EX2 MALDIGESTION, GERD, GALLBLADDER DISEASE
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
MALDIGESTION
what digestive problems/disorders contribute to maldigestion?
GERD, Gallbladder disease (also pancreatitis, and stomach surgeries may contribute)
what are the main 2 factors that contribute to maldigestion?
mechanical failures and enzymatic/chemical failures
which digestive problems/disorder are maldigested due to enzymatic/chem failures?
Pancreatitis (may lead to fat malabsorption)
Stomach surgery (may lead to dumping syndromes)
GERD
for maldigestion, what is important concerning nutrition assessment (athropometrics)
weight history
for maldigestion, what is important concerning nutrition assessment (biochem )
Anemia labs, electrolytes, micronutrients of potential concern
for maldigestion, what is important concerning nutrition assessment (client history)
Other digestive or surgical history that may impact condition
for maldigestion, what is important concerning nutrition assessment (dietary assessment)
Probe for food intolerance and/or meal intolerance: Rapid fullness, belching, etc.
Dietary factors that are associated with worsened symptoms
N/V/D
for maldigestion, what is important concerning nutrition assessment (nutrition-focused physical)
Affect, overall view, oral cavity (pallor, erosion), muscle or adipose wasting (malnutrition exam)
what are potential nutritional diagnosis for GI issues/disease
Inadequate oral intake
Inadequate fluid intake
Intake of types of carbohydrates inconsistent with needs (simple sugars)
Excessive fiber intake
Excessive fat intake
Altered GI function
Food and nutrition-related knowledge deficit
Undesirable food choices
Limited adherence to nutrition-related recommendations (only once they have been told and still have not adhered)
nutrition intervention/ MNT for patients with symptoms of maldigestion
promote adequate intake (alter diet?)
nutrition education (on dietary modifications)
nutrition counseling (motivational interviewing, goal-setting)
coordination of care (referrals to other disciplines or support where needed)
GERD
what is GERD?
Reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus
common symptoms of GERD include:
other symptoms include:
common: Heartburn, regurgitation of acid
other: Abdominal pain, bad breath, epigastric pressure, chronic cough, sore throat, dental erosions, wheezing, or difficulty swallowing/dysphagia
the main issue with GERD is that severe GERD may lead to
Barret’s esophagus which is a pre-cancerous condition of the esophagus which can then become cancer
what causes GERD (simple)
multifactorial
what lifestyle factors contribute to GERD
obesity
smoking
tight clothes
what functional/bodily factors contribute to GERD
Anything contributing to incompetence or transient relaxations of the LES
Factors increasing gastric pressure (weaken LES)
what is hiatal hernia?
Pushing of the stomach up through a weakened opening in the esophagus
what factors effect LES competence (6 + others)
increased secretion of gastrin, estrogen, progesterone (in pregnancy)
pregnancy
smoking
dietary fat
alcohol
caffeine
other: coffee, tea, chocolate, spearmint, peppermint, capsaicin, black and red pepper
factors that increase gastric pressure (6)
Hiatal hernia
Scleroderma
Obesity
Pregnancy
Delayed gastric emptying (gastroparesis, gastric outlet obstruction)
Overeating
lifestyle modifications for GERD (5)
Sitting upright after meals (30 minutes to 3 hours)
Weight loss if have overweight or obesity
Quit smoking
Elevate HOB (head-of-bed)
Loose-fitting clothing
MNT focuses on what regarding GERD
reducing foods that decrease LES pressure or cause transient relaxation
what are ways we can help decrease LES pressure/transient relaxation? (4)
food diary to identify key triggers
basic elimination diet
smaller, more frequent meals (decrease stomach fullness)
less fluid intake with meals (decrease stomach fullness)
what types of medications are used for GERD (4)
antacids, H2 agonist, PPI’s, prokinetics
Antacids
what are antacids
what do they do
issues
made up of magnesium, calcium, and aluminum (Tums, MOM, Maalox)
neutralize acids chemically
may contribute to diarrhea or constipation
H2 agonist
what are H2 agonist
what do they do
effectiveness?
Tagamet, Pepcid, Zantac 360 (HCl)
Block histamine receptors that stimulate acid
Effective for about 50% of GERD sufferers
PPI’s
names
function
risk
prisolec, protonix, prevacid
block k/ATPase enzymes-stopping HCL production
associated with lower Ca consumption (risk of fractures) and higher risk for CKD
prokinetics
function
issues
Promote motility
Can have extrapyramidal symptoms; drug-induced movement disorders (dystonia); and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS; fever, confusion, muscle stiffness, irregular heartbeat)
for patients on PPI’s what is encouraged
increase of dietary calcium (more absorbable, especially with meal)
calcium citrate supplement (does not require acid)
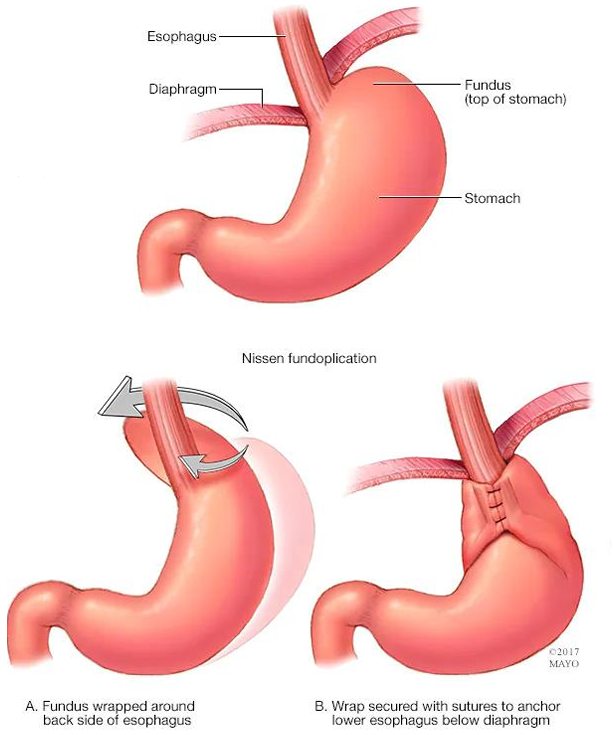
what is the surgical procedure for GERD
Nissen fundoplication
which wraps the stomach around the esophagus but this can loosen over time and limits ability to vomit SO is not commonly used
GALLBLADDER DISEASE
what are the risk factors for gallbladder disease*** (7)
>65 years old
woman have 2x risk
obese
pregnant
diabetic
western diet increases risk
rapid weight loss or surgery
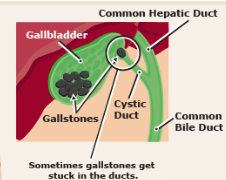
what causes gallstones?
too much absorption of water from bile
too much absorption of bile acids from bike
too much cholesterol in bile
inflammation of epithelium
what are the 4 types of gallbladder disease?
in order from lowest to highest severity
cholelithiasis
cholecystitis
choledochonlithiasis
cholangitis
-lithiasis means
-itis means
-thiasis = stone
-itis= inflammation
what is cholecystectomy
removal of the gallbladder
what is cholelithiasis?
the presence of gallstone in the gallbladder or biliary duct
but no inflammation
cholelithiasis symptoms
RUQ pain (colicky-not continuous)
what is cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder due to stones
usually due to blockage
cholecystitis symptoms
RUQ pain (constant), fever, leukocitis (high WBC)
choledocholithiasis is what
the presence of gallstone in the common bile duct (CBD)
but usually no inflammation
choledocholithiasis symptom
obstructive jaundice, no major pain, no fever or leukocytosis
choledocholithiasis can lead to (3)
obstructive jaundice
secondary biliary cirrhosis
dilated hepatic bile duct
what is cholangitis
cholelithiasis + infection
cholangitis symptoms (2 categories)
Charcot’s Triad
Fever, Jaundice, RUA pain
can progress
Reynold’s Pentad
Fever, Jaundice, RUA pain
Hypotension
Cognitive impairment
what does cholelithiasis and/or cholecystectomy cause
decreased ability to digest fat (long-chain FA) presented by indigestion pain
MNT for gallbladder disease (4)
reduce dietary fat intake if causes symptoms
low fat diet (<30% fat) with modest protein (aid in controlling symptoms until surgery)
small, frequent meals
gradual weight loss indicated