343: Osmoregulation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Osmoconformers
organisms that maintain internal osmotic balance by matching their body fluid concentration to that of their surrounding environment, often found in marine environments.
Osmoregulators
organisms that actively regulate their internal osmotic pressure by controlling the concentration of solutes and water in their bodies, allowing them to thrive in various environments.
Hypertonic
cell shrinks and wrinkles up.
hypotonic
cells swells up and bursts
isotonic
solution where the concentration of solutes is equal inside and outside the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
Kidneys
major excretory organs that consist of tubular elements. produce and void aqueous solutions derived from blood which regulates that composition and volume of blood.
Uretors
tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Urinary bladder
temporarily stores urine
Urethra
transport urine out of the body.
Urine is a solution of various organic and inorganic solutes and water that blood does not want.
water in urine is composed of
the amount that is required to accompany excreted solutions and an amount that is additional that may/may not be excreted / regulated
urea
amino acid breakdown
creatinine
metabolized creatine
What are normal solutes found in urine?
Na, K, PO4, SO4, Ca, Mg, HCO
What should not be found in urine?
blood, WBCs, bile pigments
Nephrons
are the functional units of the kidney that filter blood and produce urine.
Nephrons consist of ?
renal corpuscle and renal tubule
renal corpuscle
is the initial filtering component of the nephron
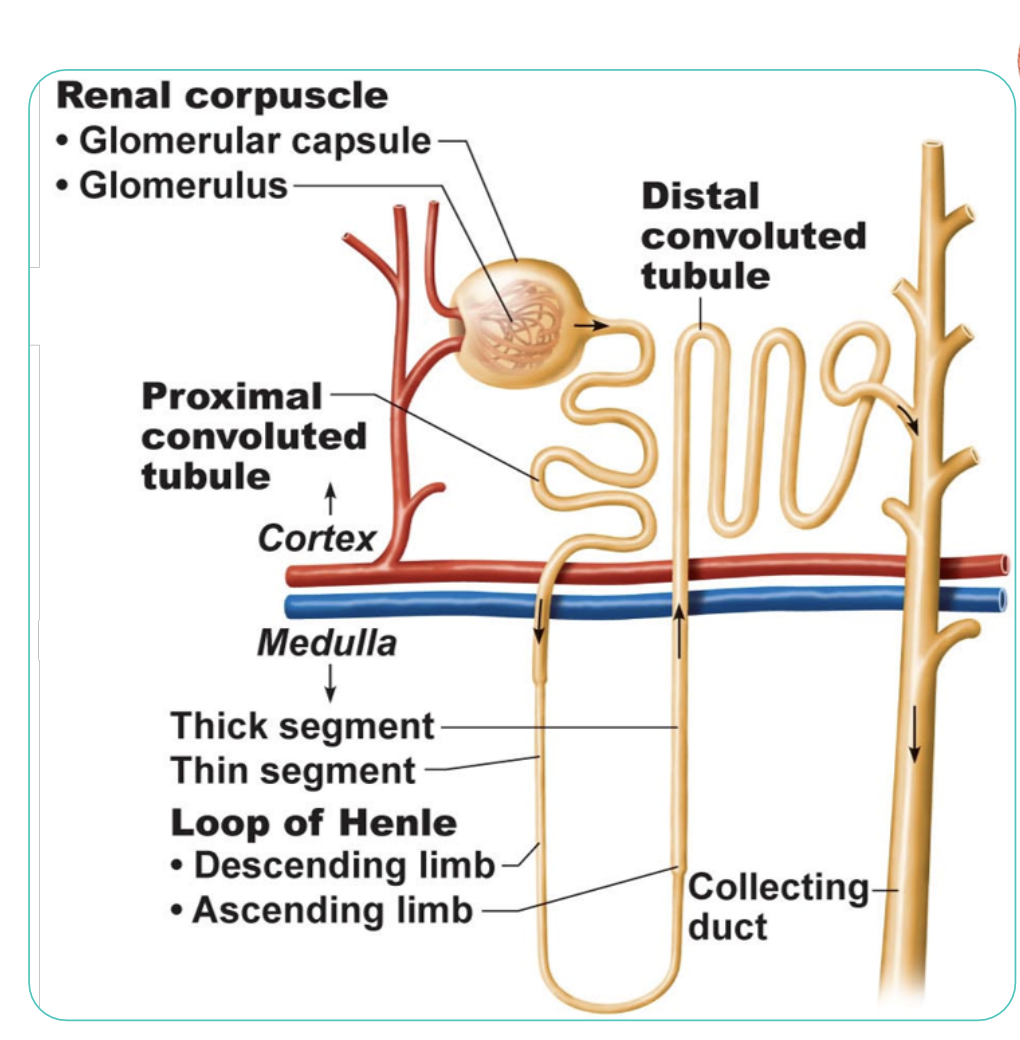
Glomerculus
is a network of capillaries within the renal corpuscle that facilitates the filtration of blood.
Glomercular filtration (1)
is a passive process in which hydrostatic pressure higher in the glomerculus forces fluids and solutes through filtration. Reabsorption does not happen here! glucose, ions, amino acids can pass though
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) (2)
is the segment of the nephron following the glomerulus where significant reabsorption of water, ions, and nutrients occurs.
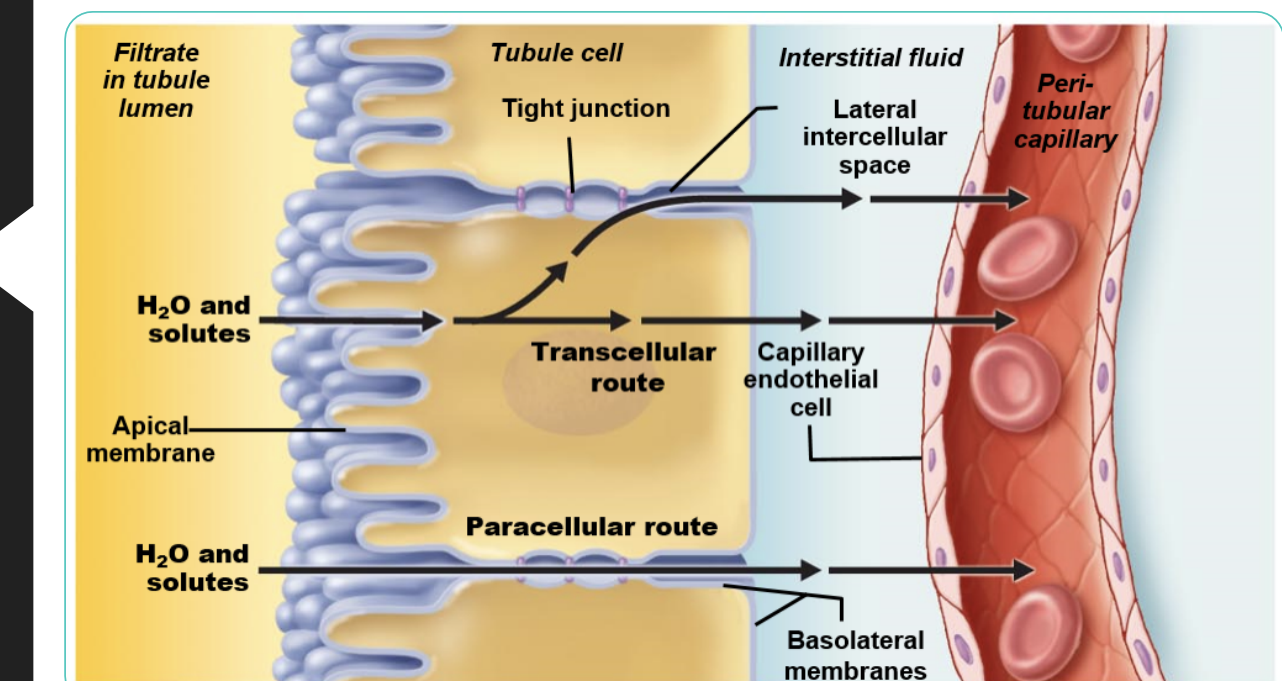
Transcellular reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule
is the process by which substances are reabsorbed from the filtrate through the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule.
Explain how transcellular reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule works
substances enter on the apical side of the cell, then pass through the cytoplasm, and exit into the interstitial fluid via the basolateral membrane and picked up by the bloodstream. This process is a form of secondary active transport.
Glucose reabsorption
transport max is the maximum rate at which glucose can be reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule, determined by the number of available transport proteins.
glycosuria
too much glucose in the urine
A glucose molecule is placed in breaker with 100mOsm/L. Its separated by a semipermeable membrane which has an osmotic pressure of 150 mOsm/L. Which way will the molecule want to travel?
The glucose molecule will travel from the area of lower osmotic pressure (100 mOsm/L) to the area of higher osmotic pressure (150 mOsm/L) through the semipermeable membrane.