Biology - Unit 11: Transport in Humans
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what is circulatory system?
a system of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one-way flow of blood
what is double circulation?
a system in which blood passes through the heart twice for each complete circuit.
what does double circulation provide?
a low pressure circulation to the lungs and a high pressure circulation to the body tissue.
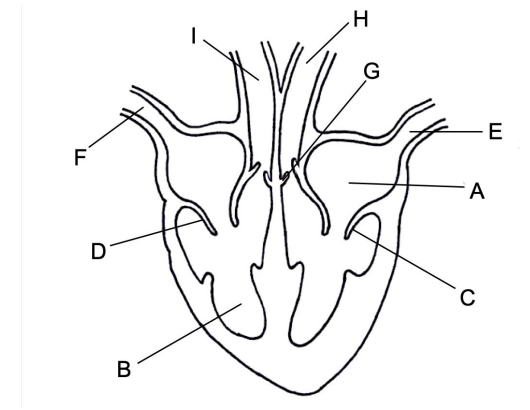
label this image
why are the walls of the left ventricle thicker than the right ventricle?
the left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle as it has to pump blood at high pressure around the entire body, whereas the right ventricle pumps blood at lower pressure to the lungs.
why are the walls of the ventricles thicker than the atria?
the ventricles have thicker muscle walls than the atria as they pump blood out of the heart and so need to generate at a higher pressure.
describe the functioning of the heart.
deoxygenated blood from he body flows into the right atrium via the vena cava
once the right atrium is filled with blood, the heart gives a little beat and the blood is pushed through the atrioventricular valve into the right ventircle
the walls of the ventricle contract and the blood is pushed into the pulmonary artery through the semilunar valve, which prevents blood from flowing backwards into the heart
blood travels to the lungs and moves through the capillaries past the alveoli where gas exchange take place which is why there has to be low pressure on this side of the heart — blood is going directly to capillaries which would burst under high pressure
oxygen-rich blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein
it passes through the atrioventricular valve into the left ventricle
the thicker muscle walls of the ventricle contract to push the blood forcefully into the aorta and all the way around the body
the semilunar valve in the aorta prevents the blood from flowing back down into the heart
how does blood move in the heart?
blood is pumped away from the heart in arteries and returns to the heart in veins.
how can the activity of the heart be monitored?
ECG
pulse rate
listening to the sounds of valves closing
describe coronary heart disease.
heart pumps blood around the body
however, the heart muscles themselves also need a blood supply because they too, are respiring muscles
coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscles
coronary heart disease is when the coronary artery becomes blocked, leading to blood (and therefore oxygen) starvation in the heart muscles which can lead to a heart attack
coronary heart disease is caused by the buildup of cholesterol and other fatty substances within coronary arteries
what are possible risk factors of coronary heart disease?
diet
lack of exercise
stress
smoking
genetic predisposition
age (risk increases as you grow older)
gender/sex (risk increases for males)
how can we reduce the risk of coronary heart disease?
quit smoking
maintain a healthy diet with reduced animal fats
exercise regularly
what is the function of the pulmonary artery?
transports deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs.
what is the function of the pulmonary vein?
transports oxygenated blood from the lungs, into the heart.
what is the function of the aorta?
transports oxygenated blood away from the heart, to the rest of the body.
what is the function of the vena cava?
transports deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body, into the heart.
what is the function of the hepatic vein?
transports deoxygenated blood from the liver, into the vena cava.
what is the function of the hepatic artery?
transports oxygenated blood away from the heart, into the liver.
what is the function of the hepatic portal vein?
transports nutrient-rich blood from the digestive system to the liver.
what is the function of the renal artery?
transports oxygenated blood away from the heart, into the kidneys.
what is the function of the renal vein?
transports deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys, into the vena cava.
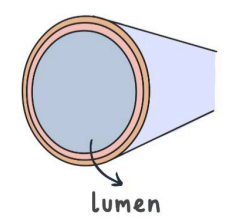
what blood vessel is this?
vein
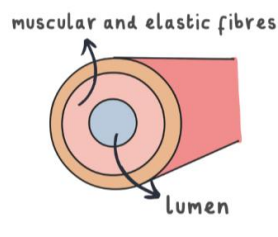
what blood vessel is this?
artery
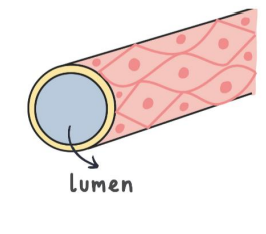
what blood vessel is this?
capillary
describe the structure of an artery
they have thick muscular walls to withstand blood being carried at high pressures.
the walls of arteries also have elastic fibres.
they have narrow lumen to maintain the high blood pressure.
they don’t have valves since high BP prevents backflow.
describe the structure of a vein
they have thin muscular walls.
the walls of veins have little elastic fibres.
veins have a large lumen.
valves are present in veins to prevent blood backflow.
describe the structure of a capillary
the capillary walls are one cell thick.
they have a very narrow lumen, just wide enough for a red blood cell to pass through.
capillaries have very thin permeable walls.
how does the structure of an artery relate to its function?
have thick, muscular walls containing elastic fibres to withstand the high pressure of blood and maintain the blood pressure as it recoils after the blood has passed through
have a narrow lumen to maintain high pressure
how does the structure of a vein relate to its function?
have a wide lumen as blood pressure is low
contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood as it is under low pressure
how does the structure of a capillary relate to its function?
have walls that are one cell thick so that substances can easily diffuse in and out of them
have ‘leaky’ walls so that blood plasma can leak out and form tissue fluid surrounding the neighbouring cells
are narrow so that red blood cells have to touch the sides as they pass through in single-fil
this reduces the diffusion distance for gas exchange as the cells bind/release oxygen molecules
what is this?
red blood cells
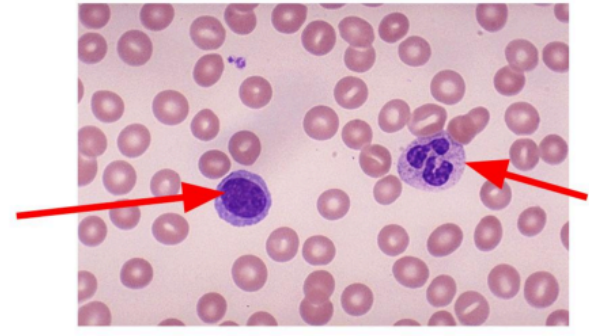
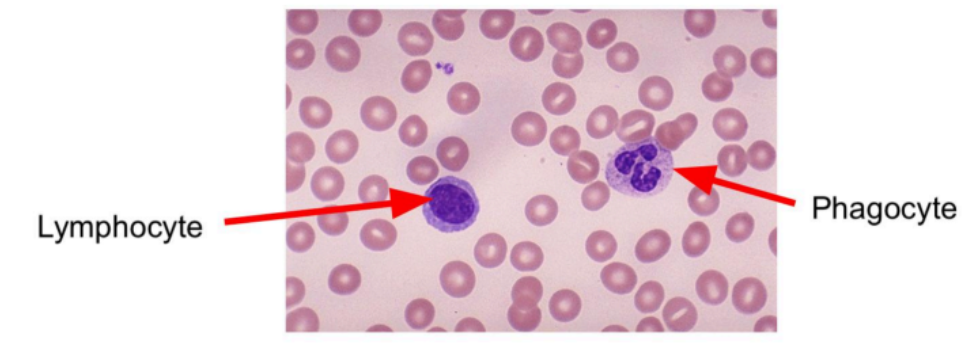
what are the components of blood?
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets
plasma
what is the function of red blood cells?
oxygen transport
what is the function of white blood cells?
antibody production by lymphocytes and engulfing pathogens by phagocytes
what is the function of platelets?
clotting by converting soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin to prevent blood loss and the entry of pathogens
what is the function of plasma?
transport substances like blood cells, ions, glucose, amino acids, hormones, carbon dioxide, urea, vitamins and plasma proteins
describe the transfer of substances between blood in capillaries, tissue fluid and body cells.
plasma, mostly water, carries dissolved substances around the body.
as blood flows through capillaries, some plasma is forced out to form tissue fluid, which surrounds cells.
this fluid allows nutrients and gases to move between blood and cells, while waste products like carbon dioxide diffuse back into the capillaries.
most proteins stay in the blood because they’re too large to pass through.
how can we investigate the effect of physical activity on heart rate?
record the pulse rate at rest for a minute
exercise for a while
record the pulse rate every minute until it returns to the resting rate
this experiment will show that during exercise, the heart rate increases and may take several minutes to return to normal