A/P II Lab Practical 3
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What protective layers cover the heart? List them from innermost to outermost order.
Endocardium
Myocardium
Epicardium
List the composition and role of the endocardium protective heart layer.
Innermost Layer
Composition: Connective Tissue
Role: Lines Inner Chambers
List the composition and role of the myocardium protective heart layer.
Middle Layer
Composition: Muscle Cells
Role: Contractions
List the composition and role of the epicardium protective heart layer.
Outermost Layer
Composition: Adipose CT
Role: Protection
How many chambers does the human heart have?
Four
What are atria? How many are there in the heart? What is their role?
Def: Chambers of the heart where blood ENTERS the heart.
Two Atria
What are ventricles? How many are there in the heart? What is their role?
Def: Chambers of the heart that contract to pump blood OUT of the heart.
Two Ventricles
Which chambers carry oxygenated blood? Which chambers carry deoxygenated blood?
Right Side
Right Atrium
Right Ventricle
Oxygenated: Left Side
Left Atrium
Left Ventricle
What is the systemic circuit? Which heart chambers serve the systemic circuit?
Def: The circuit of blood vessels that goes from heart to organs/tissues to heart.
Served:
Right Atria - low-O2 blood returns from systemic circuit.
Left Ventricle - high-O2 blood sent to the systemic circuit.
What is the pulmonary circuit? Which heart chambers serve the pulmonary circuit?
Def: The circuit of blood vessels that goes from the heart to lungs and heart.
Served:
Left Atria - high-O2 blood returns from pulmonary circuit.
Right Ventricle - low-O2 blood sent to pulmonary circuit.
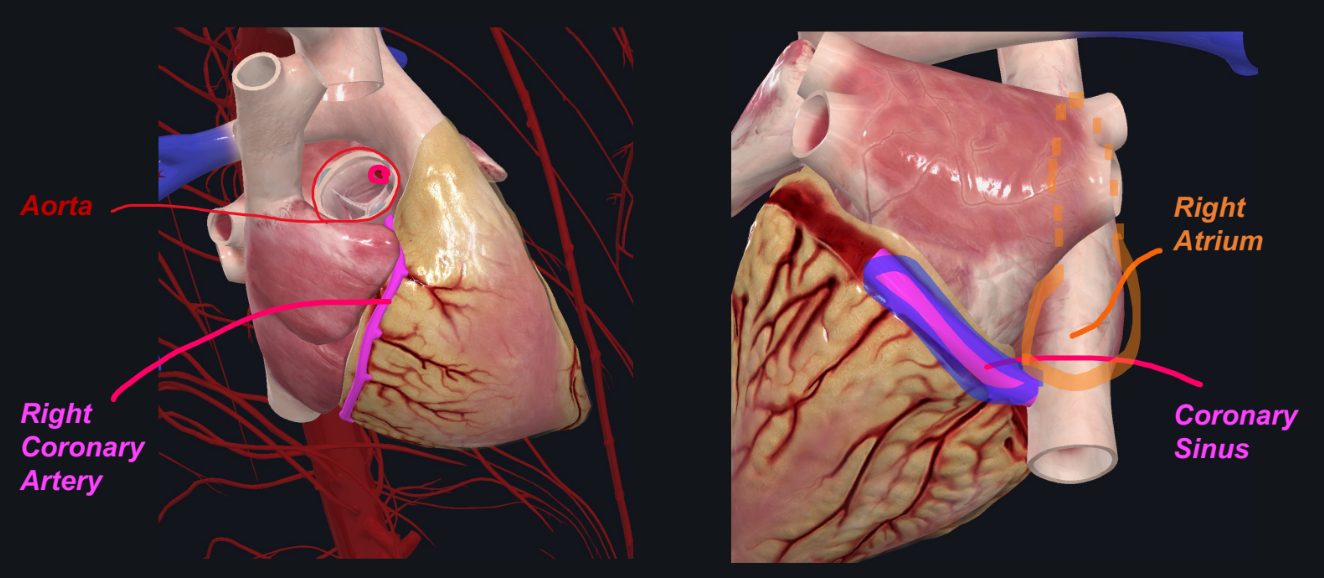
What is the coronary circuit? Why is it needed? Which heart chambers connect to the coronary circuit?
Def: A separate circuit that supplies oxygen to heart muscle tissue.
It is needed because although the heart is continuously full of blood, cells do not get their oxygen from the chambers.
Connected To:
Left Coronary Artery (leaves Aorta)
Right Coronary Artery (leaves Aorta)
Coronary Sinus (enters Right Atrium)
Which heart chamber has the thickest myocardium? Why?
Left Ventricle
Because it has to push blood through the larger systemic circuit, ensuring sufficient blood flow to all body tissues.
What is the function of the papillary muscles and the chordae tendineae?
Prevents eversion of AV valves, stopping backward blood flow into atria.
What is the fossa ovalis? What defects can be associated with it?
Def: A depression or shallow indentation located in the interatrial septum of the heart, specifically in the right atrium.
Remnant of: Fetal Foramen Ovale
Defect: Patent Foraemn Ovale
When the foramen ovale fails to close properly after birth, leaving a small opening between the right and left atria…persists until adulthood.
What is the ligamentum arteriosum? What is it a remnant of?
Def: A small, fibrous band of tissue located between the pulmonary artery and the aortic arch in the adult heart. It plays no active role in circulation after birth but is an important remnant of fetal circulation.
Remanant of: Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Defect: Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Which valves open as ventricles contract?
Semilunar Valves
Aortic Semilunar Valves
Pulmonary Semilunar Valves
Into what chamber does the following vessel dump its blood: Coronary Sinus
Drains deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle to the right atrium.
Into what chamber does the following vessel dump its blood: Superior- & Inferior Vena Cava
SVC: Returns deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium.
IVC: returns deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium.
Into what chamber does the following vessel dump its blood: Pulmonary Veins
Carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Into what chamber does the following vessel dump its blood: Pulmonary Arteries
Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lung.
Into what chamber does the following vessel dump its blood: Aorta
Carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body.
Into what chamber does the following vessel dump its blood: Coronary Arteries
Supplies oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
Which coronary artery usually gives rise to nodal arteries that supply both the SA and AV nodes?
Right Coronary Artery—-contains pacemaker cells that trigger APs (trigger heartbeat).
To what vessel do all of the coronary veins return blood? Where does this vessel empty the blood?
Coronary Sinus
Empties blood into the right atrium of the heart.
What is the intrinsic cardiac conduction network?
The intrinsic cardiac conduction network is a specialized network of cells that conduct action potentials throughout the heart to ensure coordinated contraction.
Describe how action potentials control the cardiac cycle as they move through this network.
SA Node: The SA node generates an action potential, which spreads through the atria, causing atrial contraction (P wave in ECG).
AV Node: After a brief delay at the AV node, the action potential moves down the Bundle of His to the ventricles, causing ventricular contraction (QRS complex).
AV Bundle & Purkinje Fibers: These structures rapidly transmit the action potential throughout the ventricles, ensuring coordinated contraction and efficient pumping.
Describe how ECG/EKG waves “match-up” with action potential moving through the heart.
P wave: Corresponds to atrial depolarization, which is triggered by the action potential originating in the SA node.
QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization, caused by the action potential traveling through the Bundle of His and Purkinje fibers.
T wave: Reflects ventricular repolarization, as the ventricles recover from the action potential.
Describe how ECG/EKG waves correlate with contraction/relaxation events of the cardiac cycle.
P Wave: Atrial Contraction (Atrial Systole)
QRS Complex: Ventricular Contraction (Ventricular Systole)
T Wave: Ventricular Relaxation (Ventricular Diastole)
Define: Tachycardia
When a heart beats too fast.

Define: Bradycardia
When a heart beats too slow.

Define: Heart Rate
The number of beats/minute.
What happens to heart rate/pulse after you stand up? After you hyperventilate (or exercise)?
Increases
Define: Stroke Volume
The volume of blood pumped out by one ventricle with each beat.
*Each ventricle pumps out about 70 mL of blood with each beat, which is about 60% of the blood in the ventricle.
Define: Cardiac Output
The volume of blood pumped out by each ventricle in one minute.
*CO (ml/min) = HR (beats/min) x SV (ml/beat)
Define: Preload
The degree of which cardiac muscle cells are stretched before they contract.
*Higher Preload = Higher Stroke Volume
Define: Afterload
The pressure that the ventricles must overcome to eject blood; 80 mmHg in aorta and 10 mmHg in pulmonary trunk.
Define: Blood Pressure
The force exerted on the interior walls of vessels by blood as it surges through them.
What is the tool used to measure blood pressure called?
Sphygmomanometer
What are baroreceptors? Where are they found?
Def: Mechanoreceptors that detect blood pressure (BP).
Found:
Aortic Arch
Carotid Sinuses/Arteries
What are chemoreceptors? Where are they found?
Def: Receptors that monitor CSF pH in the brain and pH, amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) and amount of oxygen (O2) in blood.
Higher CO2 Concentration —> Lower pH (Acidic)
Found:
Medulla Oblongata
Carotid & Aortic Bodies
What is systolic blood pressure? What is diastolic blood pressure?
Systolic Pressure: the highest pressure in the arteries during ventricular systole.
Diastolic Pressure: the pressure in the arteries during diastole; the lower value when taking blood pressure.
What causes heart sounds?
Valves Closing
Fill in the blank: Arteries carry blood ___ from heart; ____ (Hint: Oxygenated or Deoxygenated), except for the ____ (Hint: Pulmonary Circuit or Systemic Circuit).
Away
Oxygenated
Pulmonary Circuit
Fill in the blank: Veins carry blood ___ from heart; ____ (Hint: Oxygenated or Deoxygenated), except for the ____ (Hint: Pulmonary Circuit or Systemic Circuit).
Toward
Deoxygenated
How are veins and arteries different?
Veins
Carries blood towards heart.
Contain Valves
Low Pressure
Arteries
Carries blood away from heart.
No Valves
High Pressure
Define: Capillaries
A type of blood vessel that has direct contact with tissue cells; directly serve cellular needs (gas exchange via diffusion).
The walls of all vessels, except capillaries, contain three tunics/layers. List them from outermost to innermost order.
Tunica Externa
Tunica Media
Tunica Intima
Capillaries are covered by ____.
Basement Membrane
List characteristics of the tunica externa of blood vessels.
Tissue Type: Collagen (Veins & Arteries)
Vasa Vasorum (Veins & Arteries)
List characteristics of the tunica media of blood vessels.
Tissue Type: Smooth Muscle (Veins & Arteries)
External Elastic Membrane (ONLY Arteries)
List characteristics of the tunica intima of blood vessels.
Tissue Type: Endothelium/Endothelial Tissue
Subendothelial Layer (i.e. “Basement Membrane”)
Endothelial Valves (ONLY Veins)
Internal Elastic Membrane (ONLY Arteries)
Define: Capillary Beds
Ensure maximum coverage and surface area of exchange in tissues.
What are some methods used to control blood flow through capillary beds?
Constriction
Dilation
Which blood vessels contain valves? Why does this type of blood vessel need valves when other vessels don’t?
Veins is the only type of blood vessel that contains valves; aid in preventing backflow of blood and in returning blood to the heart in low pressure.
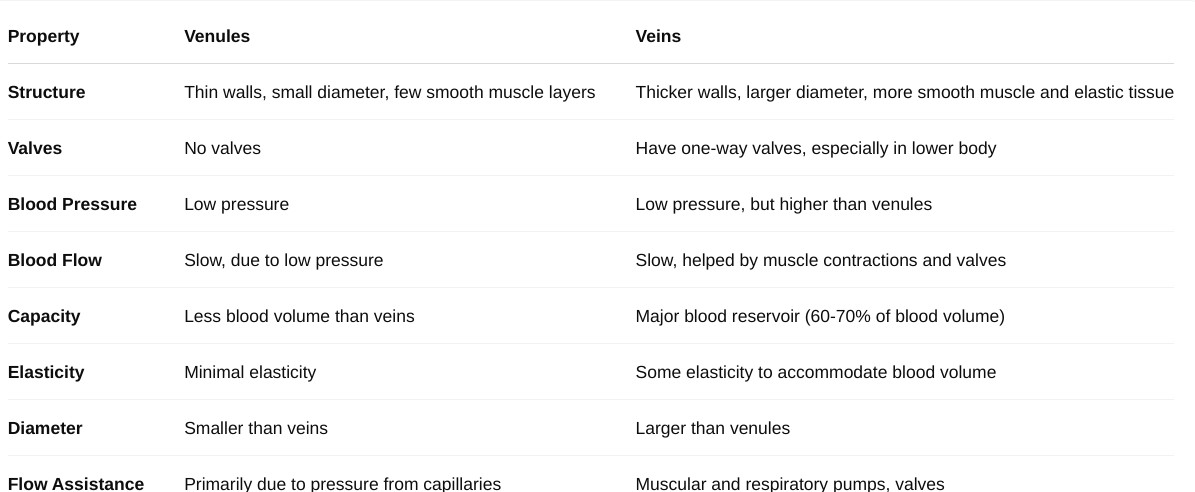
How do veins deal with getting blood to the heart under low pressure conditions?
Skeletal muscle contractions coupled with valves.
What is the effect of vasoconstriction on blood flow and blood pressure.
Blood Flow: Decreases
Blood Pressure: Increases
What is the effect of vasodilation on blood flow and blood pressure.
Blood Flow: Increases
Blood Pressure: Decreases
What are the main functions of blood?
Transport
Regulation
Defense
List the components of blood.
Plasma
Buffy Coat
Red Blood Cells
Blood Components - List the relative percentage of plasma in blood.
55%
Blood Components - List the elements and relative percentage of the buffy coat.
Elements:
White Blood Cells
Platelets
1%
Blood Components: List the relative percentage of red blood cells.
45%
Define: Hematocrit
The percentage of your blood that is made up of red blood cells (RBCs).
Define: Antigens
Surface proteins that determine blood types; found in red blood cells.
Define: Antibody
Proteins made by individuals immune system to detect and fight off foreign substances (e.g bacteria, viruses, and toxins).
Detect: Antigens
Trigger: Immune Responses
How do ABO blood types influence blood transfusions?
If you get a mismatched transfusion, your antibodies may attack the donor's red blood cells.
Can cause a hemolytic reaction—cells break apart, leading to serious complications like kidney failure, shock, or even death
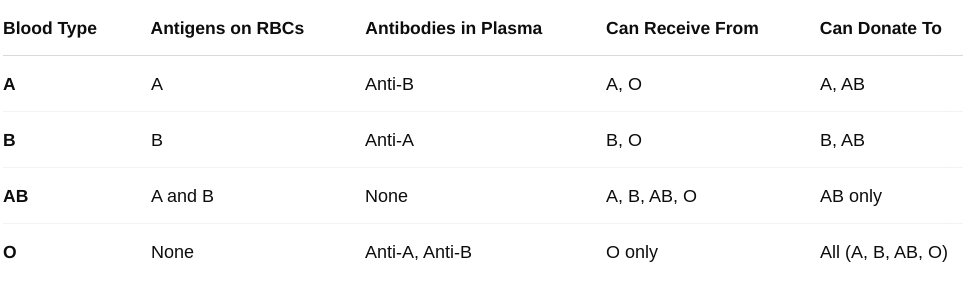
Define: Rh Factor
A protein that is present on the surface of red blood cells.
If you have it, you're Rh-positive (e.g., A+, B+).
If you don’t, you're Rh-negative (e.g., A-, O-).
Rh+ is dominant to Rh-!

What is Anti-D?
Accounts for antibodies against the Rh(D) antigen.
Describe how the Rh factor blood type influences pregnancy (Think: Erythroblastosis Fetalis).
When an Rh- mother carries an Rh+ fetus she develops the Rh antibody, which would attack the fetus’s Rh+ red blood cells; can cause hemolytic disease (fetal death) in future pregnancies.
What combination of Rh+ and Rh- in the mother and fetus is dangerous?
Mother: Rh-
Baby: Rh+ (inherited from Rh+ father)
How can erythroblastosis fetalis (hemolytic disease of the newborn) be resolved?
Prescribing RhoGAM medication to pregnant women to prevent the formation of anti-Rh antibodies in expecting mothers.
What antibodies would you expect to find in any Rh+ blood? Why?
None because an individual would expire/die if exposed to an Rh antibody.
How do hemoglobin concentrations vary between males and females?
Males tend to have higher hemoglobin concentrations compared to females as a result of increased muscle mass and testosterone levels.
What is the significance of testosterone and erythrocytes (red blood cells)?
Testosterone stimulates the kidneys to release erythropoietin, which enhances the production of erythrocytes (red blood cells).
What is the difference between granulocytes or agranulocytes?
Granulocytes contain granule proteins in their cytoplasm; agranulocytes do not!
List the leukocyte classes and their subclasses.
Granulocytes
Neutrophils
Eosinophil
Basophil
Agranulocytes
Lymphocyte
Monocyte
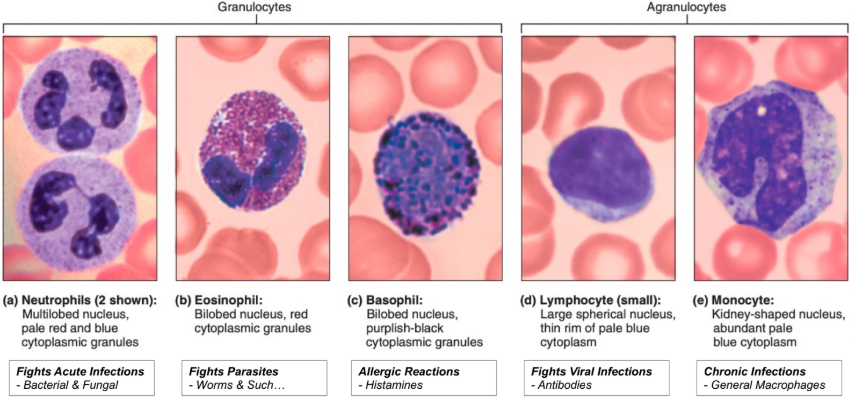
List the function of—-Neutrophils.
Phagocytosis
Antigen Presenting
List the function of—-Eosinophil.
Responds to parasitic infections by releasing digestive enzymes.
List the function of—-Basophil.
Release Histamine
Promote Inflammation
Promote Allergic Reactions
List the function of—-Lymphocyte.
Contains:
T-Cells
Function: Destroy Viral- & Cancerous Cells
B-Cells
Function: Produce/Release Antibodies
List the function of—-Monoocyte.
Phagocytosis/Become MACROPHAGE
Antigen Presenting
List the function of—-Erythrocyte.
Transports oxygen (via hemoglobin) & removes carbon dioxide.
List the function—-Platelet.
Blood Clotting
What is the pH of blood under normal conditions?
7.35-7.45