Physics 2 midterm
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
electron charge is…
conserved and quantized
conductors:
-outer electrons of atom are free to move from atom to atom and charges move freely
-metals
-when charge, the charge distributes over the entire surface
-electric field shields; if placed in a field the charges redistribute until the total field inside the conductor = 0
insulators
-electron associated with a particular atom and very few electrons move
-if placed in a field, dipoles form until the field inside the insulator is less than outside but greater than 0
semiconductors
-some free electrons
-electron properties can be changed by the addition of controlled amounts of certain atoms
charge by rubbing
electrons move from one object to another by contact and one becomes - the other +
induced charge
positioning an external electric charge close to a conductor will redistribute its charge
polarization
positioning an external electric charge close to an insulator makes it become dipole
which is greater induction or polarization
induction
gravitational forces …
are very small and most everyday forces are electric
is electric field vector or scalar
vector; it has both magnitude and direction
if a charge (q) is positive then the electric field (E) …
points away from the charge which is sourcing the field
if a charge (q) is negative then the electric field (E) …
points toward the charge which is sinking the field; antiparallel
if a charge (q) is positive then the electric force (F) …
is parallel to the electric field (E)
if a charge (q) is negative then the electric force (F) …
is antiparallel to the electric field (E)
what do field lines depend on
direction and strength of the field and the force exerted on the test charge
if a field is uniform the acceleration is …
constant
parallel plate capacitor
two conductive planes with area (A) parallel to each other, a storage bucket for charges, a plate connected to the hot terminal of the battery (Q+), and a plate connected to low voltage/ ground terminal of battery (Q-)
outside a capacitor the electric field (E) = …
0
electrostatic equilibrium
no net motion of charge within a conductor; E = 0
electric forces depend only on …
initial and final positions
if only conservative forces act then the Efinal = …
Einitial
work is done a charge (q) by
the electric field (E)
electric potential energy is scalar or vector
electric potential energy (Uel) is scalar, it has just magnitude
same signs make Uel …; opposite signs make Uel …
+, to bring them together
-, to keep them apart
voltage (V)
-also called electric potential
-scalar
-what a force would be if a charge was placed at any point; so it has value at any point
-independent of value of test charge and it can exist without the test charge
if V = 0 then r =
infinity
if V = infinity then r =
0
electron volt (eV)
the energy a charge acquires if accelerated by the electric forces between 2 points with the difference of 1 Volt
1 eV= |charge of e-|
equi-potential lines
lines of constant voltage perpendicular to electric field lines
if the electric field inside a region = 0 then the change in voltage =
0, its constant
electric field lines always point in the direction of …
decreasing potential energy
capacitors
store electric charge, made of 2 conductors (plates) with equal and opposite charges which create a potential difference
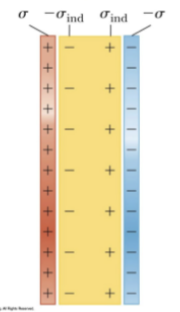
dielectric
nonconducting material that when placed between plates of a capacitor increase the capacitance; polar molecules
d (capacitor)
d is the maximum voltage that can be applied to a capacitor without causing a discharge and it depends on the dielectric strength of the material
how do dielectrics affect capacitance
they can increase C by increasing the maximum operating V; possible mechanical support between plates
tubular capacitor
metallic foil interlaced w/ mylar rolled into a cylinder
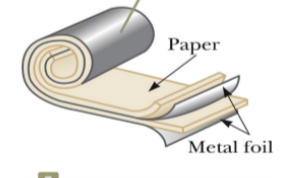
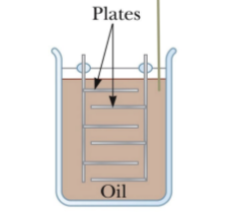
oil filled capacitor
high voltage; interwoven metallic plates immersed in silicon oil
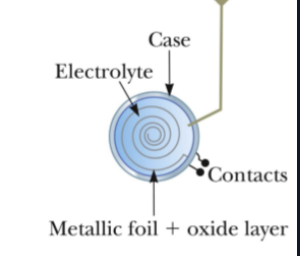
electrolytic capacitor
-stores large amounts of charge at low V; conducts electricity through motion of ions
-V applied between foil and electrolyte and a thin layer of metal oxide forms and is dielectric
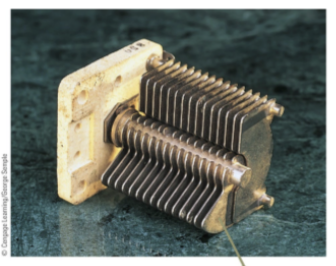
variable capacitors
2 interwoven sets of metallic plates, one fixed, the other moveable; the contained air is dielectric
in the absence of an electric field dielectric molecules are
dipoles and randomly oriented
describe dielectric molecules when an external electric field is applied
-a torque is produced and the molecules partially align with the field; the degree of alignment depends on temperature and the magnitude of the field
-the molecules produce an induced electrical plate opposite the original
for F=qE, if the charge (q) is - and you want the force (F) to point positive then …
E must point negative