CHAPTER 11 – MOTIVATION AND EMOTION
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is motivation?
Motivation is an internal state that activates and directs thoughts and behaviors, influencing the intensity, persistence, and direction of actions.
What are the two main components of motivation?
Motivation comes from internal drives (biological needs) and external cues (rewards or environmental factors).
What does the term "motivation" originate from?
The term "motivation" comes from the Latin word "movere," which means "to move."
What is the primary difference between primary and psychological motives?
Primary motives are biological and essential for survival (e.g., food, water), while psychological motives are not directly related to survival and are influenced by learning and social factors
What is Hull’s Drive Theory?
Hull’s Drive Theory states that behavior is motivated by internal drives that arise when homeostasis is disrupted, pushing individuals to restore balance (e.g., hunger or thirst).
What is expectancy theory?
Expectancy Theory suggests motivation is determined by the expectancy (likelihood that efforts will lead to success), instrumentality (perceived connection between performance and rewards), and valence (the value placed on the rewards).
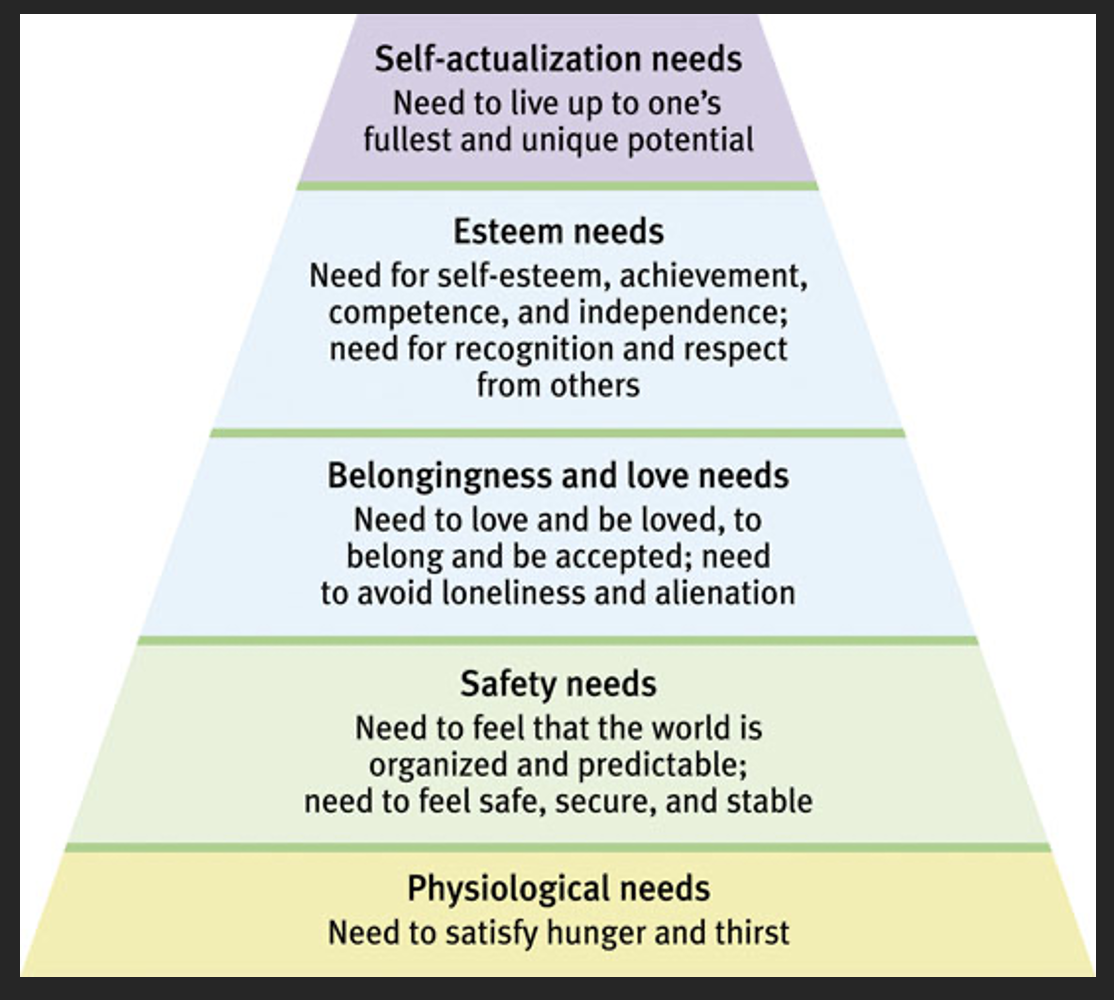
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
Maslow's theory proposes that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, starting with physiological needs at the base and ending with self-actualization at the top. Lower needs must be fulfilled before higher needs can be pursued.
What is the Self-Determination Theory (Deci & Ryan)?
This theory posits that motivation is influenced by the fulfillment of three basic psychological needs: competence(mastery), autonomy (control), and relatedness (connection with others).
What are the primary motives for survival and growth?
Primary motives include basic needs like food, water, shelter, and love, which are governed by the midbrain and hypothalamus
What is the difference between mastery and performance goals in achievement motivation?
Mastery goals focus on personal growth and learning, while performance goals focus on outperforming others and receiving external rewards.
What is the psychological impact of emotions on motivation?
Emotions motivate action by focusing attention and influencing behavior. Positive emotions broaden attention, while negative emotions narrow focus.
What are the six basic emotions?
The six basic emotions are happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, and disgust.
How does the James-Lange Theory explain emotions?
The James-Lange Theory posits that emotions result from the body’s physiological response to a stimulus (e.g., you feel afraid because you tremble).
How does the Cannon-Bard Theory differ from the James-Lange Theory?
The Cannon-Bard Theory argues that physiological responses and emotions occur simultaneously and independently, rather than one causing the other.
What is cognitive appraisal in emotion theory?
Cognitive appraisal refers to the process by which an individual evaluates a situation and interprets physiological arousal to determine the emotion they are feeling.
What are the two neural pathways involved in emotional processing according to the dual pathway model?
One pathway leads to the amygdala for an immediate emotional and behavioral response, while the other leads to the cerebral cortex for conscious interpretation.
What is the role of the amygdala in emotions?
The amygdala processes emotional responses, particularly fear and anger, and plays a role in the body’s immediate reaction to perceived threats.
What is the difference between mood and emotion?
Emotions are short-lived and specific, while moods are longer-lasting and more diffuse, affecting one's overall outlook.
What is the difference between approach-approach and avoidance-avoidance conflicts?
Approach-approach conflict involves choosing between two desirable goals, while avoidance-avoidance conflict involves choosing between two undesirable options.
How do emotions influence social interactions?
Emotions regulate social interactions by signaling approach or avoidance behaviors, helping individuals navigate relationships and group dynamics.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) in emotions?
The ANS helps mobilize the body’s physiological responses to emotions, with the sympathetic system preparing for action (fight or flight) and the parasympathetic system calming the body down.
How does culture influence emotional expression?
Cultural differences affect how emotions are expressed and perceived. For example, some cultures emphasize emotional restraint, while others encourage open displays of emotion.
What are self-conscious emotions?
Self-conscious emotions, such as guilt, pride, and embarrassment, develop after infancy and are influenced by social interactions and cultural norms.
How do defense mechanisms like procrastination relate to motivation?
Defensive avoidance, like procrastination, is a way of avoiding decisions or actions that trigger discomfort or conflict, often affecting motivation and performance.
How can motivation be measured?
Motivation can be measured through instruments like the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), which assesses needs for achievement and affiliation based on responses to ambiguous pictures.
Hierarchy of Needs