Nuclear Physics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
nuclei with higher binding energy per nucleon is
more stable
nuclei with large mass deficiency have
higher Binding energy
A<60 release energy by
Nuclear fusion
A>60 release energy by
Nuclear fission
binding energy per nucleon increases as the
mass number increase till 60
binding energy per nucleon ………..when A>200
decreases
when A>200 it means nuclei is……….stable
less, tends to undergo radioactive decay
The strong nuclear force
(an attractive force inside the nucleus).
The Coulomb force
(a repulsive electric force acting between the alpha particle and the nucleus)
when disintegration energy is lower then potential energy barrier that means alpha perticle
doen’t have enough energy to escape
Since the alpha particle cannot classically overcome the barrier, it instead tunnels through it due
to……………... This tunneling probability is ……..
quantum mechanical effects, very low,
why are even-even nuclei more present in nature
the are energticly favorble mor estable .>………………………………..rvmriovjeroa
neutrino, a neutral particle with extremely small mass.
Neutrinos
interact with matter, making them difficult to detect.
…………..they play a crucial role in conserving energy and momentum during ………..decay
Neutrinos,beta
nuclei create these particles (positron- nuterino) during the
beta decay process.
only the identity of a nucleon changes (neutron ↔ proton) but the total nucleon count …………
remains the same
Gamma decay is a nucleus emits a gamma ray, which is
a high-energy photon 𝛾
(A) of the nucleus does not change during
beta decay.
Mean life (𝜏) – which is the time at which N has been reduced to…..
𝑒−1 of their initial values
(even-even nuclei) have zero nuclear spinto the hypothesis that spins of nucleons inside
a nucleus are
very strongly paired to cancel their overall effect
Every charged particle has a magnetic dipole moment associated with its spin,
given by
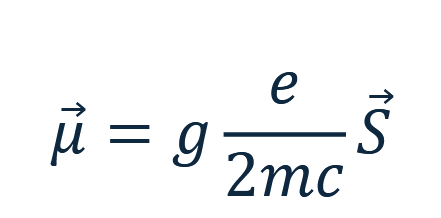
from quantum mechanics that
orbital angular momentum can take on
only integral values
The total angular
momentum of the constituents is given by the vector sum of the
orbital and
intrinsic spin angular momenta
nuclei with even atomic number have ………….
nuclear spin
integral
odd atomic number have ……..nuclear
spin
half-integral
even-even nuclei) have………………spin.
zero nuclear
large nuclei have very ………..nuclear spins in their ………………
small , ground states.
g is known as the Lande factor (g-factor), which for a point
particle, such as the electron, is expected to have the value
𝑔 = 2.
When 𝑔 ≠ 2, the particle is said to possess an ……………………….
which is usually ascribed to the particle having a …………….
anomalous magnetic moment,substructure
the dipole moment 𝜇𝑒 ≈ 𝜇𝐵, where 𝜇𝐵 is the Bohr magneton, defined as
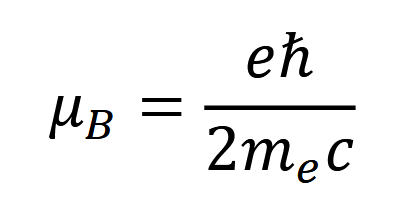
From the ratio of 𝑚𝑝/𝑚𝑒
we deduce that the Bohr magneton is about 2000 times
………….than the nuclear magneton.
larger
𝜇𝑝 =
2.79𝜇𝑁
𝜇𝑛 =
−1.91 𝜇𝑁
𝑔𝑝 =
+5.58
𝑔𝑛 =
-3.826
both nucleons have large anomalous contributions to their
moments. This provides indirect evidence that these particles…………..
have additional structure.
since the neutron is electrically neutral sizable magnetic
moment is particularly dramatic which points to the fact that the neutron must………….
have an extended charge distribution ************
measurement of magnetic dipole moments for different nuclei has yielded
−3𝜇𝑁 and 10𝜇𝑁
This again
is evidence for strong pairing inside the nucleus
Furthermore, this also shows that electrons cannot be present inside nuclei
because it would then be particularly hard to explain the small values of nuclear
moments, since even one electron would produce a moment a thousand times
that observed for nuclei.
Furthermore