Lecture 10: Annelids
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Phylum Annelida
segmented worms
marine, freshwater, & terrestrial habitats
metamerism
paired setae (bristle like feet made of chitin)
metamerism
repeating body segments
coelom in segments separated by a wall called Septa
Hirudinae group
ex: leeches
have oral & posterior suckers
no setae
no septa between segments
coelom full of connective tissue not fluid
channels & sinuses are the circulatory system
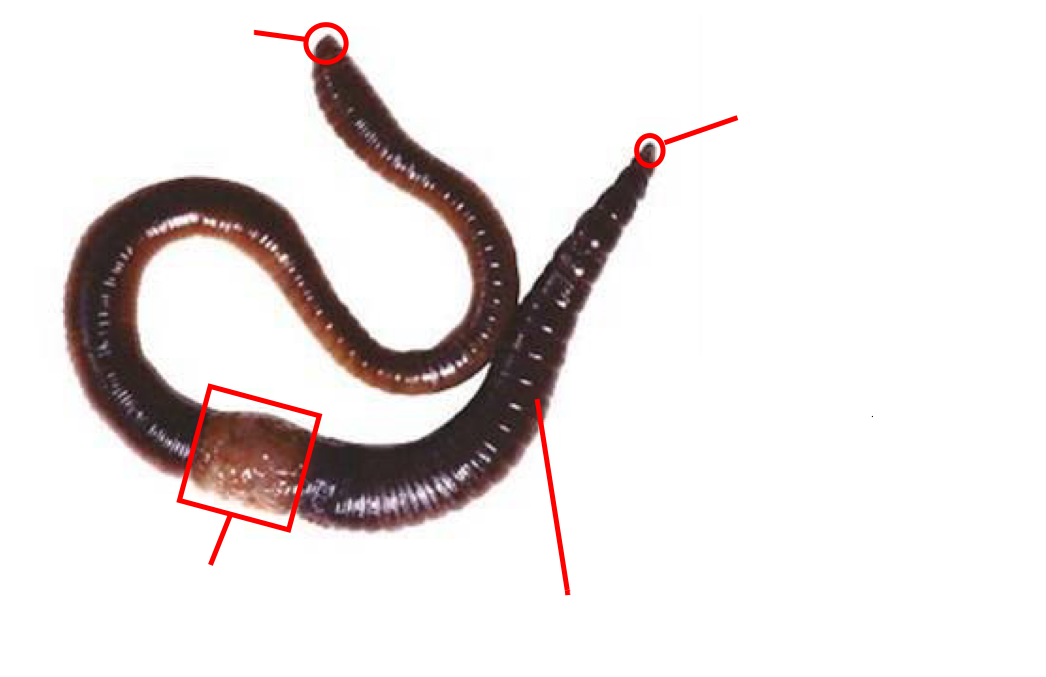
Oligocheates group
soil burrowing worms
no parapodia
no suckers
ex: earthworms
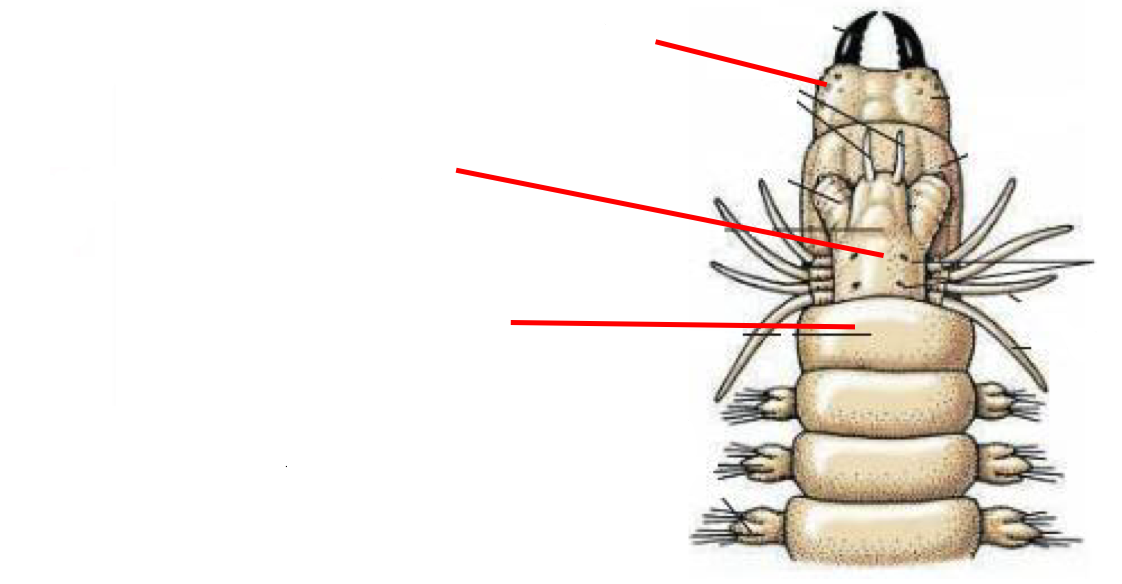
Polycheates group
marine worms with parapodia
no suckers
class Errantia
free living worms w/ Polychaete body plan
Class Sedentaria
sedentary (dont move much) and live in tubes/burrows
polychaete body plan
has the Order Clitellata
Order Clitellata
free living segemented worms with no parapodia
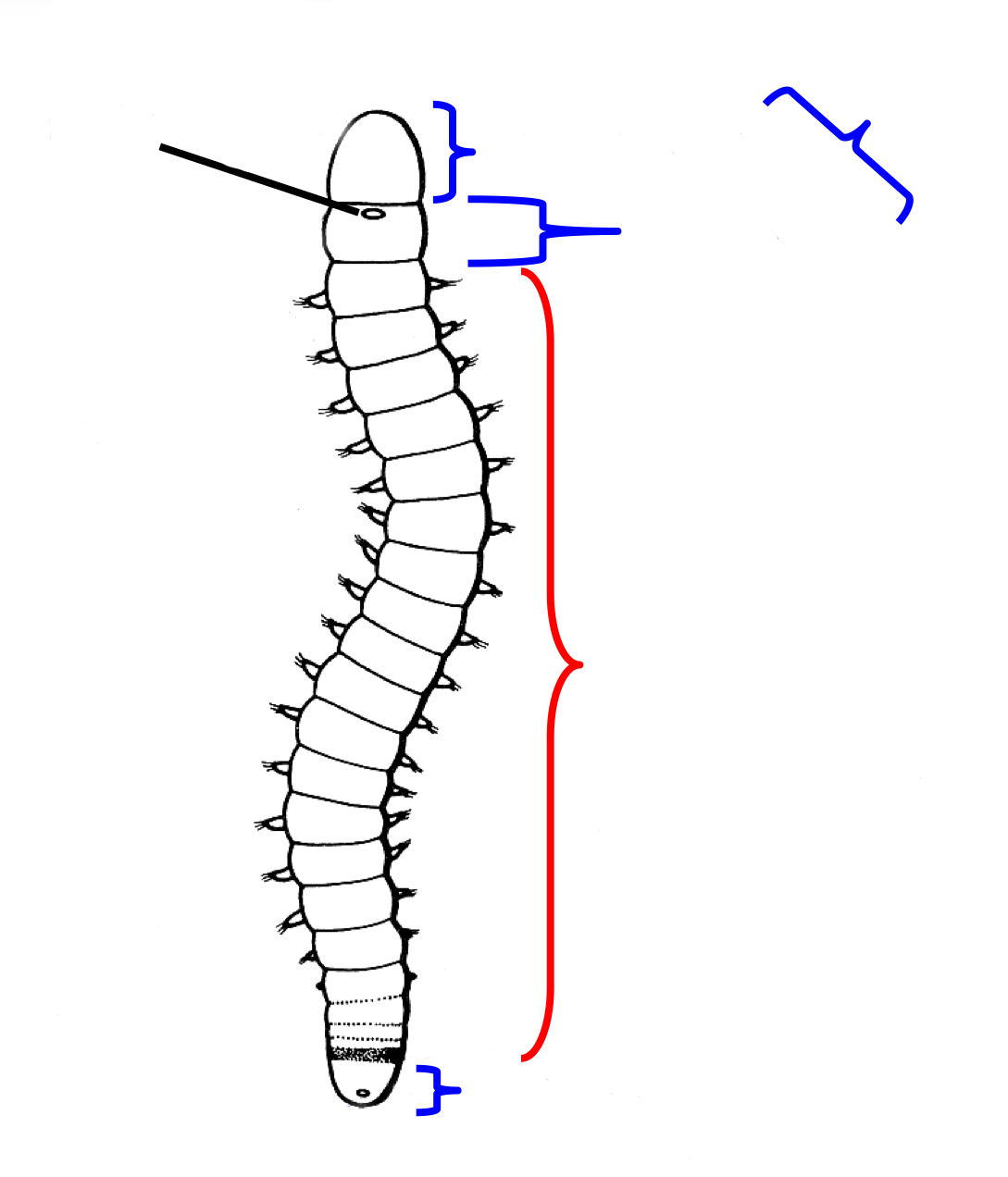
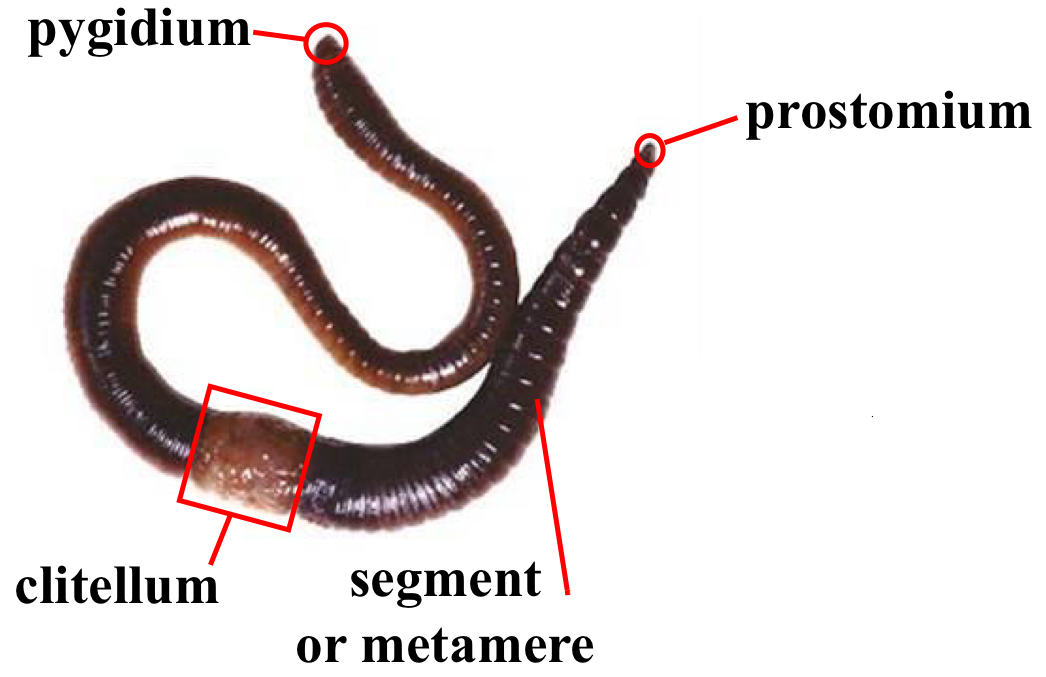
Annelida body structure labelled
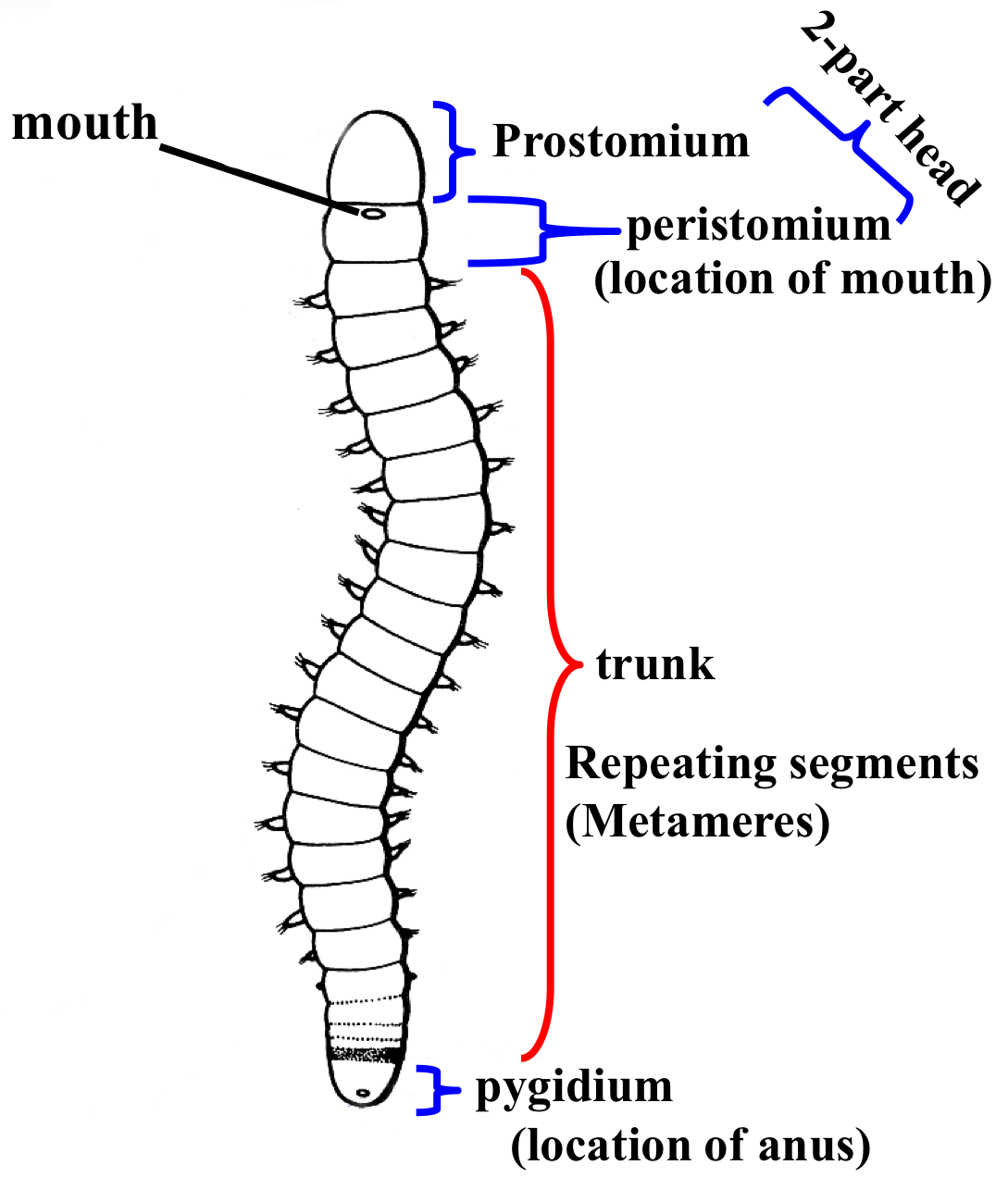
segments are added in which area of the worm?
teloblastic growth zone (above anus)
youngest segment infront of pygidium , oldest segment behind peristomium
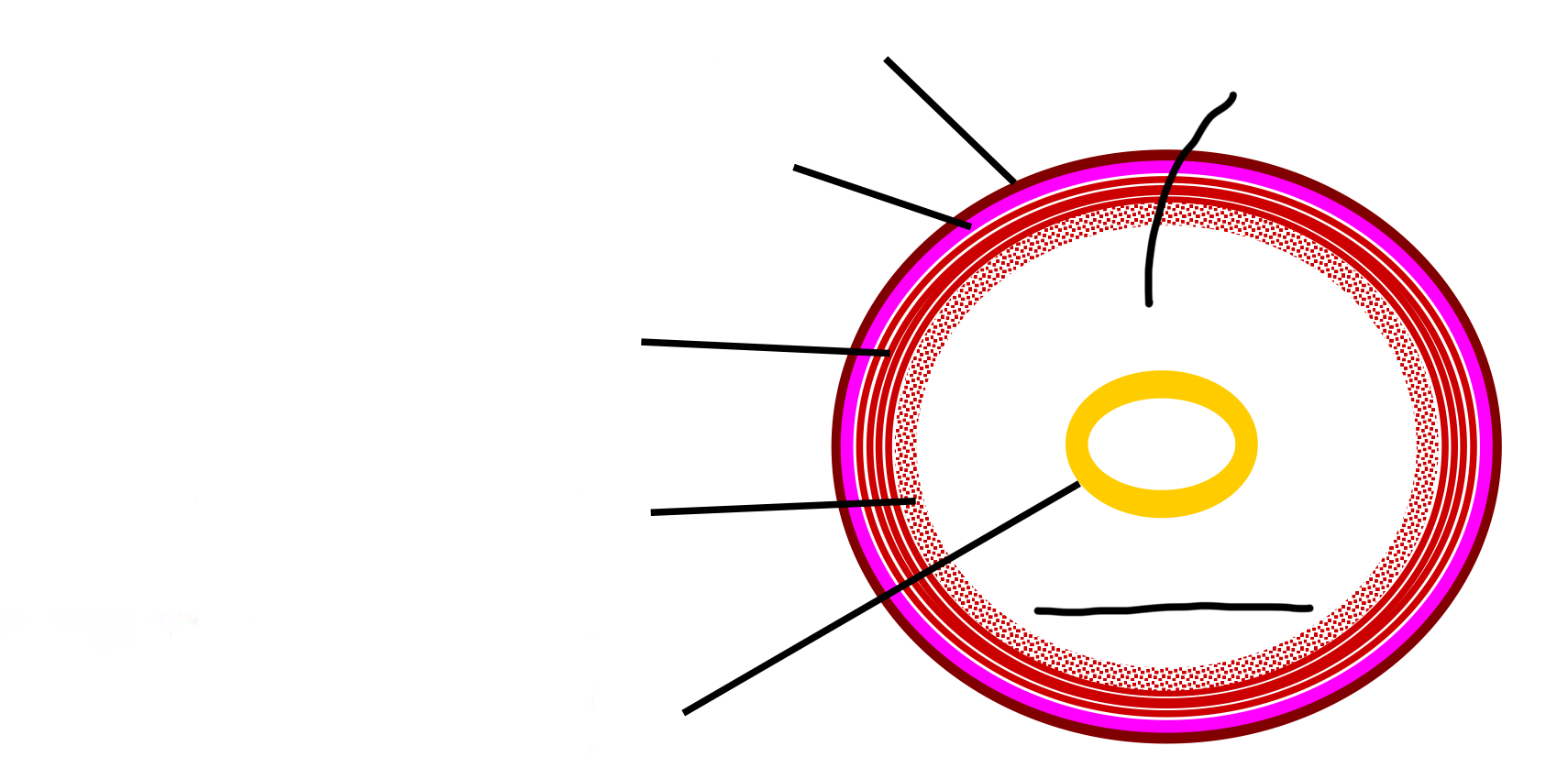
Annelida internal body plan layers labelled
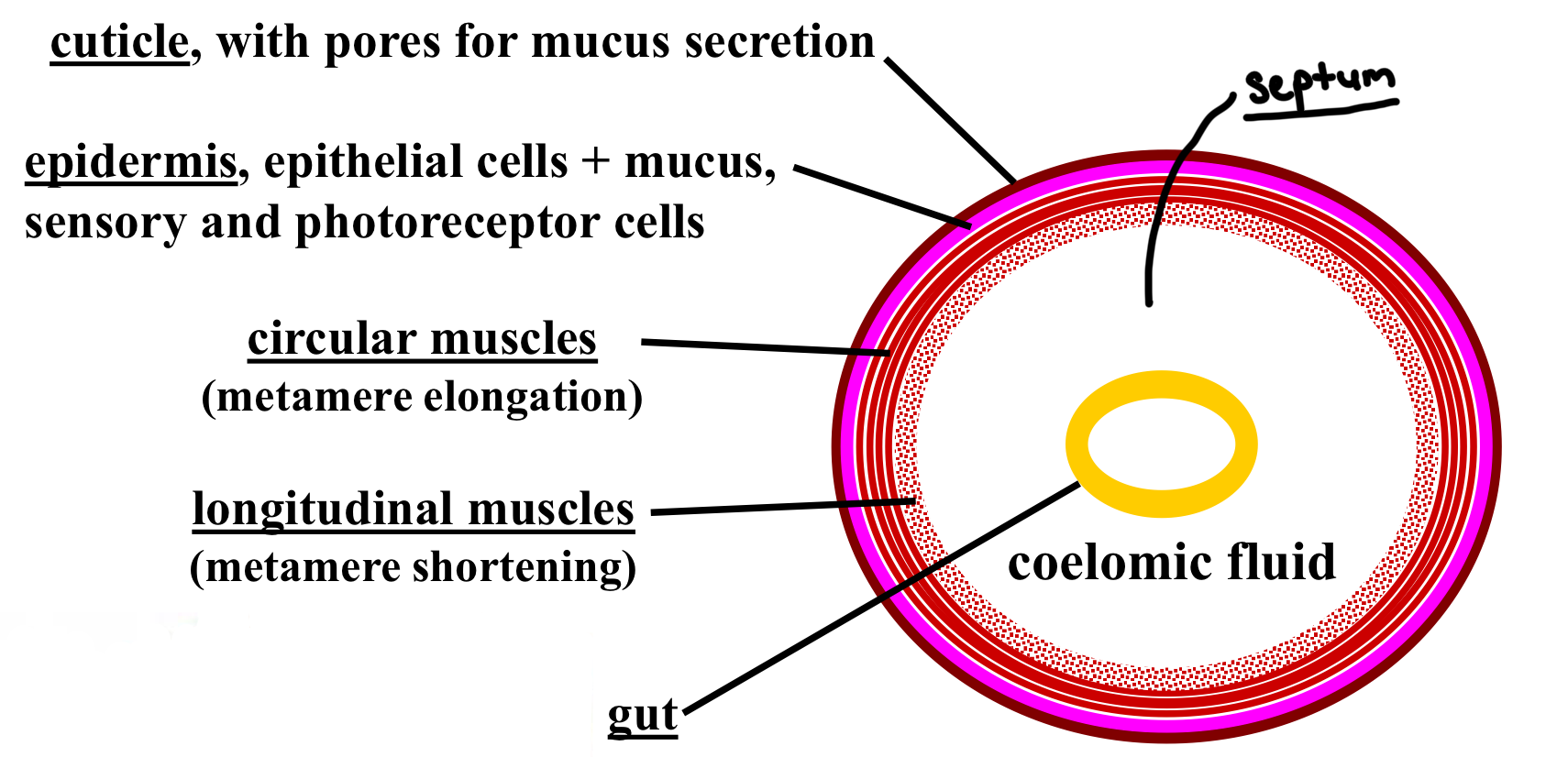
How do Annelids’ gut stay suspended in the center and form a hydrostatic skeleton?
Paired mesenteries hold the gut in the center by double lining the coelom.
supports internal organs (viscera)
fluid filled / constant volume
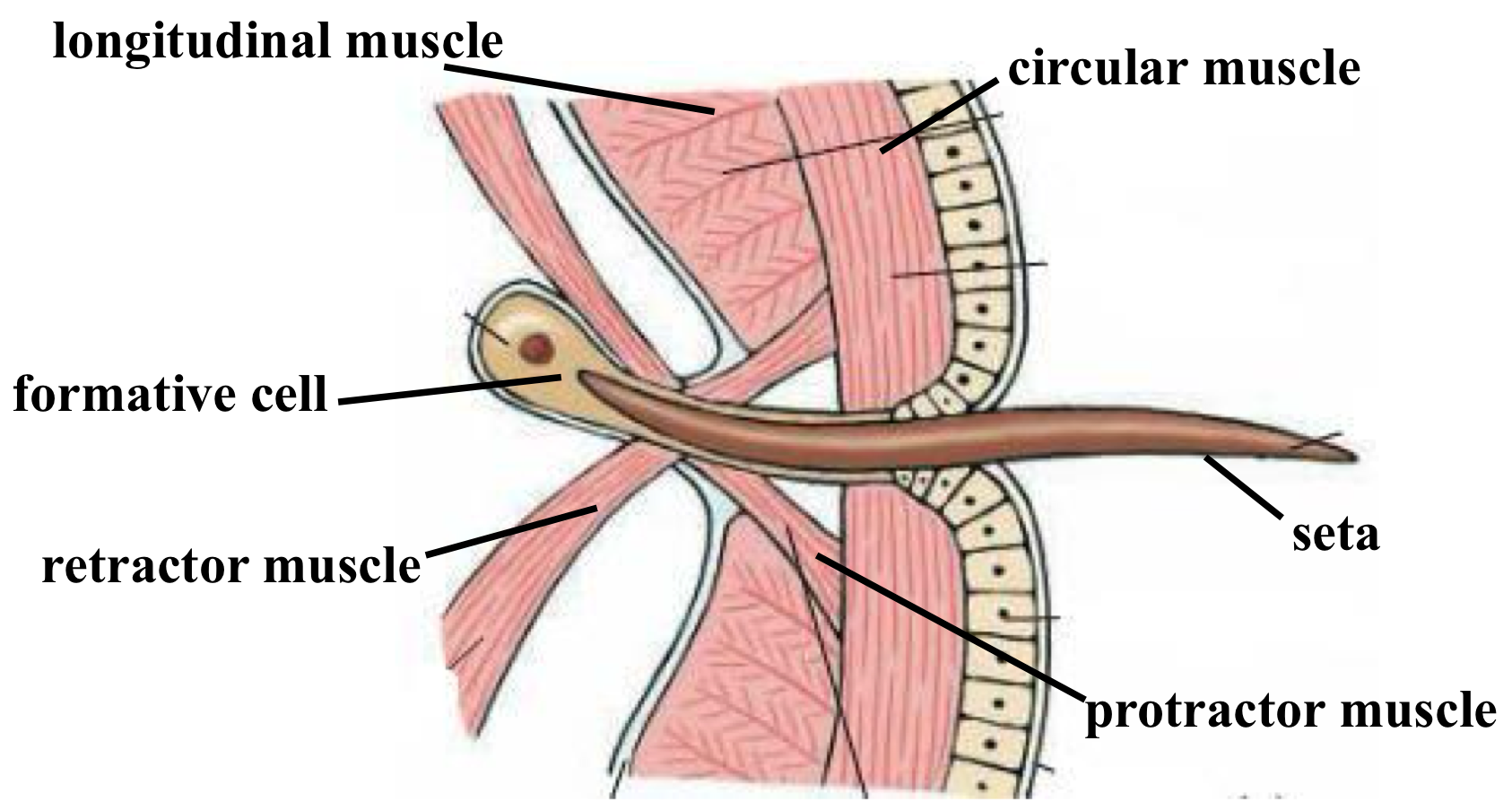
how do muscles control the movement of setae ?
formative cell = makes the seta
longitudinal & circular muscle = control body shape & movement
protractor muscle = push seta out to grip
retractor muscle = pulls seta back in
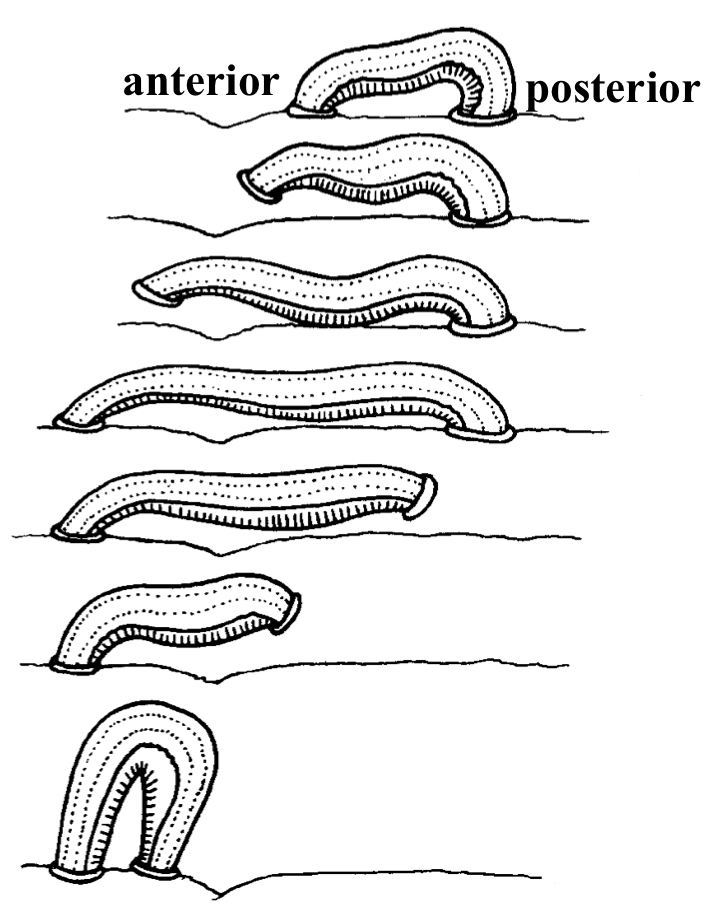
Locomotion of Leeches
anterior sucker detaches
circular muscles contract → body stretches forward
anterior sucker reattaches to surface
circular muscles relax, posterior sucker detaches
longitudinal muscles contract → body shortens, pulling the back end forward
posterior sucker reattaches
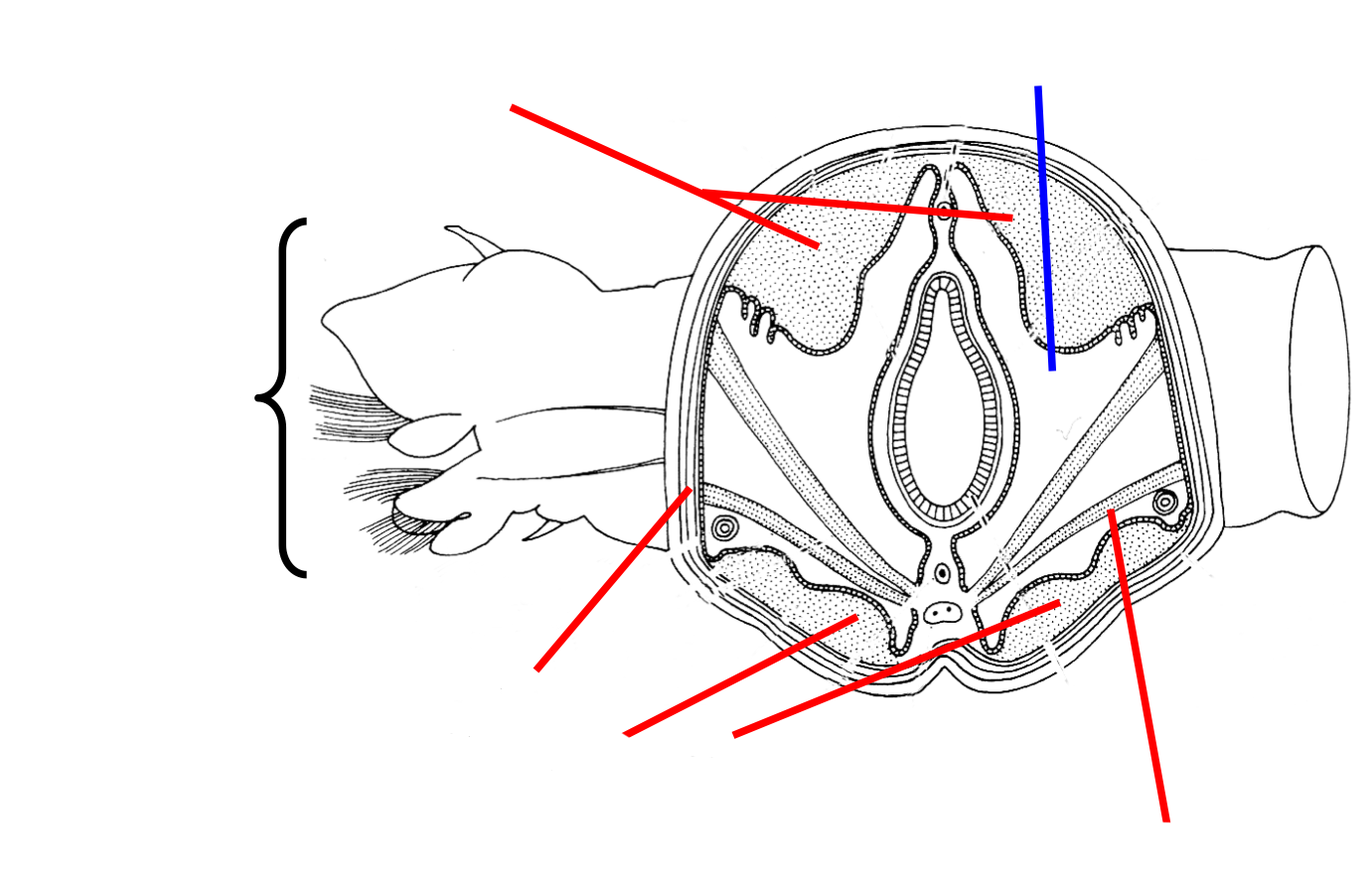
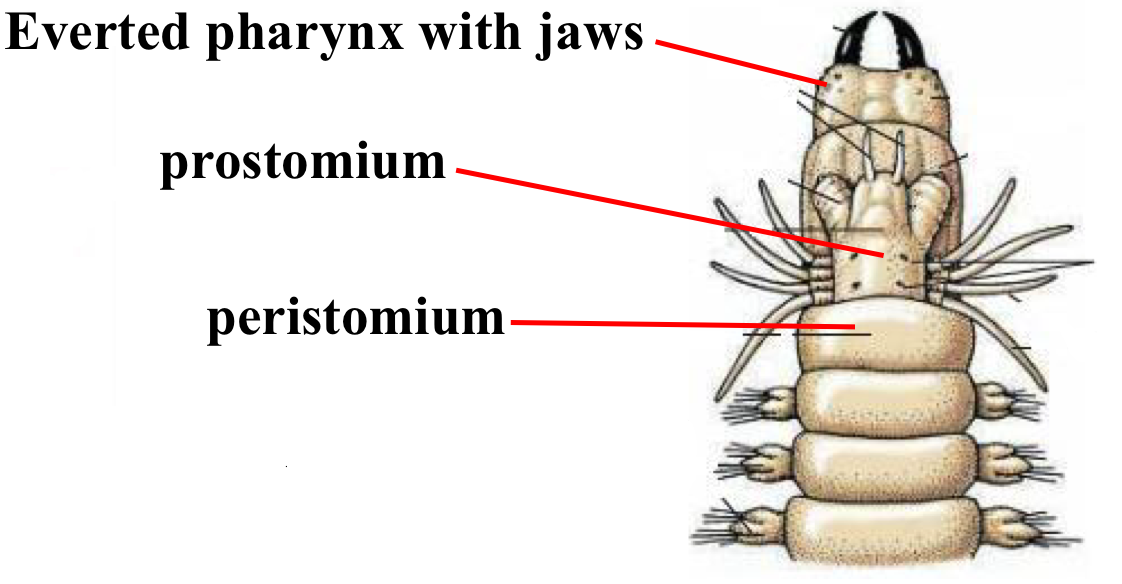
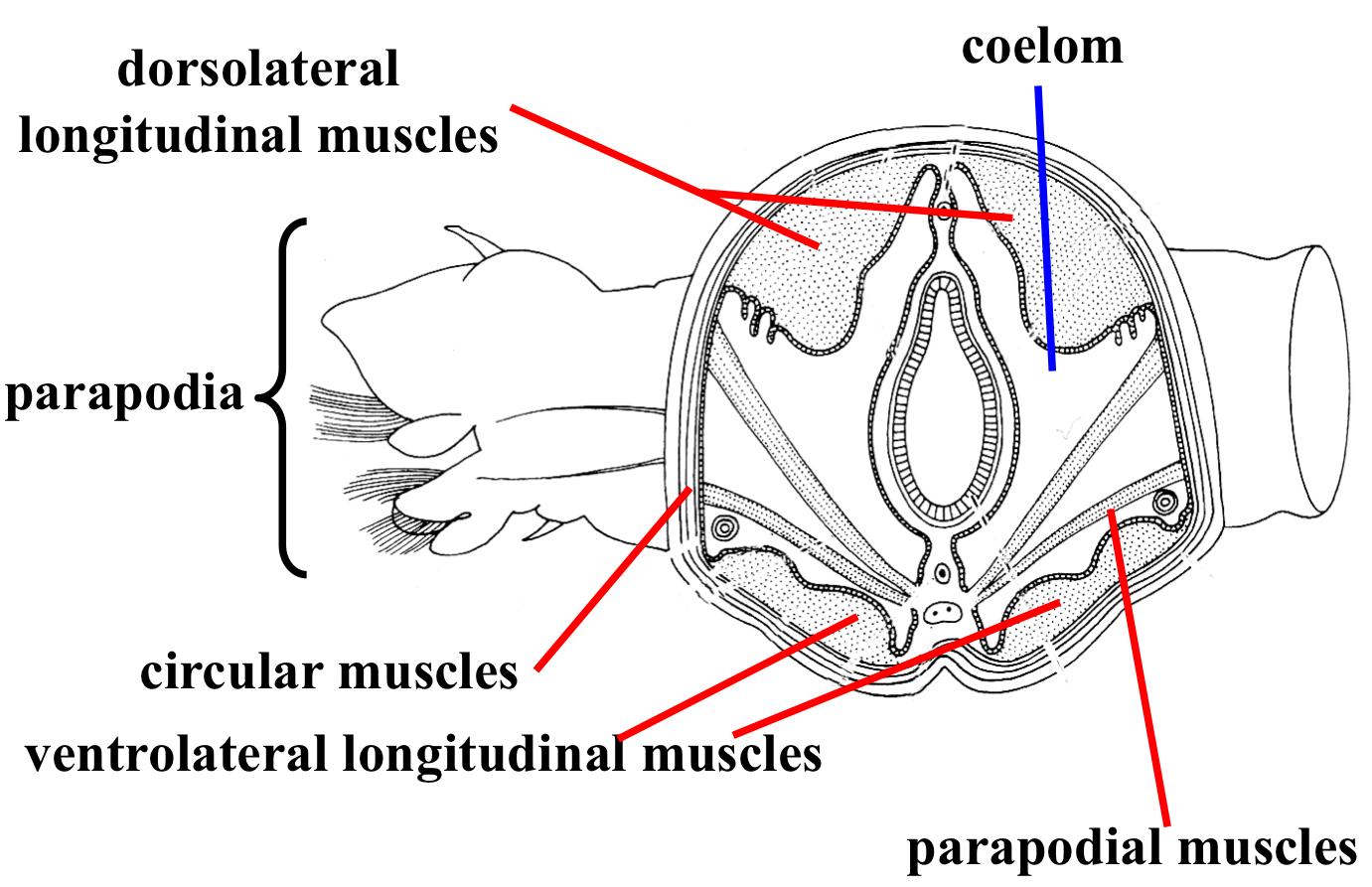
Errantia Polychaete Body plan labelled
What are the 3 speeds of locomotion for Polychaeta?
Slow crawling: mainly parapodia muscles
parapodia sides move in opposite direction
6 - 8 segments used
Fast crawling: parapodia & body muscles used tg
wiggle side to side motion
14 segments used
Swimming: parapodia & muscles used tg (more segments involved)
40 segments used
Annelid circulatory system
closed
dorsal vessel = carry blood forward
efferent vessels = carry oxygenated blood to the dorsal vessel
ventral vessel = carry blood backward
afferent vessels = bring blood from ventral vessel to parapodia
valves in vessels = keep blood flowing in one direction
capillaries = tiny vessels where gas exchange happens between blood & tissues
parapodial vasculature capillaries = exchange gas between blood & outside environment
circumesophageal vessels (hearts) = wrap around esophagus & help pump blood
what are the excretory organs of the adult annelid ?
Nephridia
one pair in each segment (except 1st, 3rd, & last)
Nephridiopore is where the waste exits the body
what are excretory part of the adult annelid is the opening that sucks in the coelomic fluid ?
Nephrostome