ecawns market failure
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
info failure + asymmetric
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
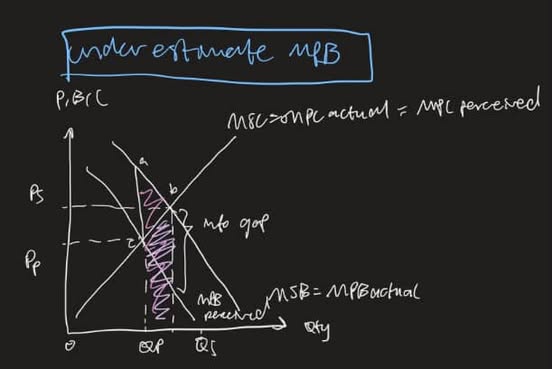
underestimate benefits (MPB) def
MPB p < MPB a
MSB>MPB p
—> UNDERALLOCATION
underestimate benefits (MPB) cause
myopic decision making
underestimate benefits (MPB) diagram
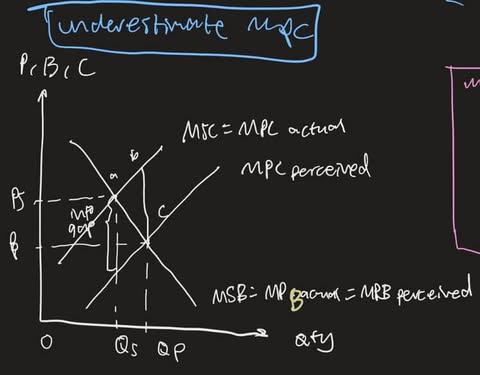
underestimate costs (MPC) - def
MPCp < MPCa
MSC>MPCp
→ overallocation
underestimate costs (MPC) - diagram
underestimate costs (MPC) - cause
addiction, myopic decision making
PIDQQD (P)
Priv costs, benefits
PIDQQD (I)
info gap
PIDQQD (D)
divergence between actual and perceived
P<A/ P>A
PIDQQD (Qp)
under estimation/ over est
QP<QS/QP>QS
PIDQQD (Qs)
under/over con/prod
social optimal qs
PIDQQD (Dwl)
dwl ABC
btw Qp and Qs, TSB>TSC / TSC> TSB
actual mpb/mpc not fully taken into account → distortion of price signals
X social optimal allocation
market failure
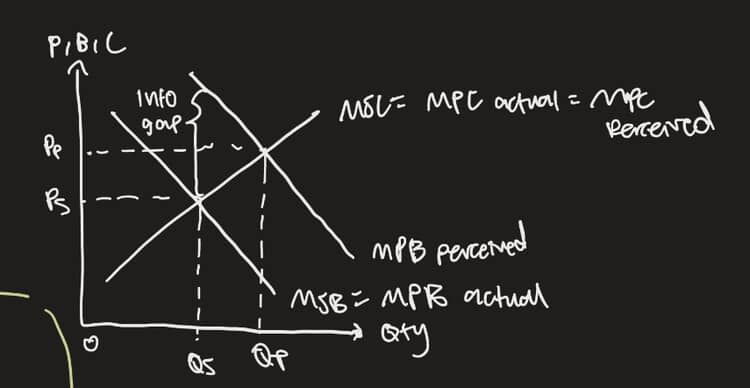
overestimate benefits - cause
persuasive advertising
product complexity (think they need stuff like RAM in laptops but dont)
overestimate benefits - diagram
govt int - imp info (2)
rules and regulatuons
public education
govt int - imp info - r&r
fx:
consider priv cost and benefits
reduce underestimation of mpc/mpb
reduce allocative inefficiency
examples:
food nutrition labels
healthcare display medical charges openly
cigarette health warnings
govt int - imp info - r&r - limitation
high admin costs, unsustainable
govt int - imp info - r&r - unintended conseq (2)
higher prices and poor quality
→ raising COP might compromise on quality
opp cost of implementation
govt int - imp info - public edu - fx
MPC and MPB perceived to actual
eg:
→ public campaign by health promo board
→ covid vaccine campaign
→ screen for life (SFL)
encourage health check ups
increase MPBp
decrease dwl
govt int - imp info - public edu - unint conseq
cost
opp cost
govt int - imp info - public edu - int conseq
directly target root cause → REAL
less exp in long run
politically favourable → regard consumer sovereignty
salience bias -> focusing on things more obvious
govt int - imp info - public edu - limitations
time lag
uncertainty of outcome → stubborness
asymmetric info - def
when 1 party has more info than other in an economic transaction
asymmetric info - problems
adverse selection
moral hazard
adverse selection (Def)
undesirable members of a pop of buyers and sellers engage in voluntary exchange
—> one know more, dw say
adverse selection - 2nd hand car market
-lemons (low quality) and cherries (high quality)
lemons dominant in market
lack of info = all cards assumed as medium quality
low quality stay, high quality exit market
further lower prices consumers willing to pay
asymmetric info, less sold
welfare loss
missing market: all cherries leave, only lemons left
adverse selection - health insurance
healthy and unhealthy buyers
unhealthy dont declare conditions -→ more likely to buy insurance
treat everyone as average
healthy want cheap, exit market
unhealthy dominatory
price increase
unprofitable
missing market: no companies want to sell insurance
govt intervention adverse selection
r&r - lemon law
r&r - lemon law
→ compulsory for used car dealers to send cars for inspection and certification
lemon law
→ consumer make claim for lemon within 6 mths
→ compulsory to repair/replace/refund/red price
→ if not, CASE (consumers association of sg) issue penalties
priv solutions
signalling
→ more informed convey info to less informed (eg warranties)
screening
→ more informed must provide less informed with info before transaction
moral hazard (def)
economic agents take greater risks than normal
→ resulting costs not borne by the agents themselves → hidden actions after transaction
moral hazard - example
health insurance
(people buy insurance, take other greater risk, think they have insurance anyw, cause excessive insurance payouts, companies exit market → missing market cuz not mutually beneficial)
moral hazard - govt int (rules and regulations)
eg in 2019
-→ law that removed full riders on new insurance policies, cannot pay nth for hospital bills → must pay 5%
moral hazard - priv solutions
insurance companies make co payments and deductibles mandatory
→ insurers include terms in their contracts
(eg fire insurance company insist sprinkler system)
govt considerations - limitations - asymmetric info (6)
info gap (Det lvl of co payment)
time lag
uncertainty of outcome
increase govt expenditure → unsustainable long term
(premium rates of low risk people increase, medishield life premiums increase, subsidies increase)
opp cost
asymmetric application → medishield life
basic and compulsory insurance → all citizens and PR → lower health care cost
—> for ADVERSE SELECTION: spread risk btw both risky and less risky consumers
deductible and co payment
—> MORAL HAZARD: buyer bear some cost