Chem study guide for Final
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
First Greek Philosopher
Democritus 400 B.C
Theory: World made of empty space and tiny particles called atoms (Discovered atoms)
Aristotle
Contracted Daltons Theory (No such things as smaller particles)
John Dalton (1808)
Created a logical hypothesis (First person to prove the existence of an atom)
Theory: Matter can not be created nor destroyed
Daltons conclusion/theory
1.) All mater composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms.
2.) All atoms of an element were exactly alike in mass, atoms of different elements were unlike in mass
3.) Law of Definite Proportions: Atoms always combine in simple ratios to form the same compound
4.) Chemical reactions happen when atoms separate, join, or rearrange. Elements will never become another element
Thompson
“All elements have negatively charged particles.”
(Plum pudding idea)
Steps:
1.) Applied high voltage in a cathode ray tube to create cathode rays
2.) Rays bent in a magnetic field indicating they were negatively charged
3.) Led to the discovery of electrons
Milikan: (Thompsons Student)
Steps:
1.) Measured tiny charged oil droplets
2.) Balancing gravitational and electric forces on droplets in an electric field.
3.) measuring the charge on the droplets he determined the charge of the electron
Conclusion: Charge of the electron
Rutherford
Steps:
1.) firing alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold
2.) particles passed through but some deflected and showed dense nucleus
(Conclusion that atoms have a central nucleus.)
Subatomic Particles
Proton- In the nucleus, (+), 1 amu
Neutron- In the nucleus, (None), 1 amu
Electron-Outside nucleus, (-), 0 amus
Isotope format:
Mass on top
Atomic number on bottom
Subtract to find Neutron

Elements
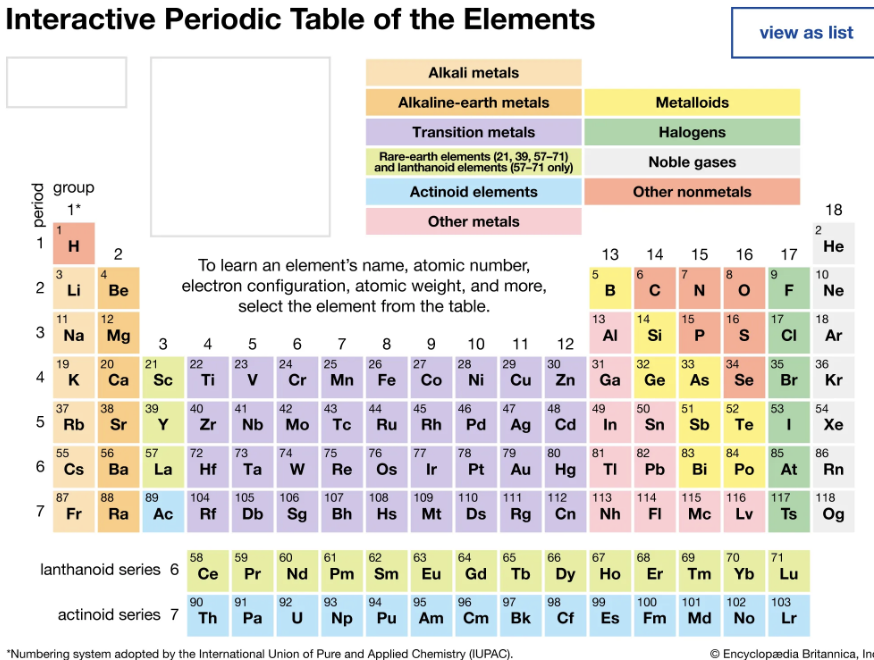
Alkali Metals
First Column
Alkali Earth Metals
Second Column
Metalloids
Staircase
Noble Gasses
Last Column
Lanthanoids
Bottom first row
Acintides
Bottom second row
Halogens
Second to last column
Metals
Everything else
Atomic Radium
Top to Bottom- Increases in size
Left to Right - Decreases in size
Electronegativity
Top to bottom- More attractive to less attractive
Left to right- Less attractive to more attractive
(Do not include noble gasses)
(Bigger the radius MEANING LESS ATTRACTIVE)
Ionization
Left to right - easier to steal to harder to steal
Top to bottom- harder to steal to easier to steal
(Bigger the radius the easier to steal)
Electron Configuration
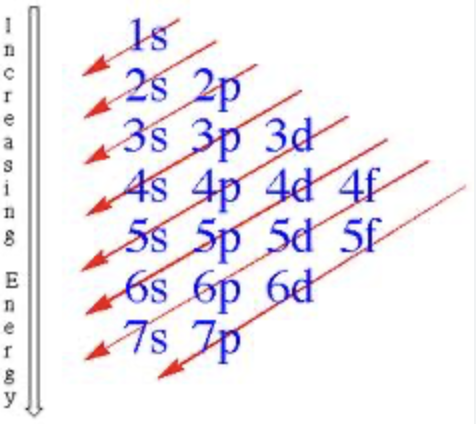
Aufbau Principle
Lower energy levels first
(When it goes out of order you know it is wrong)
Pauli Exclusion
Opposite spins when together
(Can only have max of arrows)
s=2, p=6, d=10 f=14 anything more breaks this rule
Hunds Rule
Take available orbitals first
(All arrows must point one direction before going the other)
What is Chemistry
Chemistry is the study of matter and the
changes that it undergoes.
The SI base unit for Time
Second
The SI base unit for Length
Meter
The SI base unit for Mass
Kilogram
The SI base unit for Temperature
Kelvin
Pure Research
A type of scientific investigation that seeks to gain knowledge for the sake of knowledge itself
Applied research
A type of scientific investigation that is undertaken to solve a specific problem
Model
A visual, verbal, and or mathematical explanation of data collected from many experiments
Derived unit
A unit defined by a combination of base units
Liter
The metric unit for volume equal to one cubic decimeter
Density
The amount of mass per unit volume
Graph
A visual display of data
Significant figures
The number of all known digits reported in the measurements plus one estimated digit
Example of Scientific Notation
702.0 g
7.020 × 10² g
(Making 702 smaller to 7.02 by moving 2 spaces left meaning it is power ².)
Example of Scientific Notation
00000702 g
7.02×10-6g
(Making 00000702 by making it bigger to 7.02 by moving 6 spaces right meaning it is power -6
When a small amount of sugar is dissolved in water it is a
Homogenus solution (Uniform)
Water being mixed with oil
Heterogenus solution
A change between the three states of matter (Gas, Liquid, Solid)
Physical change
Hypothesis
An explanation from observations that is tested /testable
(Example: If I drop a ball it will fall to the ground)
Theory
A well established explanation that is supported by a body of evidence
Example: Evolution
Types of Chemistry:
Prefixes
Adding & Subtracting with Significant Figures

Multiplying and Dividing with Significant Figures

Chemical Property
A chemical property relates to a substance’s ability
to undergo changes that transform it into different
substances
• A change in which one or more substances are
converted into different substances is called a
chemical change or chemical reaction.
Physical Property vs Physical Change
A physical property is a characteristic that can be
observed or measured without changing the identity
of the substance.
• melting point and boiling point
A physical change is a change in a substance that
does not involve a change in the identity of the
substance.
• grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling point
Intensive properties
do not depend on the amount
of matter present.
• melting point
• boiling point
• density
• ability to conduct electricity
• ability to transfer energy as heat
Plasma
Plasma is a high-temperature physical state of matter
in which atoms lose most of their electrons, particles
that make up atoms.
Different Mixtures
A mixture is a blend of two or more kinds of matter, each of which retains its own identity and properties.
• mixed together physically
• can usually be separated
Homogeneous mixtures are called solutions
• uniform in composition (salt-water solution)
Heterogeneous mixtures
• not uniform throughout (clay-water mixture)

Pure Substance
A pure substance has a fixed composition.
• Pure substances are either compounds or elements.
• A pure substance differs from a mixture in the
following ways:
• Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same characteristic properties
Dimensional Analysis
Tutorial
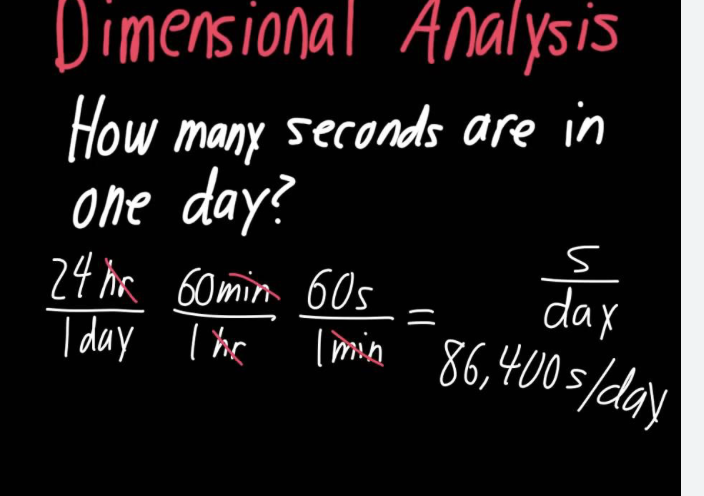
Density
Mass / Volume
Mass
Density x Volume
Volume
mass / density
How to write Mass, Volume , Density
Mass usually written as g or cm³
Density usually written as g/ml or cm³/mL
Volume usually written as mL
How to calculate Percent Error
|error| / accepted value x 100
Accuracy
Refers to how close a measured value is to an accepted value
Precision
Refers to how close a sense of measurements to another
Conversions:
(DO NOT STUDY ALL ONLY WHAT SHE GAVE)
K- Kilo (3)
H- Hecta (2)
D- Deca (1)
b- base; gram meter liter (0)
D- Deci (-1)
C- Centi (-2)
M- Mili (-3)