Ag Analysis Exam 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Commodity Markets
Bulk, Fungible, Homogenous
Non-Branded
Supply-Driven
Price Competition
Little Promotion
Standardized Products
Mass Marketing
Low Value-Added
Value-Added Markets
Farm Products
Consumer Branded Products
Business to Business Markets
Demand-Driven
Differentiated Products
Heavy Promotion
High Value-Added
Target Marketing
4 Types of Utility
Form
Place
Time
Price / Possession
Input Sector
Provide inputs that ag producers need
Production Sector
Produce crops and livestock
Processing & Manufacturing Sector
Transform and distribute products to consumers in desired form
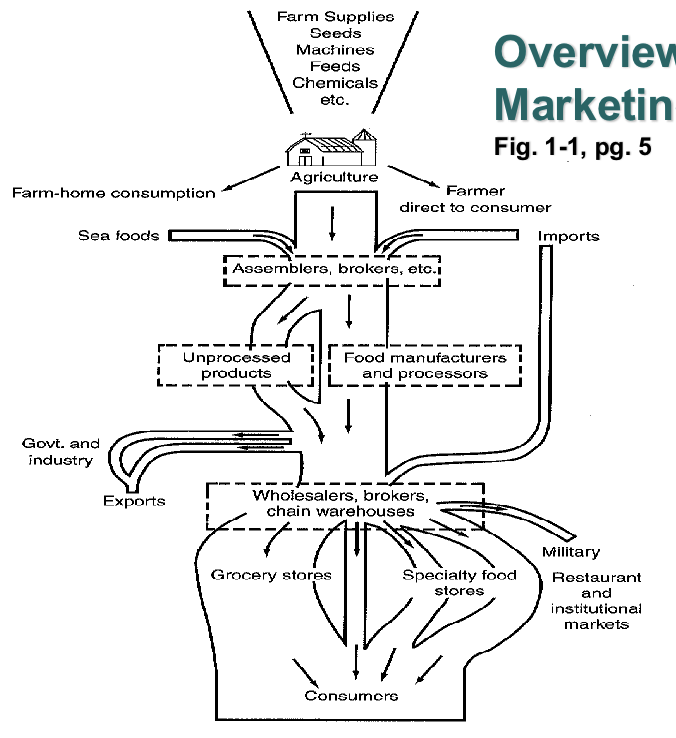
Food Marketing Channel
Consists of firms and their functions that form the industry
Famers → Assemblers and Brokers → Food Processors → Wholesalers → Retailers
Assemblers & Brokers
Sell to food processors
Food Processors
Distribute to brokers and wholesalers
Wholesalers
Sell to grocery ands specialty food stores, restaurants and institutions
Retailers
Sell to consumers
Alternate Views of Markets
Time
Location
Product
Institutional
Form Utility
Modifying the form of the product to make it more useful
Processing, packaging
Adds value
Time Utility
Actions taken to permit product availability or consumption at a time removed from production
Storage
Place Utility
Transporting the product to a location that is more beneficial to the purchaser
Possession Utility
Actions taken to assist the consumer in acquiring and taking title to products
Advertising
Market information
Macro Marketing
All activities in the flow
How food system is organized and changing
How does it operate or perform
View by economists, industry analysis, and government officials
Micro Marketing
All activities that direct the flow
What decisions are made
How to do it
View by food producer, manager, or consumer
Stages of Marketing
What can we produce?
What can we sell?
What do customers want?
What do markets do?
Facilitate Exchange
Create Value
Allocate Resources to “Best” Uses
Stimulate Efficiency
Discover Prices and Values
Summarize, Distribute Information
Resolve Conflicts
Reward, Punish Decisions
Economize on Effort
Raise Living Standards
What happens in a market?
Production and consumption
Buying and selling
Specialization and Division of Labor
Pricing
Competition
Communication, Information Flows
Value Adding
Exchange
Prerequisites for Exchange
For exchange to occur, there
must be:
1. Buyers and sellers
2. Unequal valuation
3.Communication
4. Voluntary behavior
5. Mutual benefit
6. Sum positive gains
Most Important Consequences of Markets
Increased…
Output
Efficiency
Income, and
Standards of Living
Middleman
A Marketing Firm
Approaches to the Study of Food Marketing
Functional
Institutional
Behavioral Systems
Functional Approach
Exchange Functions
Physical Functions
Facilitating Functions
Exchange Functions
Buying and selling
Physical Functions
Handle movement and change
Storage - desired time
Transportation - desired place
Processing - changing the form
Facilitating Functions
Smooth transition of exchange and physical functions
Standardization - uniform measurements
Market Intelligence - data needed to operate the market
Financing - money to carry on
Risk Bearing - possibility of loss
What do functions do?
Add value and costs to food
Functions can be performed by anyone in the system
True
Institutional Approach
Help understand why there are
specialized middlemen in the food
industry
Merchant Middlemen
Agent Middlemen
Speculative Middlemen
Processors and Manufacturers
Facilitative Organizations
Merchant Middlemen
Take title to and therefore own…
Retailers - purchase and merchandise the product
Wholesalers - sell to retailers, not consumers
Agent Middlemen
Act as a representative
Brokers - follow directions of buyers and sellers
Commission Men - limited power, fee
Speculative Middlemen
Buy and sell, profit from price movements
Processors & Manufacturers
Add time, form, place, and possession utilities
Facilitative Organizations
Aid middlemen in their tasks
Point of Functional Approach
Analyzing the functions of various
middlemen is helpful in evaluating
marketing costs.Retailing is much more costly than
wholesaling.Understand the difference in
marketing costs for various
commodities.
Economic Reasons for Middlemen
Economies of Specialization
Economies of Scale, Centralization
Transactions Cost Economies
Non-economic reasons:
farmers, consumers don’t want to do it,
can’t do it, are less efficient
Behavioral Systems Approach
Ability to understand any major change
that is currently underway in the food
system
Input-Output System
Producing an output
Power system
Good reputation to uphold
Communications Systems
Continue good communication
Drivers of Change
How to adapt to them
System Adaptation to Change
Desire to be prepared
Major Forces Shaping the Ag Sector
Competitive Marketing Strategies
Global Markets
Government Policies
Consumer Preferences
Technology
Resources
4 P’s of the Marketing Mix
Price
List, msrp, discounts, credit
Product
Quality, package
Promotion
Advertising, PR, sales
Place
Distribution channels
Keys to Successful Marketing Management
Finds Wants and Fill Them
The Consumer is King (Sovereign)
Differentiate Products
Segment Markets
Position Products In Mind
Beat the Competition
Two Types of Food Markets
Commodity
Value-Added
Farm Product Characteristics
Typically a raw commodity
Bulky and/or perishable
Quality variation
Farm Production Characteristics
Total output increasing
More than population resulting in a higher standard of living
Annual variability in production
Caused by farmers response to prices, government programs, biological processes
Seasonal variability in production
Harvest season
Livestock breeding practices
Concentration of production
Different regions specialize in different commodities
Variable cost of production
Affected by climate, technology farm size, & _____
Farm Marketing Problems
Output is not controllable
Farmers are price takers
Cost-Price squeeze
Price Squeeze
Competitive conditions of ag tend to keep prices so close to production
What are food manufacturers and processors primarily responsible for?
Adding Utility
Product Strategy (Marketing Mix)
Purchase commodities and sell differentiated, branded, high value-added end products that command a premium in the marketplace
Basic Product Strategies (Marketing Mix)
Branding
Convenience
Product Innovation
Price Strategy (Marketing Mix)
Places product in a class (status, government, value)
Place Strategy (Marketing Mix)
Distribution
Promotion Strategy (Marketing Mix)
Location of manufacturing
Affected by:
Bulkiness
Perishability
Labor
Transport Costs
The 3 Sectors
Input
Production
Processing & Manufacturing
Factors that can cause change in the food marketing system
Criticisms of the Food Industry - Cons
Too many products
Excessive advertising
Over-packing
High marketing costs
Poor diet choices
High prices
Pollution, waste
Hunger
Plant Location Decisions
Near Producers
Grains, meat, cheese, fish, eggs, etc.
Near Consumers
Milk, ice cream, pastries, further processing…
Criticisms of the Food Industry - Pros
Variety and choice
Competition, information
Safety, convenience
Leisure time
Free choice
Only 11% of income
Food Marketing System