Principles and Metrics
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Green Chemistry
Reduction in the use or generation of hazardous substances in the design, manufacture and application of chemical products using a set of principles
Anthropogenic activity
Human activities that impact the environment, either directly or indirectly
Sustainable Development
Meeting the needs of today without compromising future development
Current CO2 concentration
Currently at 400ppm, 1/3rd of this is from anthropogenic sources
3 Areas of sustainability (Triple Bottom Line)
Economic, Environmental and Social
Linear Economy
Take → Make → Use → Abuse

Circular Economy
Cradle → Cradle (doing more with less, using waste as a resource)
EU REACH
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation & Restriction of Chemicals - Chemicals must be approved as safe before they can be used
PBTM
Persistence, Bioaccumulation, Toxicity, Mobility (used to be PBT)
Yield
Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield

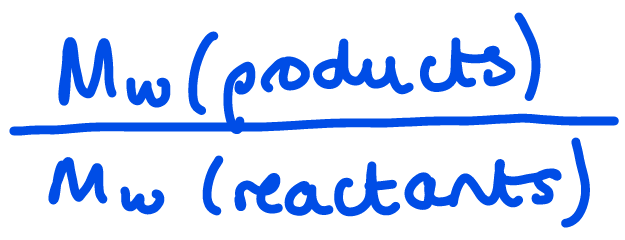
Atom Economy
Mw(product) / Mw(all reactants - not solvent etc.)
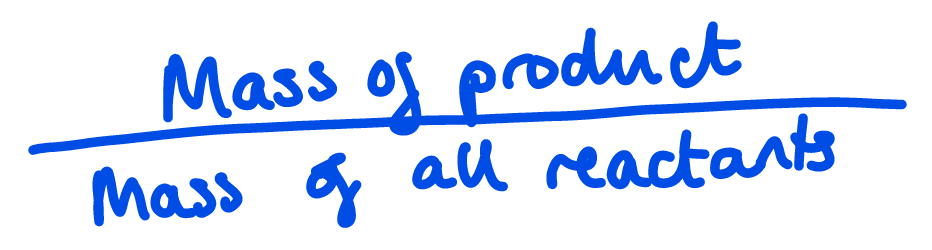
Reaction Mass Efficiency (RME)
Mass of product / Mass of all reactants (not solvent etc.)
Process Mass Intensity (PMI)
(Reactant + workup + solvents)mass / product mass

E Factor
Waste mass - product mass (PMI - 1)

Risk
Hazard × Exposure = Hazard × Dose × Time

Globally Harmonised System (GHS)
Hazard code symbols on chemicals
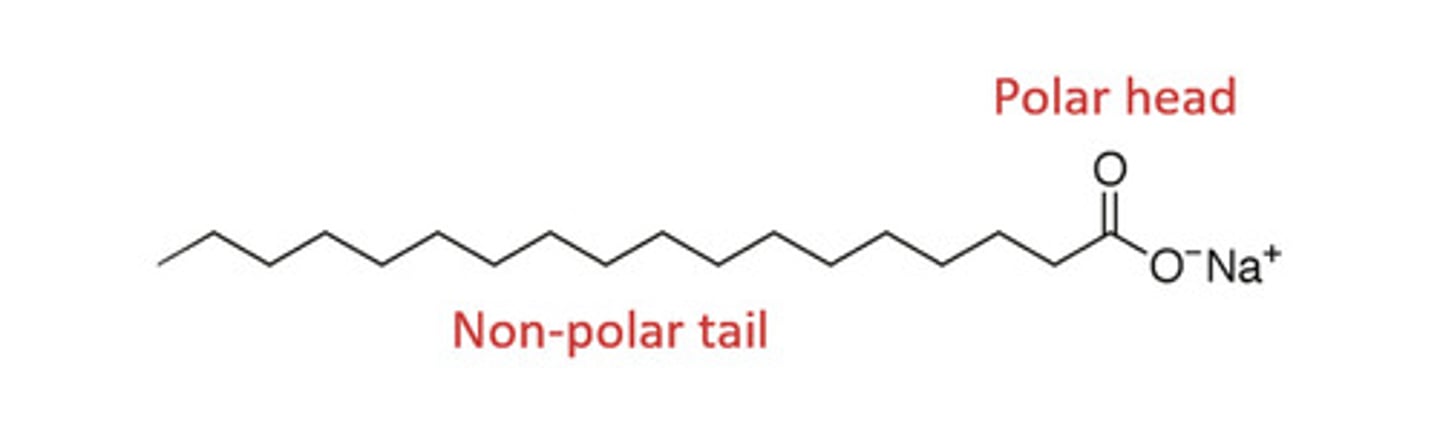
General Structure of Detergents
Hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail
Chemical degradation
-Different to normal degradation
-Molecules require functionality to degrade eg esters
Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC)
List of bad bad chemicals
Once a chemical is on this list, it almost never comes off without being banned.
Forever chemicals
A term given to PFAS (poly-fluoroalkyl substances) which are resistant to degradation.
Sin List
Substitute it now
Parabens
Para-hydroxybenzoic acid, which are endocrine disruptors and listed on SVHC.

Good (Green) Solvent Alternatives
Water, (bio)ethanol, carbon dioxide.
Decaffeination
Supercritical CO2 used instead of chloroform to decaffeinate tea/coffee; the CO2 is taken from the atmosphere.
Good (Green) Detergents
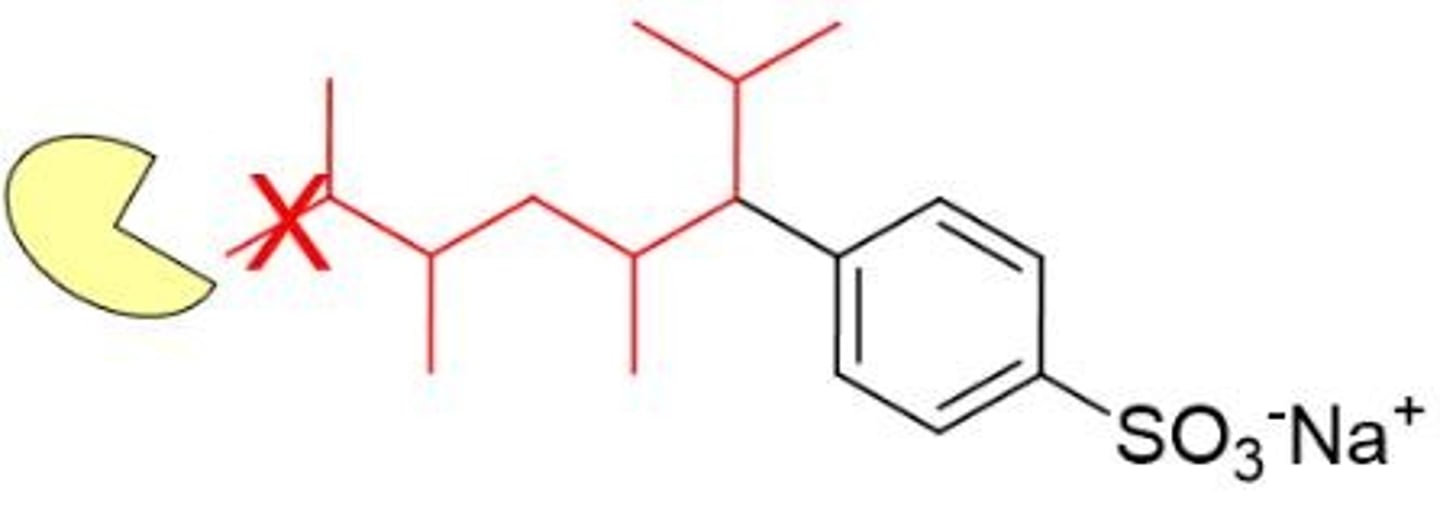
Linear Alkyl Benzenesulfonates (LABS) which have a linear chain that is easy for soil microbes/enzymes to break down. (middle structure)
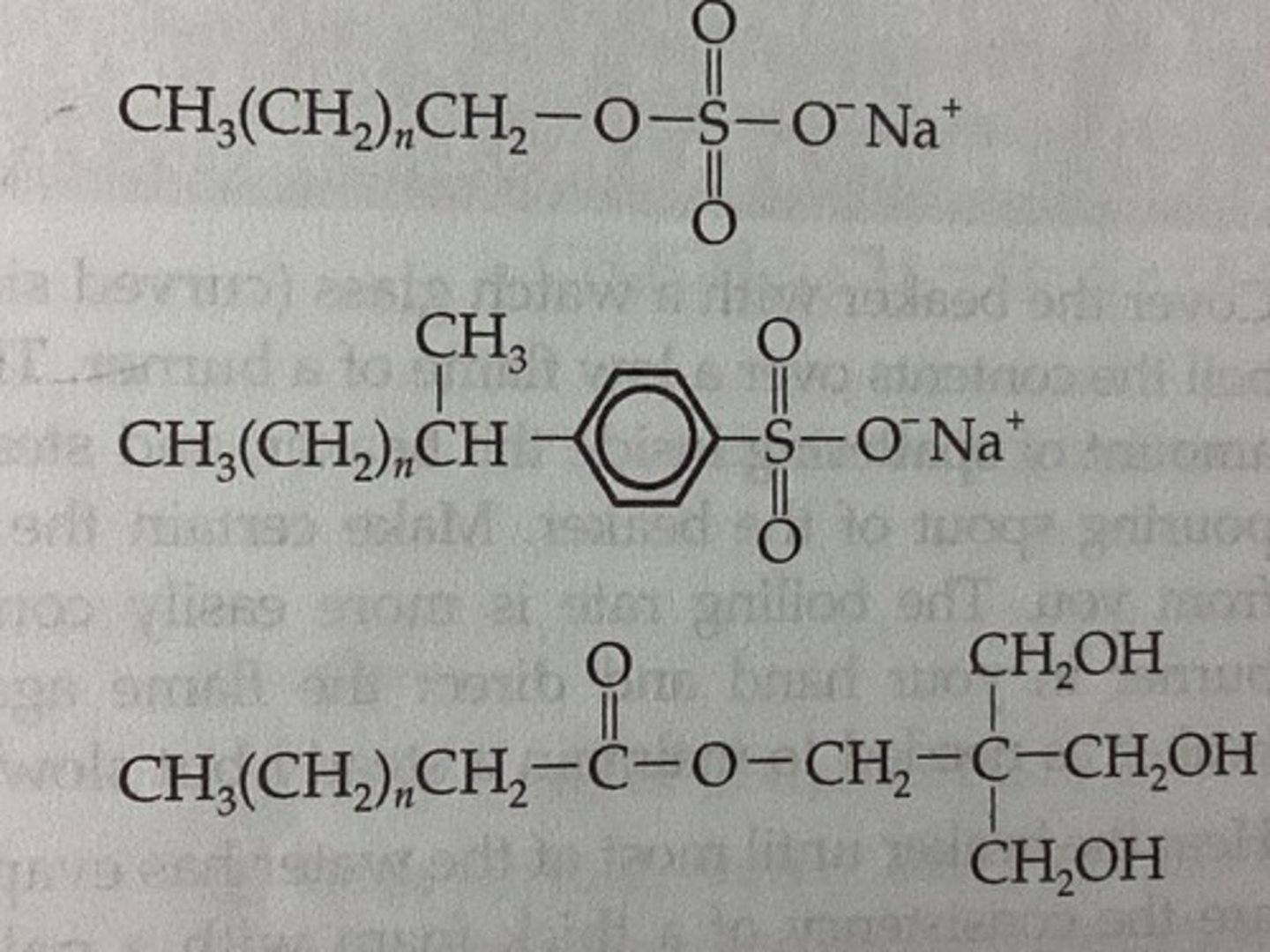
Bad Detergents
Branched Alkyl Benzenesulfonates which have a branched chain that is harder for nature to degrade.
Methods of Designing for Energy Efficiency
Utilising 'waste' energy, refluxing at 10°C below the boiling point, heating using microwaves, and improving the reactor design.
Valorisation
Producing something of more value than your starting product, eg. turning biomass into useful chemicals
Biorefinery
Producing chemicals, energy and materials from a biomass feedstock
Sources of biomass
-Agricultural co-products
-Non-food crops
-Algae and seaweed
First Generation Biorefinery (Phase 1)
Using one feedstock to make one output, e.g., sugar cane to produce bioethanol.
(Food vs Fuel land use debate)
Second Generation Biorefinery (Phase 2)
Using residues/wastes to produce an output, e.g., tree clippings, food waste, paper waste.
Third Generation Biorefinery (Phase 3)
Using algae to produce your output, including macro algae (seaweed) and micro algae grown in labs.
Micro algae can be grown in tubes in non-useful land (eg. deserts) so no competition with agriculture
Lignocellulosic
A feedstock containing cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin
Platform Chemicals
A building block derived from biomass, e.g., bioethanol, glucose.
Hetero vs Homogeneous Catalysis?
Heterogeneous catalysts are better than homogeneous catalysts; homogeneous catalysts combine with the reaction solution and are harder to separate.
Critical Elements
Rare earth elements whose supply could be compromised at any time, needed for technology like wind turbines.
Who are stakeholders?
-Society: holding companies accountable
-Consumer: sustainability considerations when purchasing
-Government: regulations to conserve resources and limit pollution (EPA)
LCA Inventory
A database of the inputs and outputs
Impact Assessment
Assessing the ecological and health impacts - Linking your results to their environmental impact (acid rain, global warming, ozone depletion, habitat destruction
Improvement Assessment
Opportunities to reduce the environmental impact
Will you prioritise sustainability or sales?
Is there a balance?
Do your changes make your product function less well?
Will you have a 3rd party check your results?
LCA System Boundary
How far you go with your LCA
Things to Define in an LCA
Your objectives and system boundaries.
Consider:
Is it an internal assessment? Who's conducting the LCA? Who's financing the LCA? Is some of the manufacture process out of your control (overseas)? Is part of the process unavoidable?
Things to Choose in an LCA
Choose what it is that you want to measure, whether it's one thing or multiple.
When choosing, consider:
How will you present your data for understandability? Report CH4 emissions as CO2 equivalents? Compare your results to a reference value like the legal limit or your competitor?
Select stage of LCA
Select your strategy for data collection
Pareto Principle
Changing something by 20% to get an 80% impact
Reasons for LCA
To award eco-labels, to justify the cost, to back up marketing claims
Cradle to Gate
Only considering the manufacturing process up until the product is made, not past the product itself