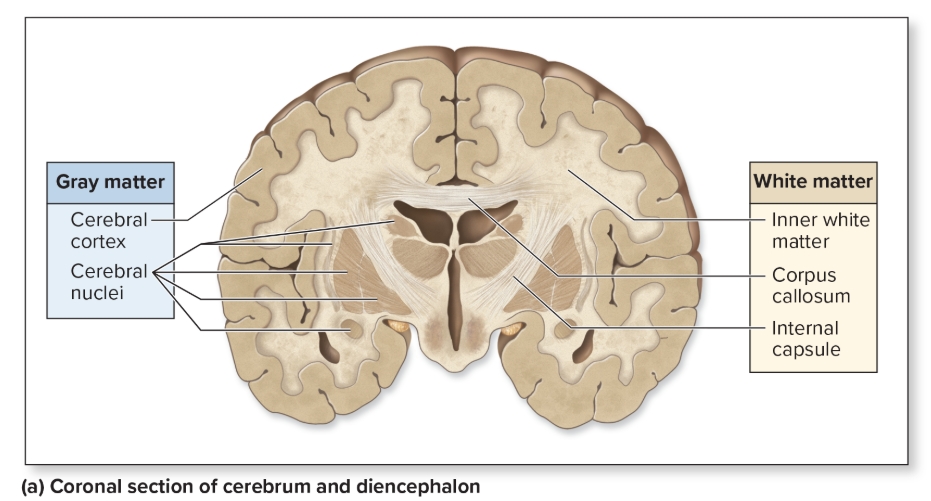
Cerebral Cortex
outer layer of brain, composed of gray matter
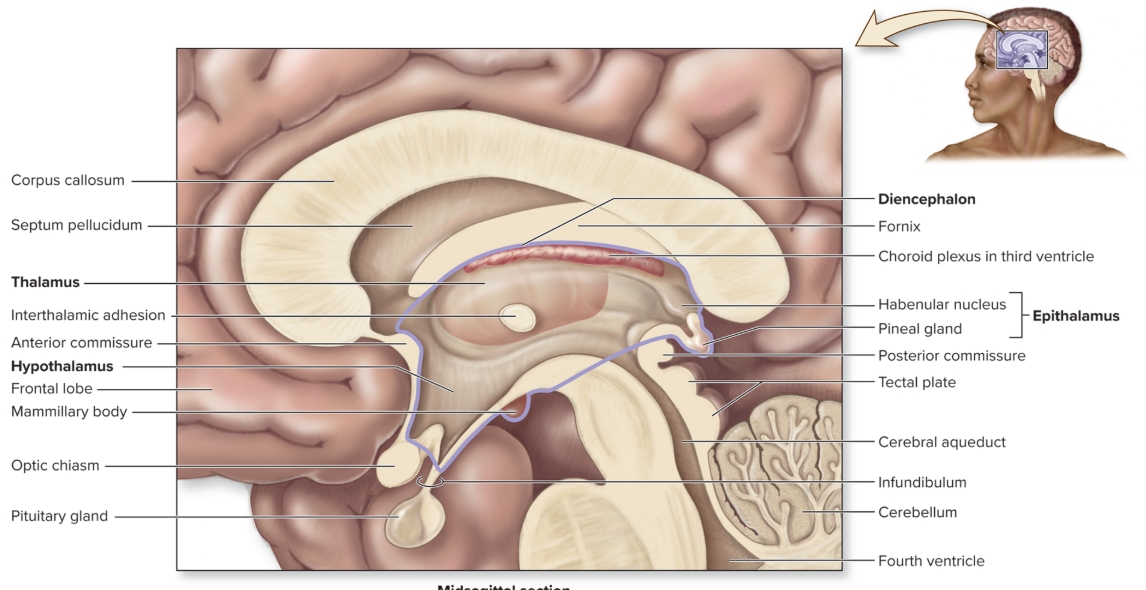
Thalamus
(part of dicephalon)
L: form walls superolateral of third ventricle between anterior commissure and pineal gland
F: relay center of sensory input to appropriate regions of cerebrum
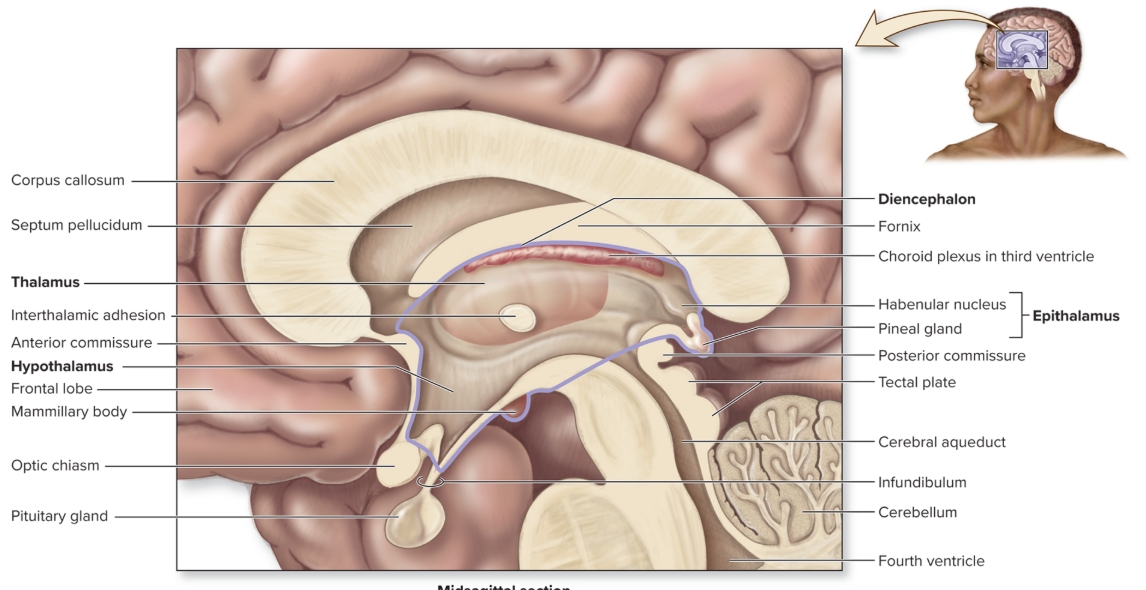
Hypothalamus
(part of diencephalon)
L: anteroinferior region of diencephalon
F: ANS, regulates endocrine system, temp regulation, water balance, hunger/thirst, sleep/wake cycles
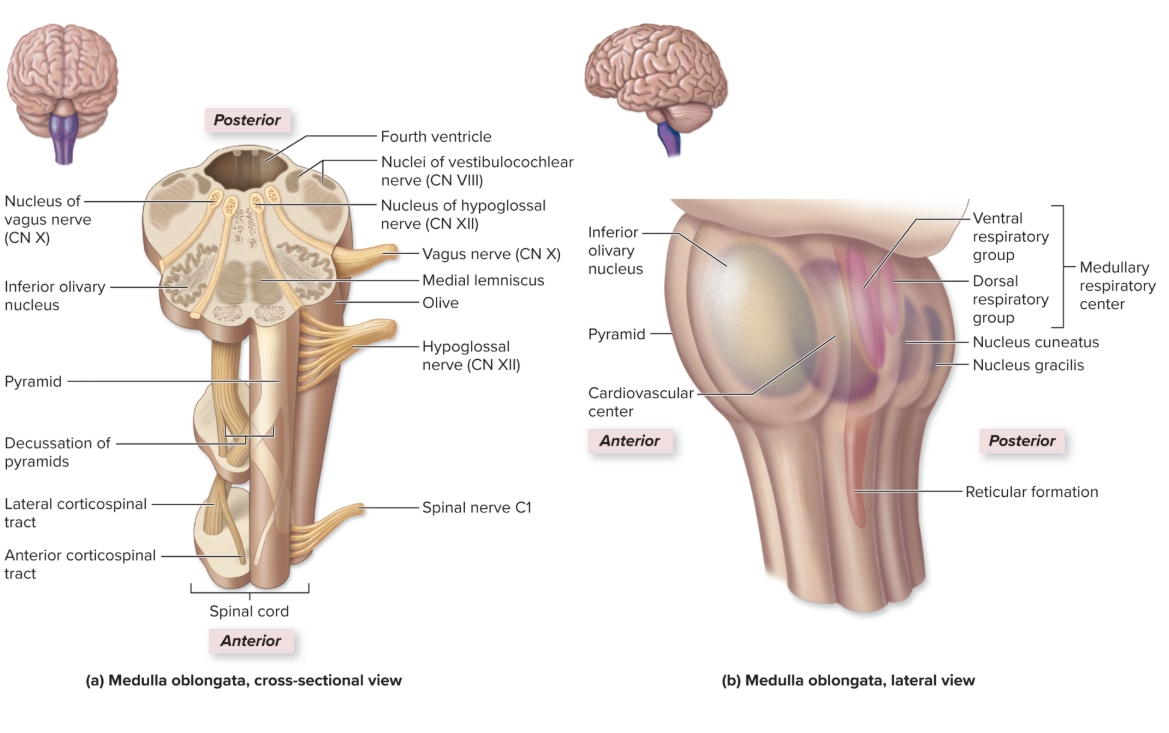
Medulla Oblongata
L: inferior part of brainstem continuous with spinal cord inferiorly
F: reflex center for vomiting, hiccupping, sneezing, coughing, regulation of heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure
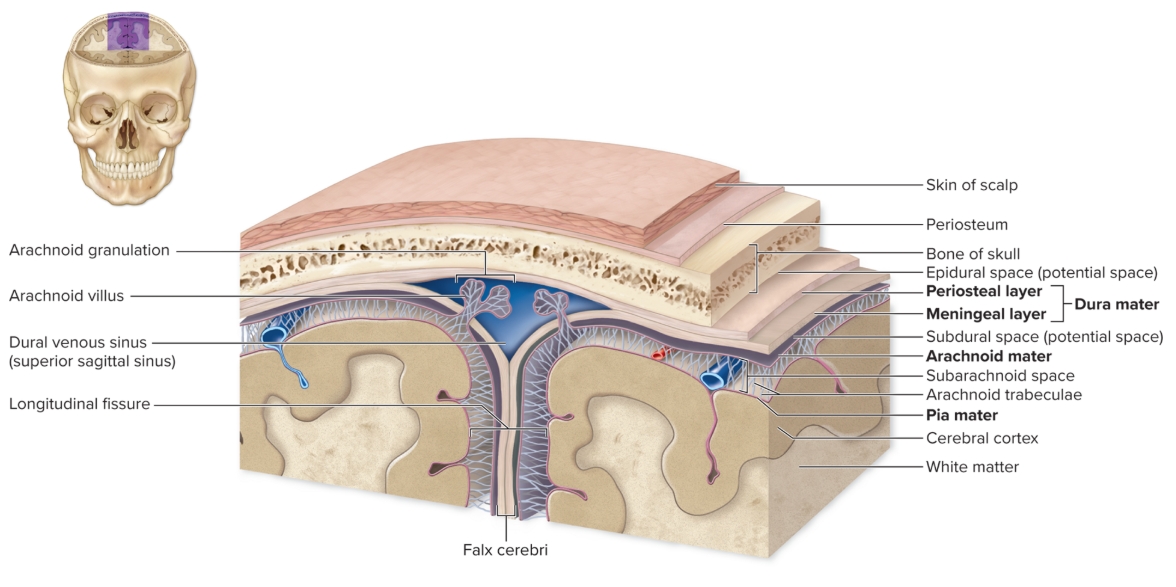
Layers of the meninges
from outer to inner
dura mater, arachnoid matter (subarachnoid space contains CSF), pia mater
Premotor Cortex
skilled, repetitive motor output comes from there (muscle memory)
Projection fiber
carry out motor output from and sensory input to the brain to opposite side of body
Association fibers
connects areas of brain within same hemisphere
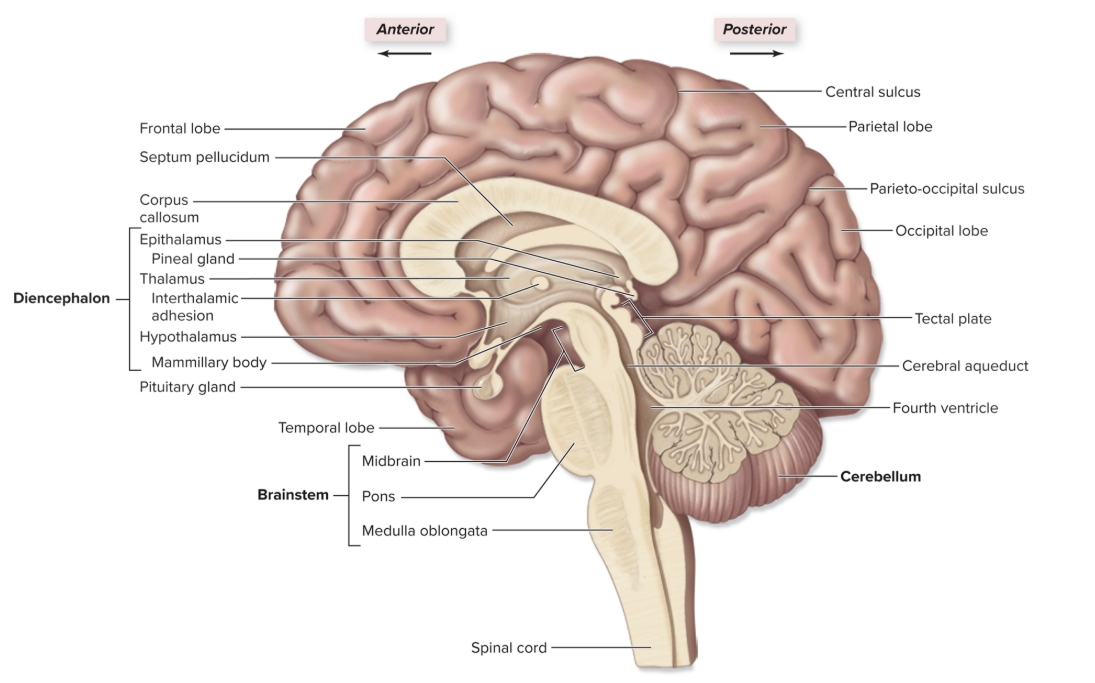
Corpus callosum
L: tracts of white matter between cerebral hemispheres
S: coordinate movement/communication between sides
Parts of reflex arc
receptor, sensory neuron, integration center (spinal cord and interneuron), motor neruon, effector
Mechanoreceptors
receptors for vibration, pressure, sound, touch, strech
Photoreceptors
receptors for wavelengths of light
Nociceptors
receptors for pain
Chemoreceptors
detect chemical signals for taste, smell, blood and CNS chemistry
Proprioceptors
receptors for balance from muscles
receptors associated with muscle spindles
Thermoreceptors
receptors for hot and cold
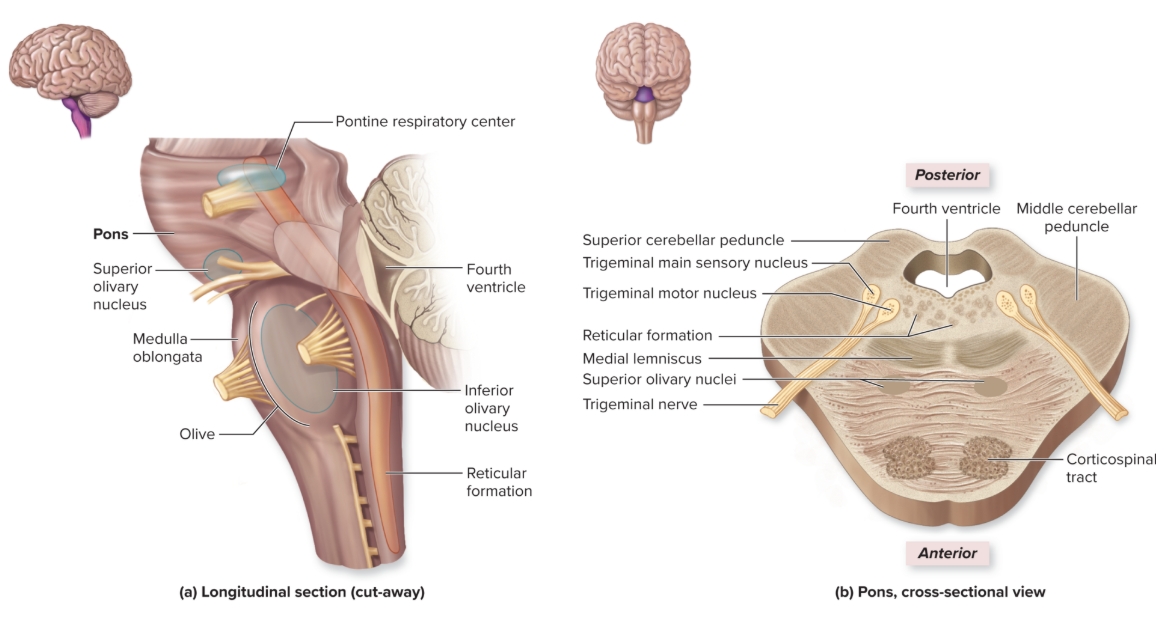
Pons
L: buldging region anterior part of brainstem
F: coordinates motor output with cerebellum and influences breathing rate
Reticular Formation
L: loosely organized gray matter projecting vertically through midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
F: sensory input from body sent to thalamus from here, muscle tone, loss consciousness or coma results from damage here
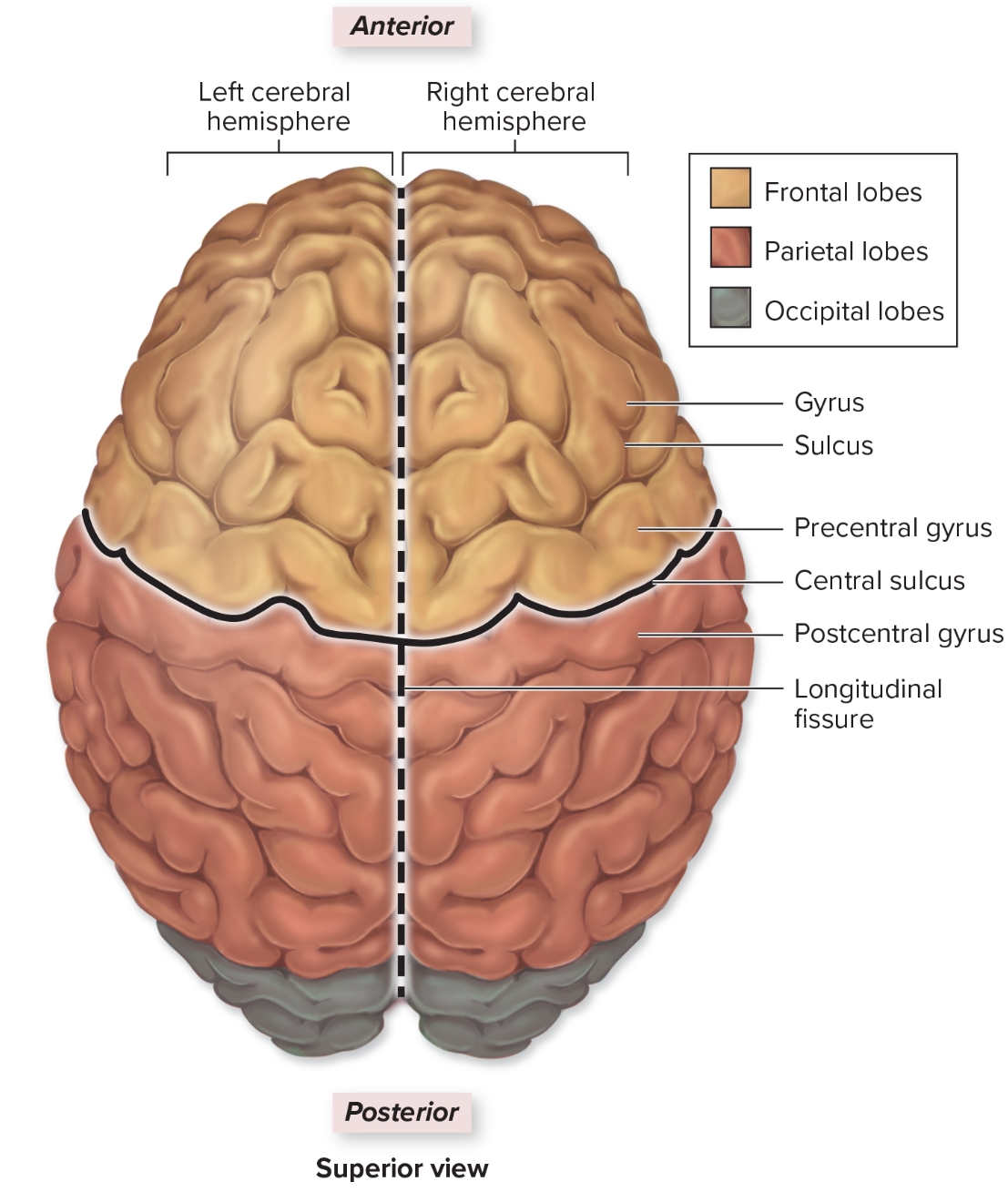
Frontal lobe
L: deep to frontal bone forms anterior cerebral hemisphere
S: personality: all judgement, decision making, planning, etc originates here
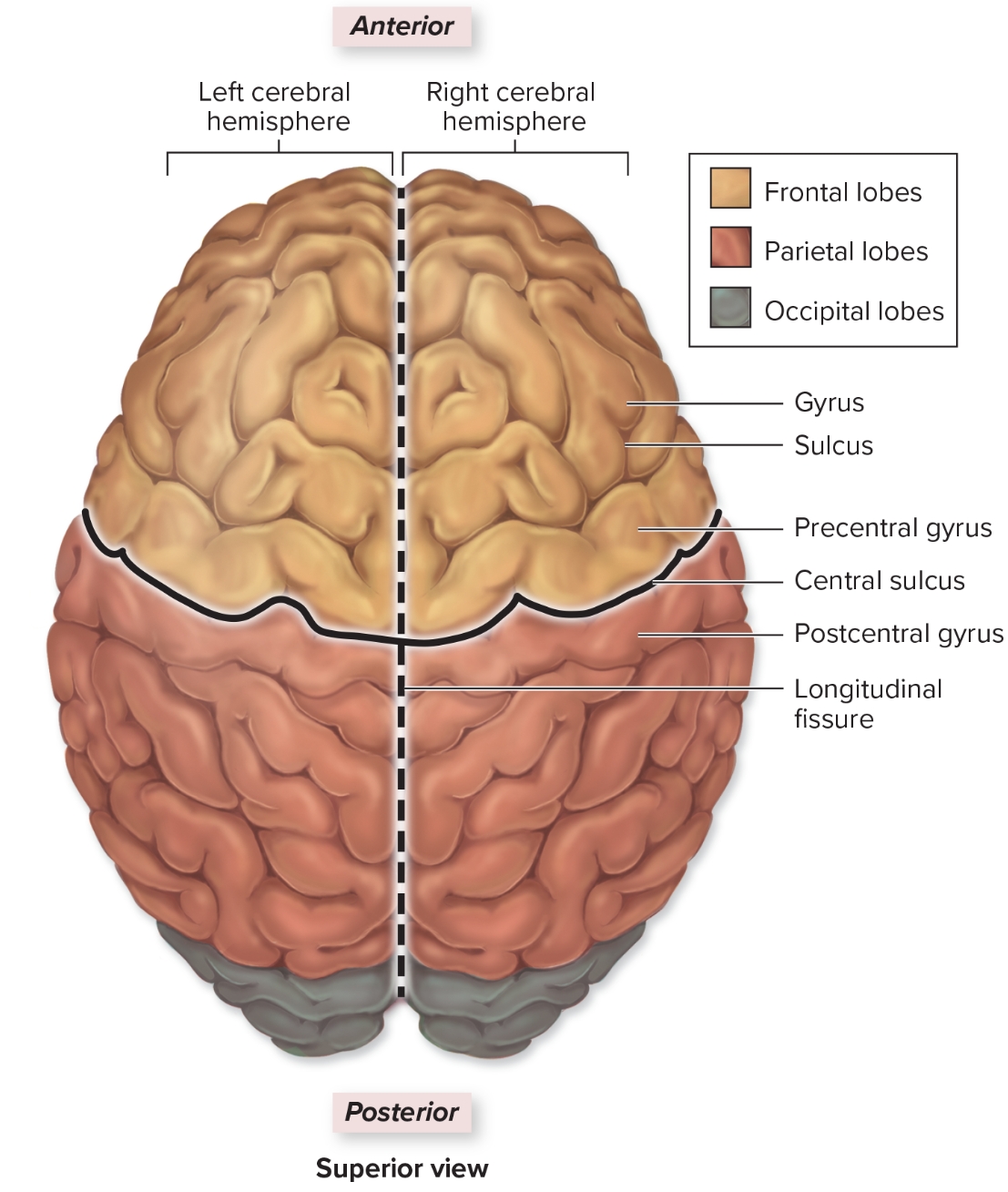
Parietal Lobe
L: deep to parietal bone forms superoposterior part of cerebral hemispheres
F: sensory input from skin and sensory input regarding body position from proprioceptors
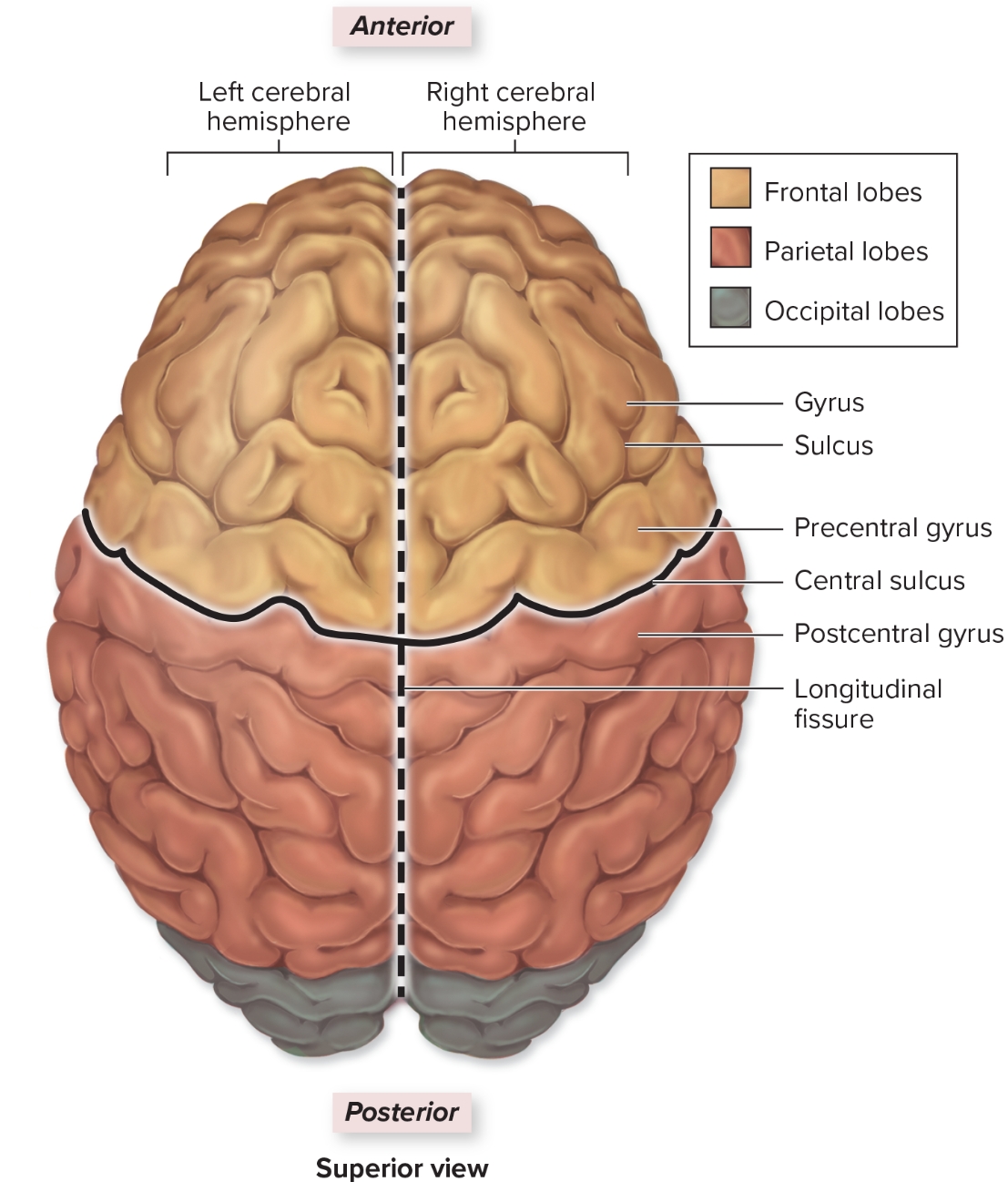
Temporal lobe
L: internal to temporal bone
F: hearing and smell
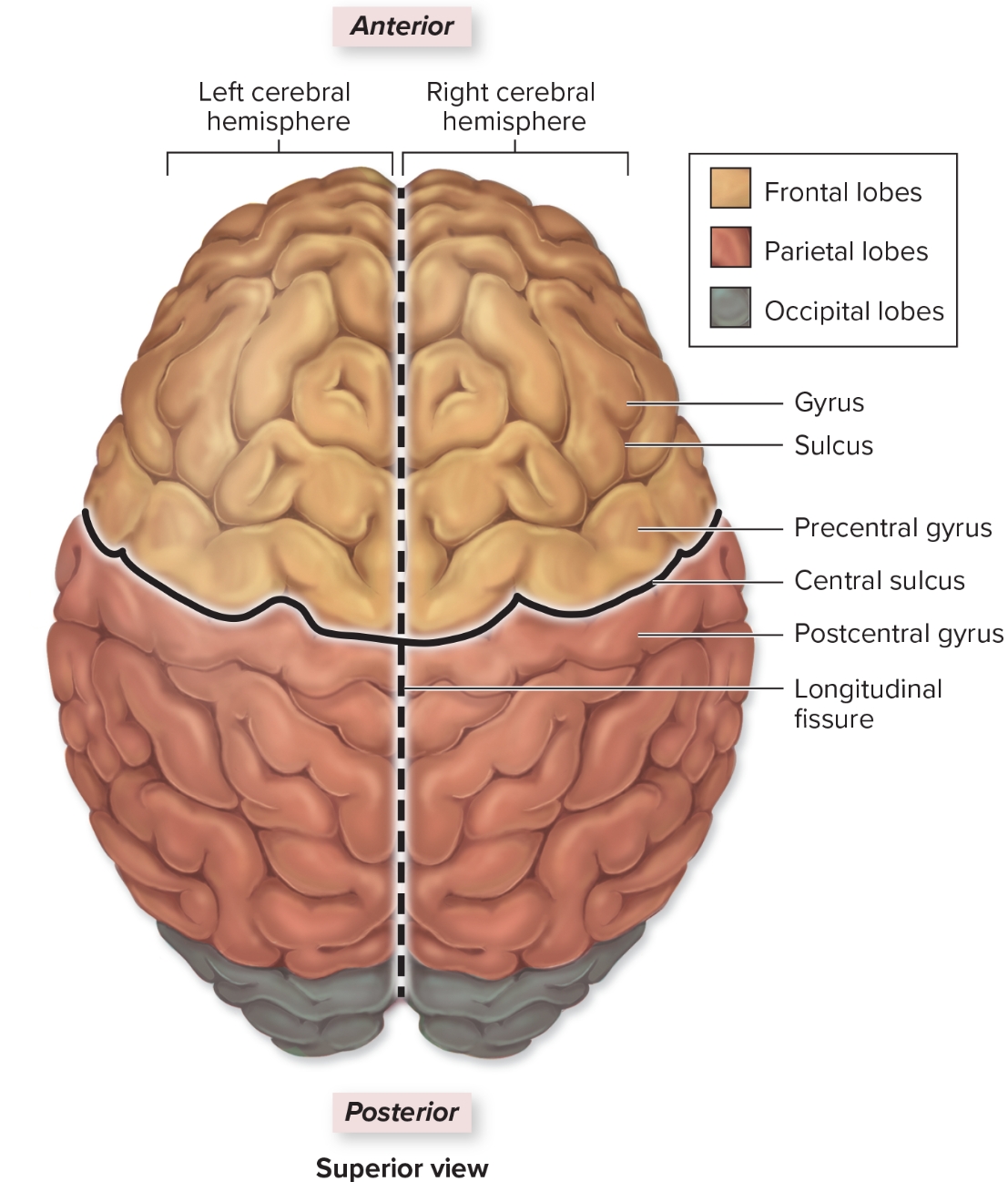
Occipital lobe
L: internal to occipital bone
F: visual input from optic nerve comes here
Insula
L: deep to lateral sulcus
F: sensory input for taste
Gyri
ridges in brain that increase surface area for interneurons
Sulci
grooves in cerebrum to increase surface area, surrounded by gray matter
Primary sensory areas in the brain
conscious awareness of senation
Association areas in the brain
necessary for understanding, integrating sensory input
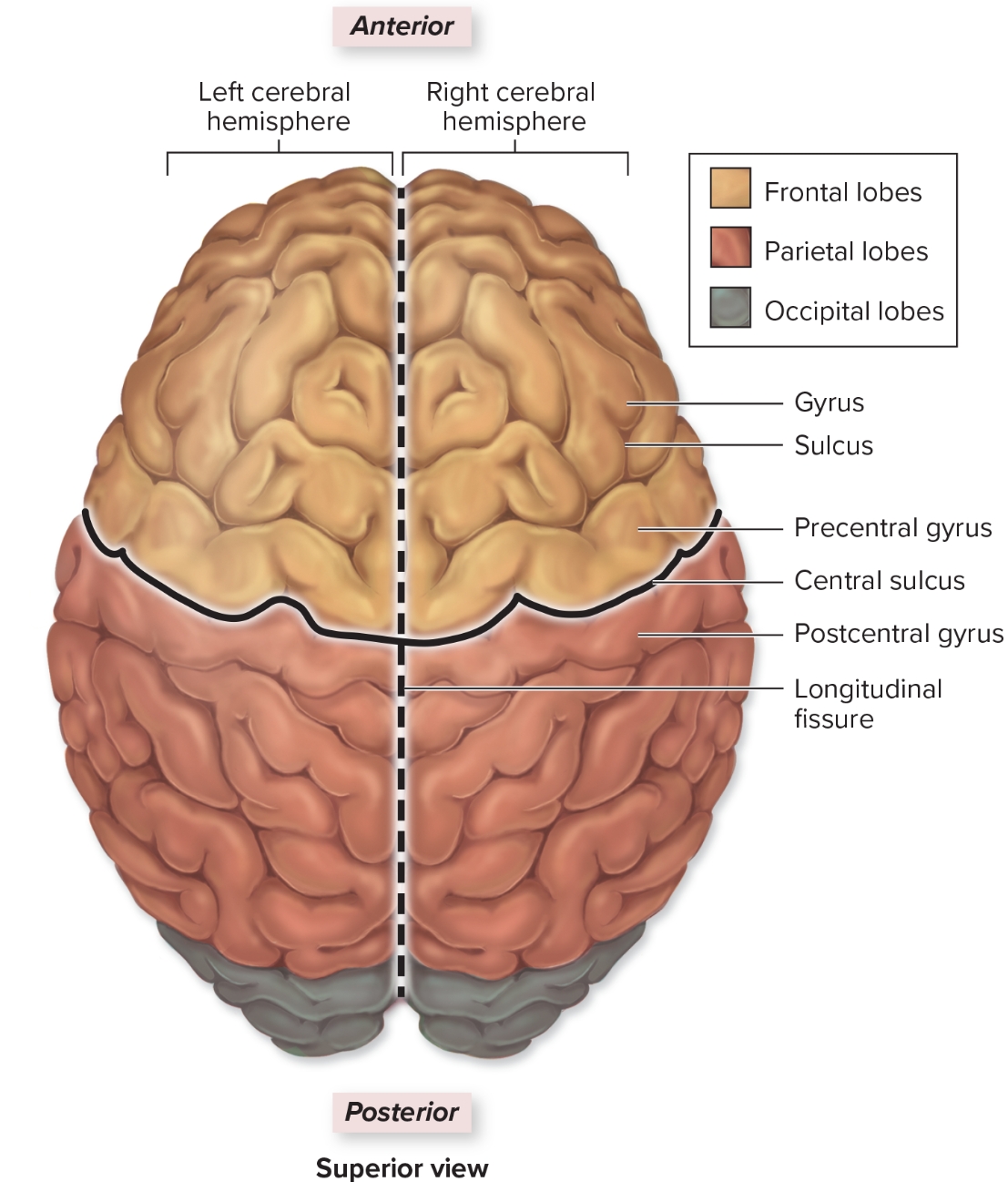
Precentral gyrus
L: anterior to central sulcus
F: all voluntary motor output
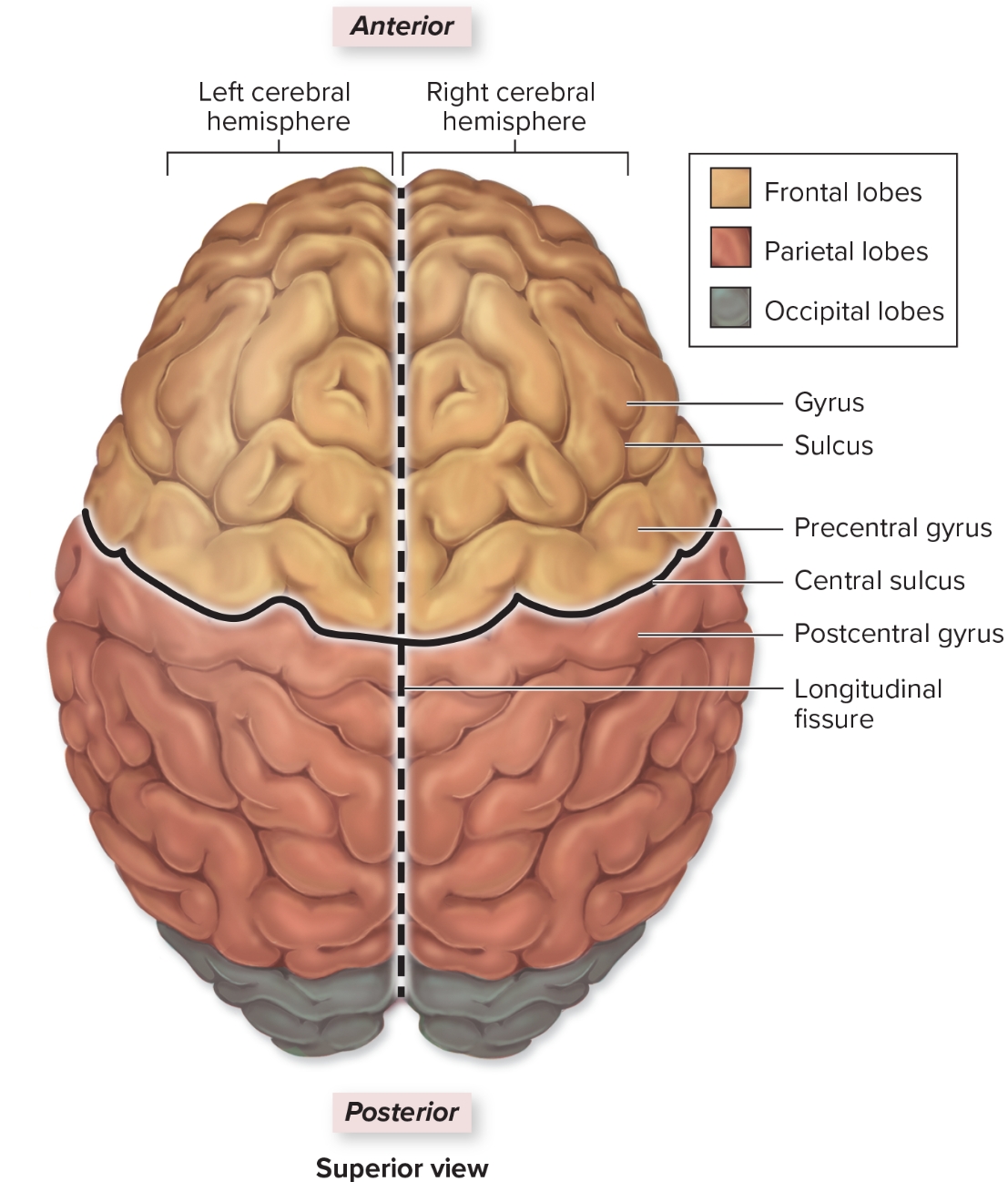
Postcentral gyrus
L: posterior to central sulcus
F: all somatosensory input (touch, temp, pressure, pain)
Broca’s area
L: inferolateral portion of left frontal lobe
F: speech production comes from there
Wernicke’s area
L: within left hemisphere overlapping parietal and temporal lobes
F: understanding speech in temporal lobe
Left hemisphere
receives sensory input from and sends motor output to right side of body
Right hemisphere
receives sensory input from and sends motor output to left side of body
Cerebellum
hand eye coordination motor output regulation
Spinal cord
consists of gray matter on the inside and white matter on the outside with 31 pairs of mixed nerves
Withdrawal/flexor reflex
also known as flexor reflex, occurs when damaging stimuli are received (touching something hot)
Crossed extensor reflex
reflex that occurs when stimulus and withdrawal reflex occur on one side while extensor reflex occurs on other (don’t fall down)
Muscle spindles
receptors wrapped around muscle fibers that allow muscle tone to occur
Golgi tendo reflex
stretch receptors in tendons that precent over contraction in muscle
Blood brain barrier
prevents harmful materials from entering CSF, astrocytes make this
Choroid plexus
makes CSF
Ventral root of spinal nerve
if cut in spinal nerve, no muscle contraction would occur but sensations would still be felt
Doral root of spinal nerve
if cut in spinal nerve, no sensatin would be felt but muscle contraction could still occur
Dermatomes
areas of skin innervated by sensory branches of each spinal nerves, where shingles appear on body
Basal ganglia
Huntington’s disease
disease caused by dysfunction of basal nuclei
Parkinson’s disease
disease caused by dysfunction of basal nuclei
Adaptation
lack of perception of sensory input even though stimuli are still present
Neural tube formation
begins a neural groove and folds from embryonic ectoderm
Babinski’s sign
toes fanning and dorsiflexing when sole of foot is stroked due to cerebral cortex damage
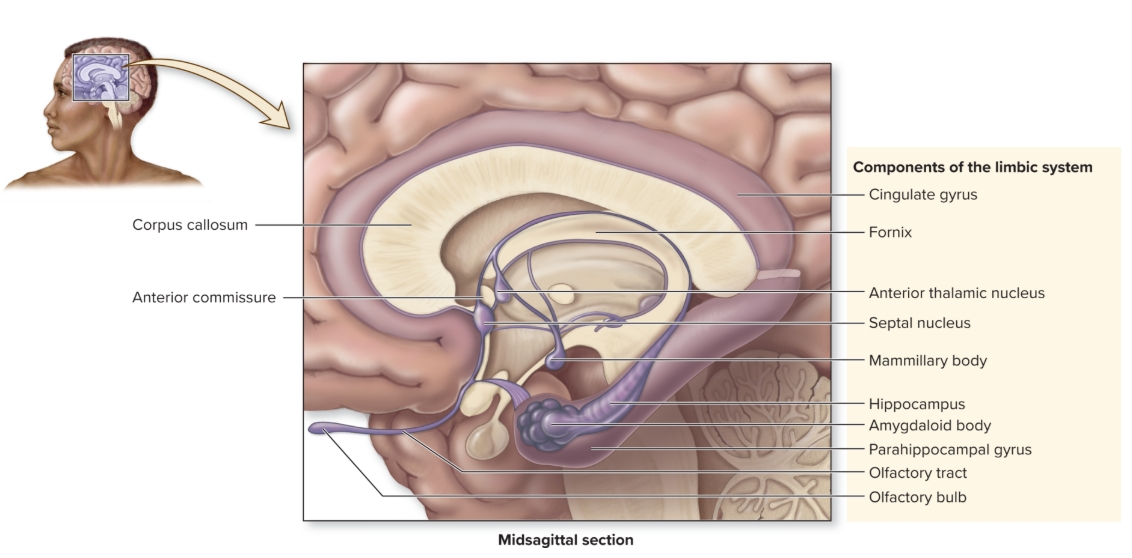
Limbic system
emotional area of brain, especially during fight or flight, fear, anger