Chemistry CT2 - Stoichiometry, Chemical energetics, metals, chemistry of the environment, organic chemistry 12.1 and 12.2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
Relative atomic mass, Ar
is the average mass of the isotopes of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of 12C.
2
New cards
molecular formula
The molecular formula of a compound is defined as the number and type of different atoms in one molecule.
3
New cards
Relative molecular mass, Mr
is the sum of the relative atomic masses. Relative formula mass, Mr , is used for ionic compounds.
4
New cards
Relative formula mass, Mr
Relative formula mass, Mr , is used for ionic compounds
5
New cards
mole
The mole, symbol mol, is the unit of amount of substance. 1 mole contains 6.02 × 1023 particles, e.g. atoms, ions, molecules. This number is called the Avogadro constant.
6
New cards
Petroleum
Petroleum is a mixture of hydrocarbons.
7
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain hydrogen and carbon only.
8
New cards
organic compounds.
These carbon compounds form the basis of a group called organic compounds. All living things are made from organic compounds based on chains of carbon atoms similar to those found in petroleum
9
New cards
fractional distillation
Chemists use a technique called fractional distillation to separate the different fractions. The different components (fractions) separate because they have different boiling points.
10
New cards
the properties of the fractions obtained from this fractional distillation change from the bottom to the top of the tower with:
» lowering boiling points
» higher volatility
» lower viscosity
» decreasing chain length.
» higher volatility
» lower viscosity
» decreasing chain length.
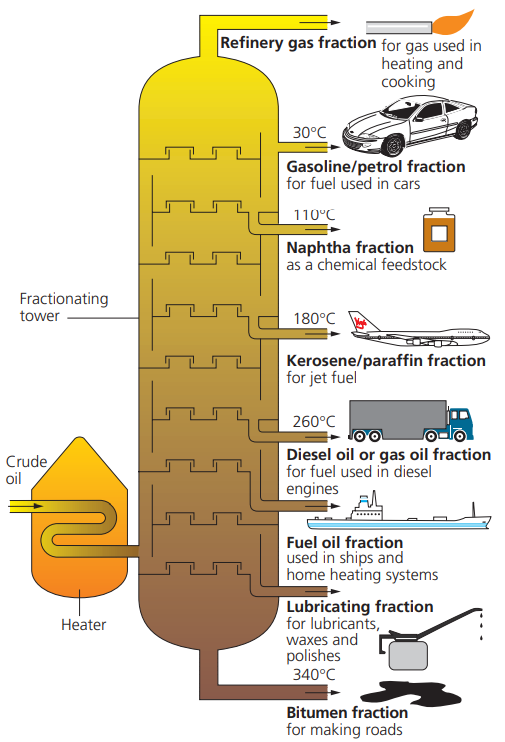
11
New cards
fuel
A fuel is any substance which can be conveniently used as a source of energy. Fossil fuels release energy in the form of heat when they undergo combustion.
12
New cards
Alternative sources to fossil fuels
* nuclear
* hydroelectric
* biomass and biogas
* hydrogen
* wind
* tidal
* wave
* geothermal
* solar.
* hydroelectric
* biomass and biogas
* hydrogen
* wind
* tidal
* wave
* geothermal
* solar.
13
New cards
Exothermic and endothermic reactions
Combustion - exothermic
cold pack is used to treat a sprain - endothermic
cold pack is used to treat a sprain - endothermic
14
New cards
exothermic reaction
An exothermic reaction transfers thermal energy to its surroundings, leading to an increase in the temperature of the surroundings.
\
The negative sign shows that the chemicals are losing energy to the surroundings: it is an exothermic reaction.
\
The negative sign shows that the chemicals are losing energy to the surroundings: it is an exothermic reaction.
15
New cards
endothermic reaction
An endothermic reaction transfers thermal energy from the surroundings leading to a decrease in the temperature of the surroundings.
16
New cards
bond energy
The bond energy is defined as the amount of energy in kilojoules (kJ) associated with the breaking or making of 1 mole of chemical bonds in a molecular element or compound.
17
New cards
enthalpy change of reaction
The transfer of thermal energy during a reaction is called the enthalpy change, ΔH, of the reaction. Bond breaking is an endothermic process and bond making is an exothermic process. The enthalpy change of a reaction is the difference between the energy required to break bonds and the energy given out when bonds are made.
18
New cards
activation energy,
The activation energy, Ea , is the minimum energy that colliding particles must have in order to react.
19
New cards
A reaction pathway diagram for methane with oxygen
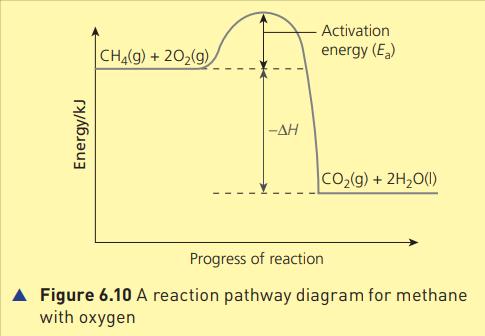
20
New cards
A reaction pathway diagram for nitrogen with oxygen
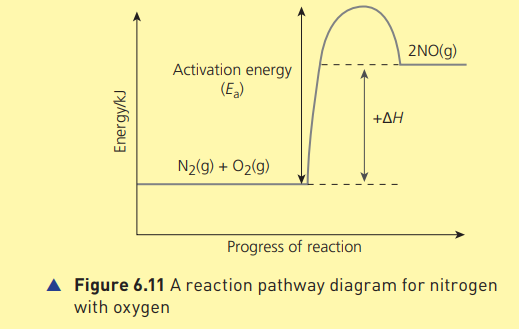
21
New cards
Properties of metals
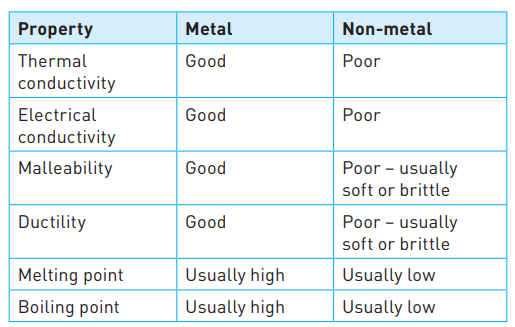
22
New cards
Metal reactions
* With acid
* With air/oxygen
* With cold water/steam
* With air/oxygen
* With cold water/steam
23
New cards
Metal With acid
* hydrogen gas
* metal salt
* metal salt
24
New cards
Metal With air/oxygen
metal oxide
25
New cards
Metal With cold water/steam
water
* metal hydroxide
* hydrogen gas
* with unreactive
steam
* metal oxide
* hydrogen
* moderately reactive
* metal hydroxide
* hydrogen gas
* with unreactive
steam
* metal oxide
* hydrogen
* moderately reactive
26
New cards
Order of reactivity
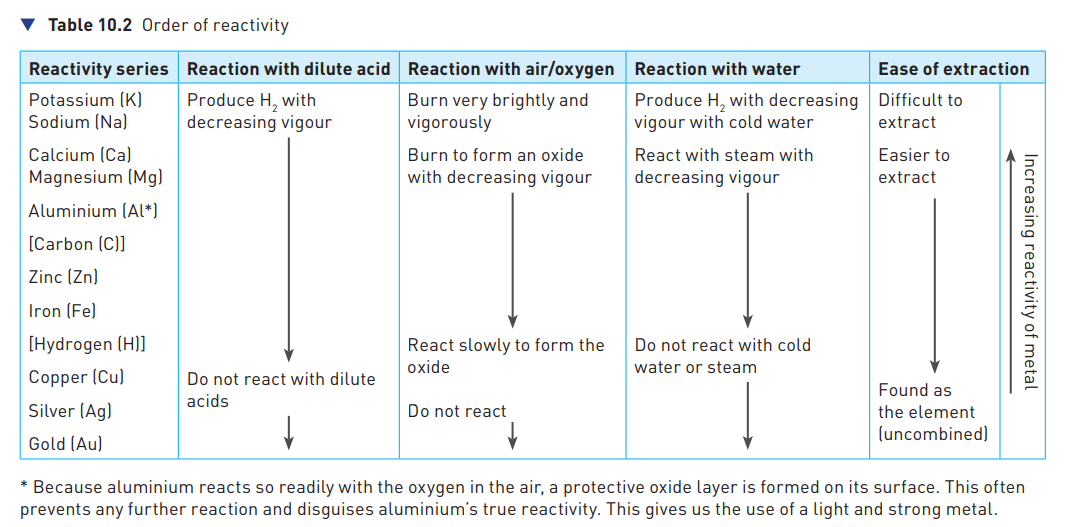
27
New cards
Aluminium
* has a protective oxide coating on its surface
* manufacture of cars, aircraft and overhead electricity cables, because of its low density and good electrical conductivity
* \
* manufacture of cars, aircraft and overhead electricity cables, because of its low density and good electrical conductivity
* \
28
New cards
sodium and potassium
* so reactive that they have to be stored under oil to prevent them from coming into contact with water or air.
* they have low melting points and are good conductors of heat, they are used as coolants for nuclear reactors.
* they have low melting points and are good conductors of heat, they are used as coolants for nuclear reactors.
29
New cards
Identifying metal ions
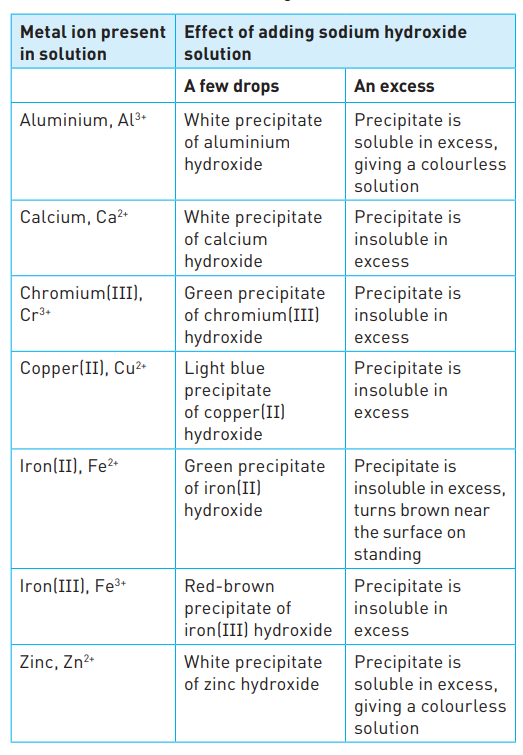
30
New cards
Extraction of metals
31
New cards
Extraction of iron
* A blast of hot air is sent in near the bottom of the furnace through holes which makes the ‘charge’ glow, as the coke burns in the preheated air.
* C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
* CaCO3 (s) → CaO(s) + CO2 (g)
* CO2 (g) + C(s) → 2CO(g)
* Carbon monoxide is a reducing agent. It rises up the furnace and reduces the iron(III) oxide ore. This takes place at a temperature of around 700°C:
* Fe2 O3 (s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2 (g)
* CaO(s) + SiO2 (s) → CaSiO3 (s)
* The slag trickles to the bottom of the furnace, but because it is less dense than the molten iron, it floats on top of it.
* C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
* CaCO3 (s) → CaO(s) + CO2 (g)
* CO2 (g) + C(s) → 2CO(g)
* Carbon monoxide is a reducing agent. It rises up the furnace and reduces the iron(III) oxide ore. This takes place at a temperature of around 700°C:
* Fe2 O3 (s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2 (g)
* CaO(s) + SiO2 (s) → CaSiO3 (s)
* The slag trickles to the bottom of the furnace, but because it is less dense than the molten iron, it floats on top of it.
32
New cards
Rusting
* Rust is an orange–red powder consisting mainly of hydrated iron(III) oxide (Fe2 O3 .xH2 O).
* Both water and oxygen are essential for iron to rust, and if one of these two substances is not present then rusting will not take place. The rusting of iron is encouraged by salt.
* Both water and oxygen are essential for iron to rust, and if one of these two substances is not present then rusting will not take place. The rusting of iron is encouraged by salt.
33
New cards
Rust prevention
* painting
* coating with plasic
* oiling/greasing
* Galvanising
* coating with plasic
* oiling/greasing
* Galvanising
34
New cards
Rusting experiment with nails
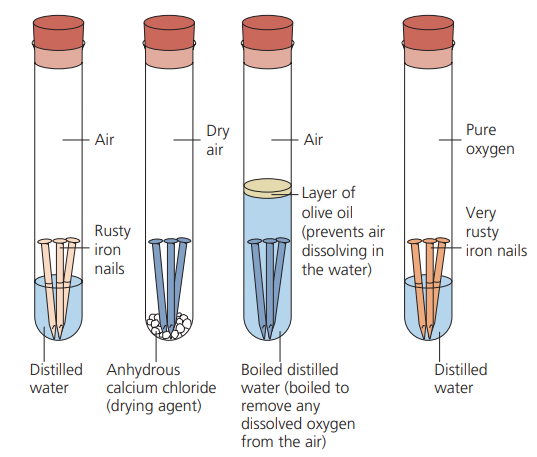
35
New cards
Corrosion
* Corrosion is the general name given to the process which takes place when metals and alloys are chemically attacked by oxygen, water or any other substances found in their immediate environment.
* The lower metals in the reactivity series will corrode to a lower extent.
* Magnesium, calcium and aluminium are usually covered by a thin coating of oxide after initial reaction with oxygen in the air.
* The lower metals in the reactivity series will corrode to a lower extent.
* Magnesium, calcium and aluminium are usually covered by a thin coating of oxide after initial reaction with oxygen in the air.
36
New cards
Alloys
Alloys can be harder or stronger than pure metals and are more useful.
* by mixing together metals which have different-sized atoms to form the alloy, the metal no longer has a repeating structure.
* Metal is malleable and ductile because its layers are able to move over one another.
* In an alloy, the different-sized atoms mean that the layers can no longer slide over each other, causing the alloy to have less malleability and ductility.
\
Brass 65% copper, 35% zinc Jewellery, machine bearings, electrical connections, door furniture
Bronze 90% copper, 10% tin Castings, machine parts
* by mixing together metals which have different-sized atoms to form the alloy, the metal no longer has a repeating structure.
* Metal is malleable and ductile because its layers are able to move over one another.
* In an alloy, the different-sized atoms mean that the layers can no longer slide over each other, causing the alloy to have less malleability and ductility.
\
Brass 65% copper, 35% zinc Jewellery, machine bearings, electrical connections, door furniture
Bronze 90% copper, 10% tin Castings, machine parts
37
New cards
Water
* Pure water is a neutral, colourless liquid which (at 1 atmosphere pressure) boils at 100°C and freezes at 0°C (Figure 11.3).
* If you try boiling tap water, you will find that it does not boil at exactly 100°C. This is because it is a very good solvent and dissolves many substances. It is the **presence of these impurities** that causes a change in the boiling point compared to pure water.
* Distilled water is therefore used in many experiments in the laboratory because it is very pure and does not contain many of these impurities, which may affect the outcome of the experiments.
* If you try boiling tap water, you will find that it does not boil at exactly 100°C. This is because it is a very good solvent and dissolves many substances. It is the **presence of these impurities** that causes a change in the boiling point compared to pure water.
* Distilled water is therefore used in many experiments in the laboratory because it is very pure and does not contain many of these impurities, which may affect the outcome of the experiments.
38
New cards
The unique properties of water
» It has an unusually high boiling point for a molecule of its relatively low molecular mass.
» It has a greater specific heat capacity than almost any other liquid.
» It decreases in density when it freezes.
» It has a greater specific heat capacity than almost any other liquid.
» It decreases in density when it freezes.
39
New cards
Water contains :-
* carbon dioxide and oxygen
* nitrates and phosphates from agricultural waste and detergents. The nitrates and phosphates encourage the growth of algae which eventually die and decay, removing oxygen from the water (deoxygenation).
* metal compounds from industrial waste water
* human waste from sewage
* insoluble impurities such as oil and plastic waste
* nitrates and phosphates from agricultural waste and detergents. The nitrates and phosphates encourage the growth of algae which eventually die and decay, removing oxygen from the water (deoxygenation).
* metal compounds from industrial waste water
* human waste from sewage
* insoluble impurities such as oil and plastic waste
40
New cards
The processes involved in water treatment
1. Impure water is passed through **screens** to filter out floating debris.
2. ==**Aluminium sulfate**== is added to coagulate small particles of clay so that they form larger clumps, which settle more rapidly.
3. Filtration through ==**coarse sand traps**== larger, insoluble particles. The sand also **contains specially grown microbes** which remove some of the bacteria.
4. A sedimentation tank has chemicals known as ==**flocculants, for example, aluminium sulfate,**== added to it to make the smaller particles (which remain in the water as colloidal clay) stick together and sink to the bottom of the tank.
5. These particles are removed by further filtration through ==**fine sand**==. This is followed by ==**carbon slurry filters**== which are there to remove unwanted tastes and odours, and a lime slurry is used to adjust the acidity.
6. Finally, a little ==**chlorine gas**== is added, which sterilises the water and kills any remaining bacteria. Excess chlorine can be removed by the addition of sulfur dioxide gas. The addition of chlorine gas makes the water more acidic and so appropriate amounts of ==**sodium hydroxide solution**== are added. ==**Fluoride**== is sometimes added to water if there is insufficient occurring naturally, as it helps to prevent tooth decay.
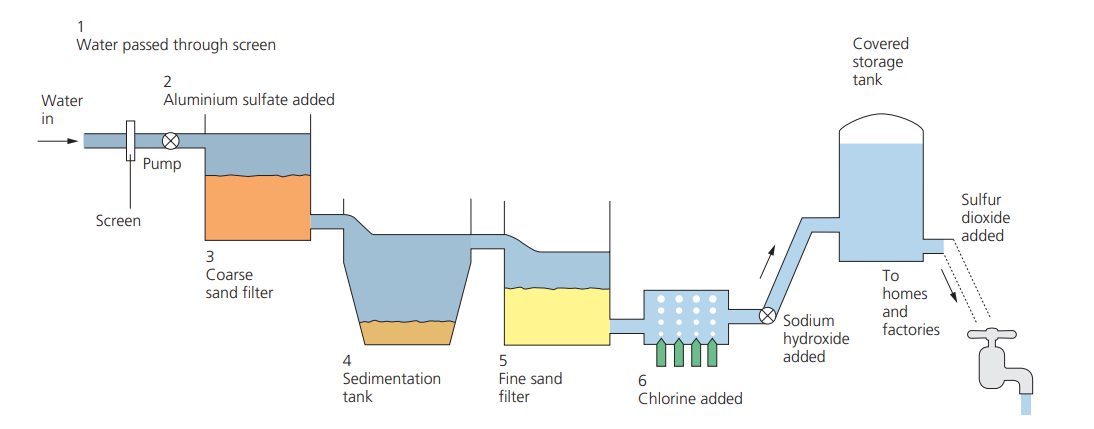
41
New cards
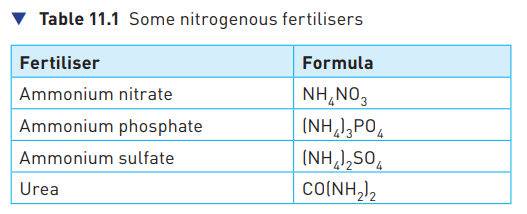
Fertiliser
Fertiliser is a chemical put onto soil to replace lost mineral salts and so make plants grow more healthily. These include ammonium salts, such as ammonium nitrate, which is one of the most commonly used fertilisers.
42
New cards
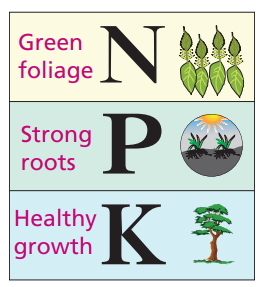
NPK
43
New cards
Leaching
* If too much fertiliser is applied to the land, rain washes the fertiliser off the land and into rivers and streams. This is known as leaching.
* This leaching leads to eutrophication: the process that occurs when fertiliser is leached, causing algae to multiply rapidly and causing the water to turn green.
* As the algae die and decay, oxygen is removed from the water, leaving insufficient amounts for fish and other organisms to survive.
* In extreme cases, no normal aquatic life can survive. There are also worries about the effect of agricultural fertilisers, especially nitrates such as ammonium nitrate, on the public water supply.
* This leaching leads to eutrophication: the process that occurs when fertiliser is leached, causing algae to multiply rapidly and causing the water to turn green.
* As the algae die and decay, oxygen is removed from the water, leaving insufficient amounts for fish and other organisms to survive.
* In extreme cases, no normal aquatic life can survive. There are also worries about the effect of agricultural fertilisers, especially nitrates such as ammonium nitrate, on the public water supply.
44
New cards
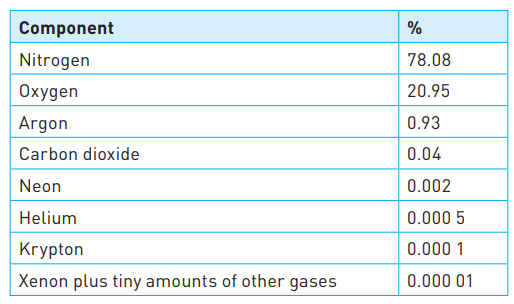
The composition of the atmosphere
45
New cards
Sources of carbon dioxide in the air
* It is also produced by all living organisms.
* Animals take in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is taken in by plants through their leaves and used together with water, taken in through their roots, to synthesise glucose (a sugar).
* produced through burning fossil fuels and the deforestation of large areas of tropical rainforest.
\
* The Earth’s climate is affected by the levels of carbon dioxide (and water vapour) in the atmosphere. If the amount of carbon dioxide, in particular, builds up in the air, it is thought that the average temperature of the Earth will rise, causing global warming. This effect is thought by scientists to be caused by the greenhouse effect. This important topic will be discussed further later in this chapter on p. 183.
* Animals take in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is taken in by plants through their leaves and used together with water, taken in through their roots, to synthesise glucose (a sugar).
* produced through burning fossil fuels and the deforestation of large areas of tropical rainforest.
\
* The Earth’s climate is affected by the levels of carbon dioxide (and water vapour) in the atmosphere. If the amount of carbon dioxide, in particular, builds up in the air, it is thought that the average temperature of the Earth will rise, causing global warming. This effect is thought by scientists to be caused by the greenhouse effect. This important topic will be discussed further later in this chapter on p. 183.
46
New cards
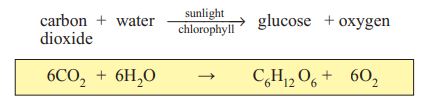
Photosynthesis
This is the process of photosynthesis. It takes place only in sunlight and only in green leaves, as they contain chlorophyll (the green pigment) which catalyses the process.
47
New cards
Pollution caused by motor vehicles
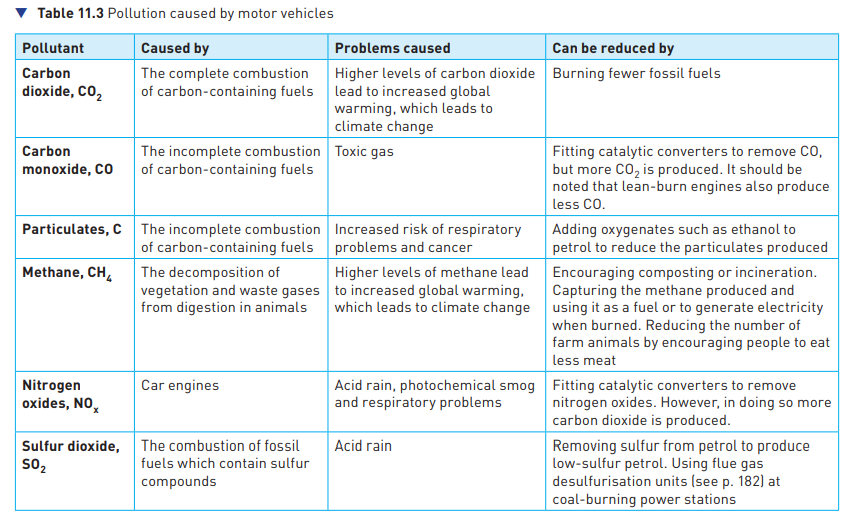
48
New cards
Catalytic converters
* In recent years, regulations have been introduced worldwide which state that all new cars have to be fitted with catalytic converters as part of their exhaust system.
* Car exhaust fumes contain pollutant gases, such as carbon monoxide (CO), formed from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons(Cx Hy ) in the fuel, and nitrogen(II) oxide (NO) formed by the reaction of nitrogen gas and oxygen gas from the air.
* They are also involved in the production of photochemical smogs which occur worldwide in major cities, especially in the summer. Photochemical smog is the most widely known and perhaps most serious air pollutant. It is formed in the atmosphere by the reaction between gaseous pollutants, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons.
* Car exhaust fumes contain pollutant gases, such as carbon monoxide (CO), formed from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons(Cx Hy ) in the fuel, and nitrogen(II) oxide (NO) formed by the reaction of nitrogen gas and oxygen gas from the air.
* They are also involved in the production of photochemical smogs which occur worldwide in major cities, especially in the summer. Photochemical smog is the most widely known and perhaps most serious air pollutant. It is formed in the atmosphere by the reaction between gaseous pollutants, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons.
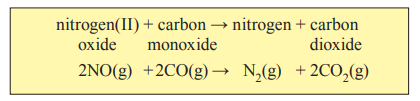
49
New cards
Alternative fuels to fossil fuels

50
New cards
displayed formula
A displayed formula shows how the various atoms are bonded and shows all the bonds in the molecule as individual lines.
51
New cards
homologous series
A homologous series is a family of similar compounds with similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group.
52
New cards
functional group
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms that determine the chemical properties of a homologous series.
53
New cards
Some alkanes and their physical properties
* For example, the melting and boiling points of the alkanes shown in Table 12.1 gradually increase.
* This is due to an increase in the intermolecular forces as the size and mass of the molecule increases.
* As you can see from Figure 12.2 and Table 12.1, the increase in size and mass of the molecule is due to the addition of a CH2 group as you descend the homologous series.
* This is due to an increase in the intermolecular forces as the size and mass of the molecule increases.
* As you can see from Figure 12.2 and Table 12.1, the increase in size and mass of the molecule is due to the addition of a CH2 group as you descend the homologous series.
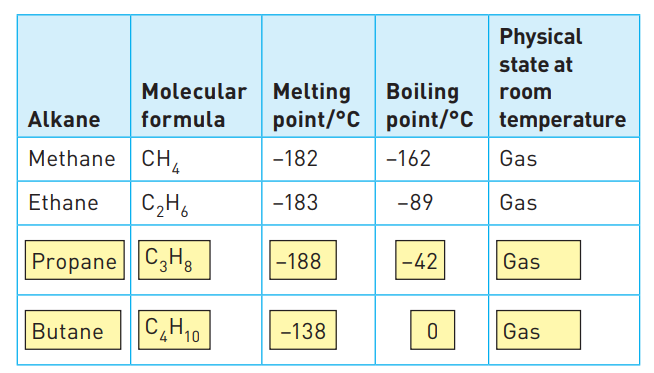
54
New cards
Structural isomers
Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula, but different structural formulae.
55
New cards
structural formula
The structural formula of an organic compound is an unambiguous description of the way the atoms are arranged, including the functional group.
56
New cards
The chemical behaviour of alkanes
1. Alkanes are shy building blocks that can catch fire and make heat.
2. Some alkanes have different hidden shapes, like toys that can change.
3. Alkanes can be used as fuels for cooking and heating homes.
4. Different shapes of alkanes can melt or boil at different temperatures.
5. Compounds with the same building blocks but different arrangements are called isomers.
6. Alkanes can trade parts with chlorine in a game called "substitution."
7. Substitution makes new compounds, like when trading pieces in a puzzle.
8. This process is a type of chemical reaction.
9. Alkanes can do cool things, like catching fire, changing shapes, and swapping parts with chlorine.