nuclear physics
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
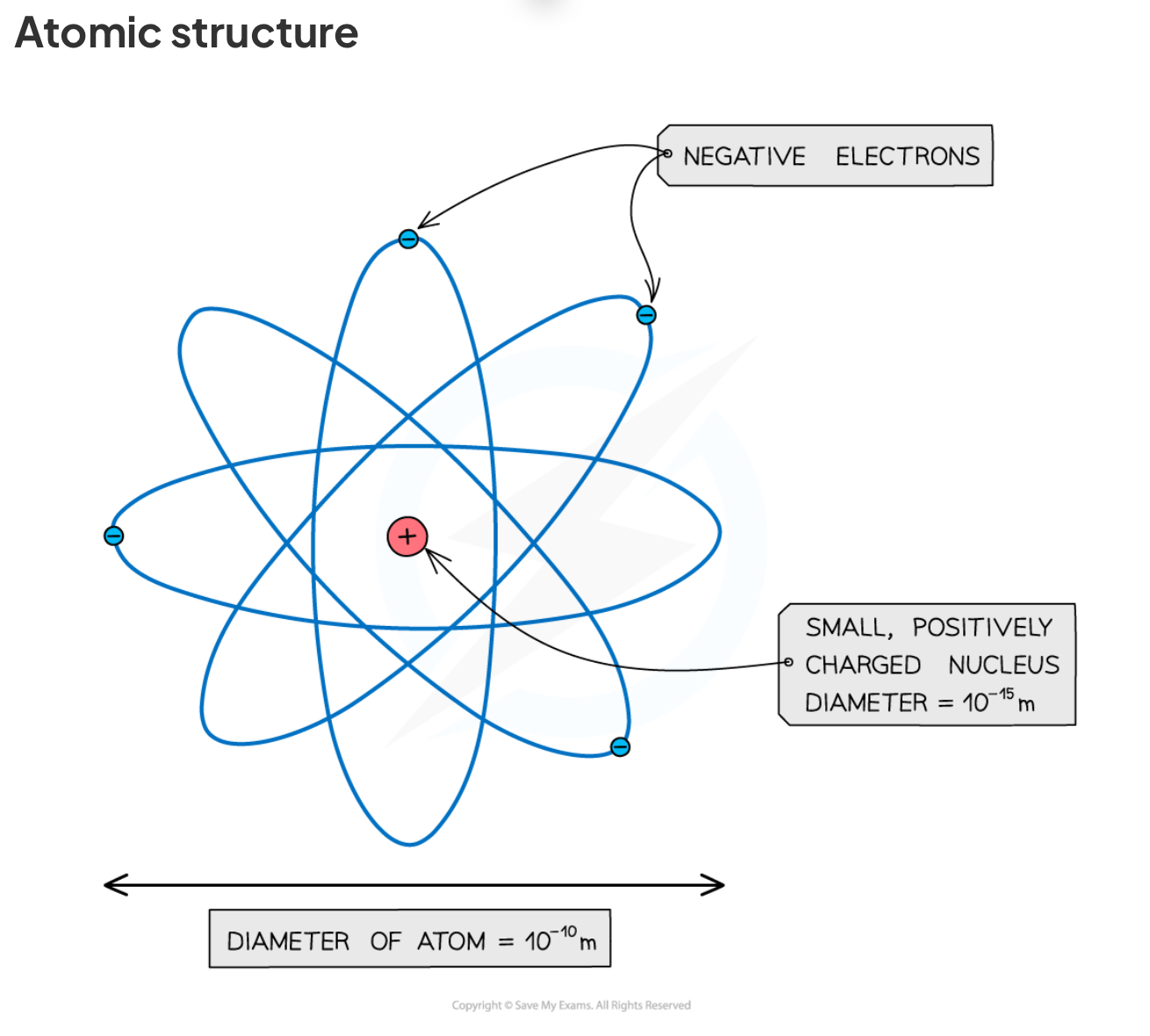
Describe the structure of an atom
Atoms are the building blocks of all matter
They consist of a small dense positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons in orbit around the nucleus
How can atoms form positive or negative ions
When an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion, when an atom gains electrons it forms a negatively charged ion
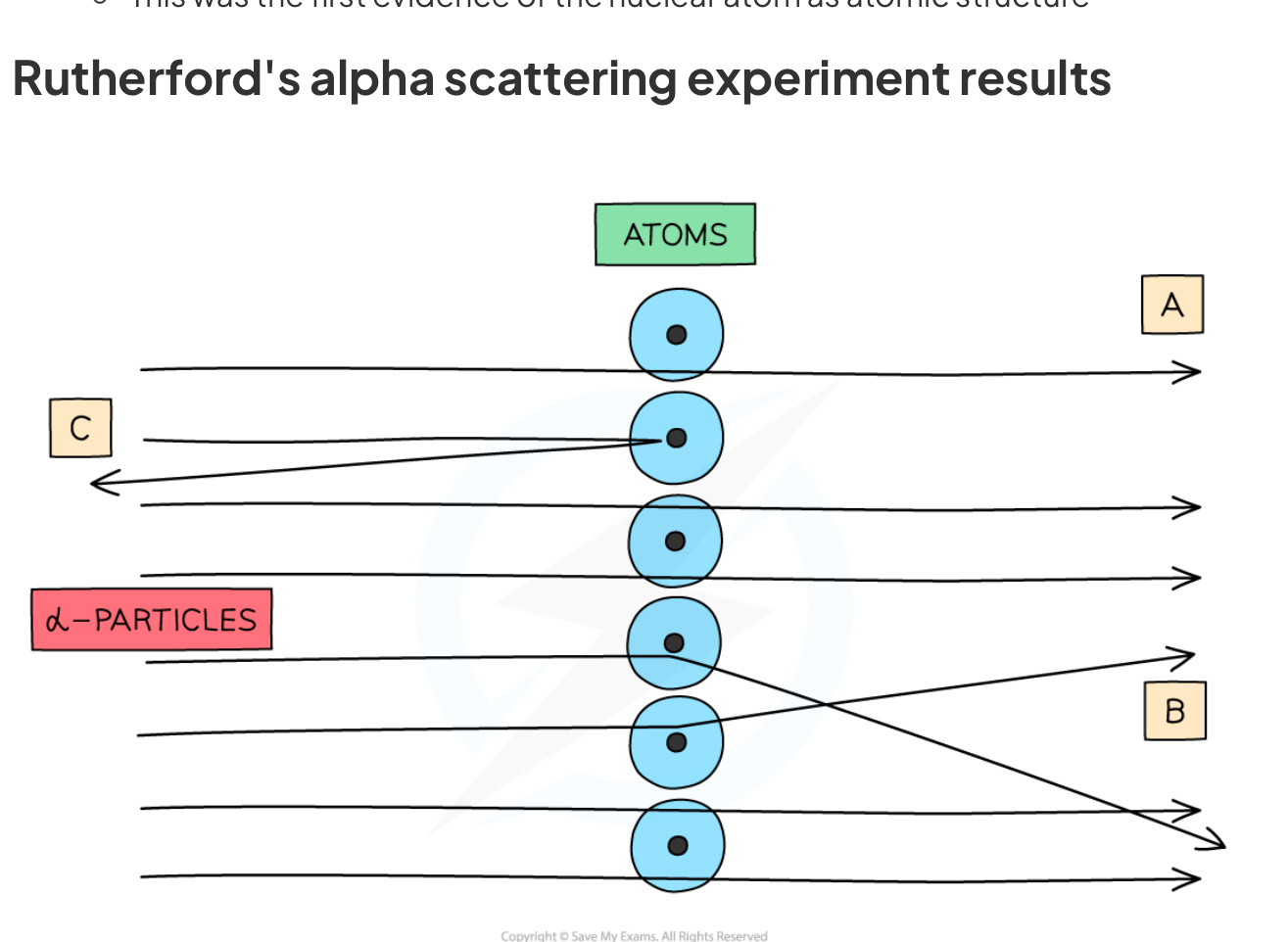
Describe how the scattering alpha particles by a sheet of thin metal supports the nuclear model of the atom
As shown in the diagram, instead they discovered that :
Most of the alpha particles passed straight through the foil because the atom is mostly empty space (A)
Some of the alpha particles were deflected (changed direction) as they passed through the foil because they came close to the positively charged nucleus, which repelled the positively charged alpha particles (B)
A few of the alpha particles bounced back off the gold foil because the nucleus is tiny
Describe the composition of the nucleus in terms of protons and neutrons
A nucleus is composed of positively charged protons and neutrally charged neutrons. Therefore the nucleus has a positive charge
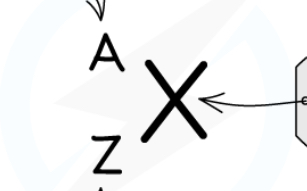
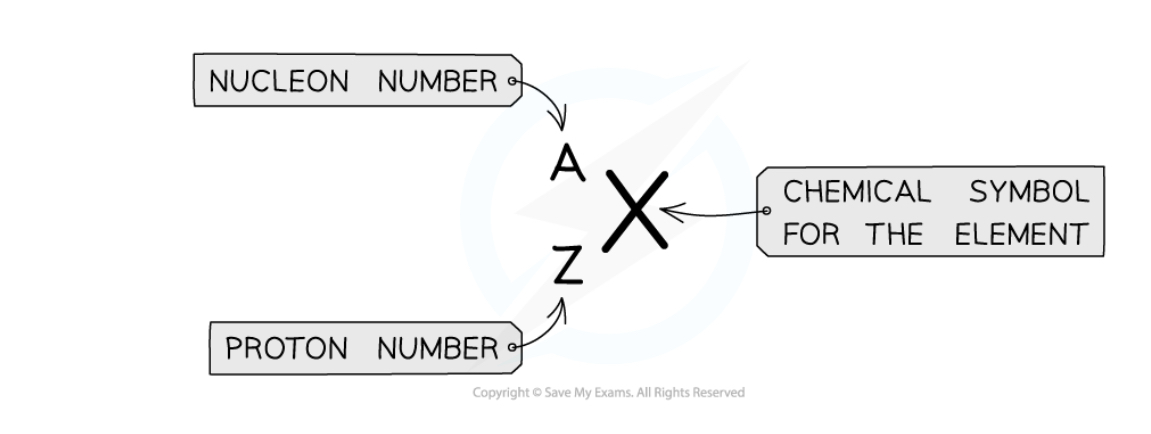
Label the nuclide notation
State the relative charges of protons, neutrons and electrons
Protons= +1
Electrons = -1
Neutrons= 0
Explain what is meant by the term isotope
Although the number of protons in a particular element is always the same, the number of neutrons can be different
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have an equal number of protons but a different number of neutrons
This means that each element can have more than one isotope
Isotopes tend to be more unstable due to their imbalance of protons and neutrons
Describe the process of nuclear fission and fusion
Nuclear fission is defined as:
The splitting of a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei
Nuclear fusion is defined as:
When two light nuclei join to form a heavier nucleus
State an equation of nuclear fusion
The amount of energy released during nuclear fusion is huge:
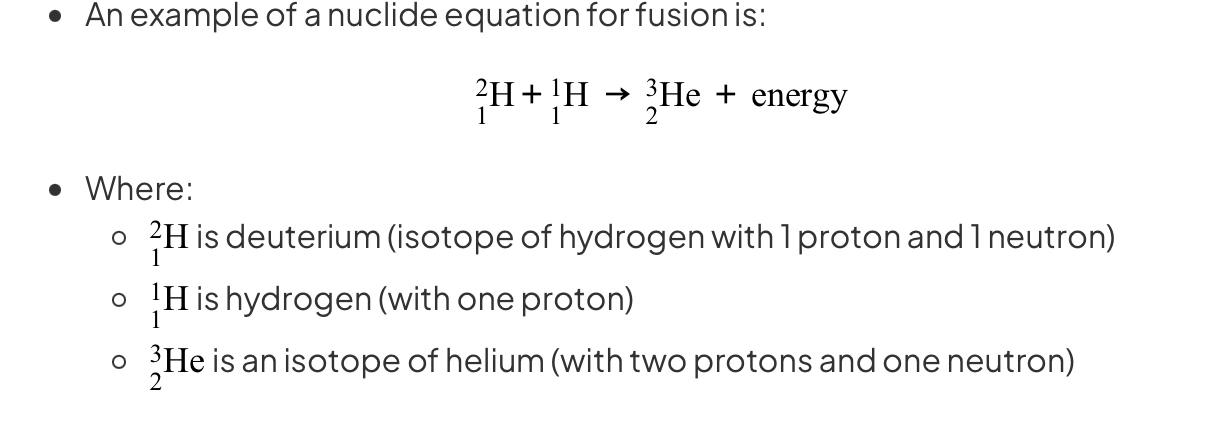
State an equation for nuclear fission
The mass of the products is less than the mass of the original nucleus
This is because the remaining mass has been converted into energy, which is released during the fission process

What is the relationship between proton number and the relativ charge of the nucleus
What is the relationship between nucleon number and relative mass of the nucleus
The relative mass of the nucleus is approximately equal to the nucleon number (A) because both protons and neutrons (nucleons) each have a relative mass of approximately 1, and the mass of the orbiting electrons is negligible
What is meant by background radiation
What are the sources that contribute to backround information
a) radon gas (in the air)
b) rocks and buildings
c)foods and drinks
d) cosmic rays
How can ionizing nuclear radiation be measured
Ionizing nuclear radiation can be measured by using a detector connected to a counter. A count rate is measured in counts/s or counts/min
5
Describe the emission of radiation from a nucleus