Lectures 7/8: Fatty Acid Catabolim
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Fatty acids are oxidized to what?
acetyl-Coa
Fatty acid oxidation provides what to the ETC and the citric acid cycle?
electrons for ETC
acetyl-Coa for citric acid cylce
What proportion of energy in mammalian heart and liver is from fatty acid oxidation?
over 80%
What is another name for fatty acid oxidation?
beta-oxidation
Fatty acids carry long poly-hydrocarbon chains and are therefore more what than carbohydrates?
more highly reduced
yields more energy
Fatty acids are very closely packed meaning what?
carry less water
non-polar
Glucose and glycogen are for fast usage and short term storage, what makes fatty acids different?
long term energy
months at a time
Fatty acids are derived from 3 major sources including…?
diet
fats in cells i.e., adipocytes
fat synthesis
Fatty acids are what?
monomers of fats
What is the structure of a fatty acid?
carboxylic acid head → hydrophillic
hydrocarbon chain → hydrophobic
amphiphillic
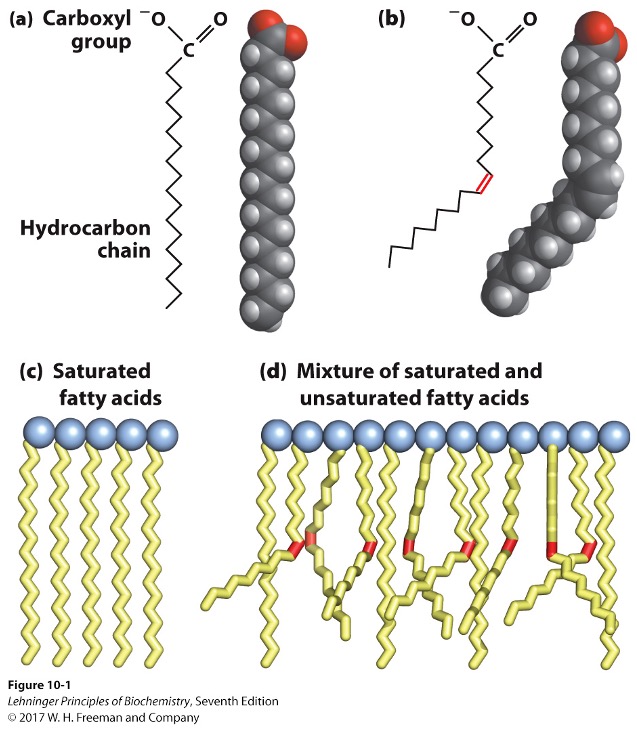
Fatty acids can be what or what?
saturated
unsaturated
Saturated fatty acid
no double bonds
filled with max number of hydrogens
straight
Unsaturated fatty acid
double bonds
not max number of hydrogens
kinked
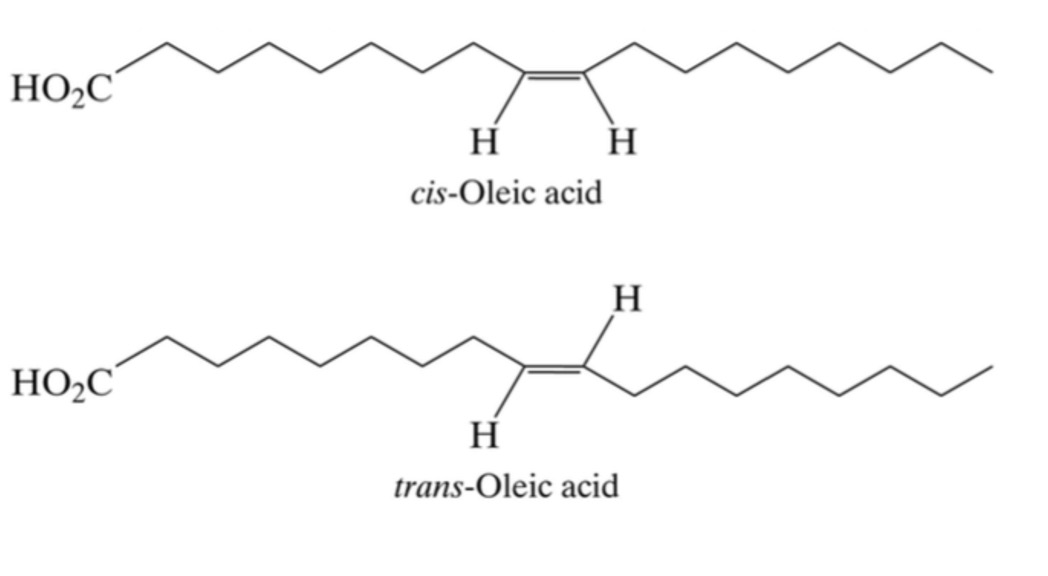
Orientation of the chain around the carbon double bond in an unsaturated fatty acid chain determines what?
whether it’s cis or trans conformation
Triacylglycerols are responsible for what form of fatty acids?
polymeric
storage form
What do the polymeric and storage forms of triacyglycerols involve chemically?
esterification of 3 fatty acid chains to a single glycerol
Most fatty acids in nature are found in what form and broken down into what?
triacylglycerol form
broken down into fatty acids
when needed for ATP synthesis
What enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of triacyglycerols into fatty acid and glycerol
lipases
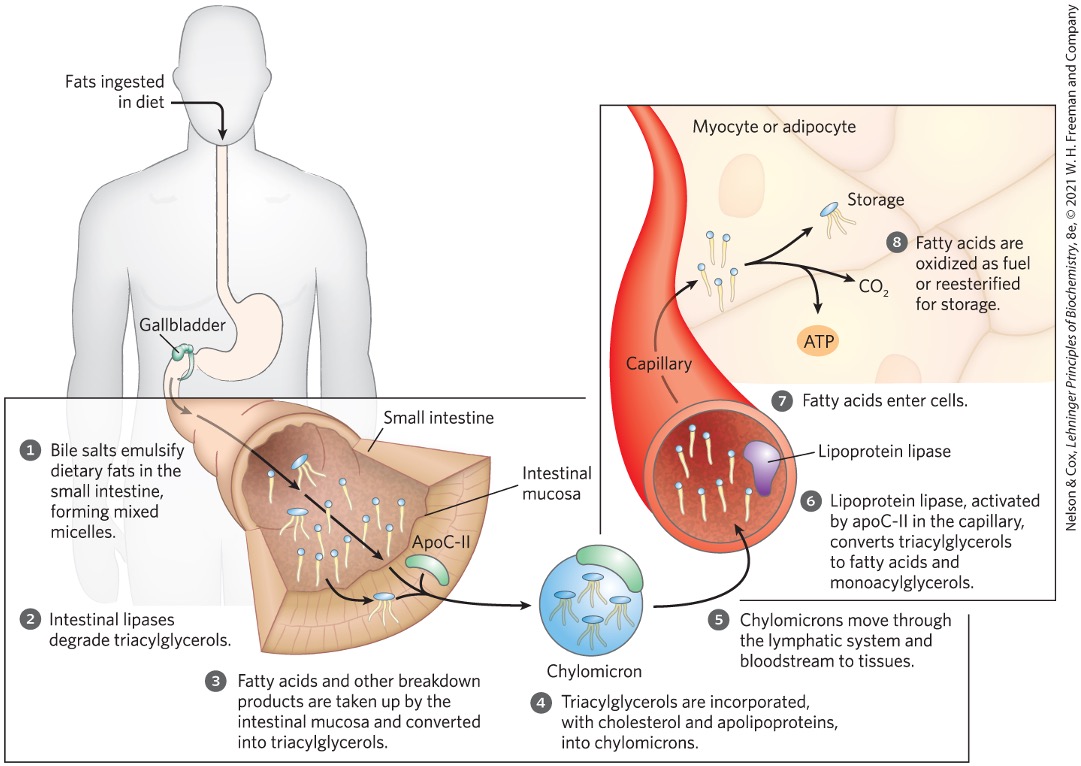
Absorption of dietary fats by intestinal walls begins with what being converted into what?
fat particles → micelles → fatty acids and glycerol
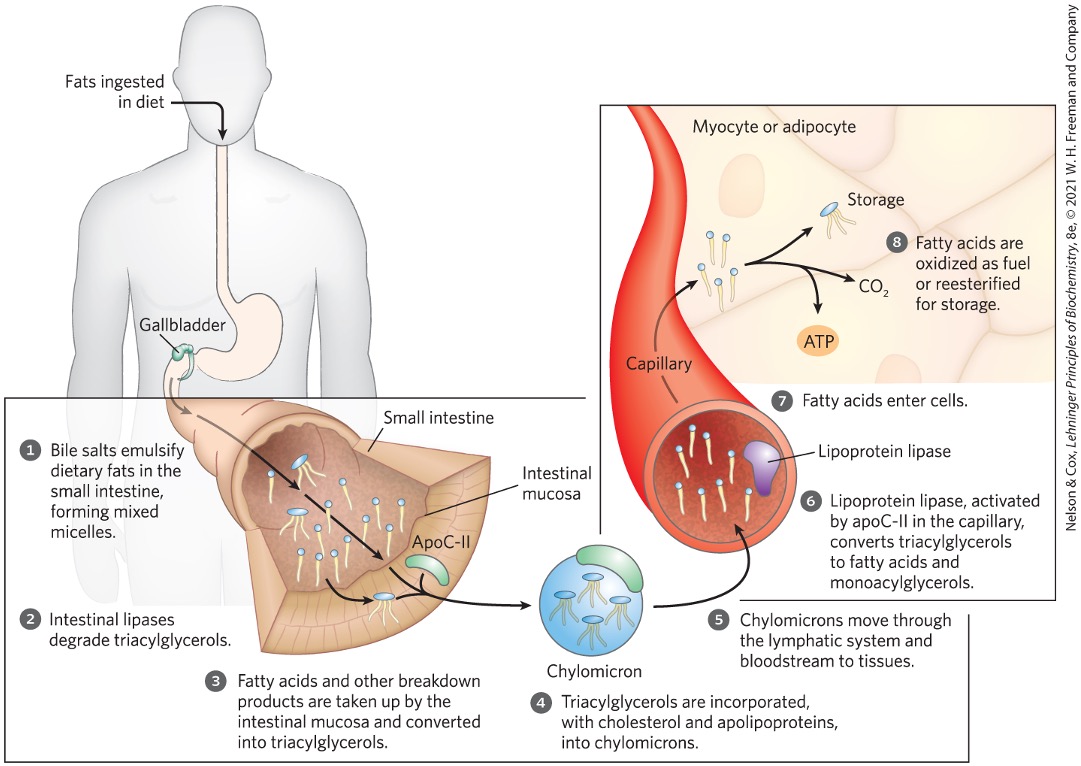
Bile salts
emulsify dietary fats in small intestine forming mixed micelles
bile salts and fatty acids
Bile salts are produced from what and are stored where?
cholesterol in the liver
gallbladder and released in small intestine
What is another name for bile salts?
taurocholic acid
Micelles increase what to the intestinal lipases?
lipid access
Lipases breakdown triacylglycerols to what?
monoglycerides
diglycerides
free fatty acids
glycerol
Where are the products of fatty acid breakdown via lipases taken up and what happens afterward?
intestinal mucosa
reconverted to triacylglycerols
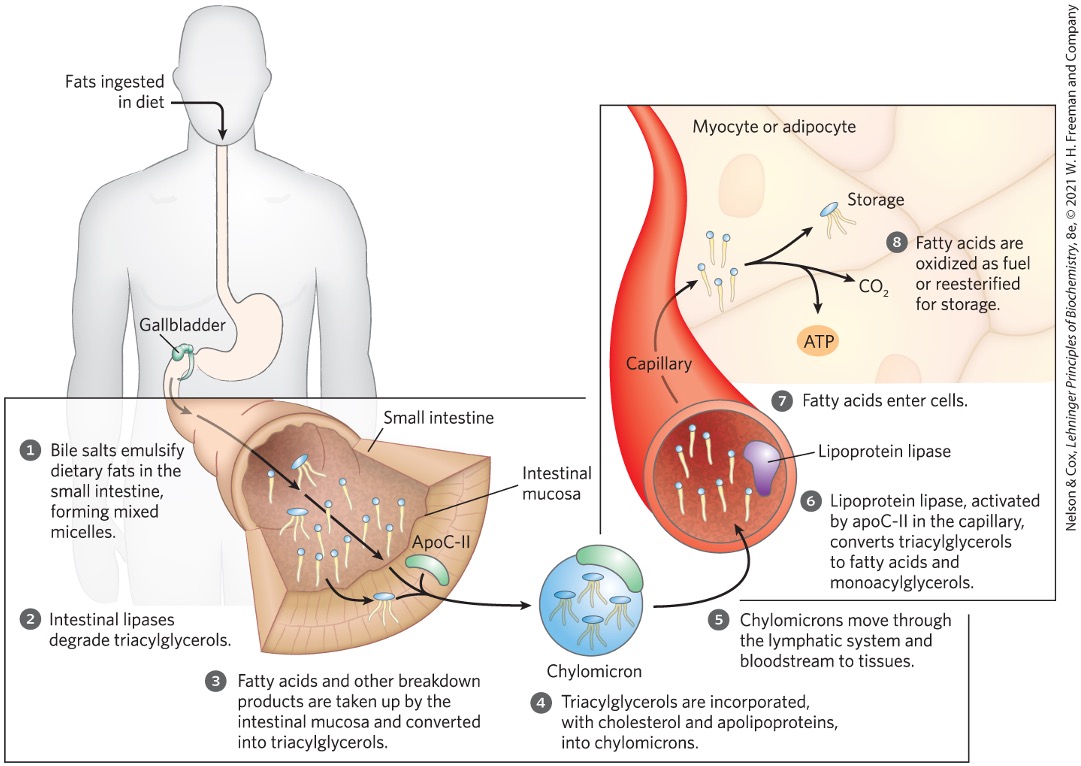
Triacylglycerols are then packaged into what?
chylomicrons
What is the structure of a chylomicron?
cholesterol and lipid-binding proteins (lipoproteins)
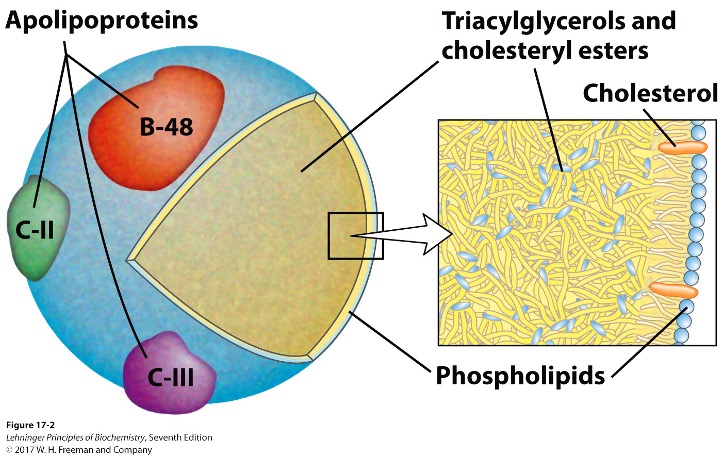
Apolipoproteins
lipid-binding proteins
transport of triacylglycerols, phospholipids, cholesterol between organs
Lipoproteins form what when combined with hydrophobic particles?
spherical aggregates
hydrophobic particles facing inward
hydrophilic exposed at surface
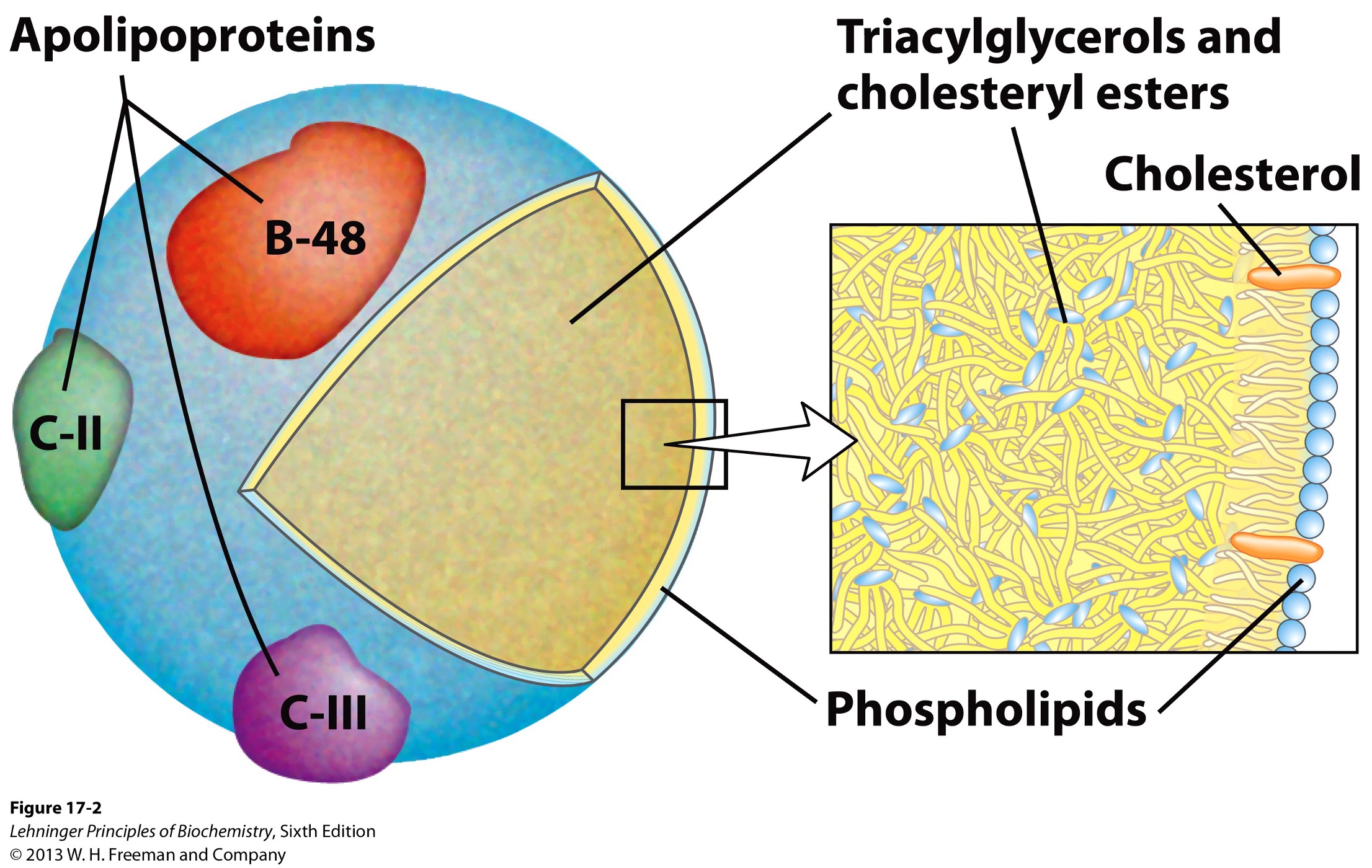
Surface of chylomicrons is composed of phospholipids and triacylglycerols pointing where?
inside
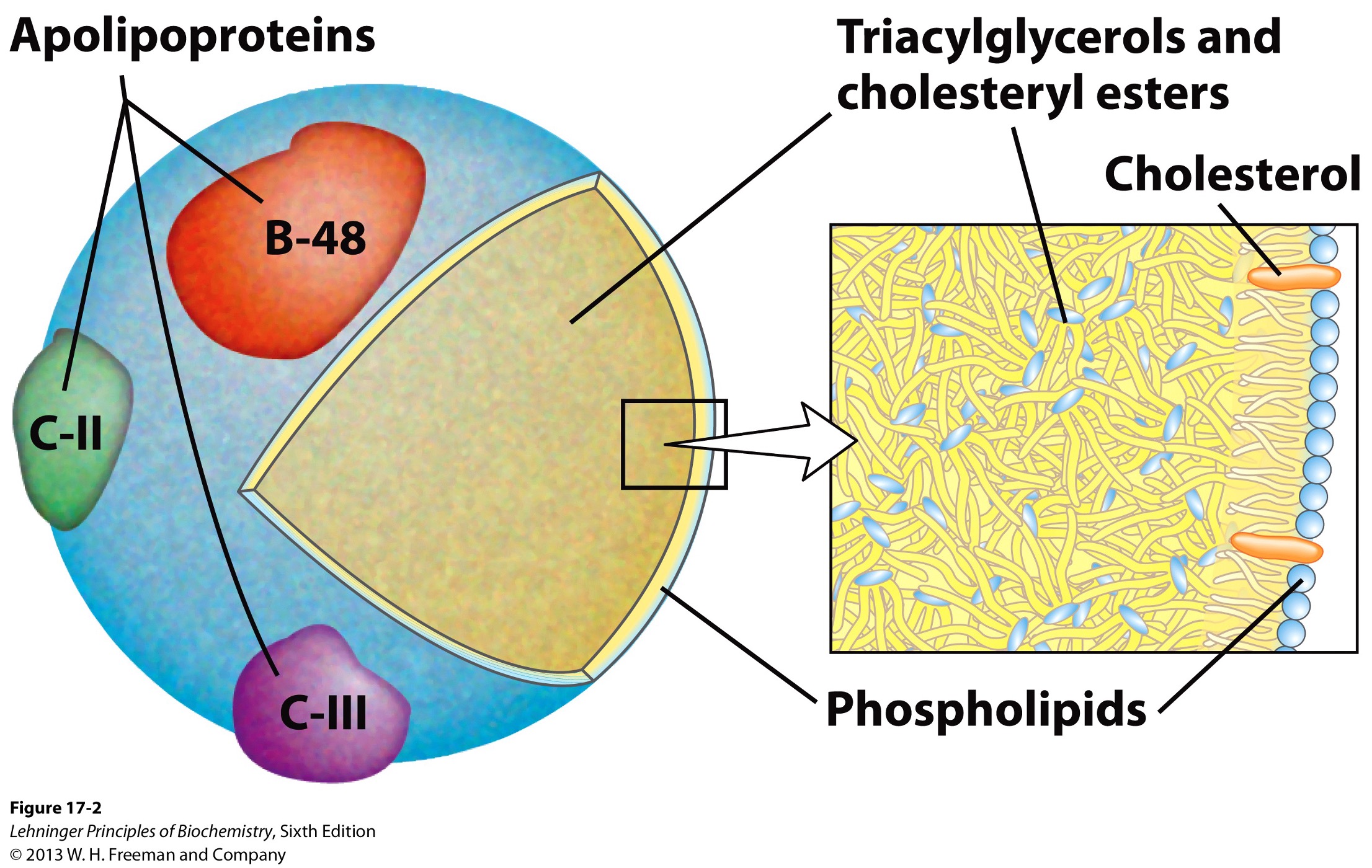
Apolipoproteins on the surface of the chylomicron signal what?
uptake and metabolism of the chylomicrons
Lipids are transported in the blood via…?
chylomicrons
Chylomicrons are synthesized where and do what?
intestinal mucosa
transport triacylglycerols through the blood to tissue
Combination of lipids and proteins creates what?
different densities of particles
can be differentiated
VLDL
made in liver
deliver liver-synthesized triacylglycerols to adipose tissue
LDL
major cholesterol carrier (BAD ONE)
liver to tissue
HDL
highest protein content
picks up cholesterol
moves it from tissue → liver (GOOD ONE)
Packaged chylomicrons are transported from the intestinal mucosa to the what and enters what?
lymphatic system
bloodstream
Once in the blood, chylomicrons do what?
deliver package to muscle and adipose tissues
Lipoprotein lipase
hyrolyzes triacylglycerols to fatty acids and glycerol
In muscle, fatty acids are oxidized for energy whereas in adipose tissue they are what?
stored as triacylglycerols
Lipids are stored in adipocytes in what form?
lipid droplets
What does the centre of lipid droplets contain?
sterol esters
triacylglycerols
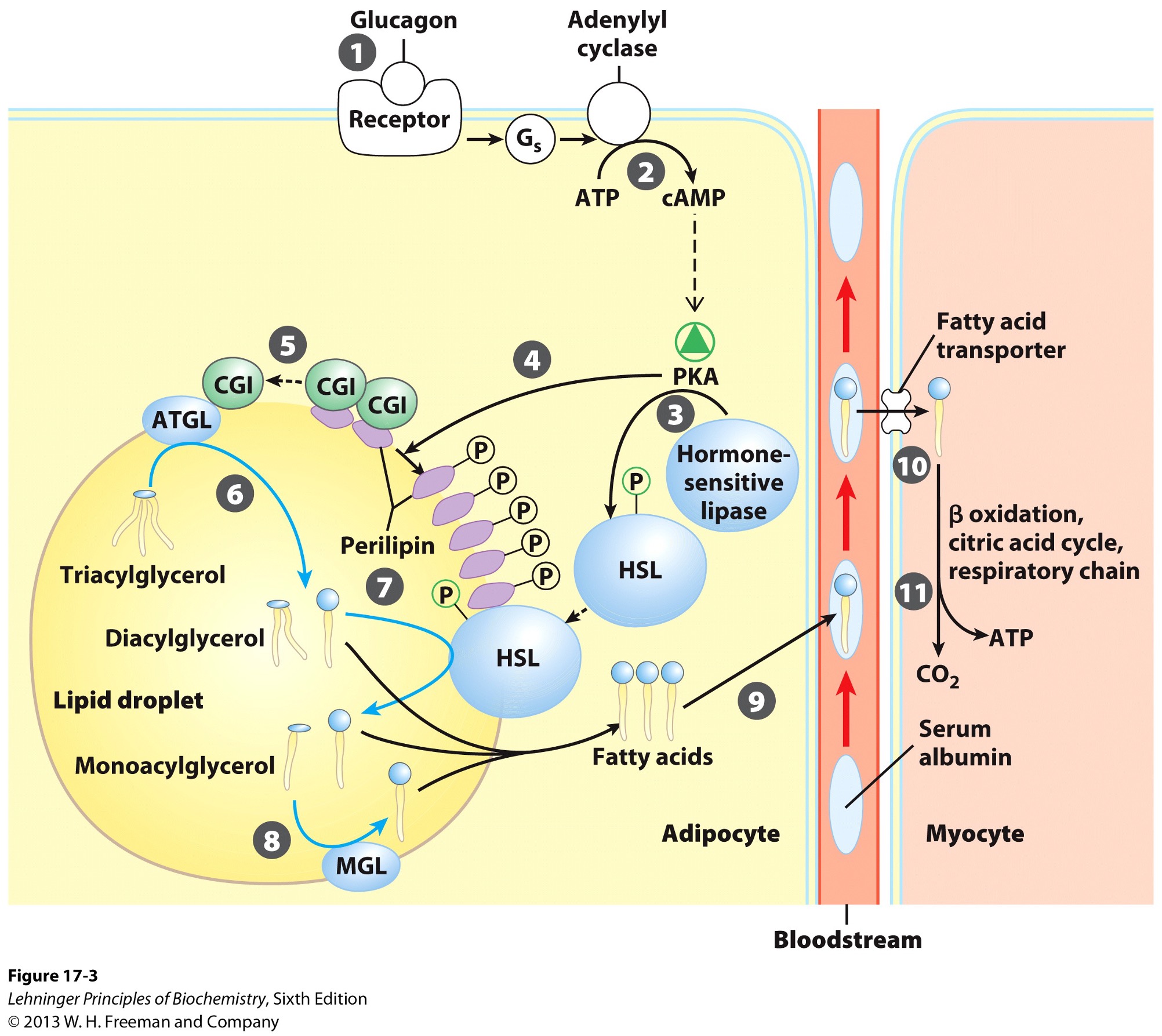
What doe the surface of the lipid droplets carry?
perilipins
phospholipids
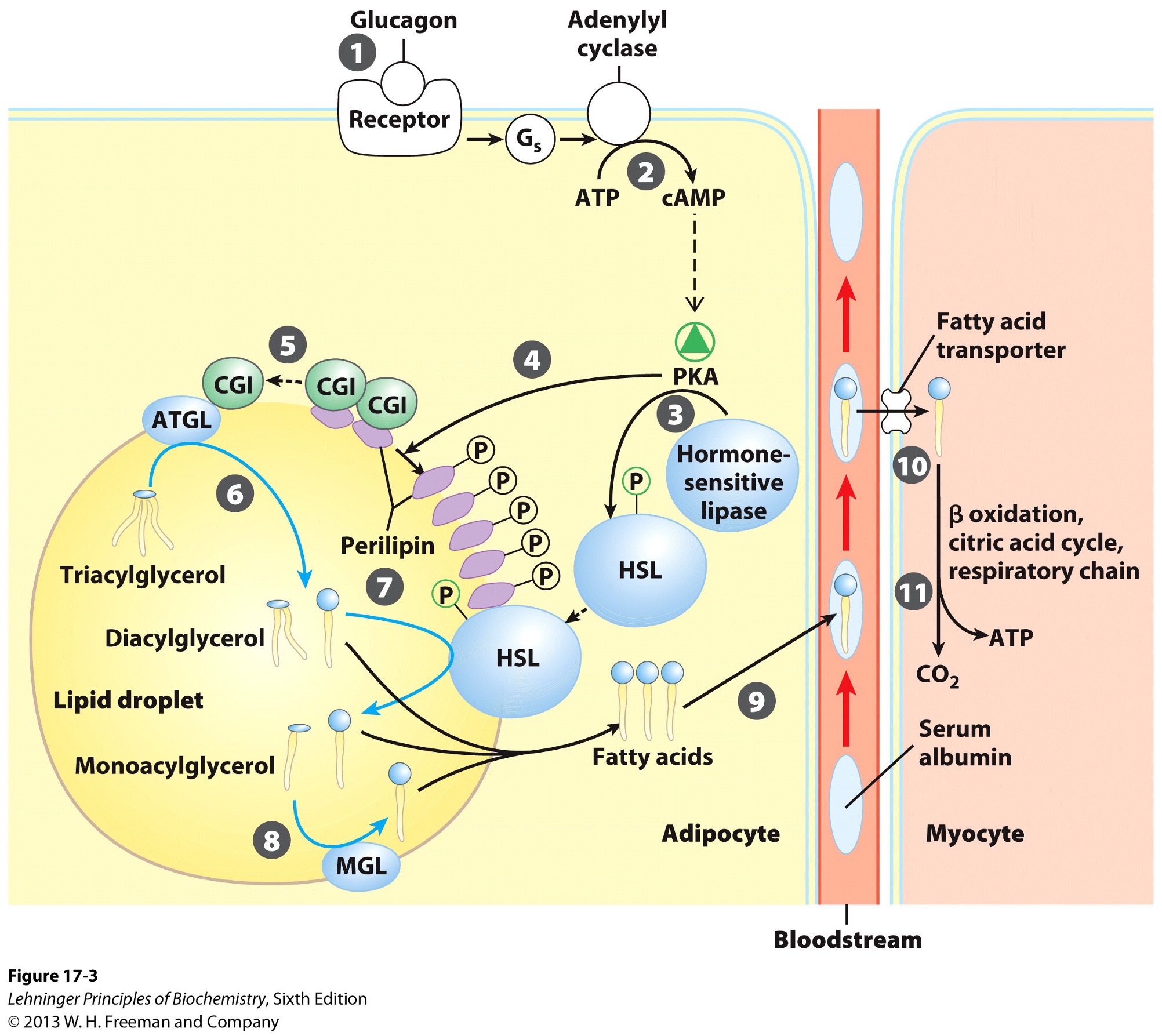
Perilipins
protein
restricts access to lipid droplets until needed
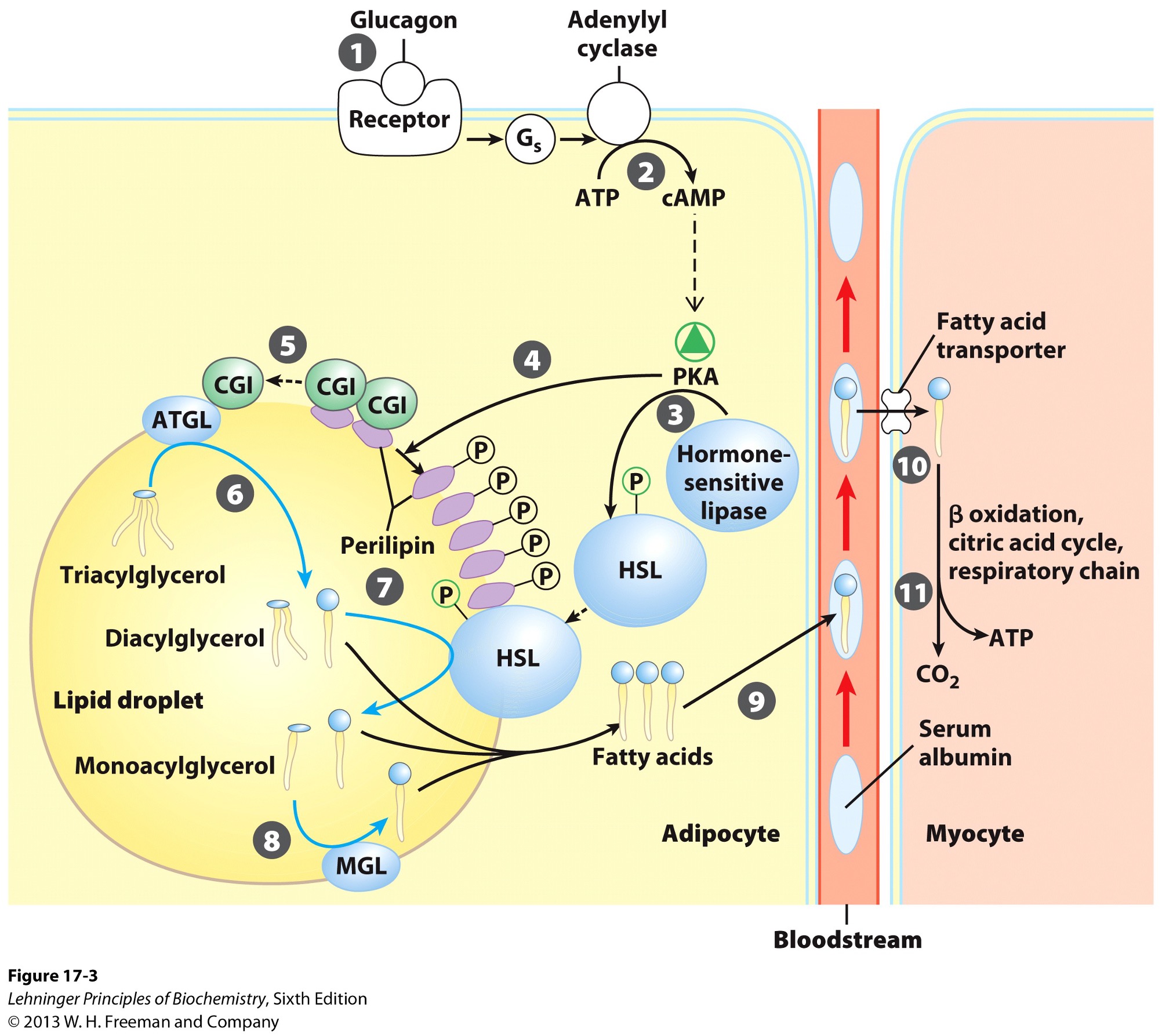
Hormones signal when metabolic energy is needed and when triacylglycerols should be what?
released from the lipid droplet
Which hormones are released when blood glucose is low?
epinephrine
glucagon
Signal from epinephrine and glucagon results in what?
activation of adenylyl cyclase in adipocytes
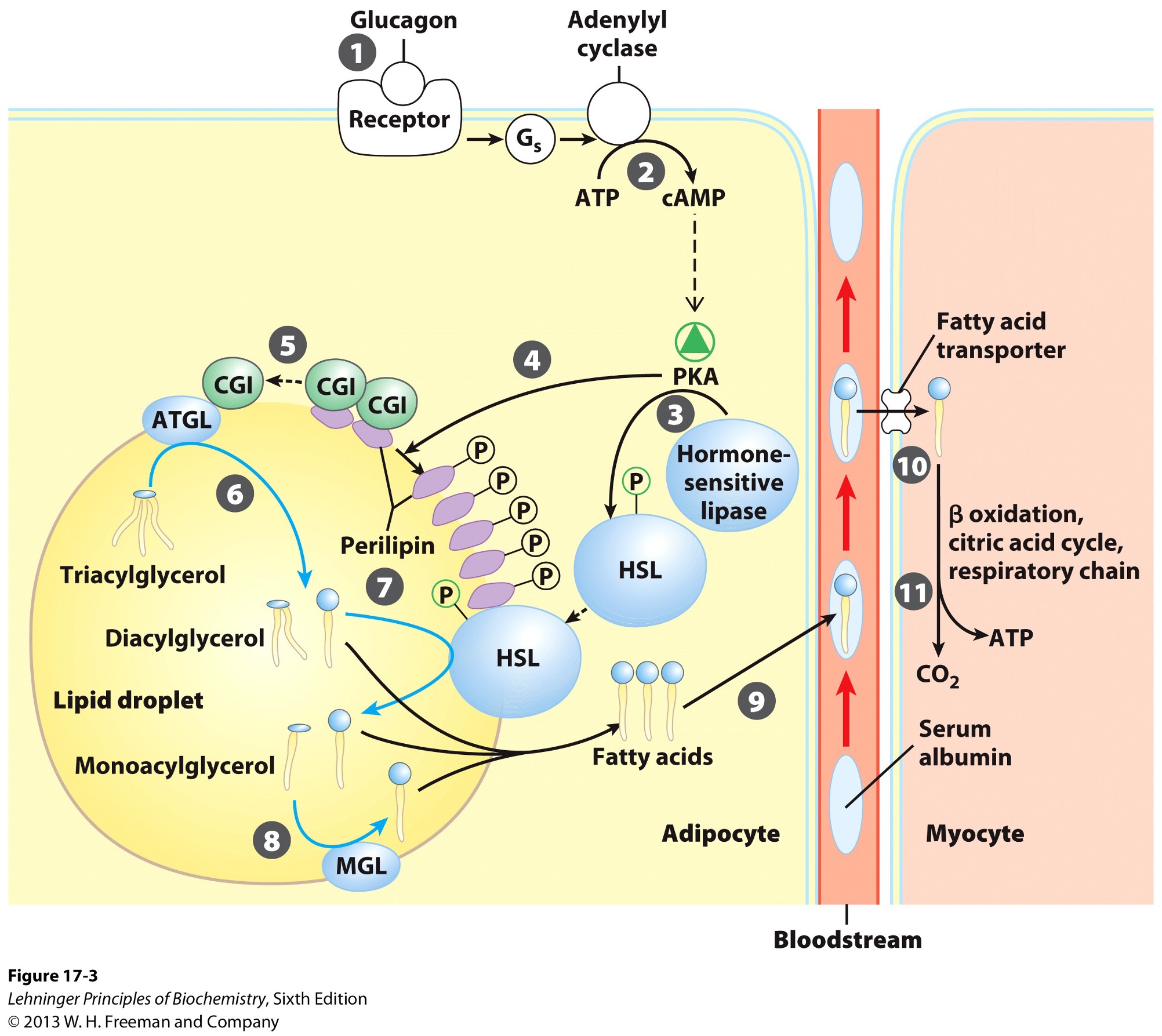
What does the activation of adenylyl cyclase produce?
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
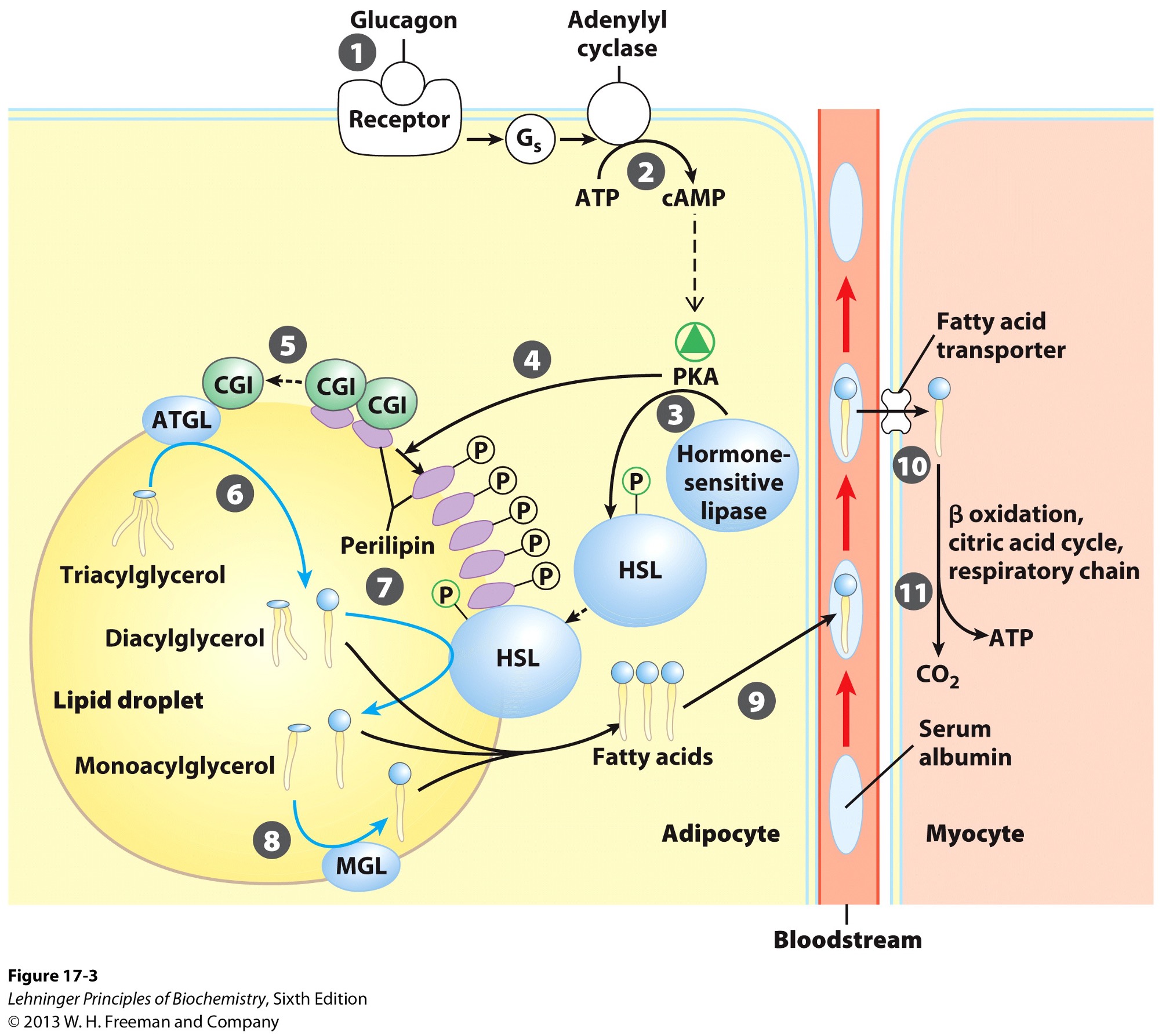
What does the production of cyclic AMP do?
activates protein kinase A
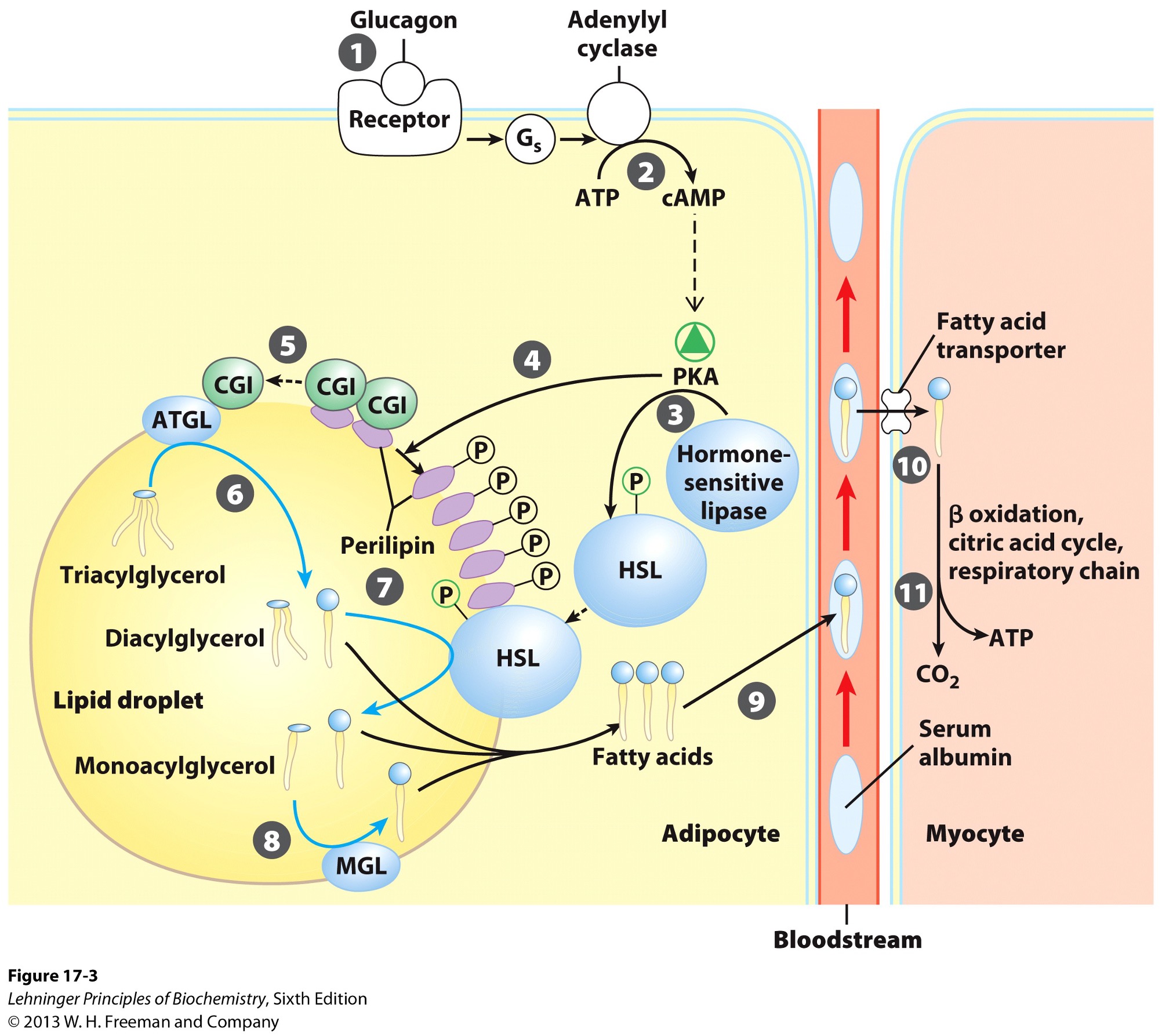
Activation of PKA (protein kinase A) results in what?
phosphorylation of hormone sensitive lipases
HSL
phosphorylation of perilipins found on lipid droplet surface
Phosphorylated perilipins signals lipases to do what?
release triacylglycerols to free fatty acids and glycerols
Phosphorylated perilipins on lipid droplet surface release what?
protein CGI
comparative genetic identification
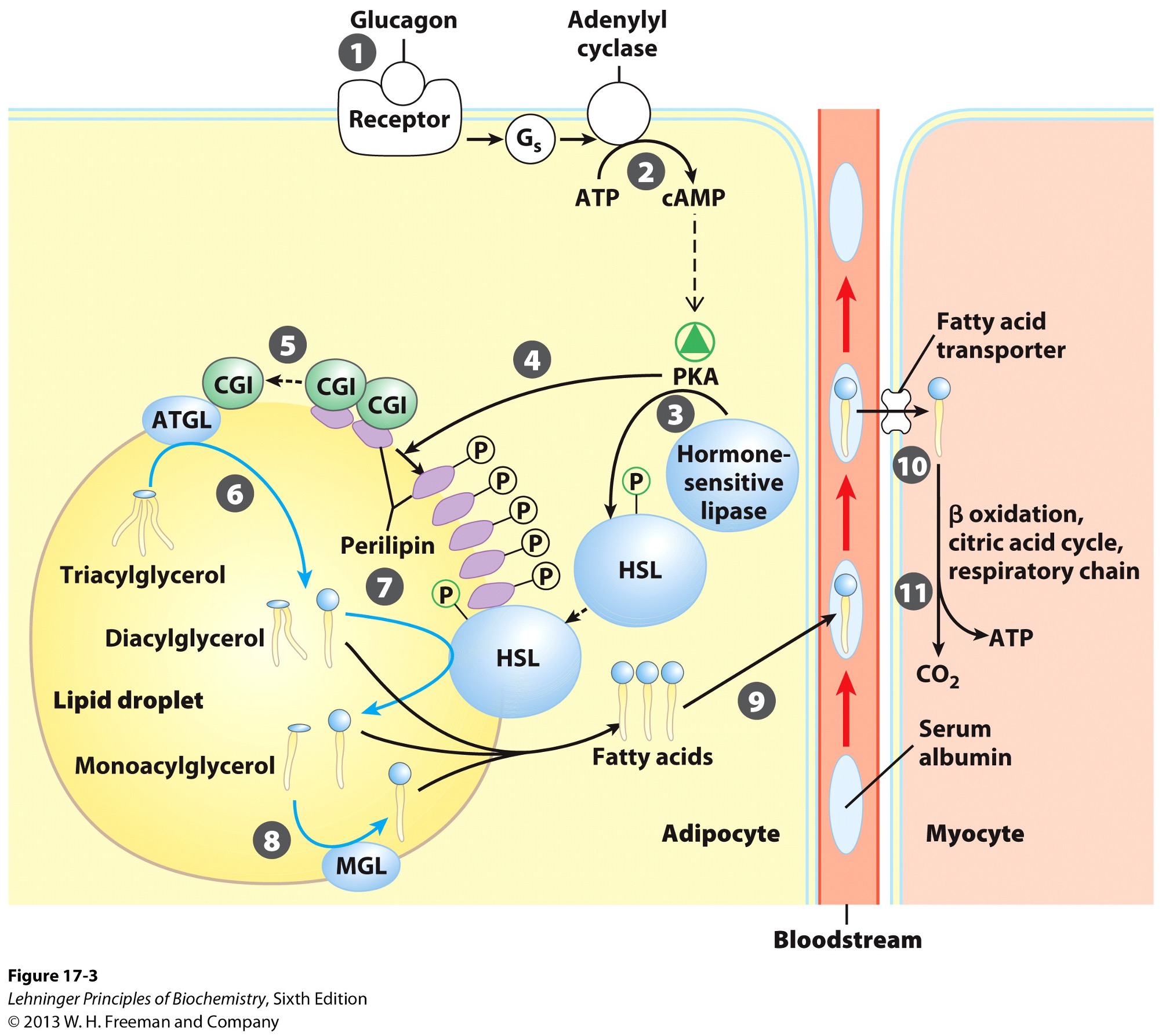
CGI associates with what?
ATGL
adipose triacylglycerol lipase
Activated ATGL hydrolyzes what to a what?
TAG (triacylglycerol) → DAG (diacylglycerol)
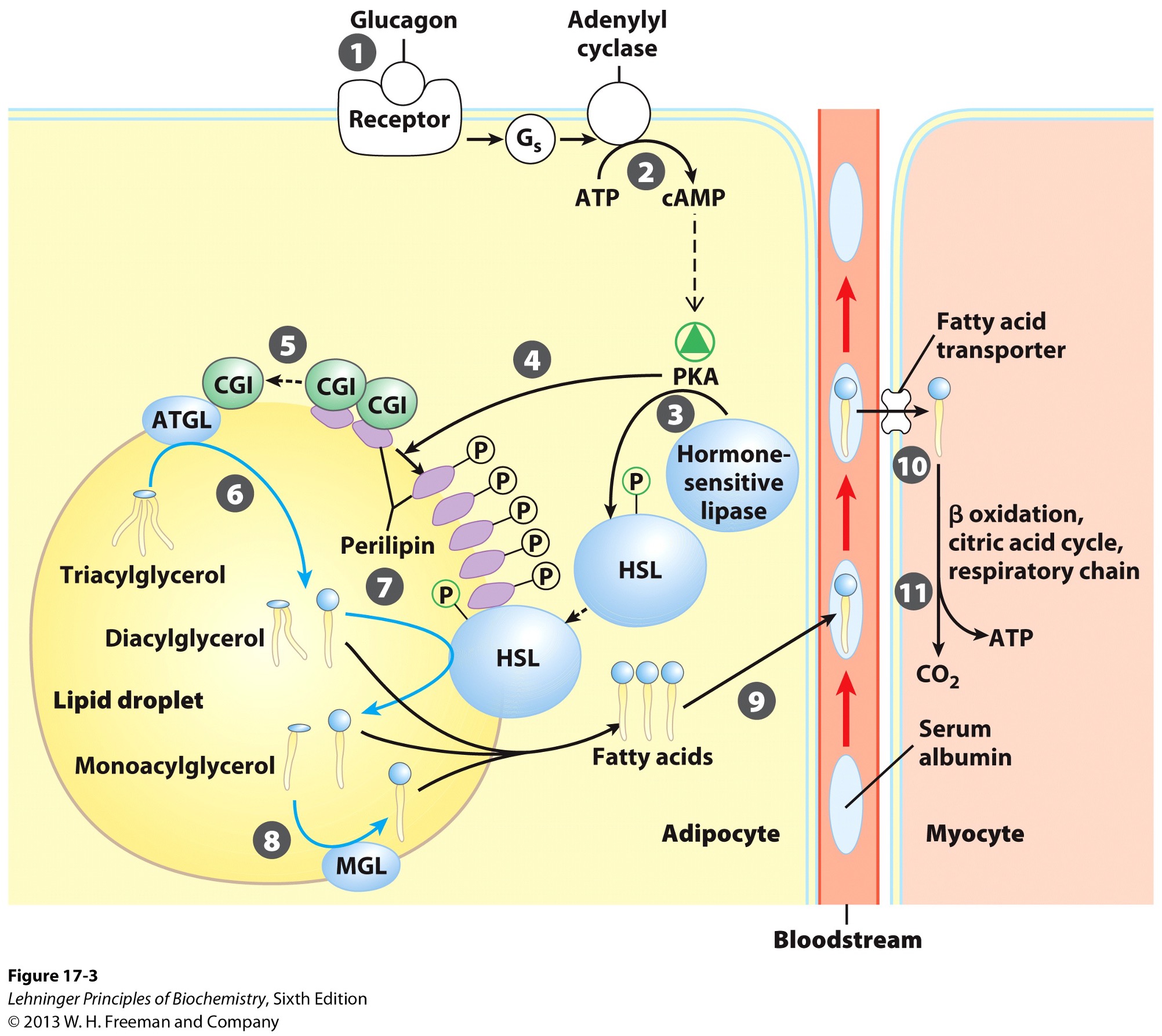
Phophorylated perilipin associates with what allowing for what to access the lipid droplet?
phosphorylated HSL (hormone sensitive lipase)
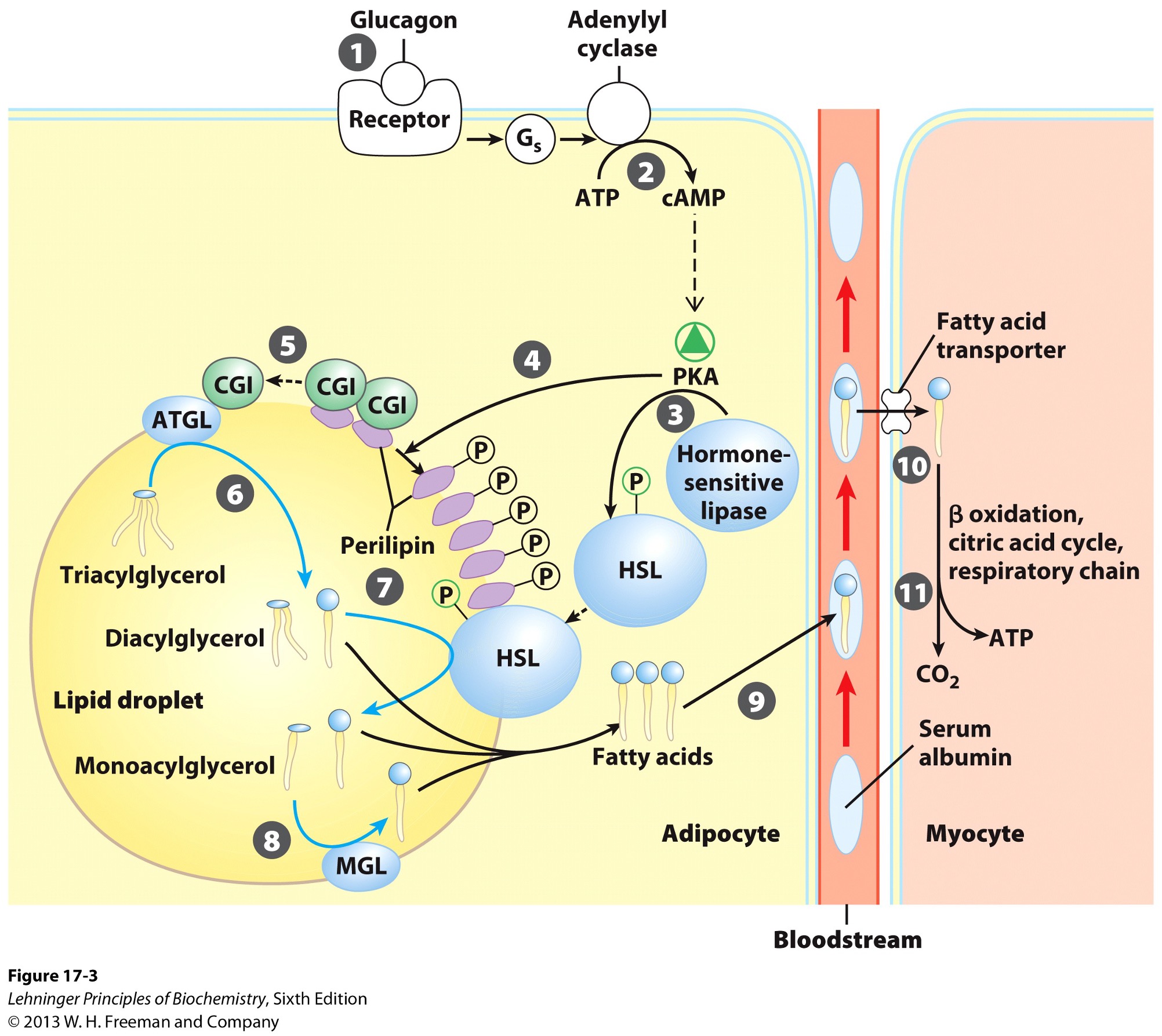
HSL hydrolyzes what to whay?
DAG → MAG (monoacylglycerol)
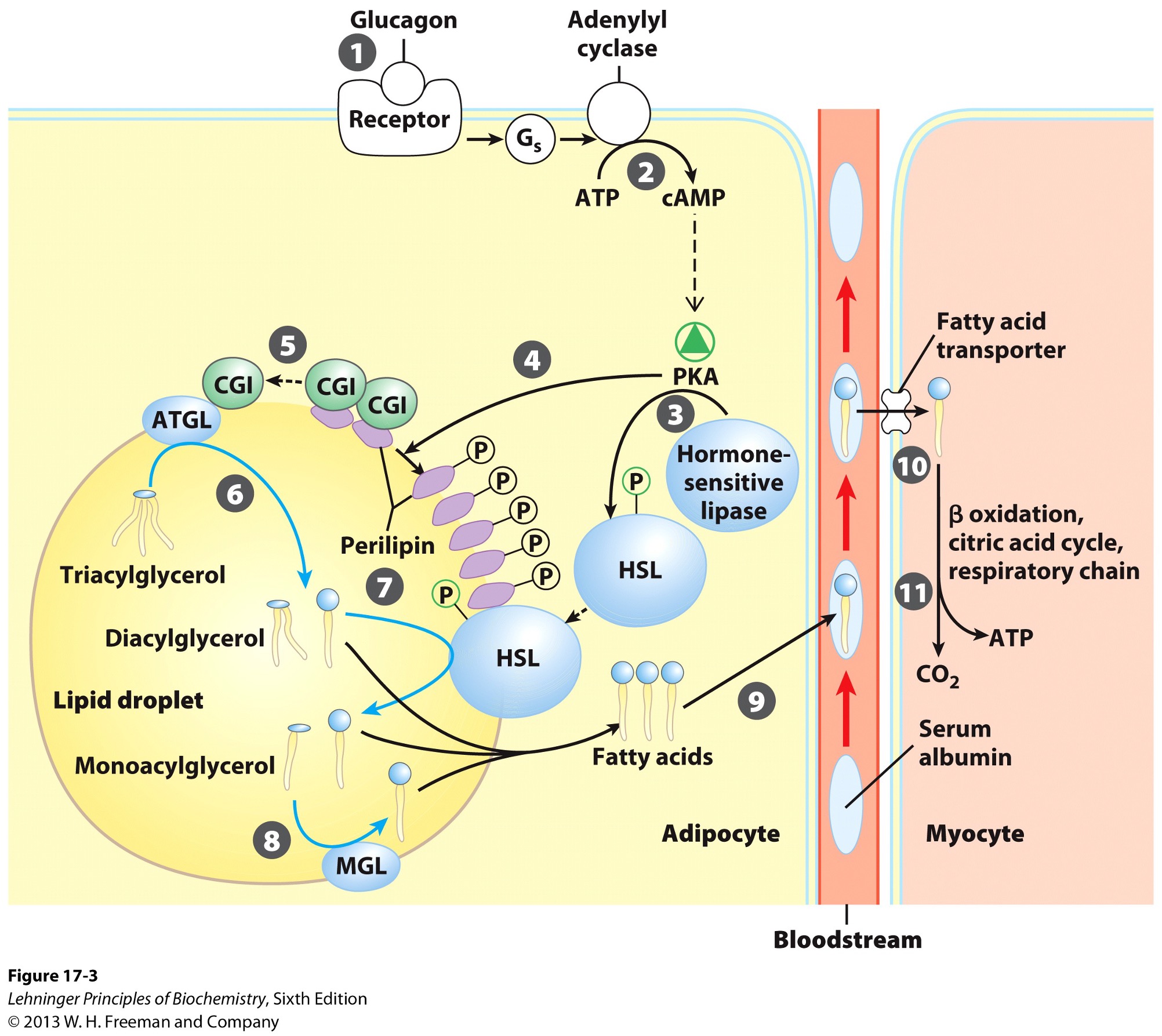
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes what to what?
MAG (monoacylglycerol) → glycerol and free fatty acid
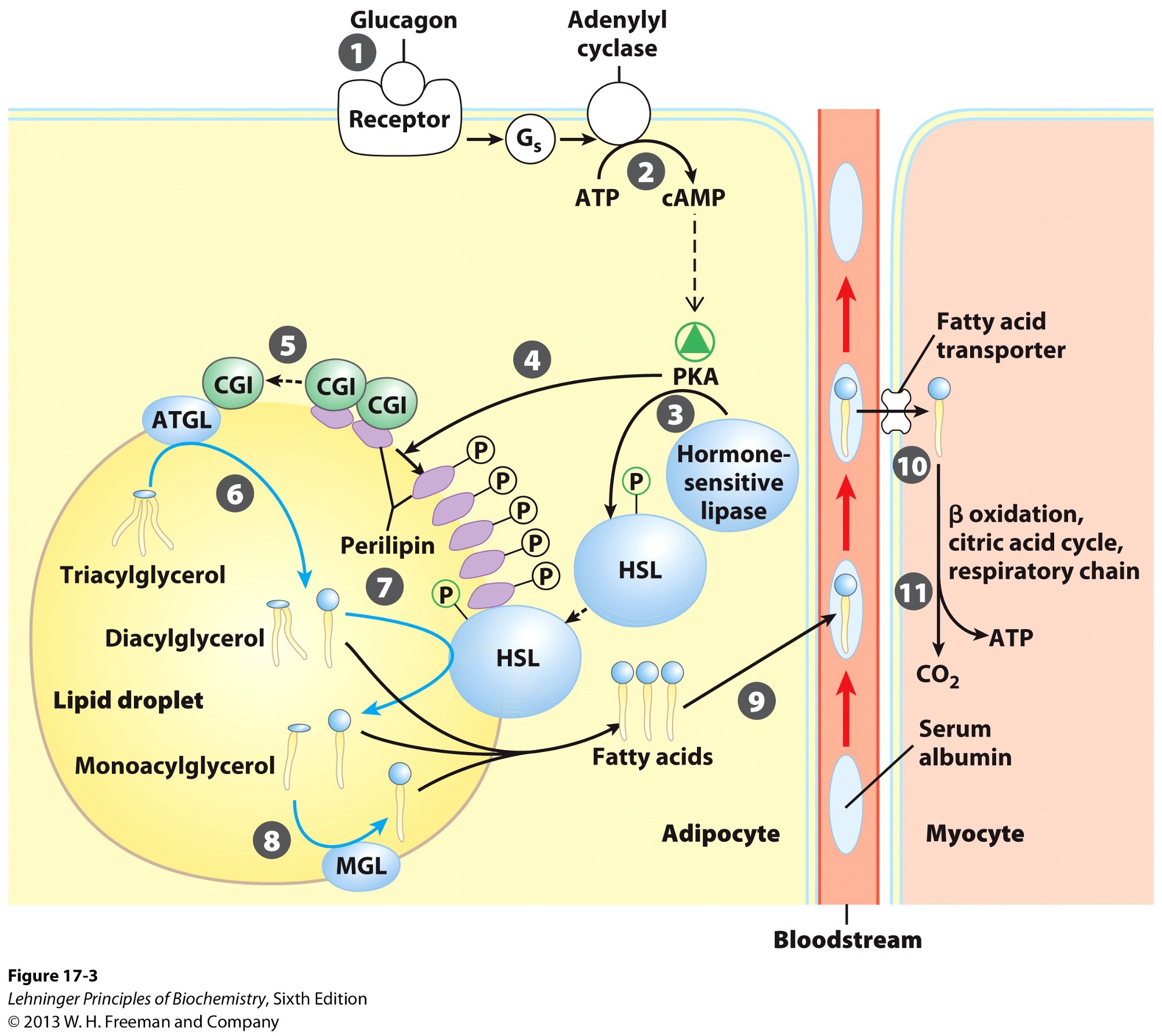
Fatty acids leave adipocyte and are transported via what?
bloodstream
bind serum albumin
Fatty acids are then released from serum albumin to enter what via what?
myocytes
specific transporters i.e., fatty acid transporters
Once in the myocyte, fatty acids undergo what?
beta-oxidation
Beta-oxidation
fatty acid → CO2
provides ATP
fuels muscle cells
Lipases cleave fatty acids from…?
glycerol backbone of triacylglycerols
Glycerol kinase activates glycerol at the expense of what allowing what?
ATP
allows limited anaerobic catabolism of fats
Entry of glycerol into the glycolytic pathway
glycerol phosphorylation via ATP
glycerol oxidized to the glycolytic intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate
DHAP continues through glycolysis
Enzymes necessary for fatty acid oxidation in animal cells are found where?
mitochondrial matrix
Fatty acids with chains 12 or less carbons long can what?
readily enter the mitochondria for oxidation
Fatty acids larger than 12 carbons i.e., > 14 require what to enter the mitochondria?
carnitine shuttle
can’t directly enter
most fatty acids from diet and stored ones
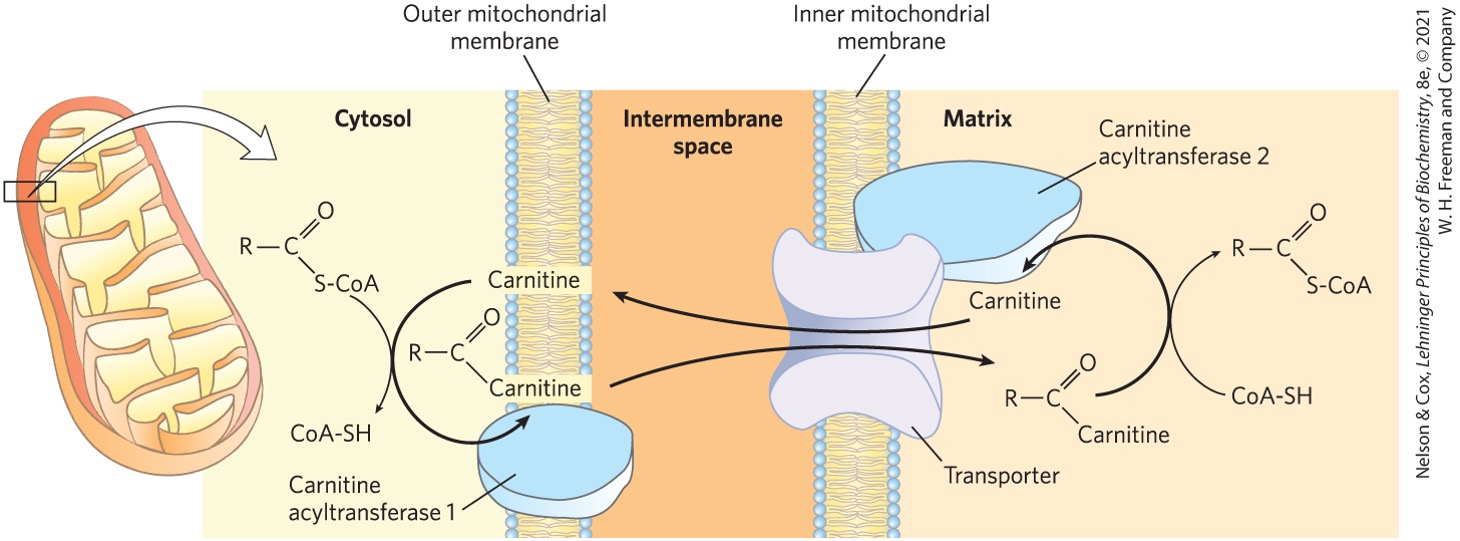
Fatty acid activation and transport to mitochondria step 1
converted to fatty acyl CoA
outer mitochondrial membrane
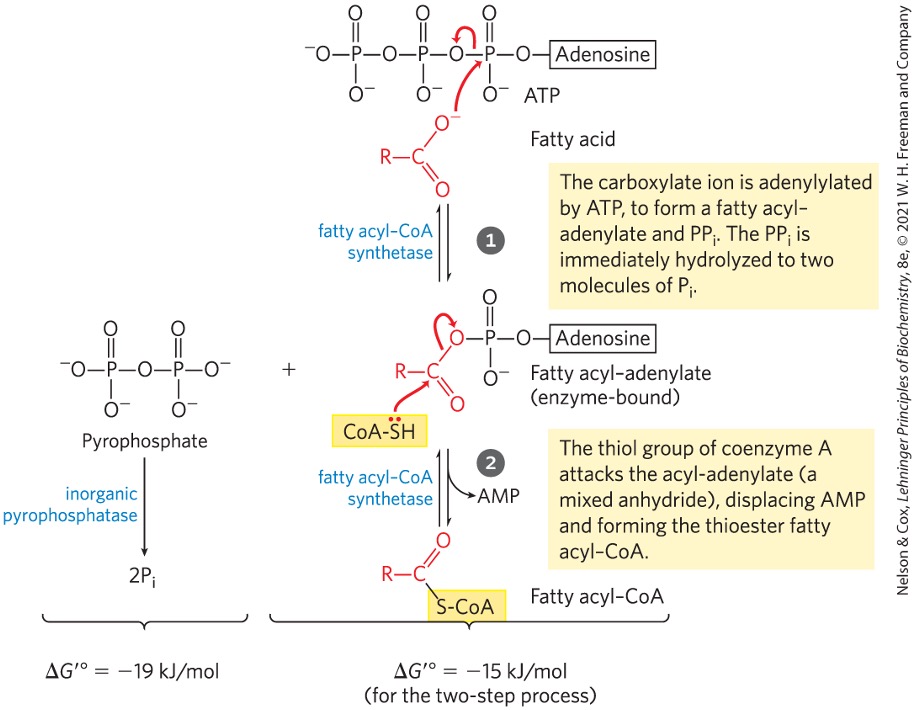
What enzyme catalyzes the conversion of fatty acid → fatty acyl CoA?
fatty acyl CoA synthetase
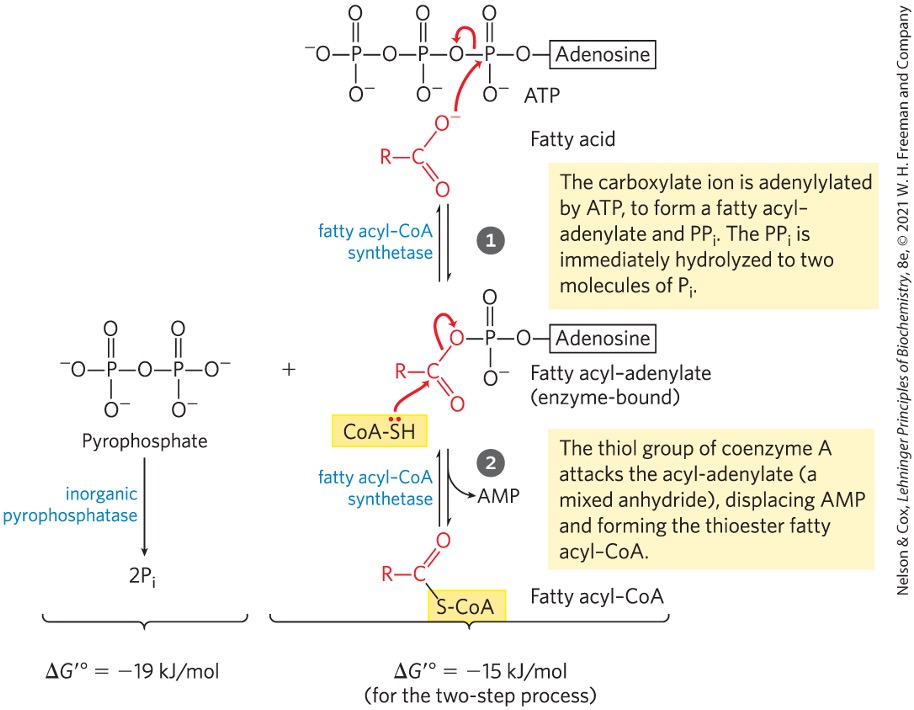
Fatty acyl-CoAs are high or low energy compounds?
high
like acetyl-CoAs
The conversion of fatty acid → fatty acyl-CoA is couple with what?
ATP hydrolysis → AMP + 2Pi
large negative standard gibbs free energy change
drives reaction forward
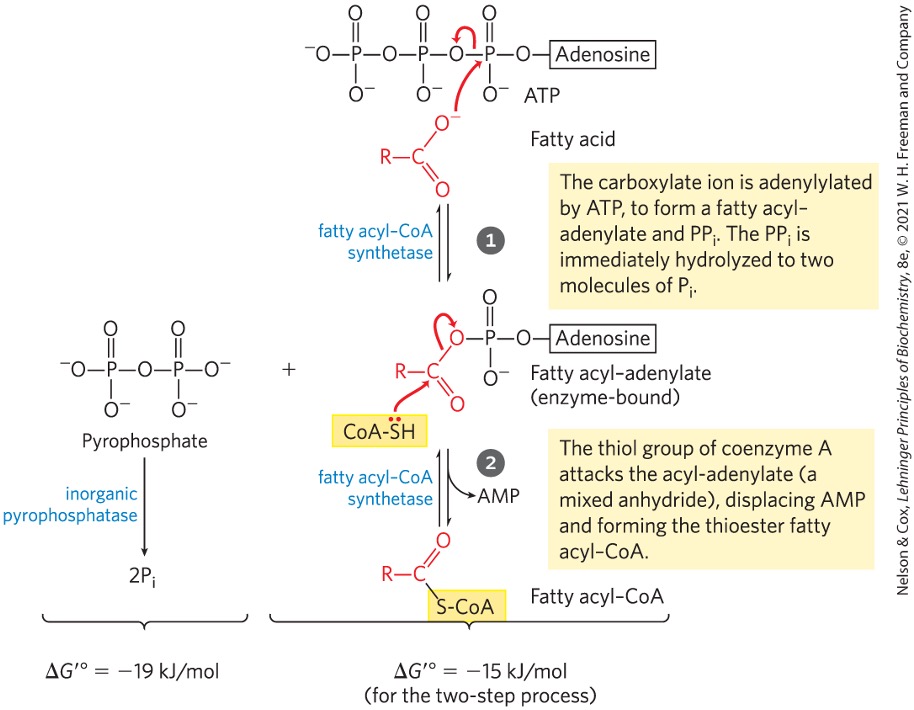
Fatty acyl CoA synthesized in the cytosolic side of the mitochondrial membrane can be one of two things…what are they?
transported to mitochondria → oxidation
used in cytosol → synthesize membrane lipids
What is the regulatory step of fatty acid oxidation?
fatty acid → fatty acyl CoA
There are different isoforms of fatty acyl CoA synthetase, why?
different kinds of fatty acids i.e., short, long chains
After fatty acyl-CoA is formed at the outer membrane/cytosol what happens?
moved to mitochondrial matrix via facilitated diffusion
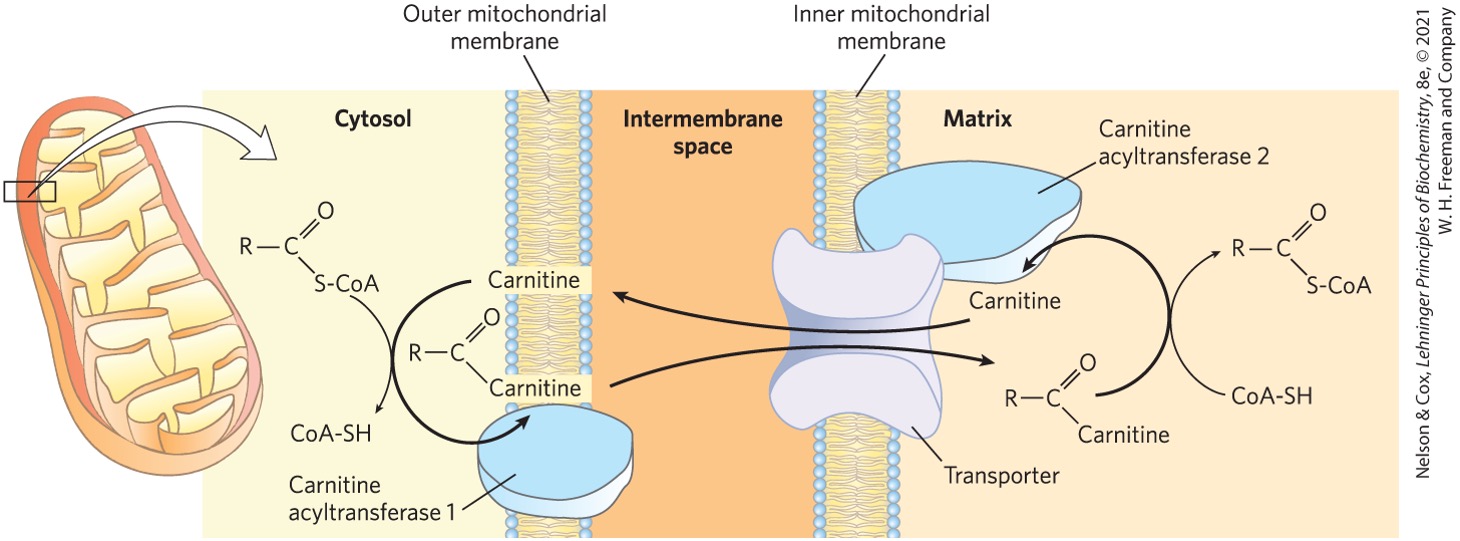
Fatty acyl-CoA binds to what forming what to enter the mitochondrial matrix?
carnitine
fatty acyl-carnitine shuttle
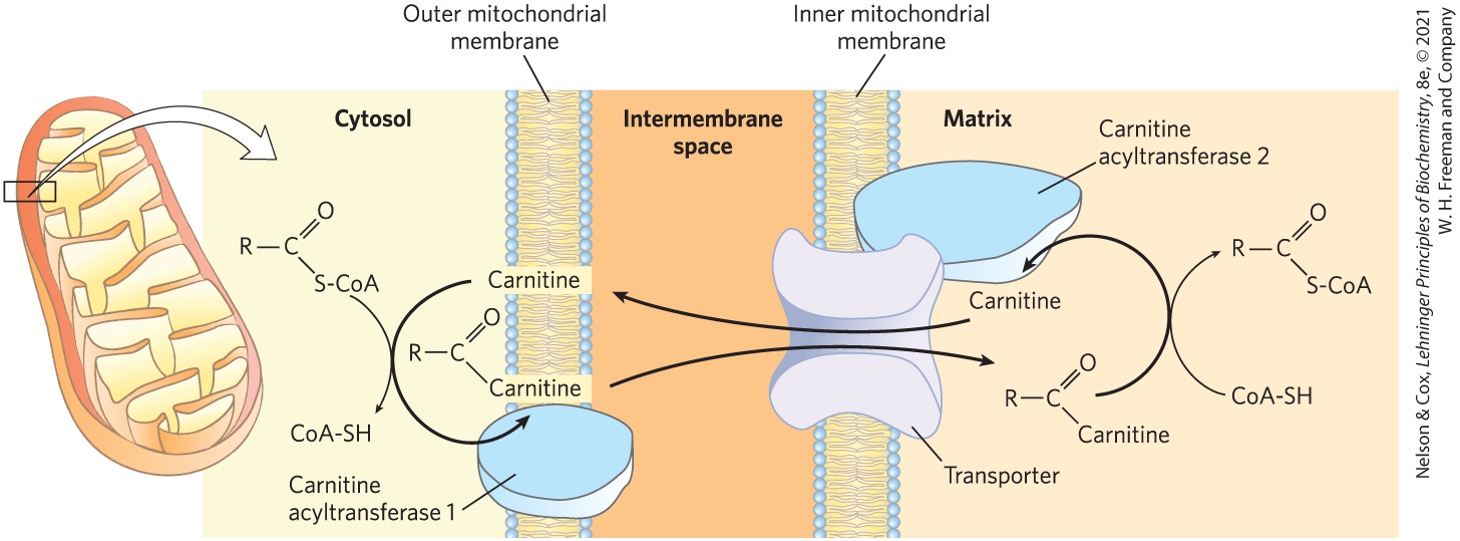
What enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the binding of carnitine and fatty acyl-CoA?
carnitine acyltransferase
Fatty acyl-carnitine formed in the outer mitochondrial membrane is shuttled where? through what structures?
intermembrane space (IMS)
large protein pores
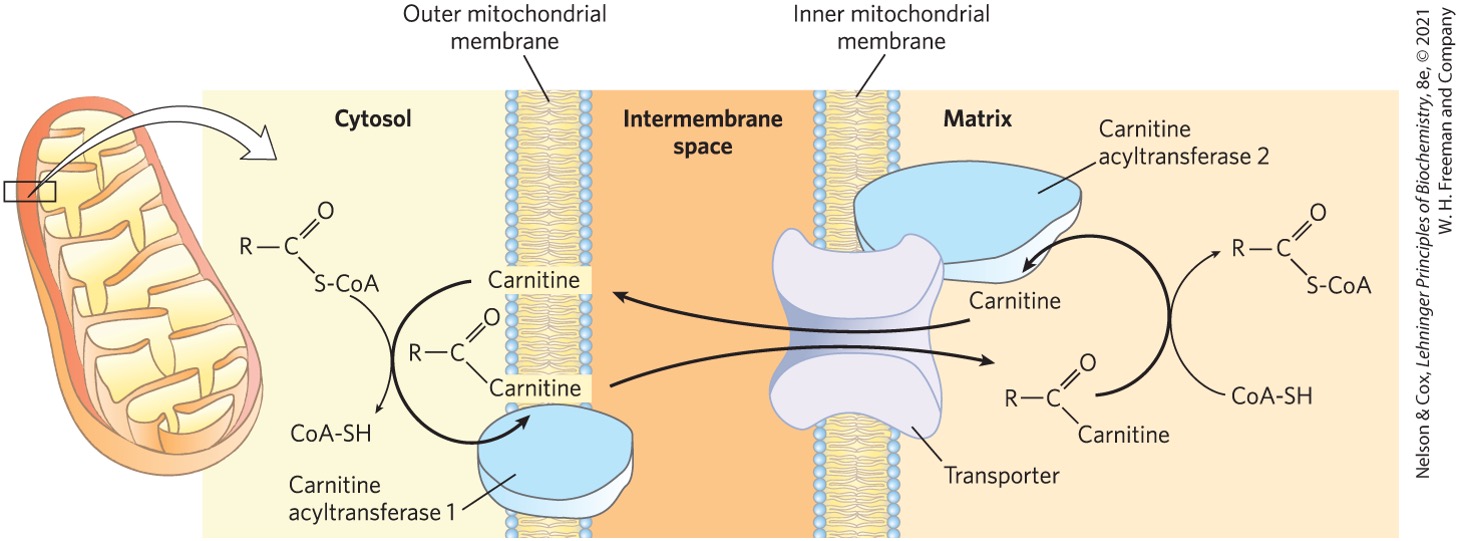
Fatty acyl-carnitine then moves from the IMS to where? via what transporter?
mitochondrial matrix
acyl carnitine/acyl transporter
located in inner mitochondrial membrane
Once fatty acyl-carnitine is inside the matrix, what is it transferred onto? what does it release?
coenzyme A
releases carnitine
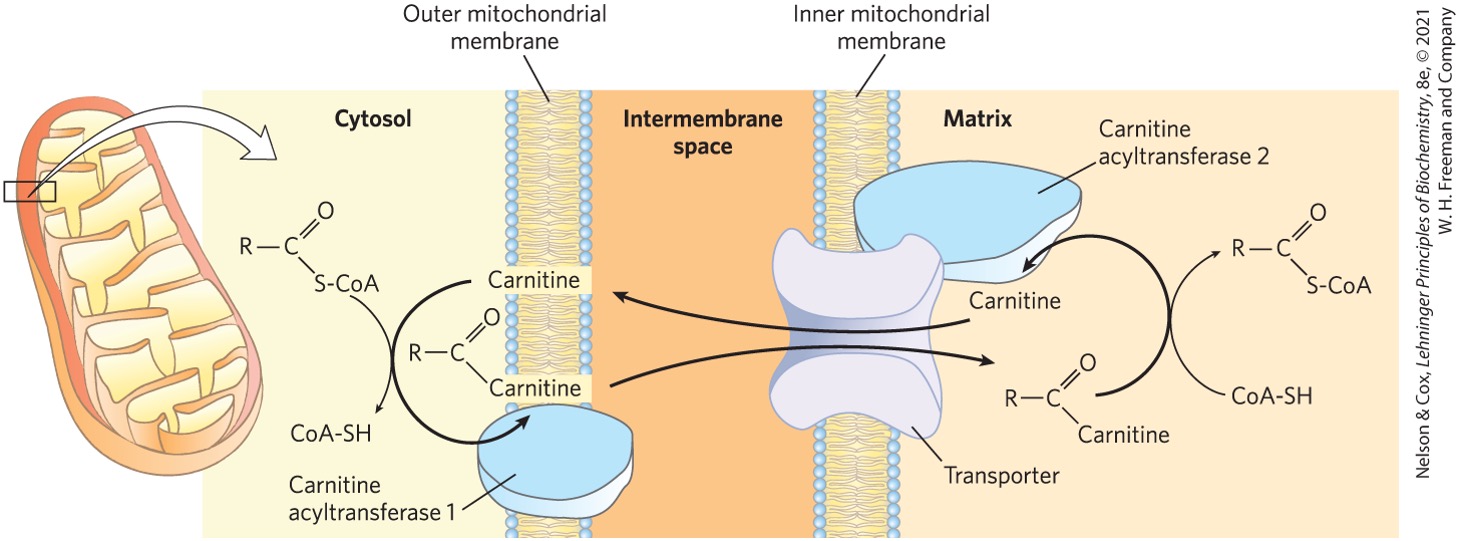
What enzyme catalyzes the transfer of fatty acyl onto coenzyme A releasing carnitine?
carnitine acyltransferase II
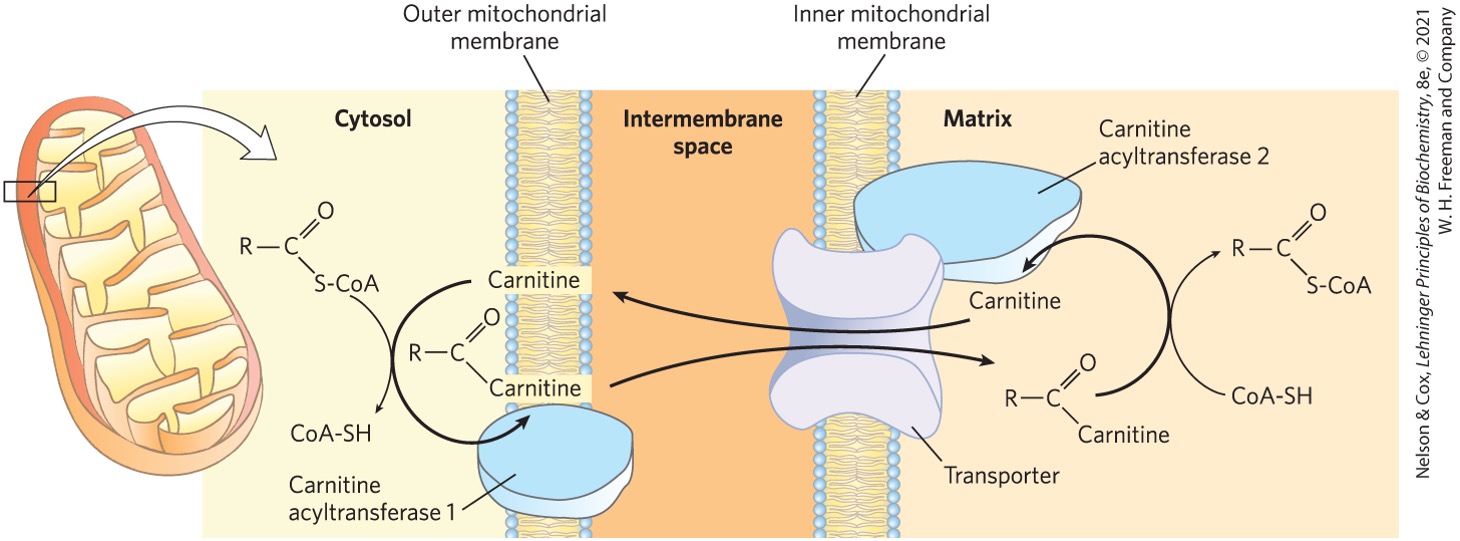
What happens to the carnitine once it is released from the fatty acyl?
returns back for another cycle of fatty acyl transfer into the matrix
Stage 1 of fatty acid oxidation
oxidative conversion of 2-C units into acetyl-CoA
release of NADH
Stage 2 of fatty acid oxidation
oxidation of acetyl-CoA into CO2 via citric acid cycle
release of NADH & FADH2
Stage 3 of fatty acid oxidation
generates ATP from NADH and FADH2 via respiratory chain
ETC
OXPHOS
Each step of beta-oxidation results in the release of what from where?
one acetyl residue
carboxyl end of fatty acyl chain
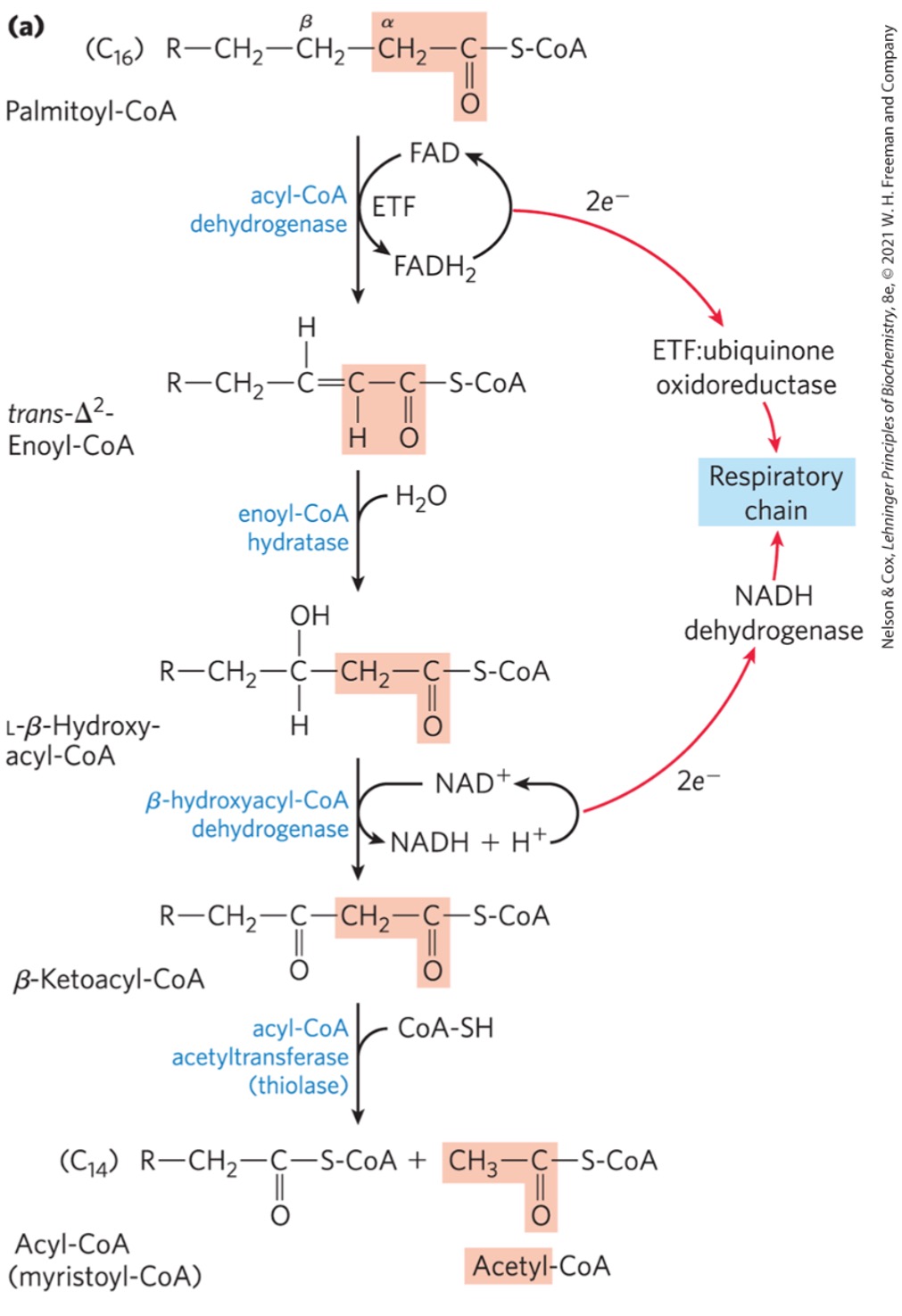
B-oxidation is a what sequence?
4 step
Palmitoyl-CoA has a 16-C long chain, meaning it releases how many acetly-CoAs?
8 acetyl-CoAs
Step 1) Dehydrogenation of fatty acvyl-CoA
forms double bond between alpha and beta carbons (C2 and C3)
reduces FAD to FADH2
makes trans enoyl-CoA
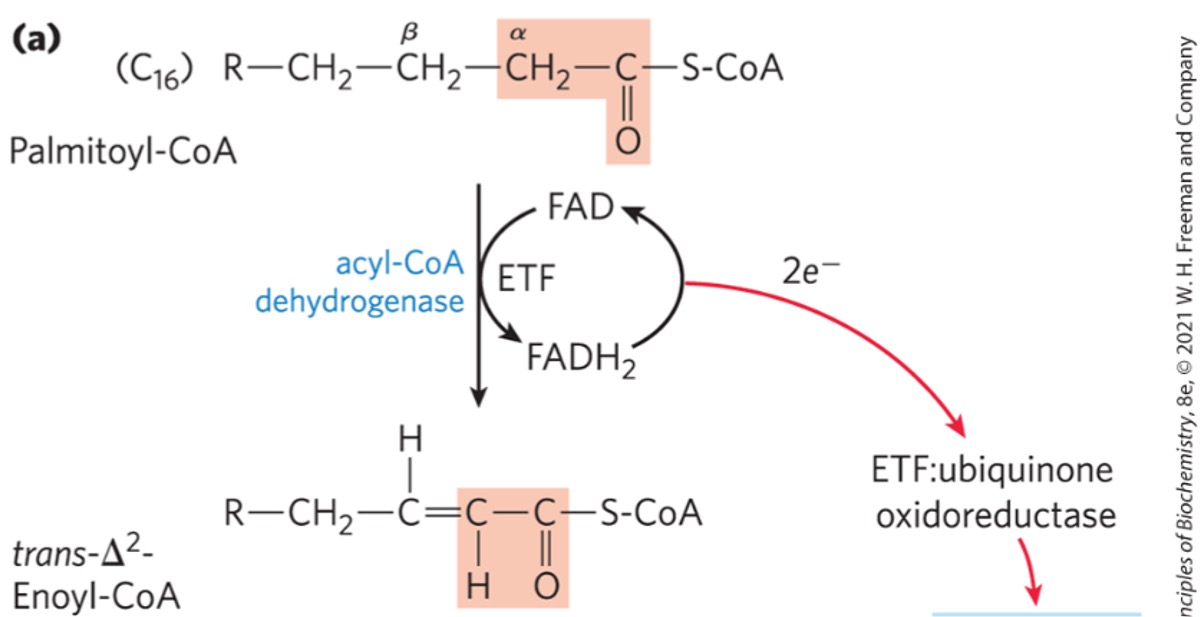
What enzyme catalyzes the first dehydrogenation step of beta oxidation?
acyl-CoA dehyrogenase
All isozymes of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase enzyme have what as a prosthetic group?
FAD
3 different isozymes of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase can be used, why?
different chain lengths
recall:
VLCAD → long i.e., 12 - 18
MCAD → medium i.e., 4 - 14
SCAD → short i.e., 4 - 8
FAD is reduced to FADH2 during the dehydrogenation step of B-oxidation, what’s the purpose of this?
electrons from FADH2 passed onto ETC via electron transferring flavoprotein (ETF)
Step 2) Hydration to alkene
water added to double bond from step 1
trans enoyl-CoA
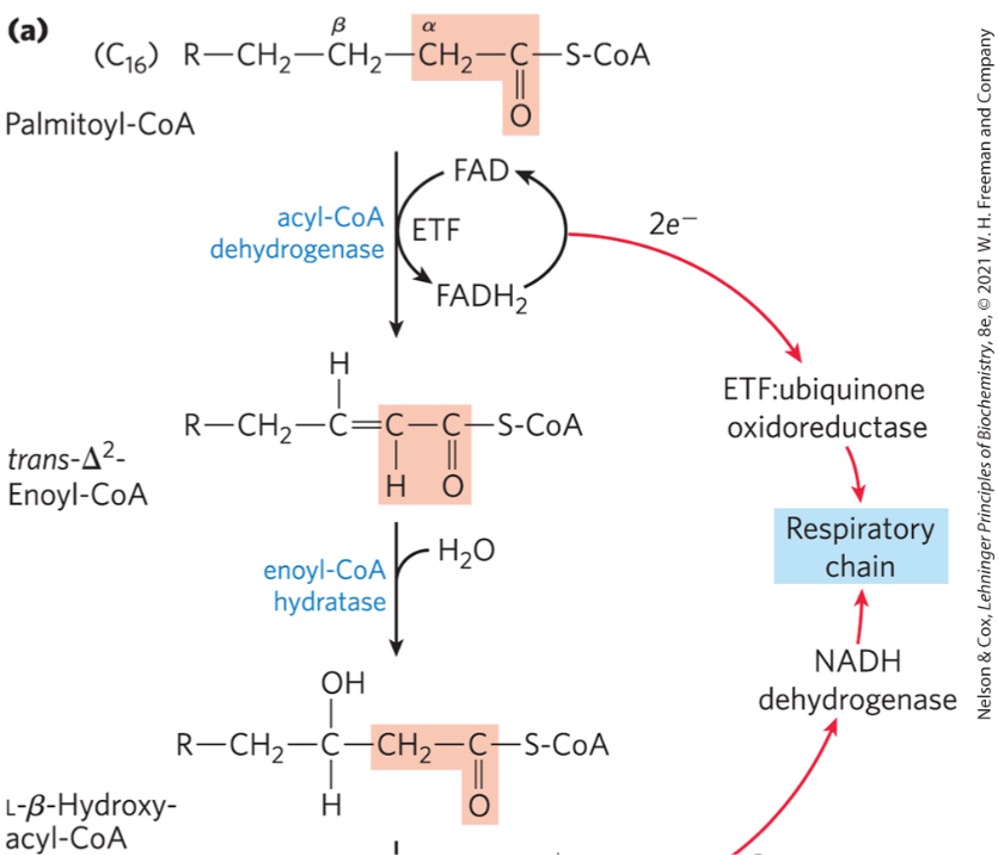
What enzyme catalyzes the hydration step of B-oxidation?
enoyl-CoA hydratase
What is the hydration step of B-oxidation analogous to in another cycle?
fumarase reaction in citric acid cycle
The hydration step is catalyzed by two isoforms of enoyl-CoA hydratase, what are they?
soluble short chain hydratase
crotonase
membrane-bound long chain hydratase
trifunctional complex
Can enoyl-CoA hydratase catalyse unsaturated fatty acid chains?
no
not a substrate for the enzyme