Ch. 17 Electric Potential
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Potential energy can only be defined for what type of force?
only for a conservative force
How are potential and kinetic energy connect in terms of change?
when there is a change in potential energy there is a negative change in kinetic energy
As a (+) particle moves to the right, what happens to the kinetic, potential, and work
Kinetic energy = increases
Potential Energy = decreases
work = done on particle by electric field (so increases)
Would a charge of 2q have more electric potential energy than a charge of q?
Yes, but same potential energy
Can work be related to force and charge?
Yes, W = Fd = qEd
if E is uniform
What is breakdown voltage?
the electric field will become strong enough to initiate a current
ex: lightning or spark
“if E is too big, you will get a spark”
What are equipotential lines?
lines indicating constant elevation/electric potential
lines are closed
Conductor = entire V and Surface are at same potential
Lines are perpendicular to electric field
How do equipotential lines look like in between 2 parallel plates?
straight lines (from + to -)
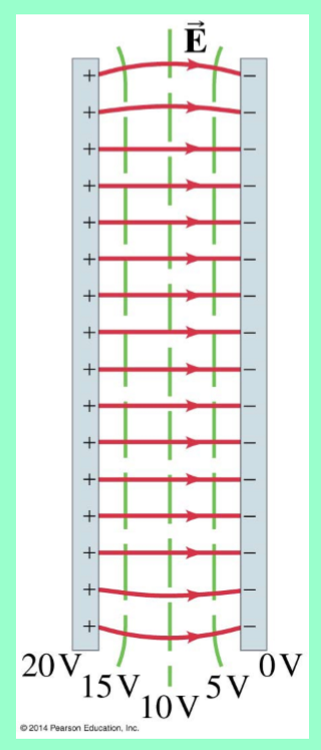
How do equipotential lines look like in between 2 point charges?
the lines of equal potential are curves
still perpendicular to E
true or false: 1V would have 1 eV
true (must always be converted to Joules)
If two points are at the same electric potential, does it mean no work is done in moving a test charge from point A to point B? How does this relate to force?
No work is done!
if you are moving at the same PE, then the formula is equal
no PE means no KE
Forces are equal and opposite to be 0
What is an electric dipole?
Two charges equal in magnitude but opposite in sign which are close together
total charge is zero but still some effect
What are electric dipole moments?
electric dipole moments are associated with molecules and SMALL
What is capacitance?
store charge (energy) on conducting plates (between 2 plates)
“condensor”
In regards to capacitance, how is V viewed as?
V = potential difference (drop the change)
What is a charge on a capacitor related to?
related to capacitance and voltage
does NOT depend on Q/V
DOES depend on physical characteristics
If capacitance is large, where does the potential lie?
it is low
What are dielectrics?
material (insulator) between plates of a capacitor increasing the capacitance
helps separate plates (get close but not too close)
breakdown less easily
more charge can be stored
True or False: energy stored is equal to the work done to charge the capacitor
true
work done to move charge from plate to plate
use average voltage
Where is energy stored?
stored in electric field
T/F: Analog signal voltages are constant
False:
analog signal voltages vary continuously
True or False: digital signals use binary #’s to represent numerical values (jump between values)
How is an analog signal converted to a digital signal?
must be sampled
What is one advantage of digital signals
they are less prone to interference (noise)
What is a cathode ray tube used for? in regard to television?
to emit electrons
they brighten the screen for a brief period when directed to a screen
How is electric charge used to measure the heart?
electrocardiogram detects heart defects by measuring changes in potential on the surface of the heart