Gravimetric Analysis
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Gravimetric Analysis
• Determination of an analyte based on the
_____________
• Simple, but __________ in chemical analysis
• Involves ___________reaction at controlled
condition to _______________________.
mass of a solid
most accurate
precipitation reaction
selectively precipitate species.
Gravimetric Analysis
selectively precipitate
removing?
removing interfering species before measurement
GRAVIMETRIC ANALYSIS
Used to find the % of ________________ in a mixture
• Involves forming a suitable ___________ with the ion in the sample
One particular component
suitable precipitate
Gravimetric Analysis
This procedure is especially suitable for determining of metal ions and anions such as _________.
This procedure is especially suitable for determining of metal ions and anions such as sulphates.
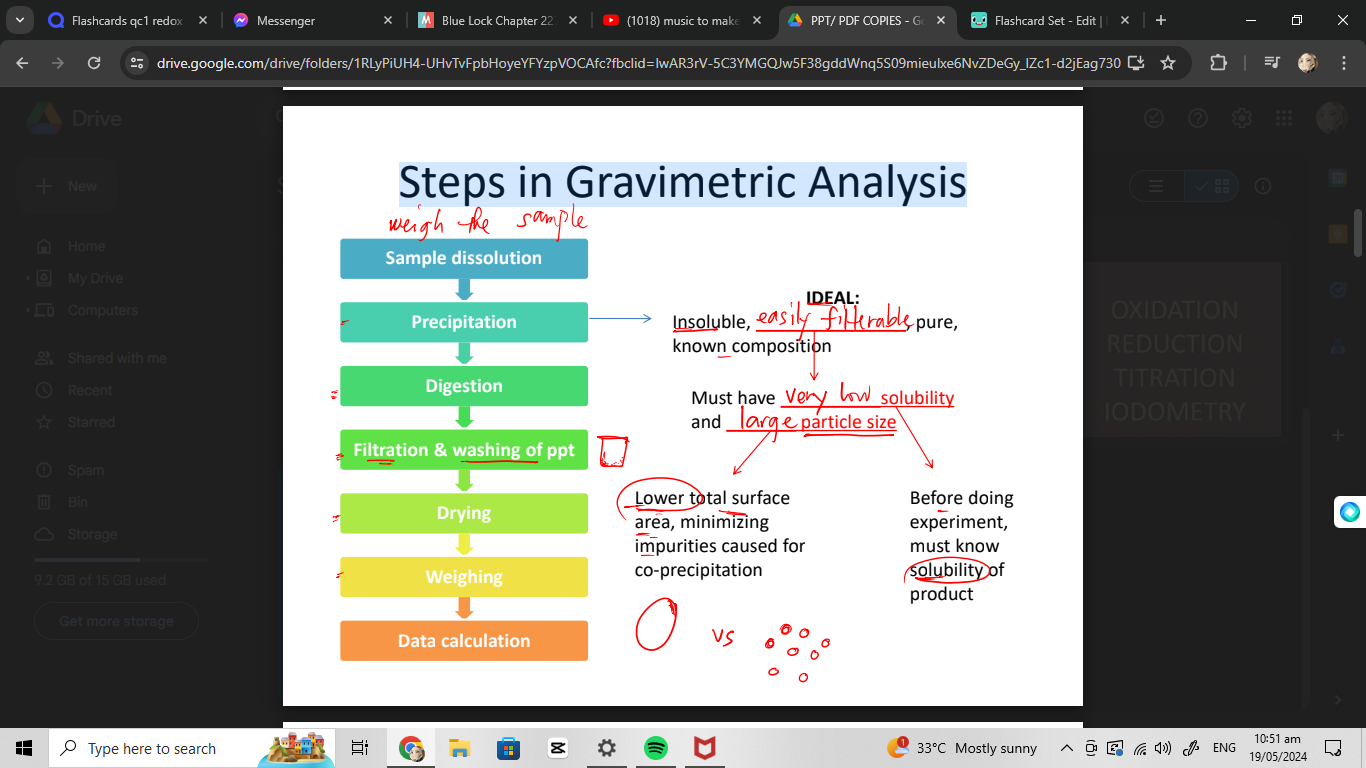
Steps in Gravimetric Analysis
wspdfdwd
weigh the sample
Sample dissolution
Precipitation
Digestion
Filtration & washing of ppt
Drying
Weighing
Data calculation
Steps in Gravimetric Analysis
precipitation
Steps in Gravimetric Analysis
IDEAL— HOW?
• Control parameters to achieve ideal precipitate
vol os sol’n
type of precipitate agent
Presence/concentration of other species in solution that may affect precipitation process
temp of sol’n
Ph of sol’n
Gravimetric Analysis
A ______________ amount of some product can be obtained from a ______ like the component of the ______ being assayed by any one of the various methods.
chemically equivalent, , reactant, sample
Gravimetric Analysis
1 may be ________ from solution
2 may be ___________ product resulting from
______ of a compound
3 may be _______ on an _______ by ___________
may be precipitated from solution.
may be decomposition product resulting from
ignition of a compound.
may be deposited on an electrode by electrolysis
Properties of precipitates
• To obtain good results, we must be able to
produce “_______” precipitate that can be
recovered with _______________.
pure, high efficiency
Criteria of Good precipitate
-Have ___ _____
-Be easy to _____ by _______
-Be _______ to air, water.
-Be something where our analyte is only a ______ portion of the ppt.
➢Have low solubility
➢Be easy to recover by filtration
➢Be unreactive to air, water...
➢Be something where our analyte is only a small
portion of the ppt.
The precipitate should:
1. Have a known _______
2. Have a _____ solubility
3. Be stable when ______ (so it does not __________ and can be easily dried
4. Not form ___________ with other _____ that are likely to be present
formula
low solubility
heated, decompose,
precipitates, ions
precipitate form by gravimetric analysis
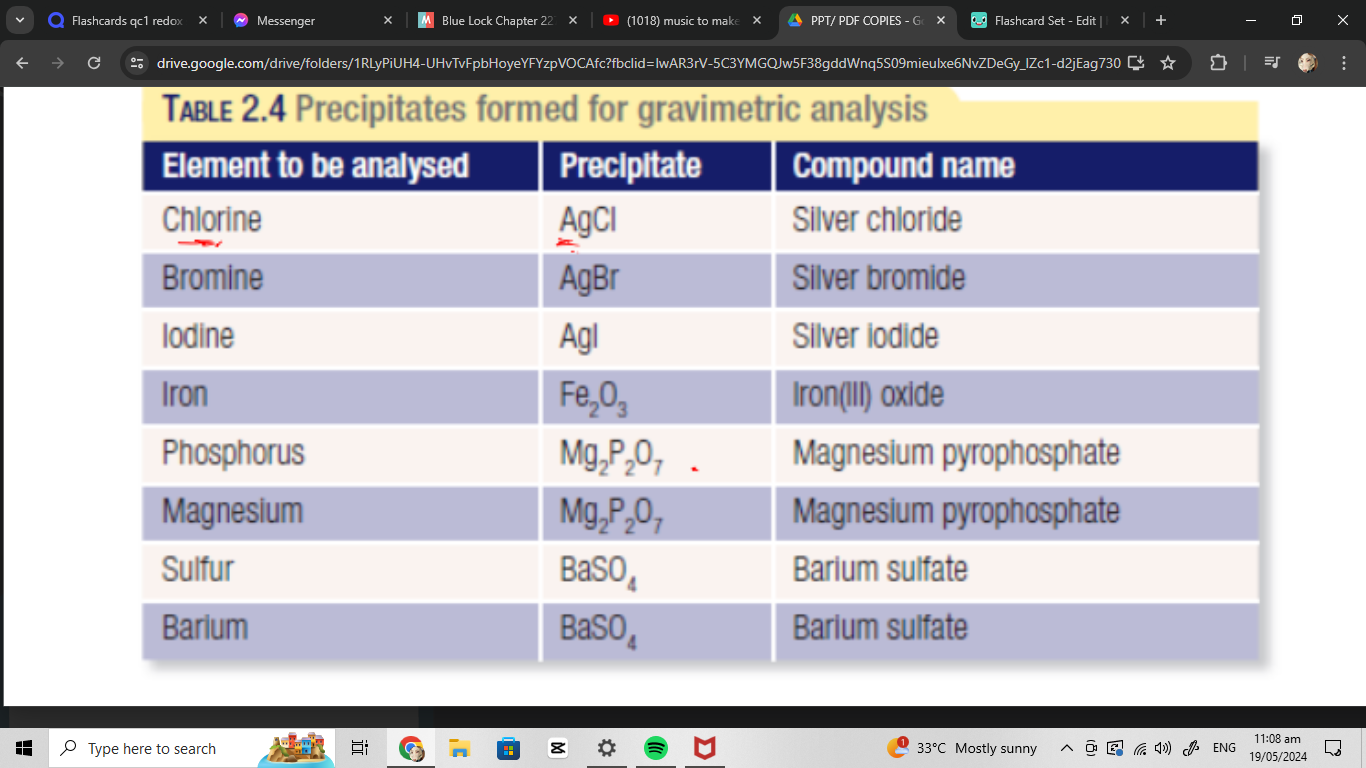
filtering
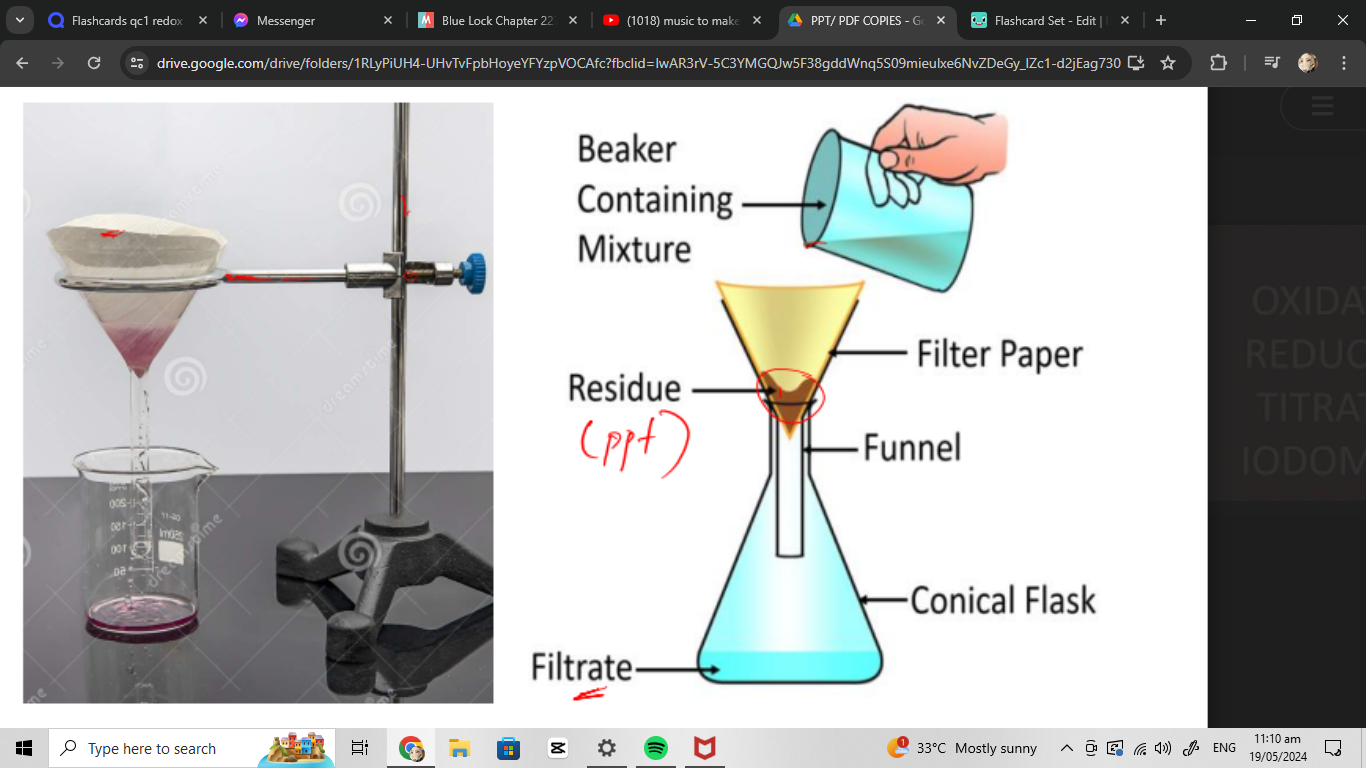
vacuum filtering apparatus
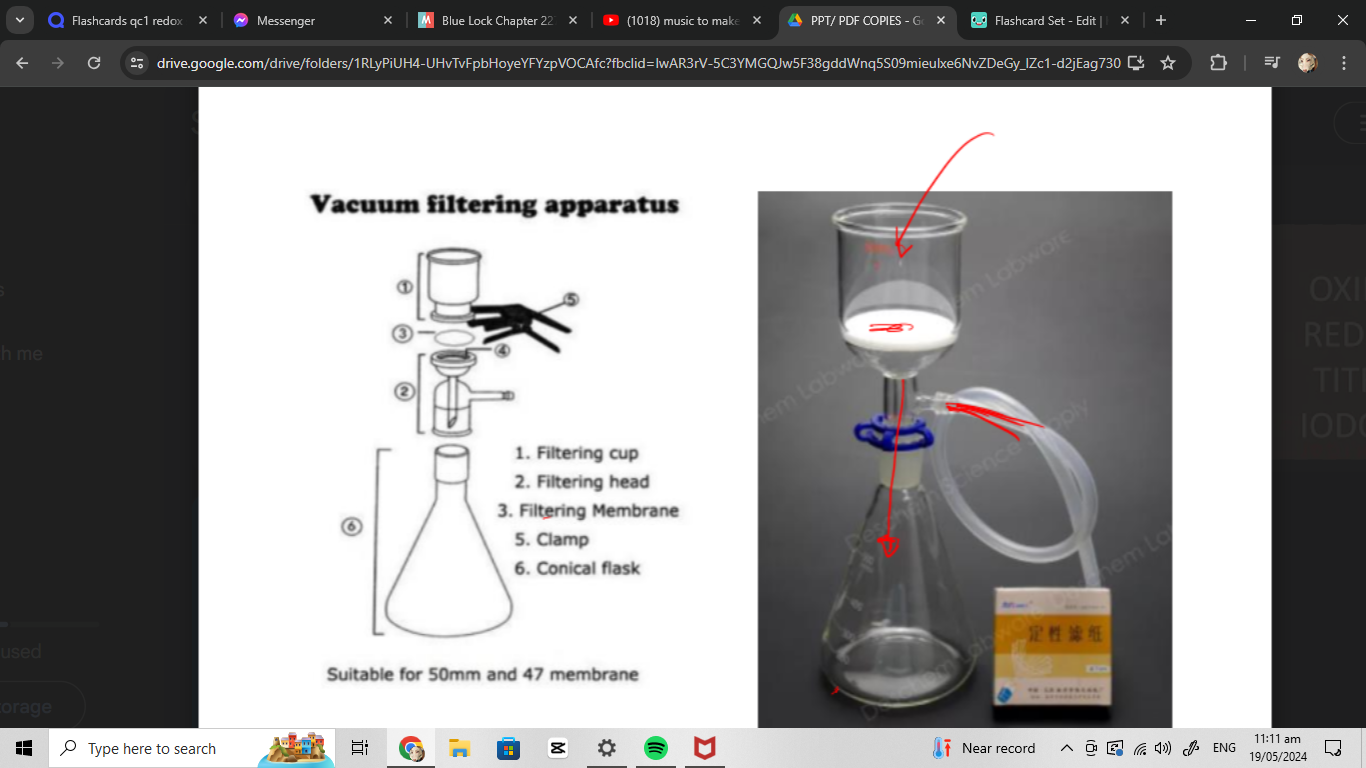
Type of suspension and filterability
Colloidal and Crystalline
Type of suspension and filterability
Colloidal
Size range :
Tendency to settle:
Filterability:
Purity:
10-6 – 10-4mm
no
Difficult or impossible
not pure
Type of suspension and filterability
Crystalline
Size range:
Tendency to settle:
Filterability:
Purity:
10-1 – 10 mm
Will settle spontaneously
Readily filtered
Typically higher purity than colloids.
THE FACTORS GOVERN THE PARTICLES
SIZE OF A PRECIPITATE
ptrt
• Precipitate solubility
• Temperature
• Reactant concentration,
• The rate at which reactants are mixed.
The net effect of these variables can be
accounted for, at least qualitatively, by assuming
that the particle size is related to a single
property of the sytem called its
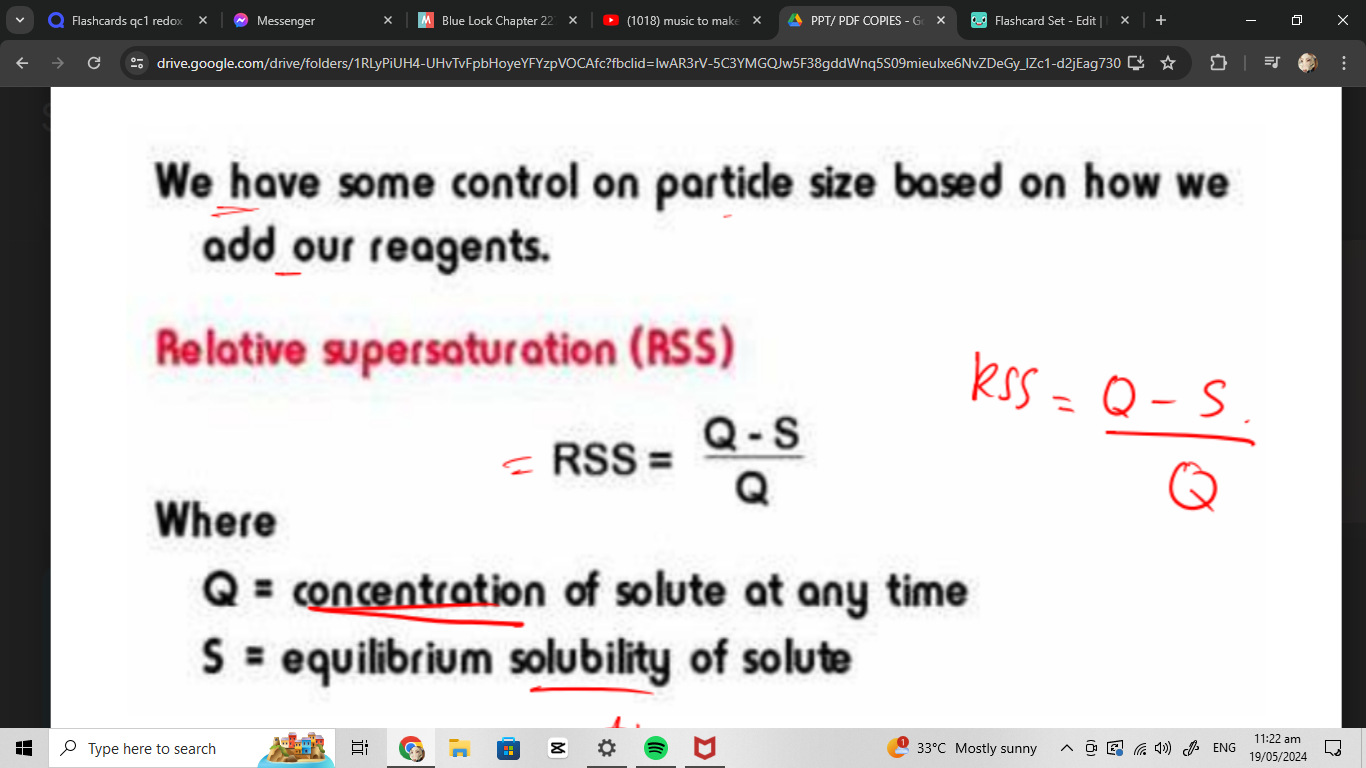
relative supersaturation RSS
The net effect of these variables can be
accounted for, at least qualitatively, by assuming
that the particle size is related to a single
property of the sytem called its
______ __________ ____
relative supersaturation RSS
relative supersaturation where
Q:
S:
Q= conc of the solution everytime
S= equilibrium solubility of the solute
______ can be used to estimate or control the type of precipitate that is formed
RSS
if RSS is large tend to form
if RSS is small tend to form
colloids
crystaline ppt
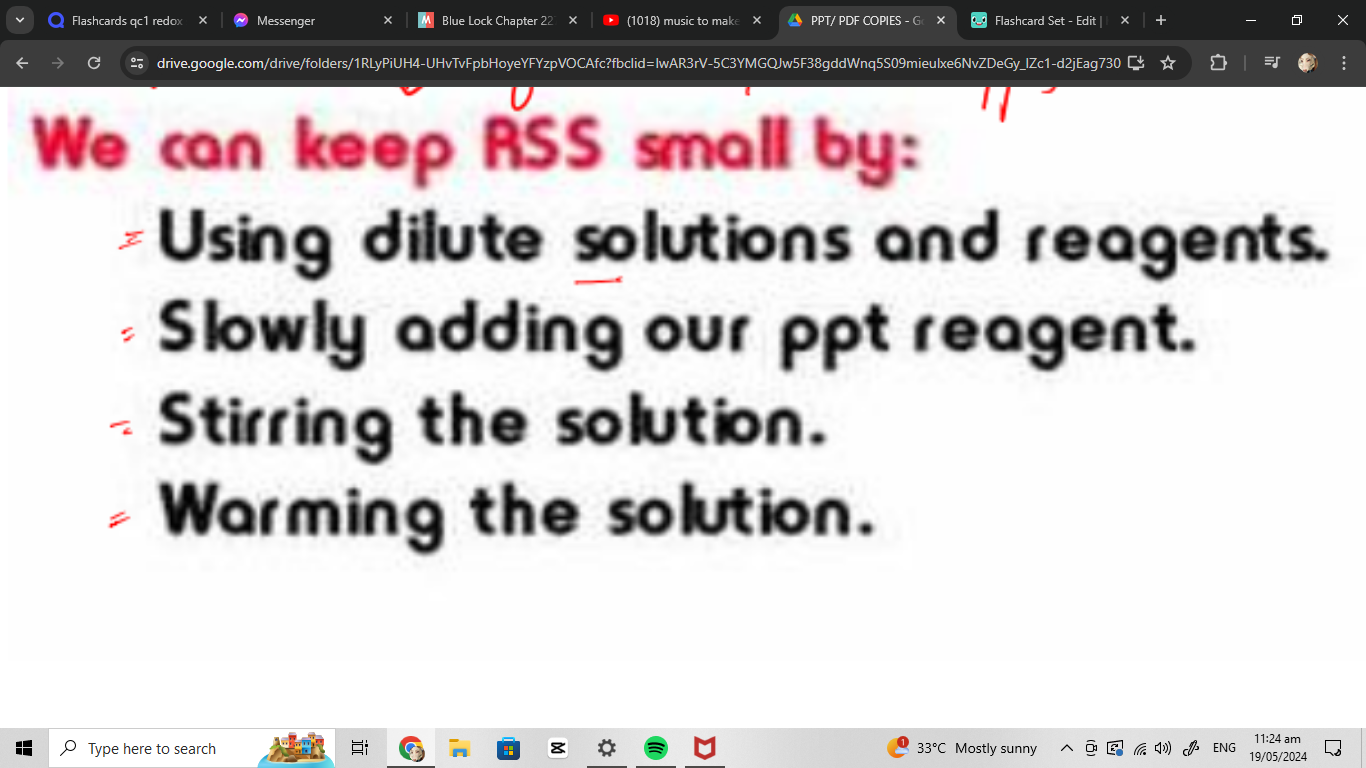
we can keep crystalline small by
When designing a _____________________ , a knowledge of the __________ of the __________ likely to be produced is important
gravimetric procedure, SOLUBILITIES, precipitates
table the solubility of compoun
Gravimetric Analysis
• Assay of ____________
• Assay of _____ ______ _____ for _________ content
• Assay of _____________________
• Assay of ______________
Sodium chloride
Sodium Lauryl sulfate for Sodium sulfate content
Mercaptomerin Sodium
Sodium phosphate solution
Sodium Lauryl sulfate tx for
surfactant emulsifying agent
Mercaptomerin Sodium tx for
congestive heart failure
Sodium phosphate
laxative to cleans colon before colonoscopy
tx for hypophosphatemid
2 types of method
precipitate and volatilization methods
precipitation method
Based on isolation of an insoluble
precipitate of known composition,
volatization method
–Analyte is volatilized, weighed and the
concentration is determined.
Gravimetric analysis
nitric acid prevent——
helps to——-
precipitation of ther subs
insol in water but sol in nitric acidcoagulate any colloidal silver chloride
Gravimetric analysis
“ The _____ has relationship with the _______
and the _______ _____ or _______ _______”
weight, analyte, material used, actually weight
Gravimetric analysis
Calculations associated with the method are
based on
stoichiometry
stoichiometry definition
quantitative rel. of reactants and products
Stoichiometry of Reaction
• A ________________ gives the ratios, in moles of
materials produced or consumed in a reaction.
balanced formula
Stoichiometry of Reaction
If the _____of anyone species used or produced is __________, the others are ______ calculated.
weight, known, readily
___________________ are simple an extension of
______________________
• Our ___________ _______ is most often based on the amount (in ______) of our analyte in the material actually weighed.
Gravimetric calculations, stoichiometric calculations
stoichiometric factor, moles