pathology final
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
mucocele
diagnosis?
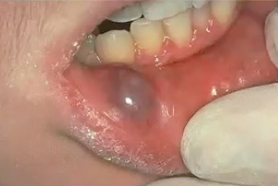
trauma
most common cause of mucocele
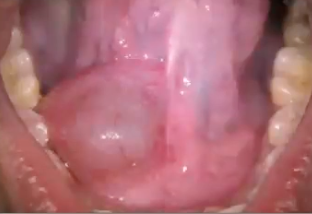
ranula
mucocele on the floor of the mouth
blandin-nuhn
mucocele on ventral tongue
surgical excision
treatment of mucocele
floor of mouth lateral to midline
location of ranula
plunging ranula
painless swelling in floor of the mouth, no epithelial lining and has breached the mylohyoid muscle, diagnosis?
removal of sublingual gland
treatment for plunging ranula
salivary duct cyst (mucus retention cyst)
epithelium lined cavity that arises from the salivary gland
upper lip
most common location for salivary duct cyst
salivary duct cyst
diagnosis?
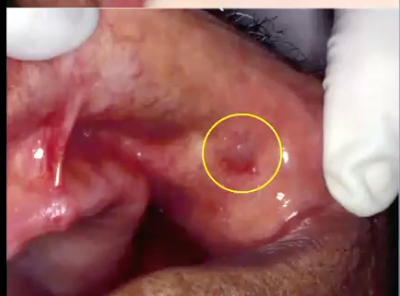
ranula affects submandibular gland (affects sublingual)
which of the following is false

cheilitis glandularis
diagnosis?
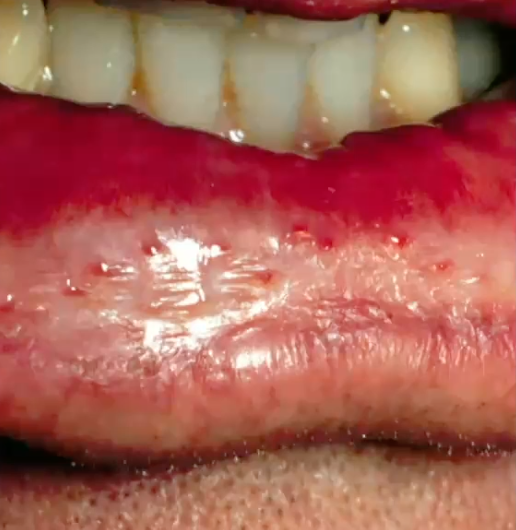
necrotizing sialometaplasia
locally destructive rapidly growing ulcer with necrosis due to inflammation of salivary gland
ischemia
cause of necrotizing sialometaplasia
hard palate
most common location of necrotizing sialometaplasia
necrotizing sialometaplasia
diagnosis?
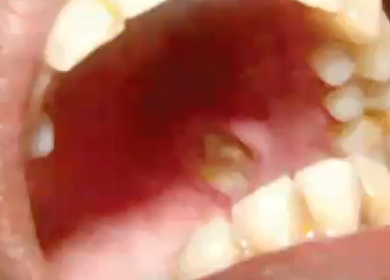
biopsy (to rule out malignancy)
treatment of necrotizing sialometaplasia
necrotizing sialometaplasia
diagnosis?
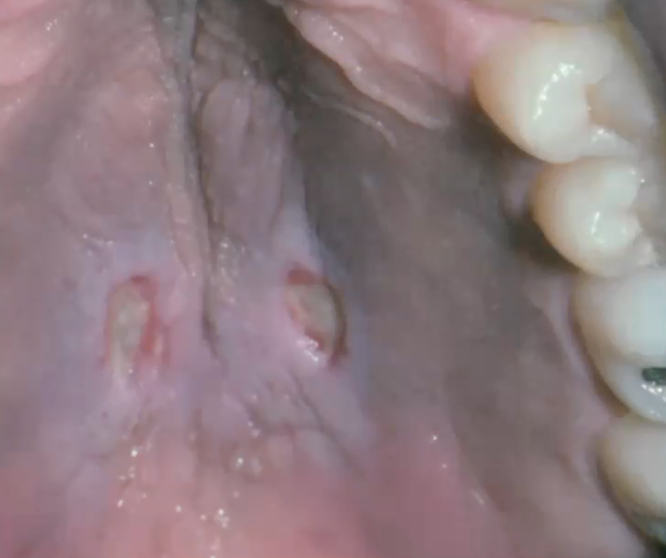
nicotine stomatitis
diagnosis?
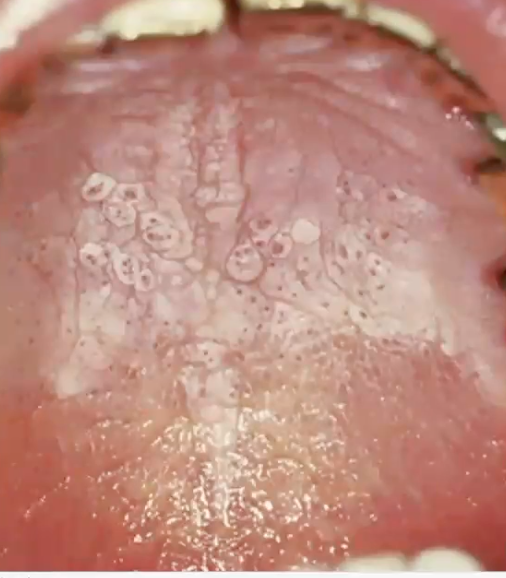
repeated contact with pipe/cigar
cause of nicotine stomatitis
false
T/F nicotine stomatitis is precancerous
lower lip
most common location of Cheilitis glandularis
sialolithiasis
calcified structures that develops within the salivary duct
submandibular
most common gland affected by SIALOLITHIASIS
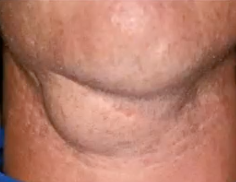
sialadenosis
enlargement of salivary gland due to non-infectious cause
bilateral parotid gland
most common gland affected by sialadenosis
stone, systemic condition, or recent surgery
causes of sialadenosis
sialadenitis
acute or chronic inflammation of salivary glands due to infection
sialadenitis
presence of purulent exudate suggests?
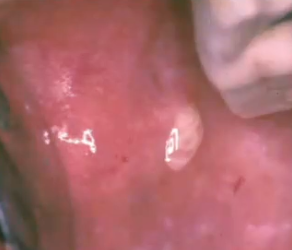
lymphoepithelial sialadenitis
an autoimmune disease affecting salivary glands, associated with Sjögren's syndrome
lymphoepithelial sialadenitis
middle aged female with sjogrens disease presents with non-tender swelling of parotid area, likely diagnosis?
sialorrhea
excessive salivation or drooling
clozapine and pilocarpine
medications associated with sialorrhea
trauma
which of the following is SIALADENOSIS NOT associated with:
bulimia
diabetes
alcoholism
trauma
xerostomia
extreme dry mouth
antihistamine, anticholinergic, antidepresants, sedatives, antihypertensive
medications associated with xereostomia
false
T/F Xerostomia exhibits excess saliva
sjogrens syndrome
autoimmune condition that causes xerostomia and keratoconjunctavitis sicca
higher risk of lymphoma (MALT)
which of the following is CORRECT regarding Sjogren Sydrome

frey syndrome/ auriculotemporral syndrome
diagnosis?
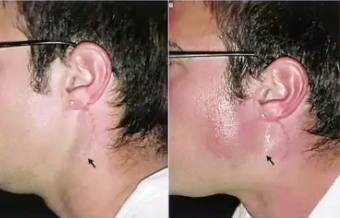
frey syndrome
facial flushing and sweating along the distribution of the aurriculotemporal nerve during mastication
damage to nerve/ parotid surgery
cause of frey syndrome
mumps (virral parotitis)
bilateral viral infection of parotid gland due to paramyxovirus
false (auriculotemporal)
T/F frey syndrome is due to damage to trigeminal nerve
sialothiasis
which condition is most likely to show up as a radiopaque mass on an occlusal radiograph
nicotine stomatitis
which condition is characterized by elevated, volcano-like papules with red central dots
sjogrens syndrome
which autoimmune condition is most strrongly associated with bilateral parotid enlargemnt and dry eyes
ranula
which lesion increases in size just before or during meals and may cause neck swelling if plunging
dry eyes
what does keratoconjuctivitis sicca refer to
mucocele
dome shaped bluish lesion on the lower lip of a child is most likely
gustatory sweating
complication of frey syndrome
pilocarpine
all of the following medications would cause xerostomia EXCEPT:
anticholinergic
pilocarpine
antidepressants
antihypertensive
parotid
most common location for salivary gland neoplasm in MAJOR glands
palate
most common location for salivary gland neoplasm of MINOR glands
pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor)
most common salivary gland tumor (benign and malignant)
palate
most common site for intraoral pleomorphic adenoma
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
most common malignant salivary gland tumor
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
most common malignant salivary gland tumor in MAJOR glands
adenoid cystic carcinoma
most common malignant salivary gland tumor in MINOR salivary gland
retromolar pad (mucoepidermoid)
most common location of malignant salivary gland tumor
carcinoma
concern with pleomorphic adenoma
parotid gland and palate
most common locations of pleomorphic adenoma
pleomorphic adenoma
salivary tumor with the best prognosis
warthin tumor
BENIGN tumor of PAROTID associated with cigarette smoking and often bilateral
parotid gland
location of warthin tumor
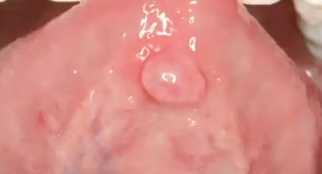
canalicular adenoma
benign salivary gland tumor almost exclusively on UPPER LIP
canalicular adenoma (monomorphic adenoma)
most likely diagnosis of this benign lesion
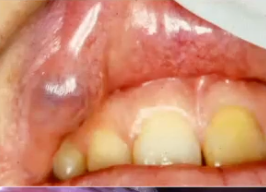
excision
treatment of canalicular adenoma
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
salivary gland tumor that can have intraosseous tumors
polymorphous adenocarcinoma
2nd most common minor salivary gland malignancy
adenoid cystic carcinoma
most common malignancy of the submandibular gland
adenoid cystic carcinoma
presents with perineural invasion, PAIN, and “swiss cheese” histological appearance
adenoid carcinoma
which neoplasm presents with pain
adenoid cystic carcinoma
CBCT showed bone destruction, diagnosis?

canalicular adenoma
what is the diagnosis
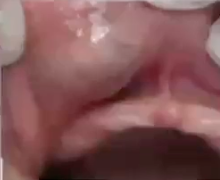
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
what is the diagnosis
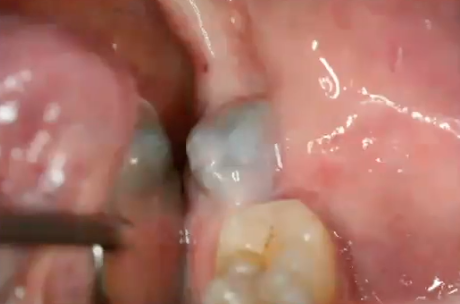
mucocele
diagnosis?
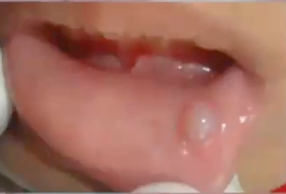
nicotine stomatitis
what is the diagnosis
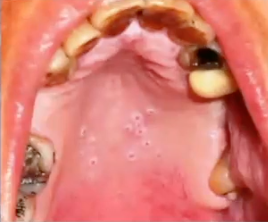
necrotizing sialometaplasia
what is the diagnosis
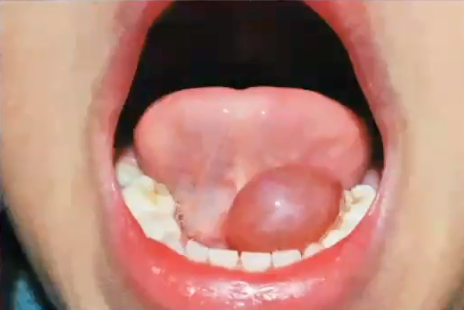
ranula
what is the diagnosis
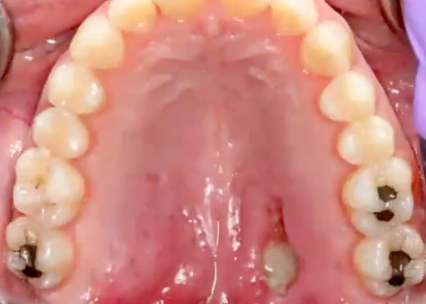
sialolithiasis
what is the diagnosis
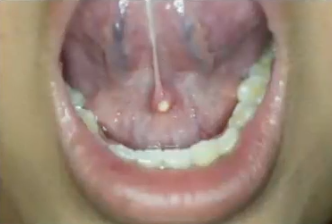
sjogren syndrome
what is the diagnosis
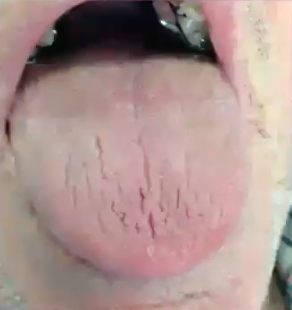
pleomorphic adenoma
slowly growing lesion, been present for over 10 year, What is the diagnosis?
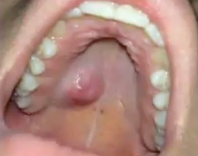
traumatic neuroma
a reative proliferation due to damage to the nerve
near mental foramen
most common location of traumatic neuroma
irritation fibroma
most common soft tissue lesion in oral cavity
irritation fibroma
reactive hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue due to irritation
cheek
most common location of irritation fibroma
surgical excision
treatment of irritation fibroma
surgical excision
treatment of traumatic neuroma
giant cell fibroma
papillary tumor with sessile or peduculated base sometimes mistaken for papilloma
giant cell fibroma
occurs in younger age group, diagnosis?
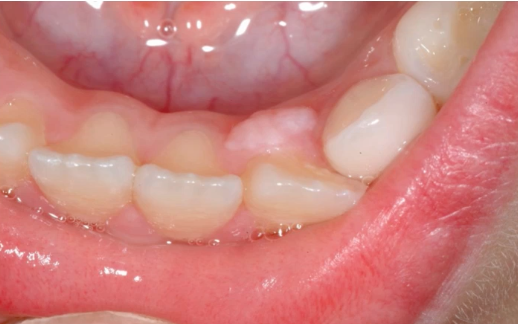
inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia/ epulis fissuratum
reactive folds is fibrous connective tissue associated with flanges of ill fitting or over extended dentures
inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia/ Epulis fissuratum
diagnosis?
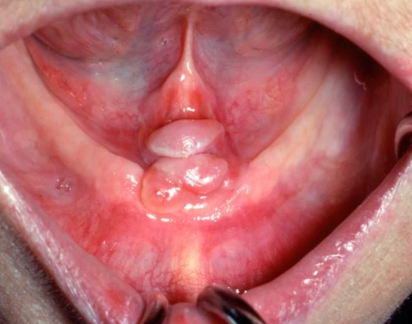
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia/ denture papillomatosis
reative response of palatal mucosa due to ill fitting denture, poor hygiene, or wearing dentures 24 hours/day
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
diagnosis?
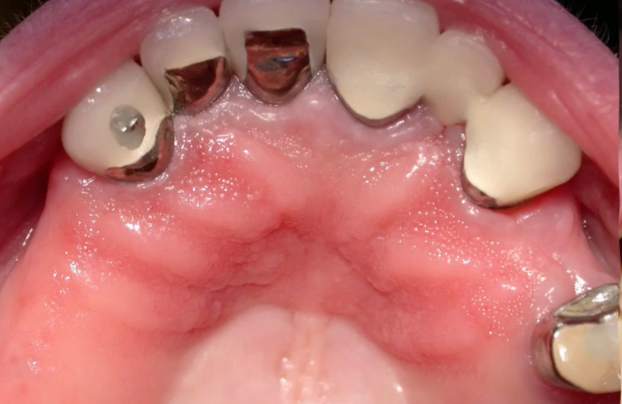
peripheral ossifying fibroma (POF)
exclusively on gingiva, reactive gingival overgrowth
peripheral ossifying fibroma
diagnosis?
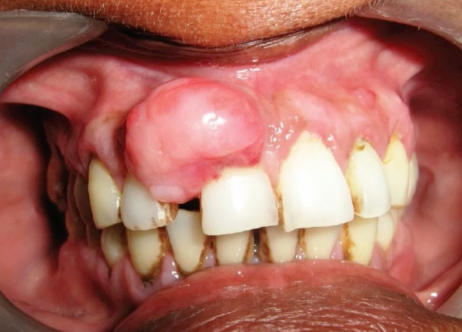
peripheral giant cell granuloma
reddish-purple sessile mass exclusively on gingiva, cupping resorption of underlying bone