Brain Parts, Studies, and Terms Review (AP Psychology)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
neurons
primary cells of the nervous system
glia
support cells of the nervous system
sensory neurons
neurons that receive and bring sensory information to the brain
motor neurons
neurons that carry motor info from the brain
interneurons
connect sensory and motor neurons, responsible for reflex arc
EEG
electric output of the brain, shows brain activity but not location (waves)
fMRI
uses magnets to ping oxygen being used by neurons to show brain activity and location in real time
lesions
brain damage
brain stem (medulla is part)
controls vital life functions (ex: heart rate, breathing)
reticular activating system
controls sleep patterns, attention, eye movement
cerebellum
controls coordination and balance
thalamus
relays sensory and motor signals to the appropriate brain areas for all signals EXCEPT smell (olfaction)
limbic system
control center for emotions, motivations, memories (contains amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus)
amygdala
FEAR and emotions
hippocampus
events and factual memory storage (not reflexes/ skill based memory)
hypothalamus
reward center of brain
eating behavior
hormones (controls the pituitary gland)
homeostasis
pituitary gland
makes and releases hormones (part of hypothalamus)
cerebral cortex
outermost layer of brain, contains your lobes
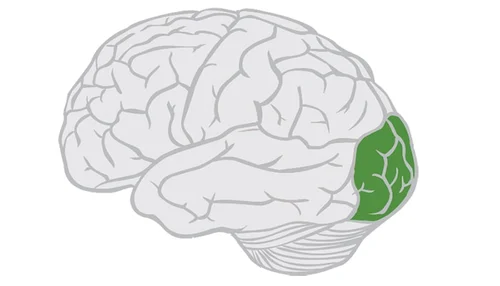
occipital lobe
vision
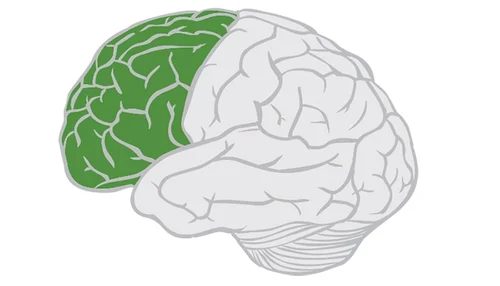
frontal lobe
language production
higher order thinking (creativity, critical thinking)
executive functioning (self-management, goals)
movement
prefrontal cortex (part of frontal)
executive functioning
primary motor cortex (part of front)
skeletal movement, sends motor neurons
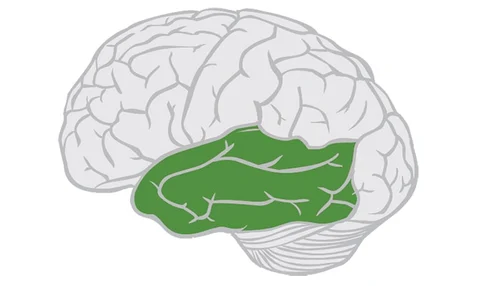
temporal lobe
audition (auditory processing)
language processing
face recognition
memory (has part of hippocampus)
prosopagnosia
face blindness, due to temporal lobe lesions or genetics
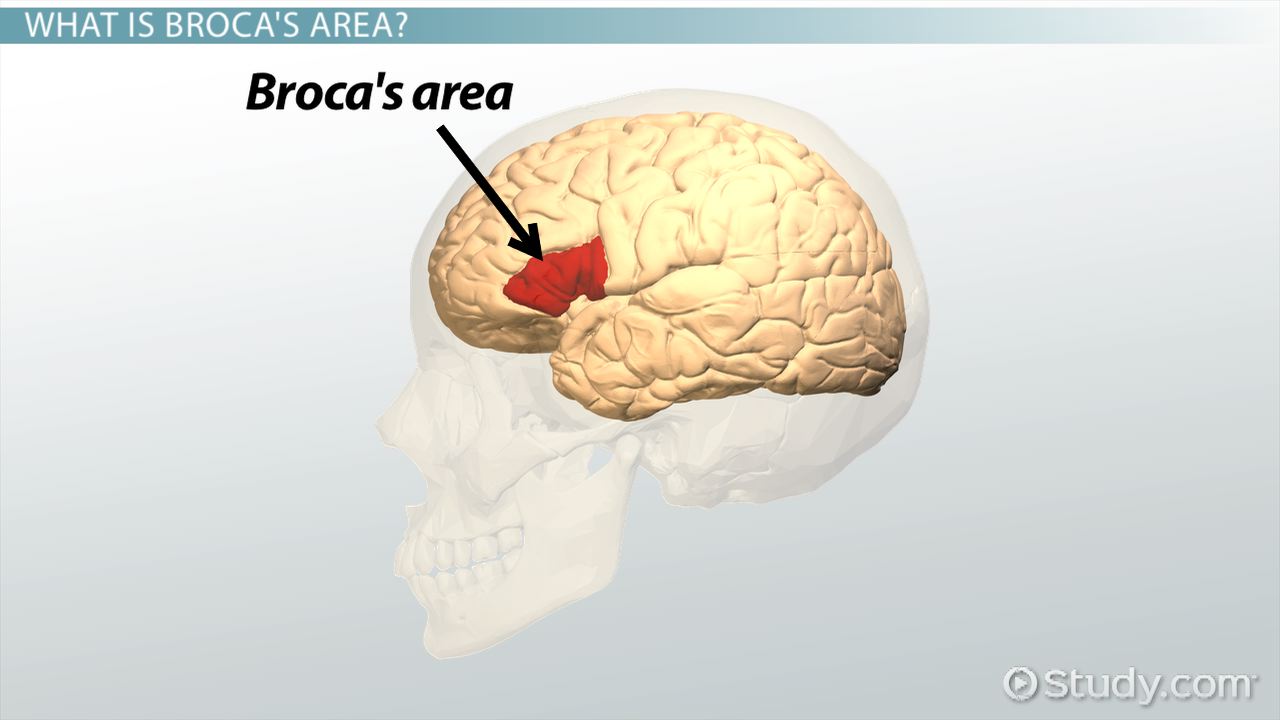
Broca’s area
speech production, left frontal
Wernicke’s area
speech comprehension, left temporal
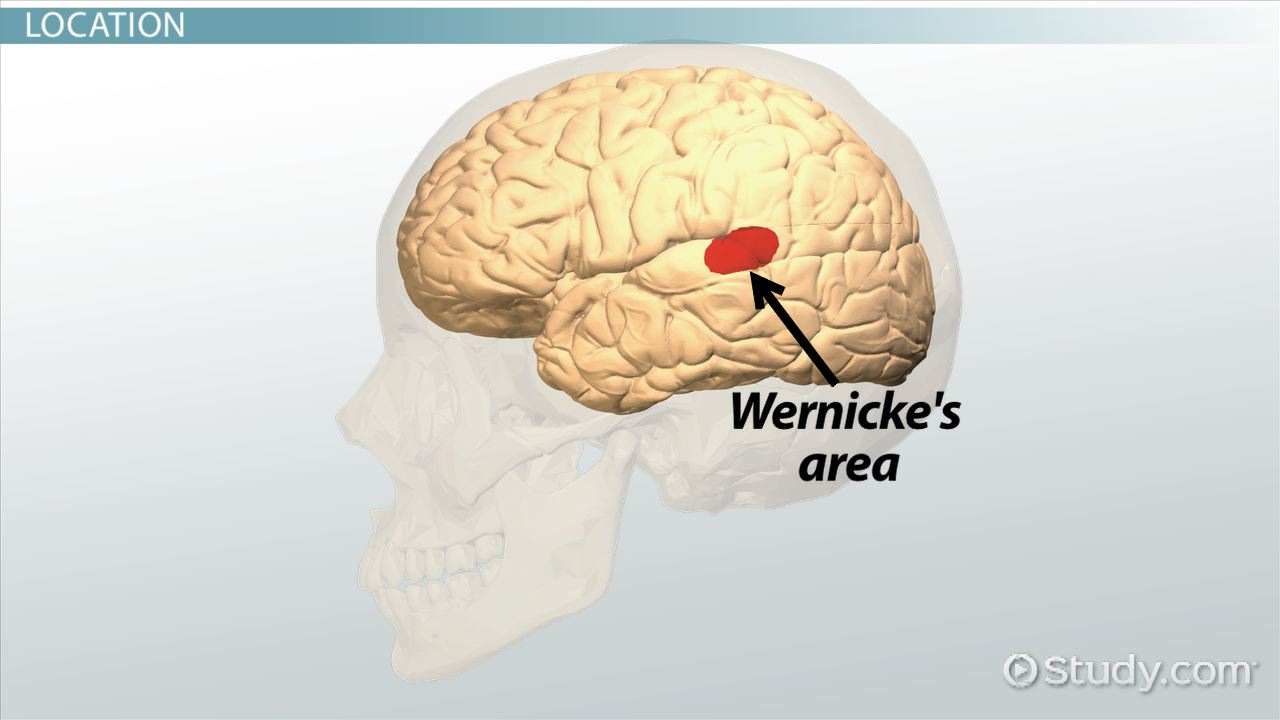
aphasia
loss of speech functions (damage to Broca’s or Wernicke’s areas)
parietal lobe
controls sensory perception and processing
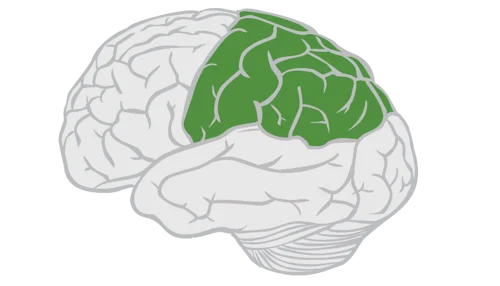
somatosensory cortex
contains touch specific sensory neurons for every designated spot on the body, helps perception for every part associated (part of parietal)
corpus callosum
connects the two hemispheres
association areas
part of the cerebral cortex that receive input from multiple areas
blindsight
due to lesions in the primary visual cortex, a person may be blinded yet still respond to visual stimuli
plasticity
brain’s ability to heal from damage
phantom limb pain
post-loss of a limb, people may still feel pain as if it is there
neurogenesis
regeneration of neurons
lateralization
brain activities being predominantly left or right