Ionization and Chirality - Lesson 10
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
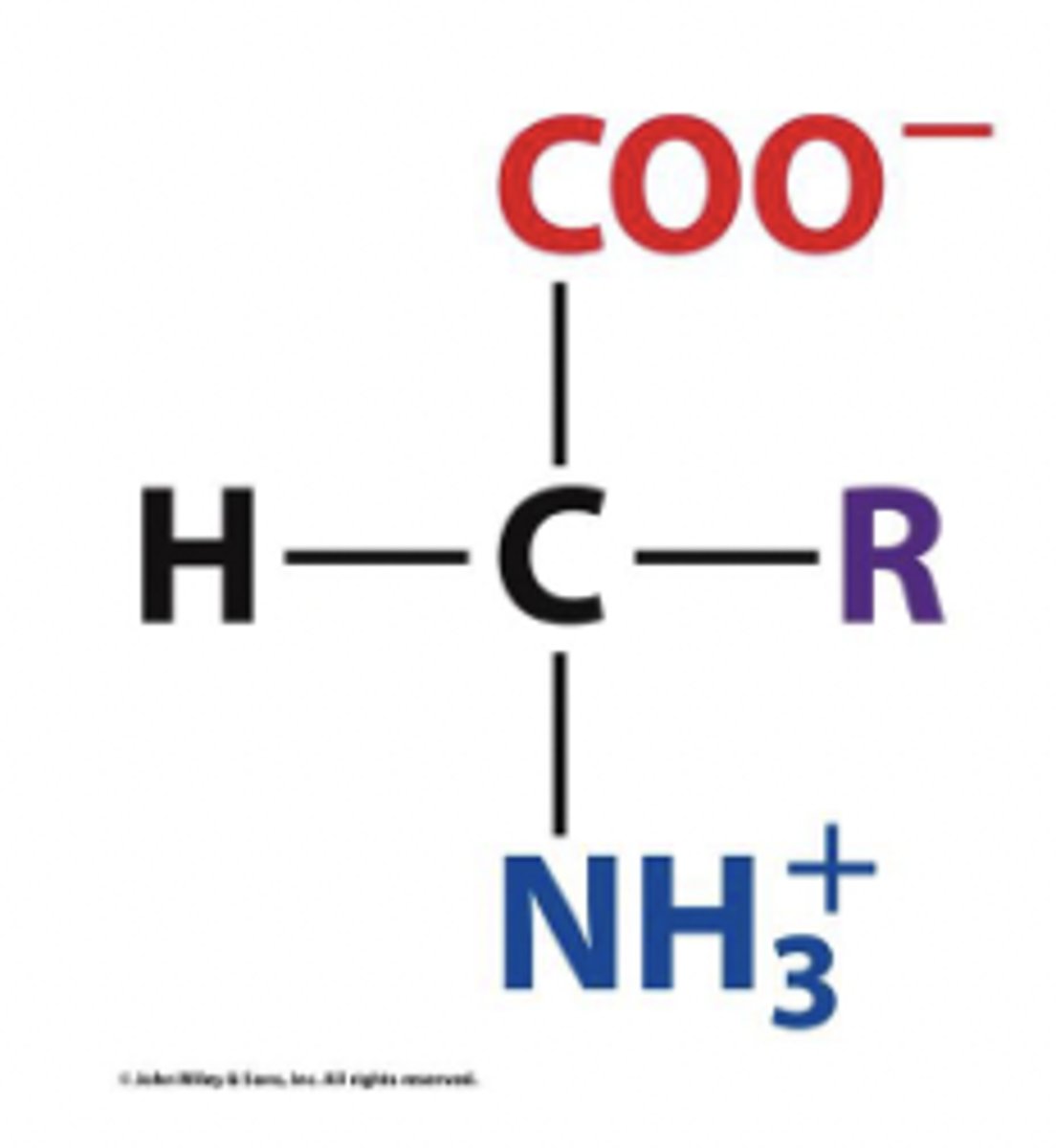
dipolar ions / zwitterions
in solution at pH 7, free amino acids exist as this
- NH3+ (protonated) and COO- (deprotonated)
- ionization state is zero
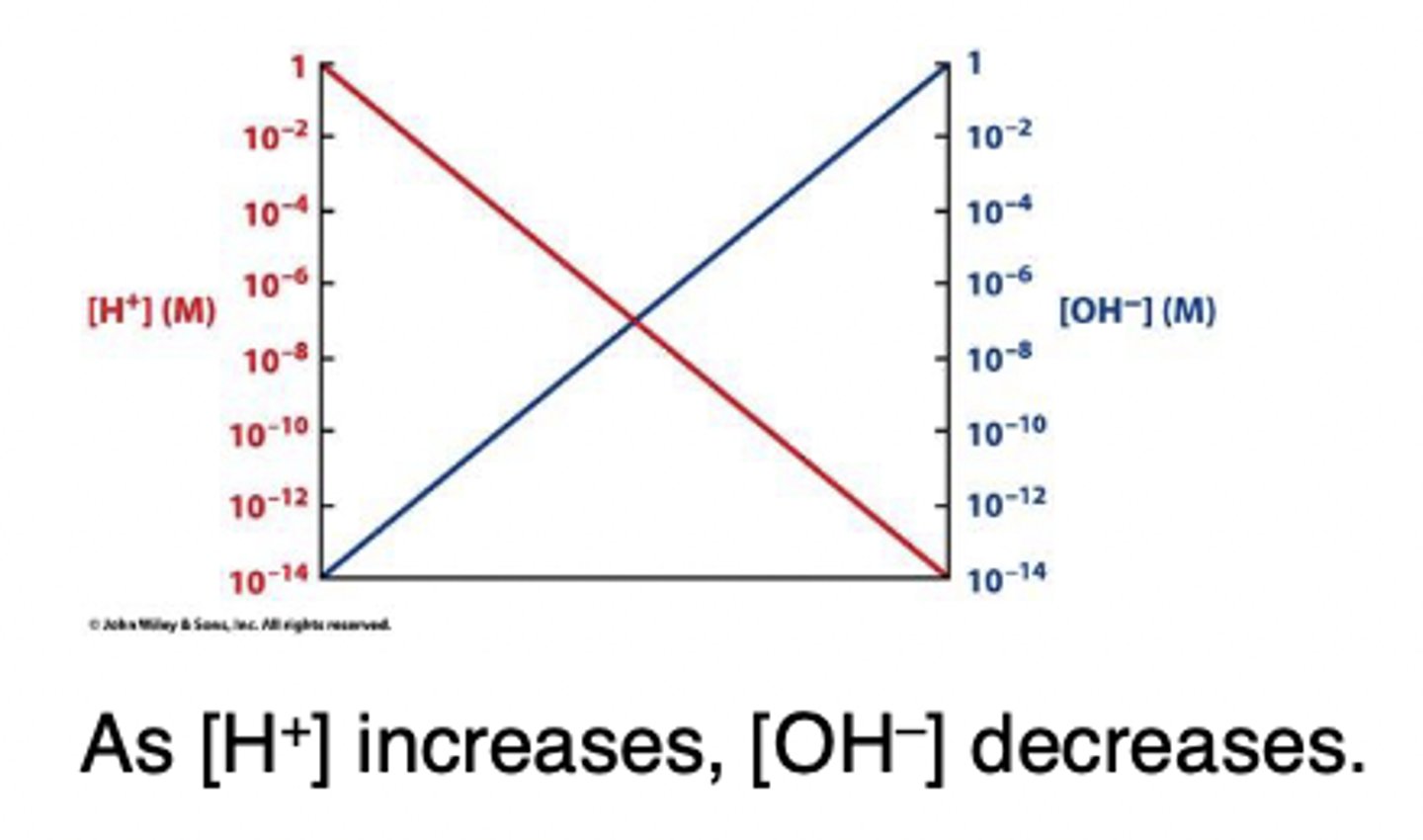
pH
a change in this will alter zwitterion's ionization state
how pH alters zwitterions
alters hydrogen ion concentrations within the solution
alter likelihood of functional group protonation or deprotonation
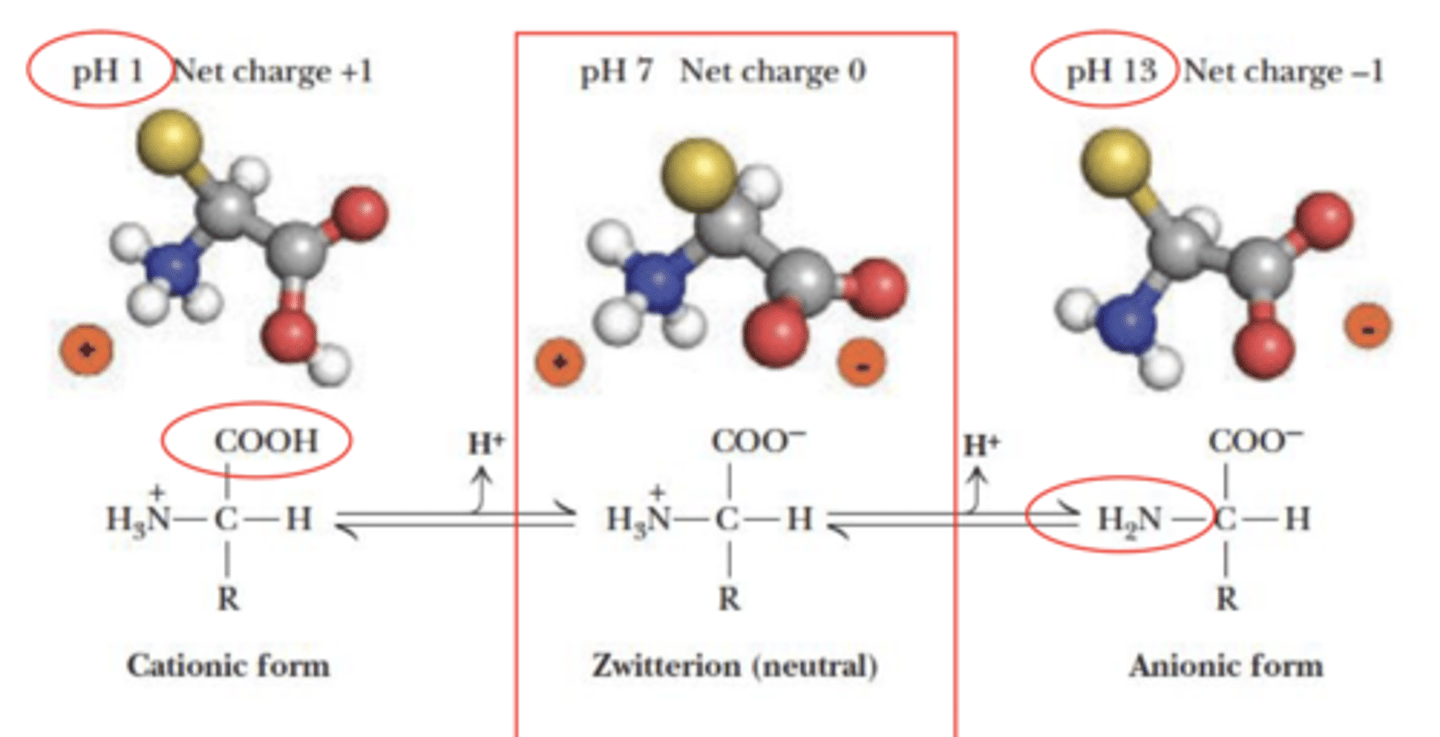
Ionic form of amino acids - Acid-base behavior of glycine
Another way to look at amino acid charged stated
pH
a measure of the hydrogen (H+) ion concentration
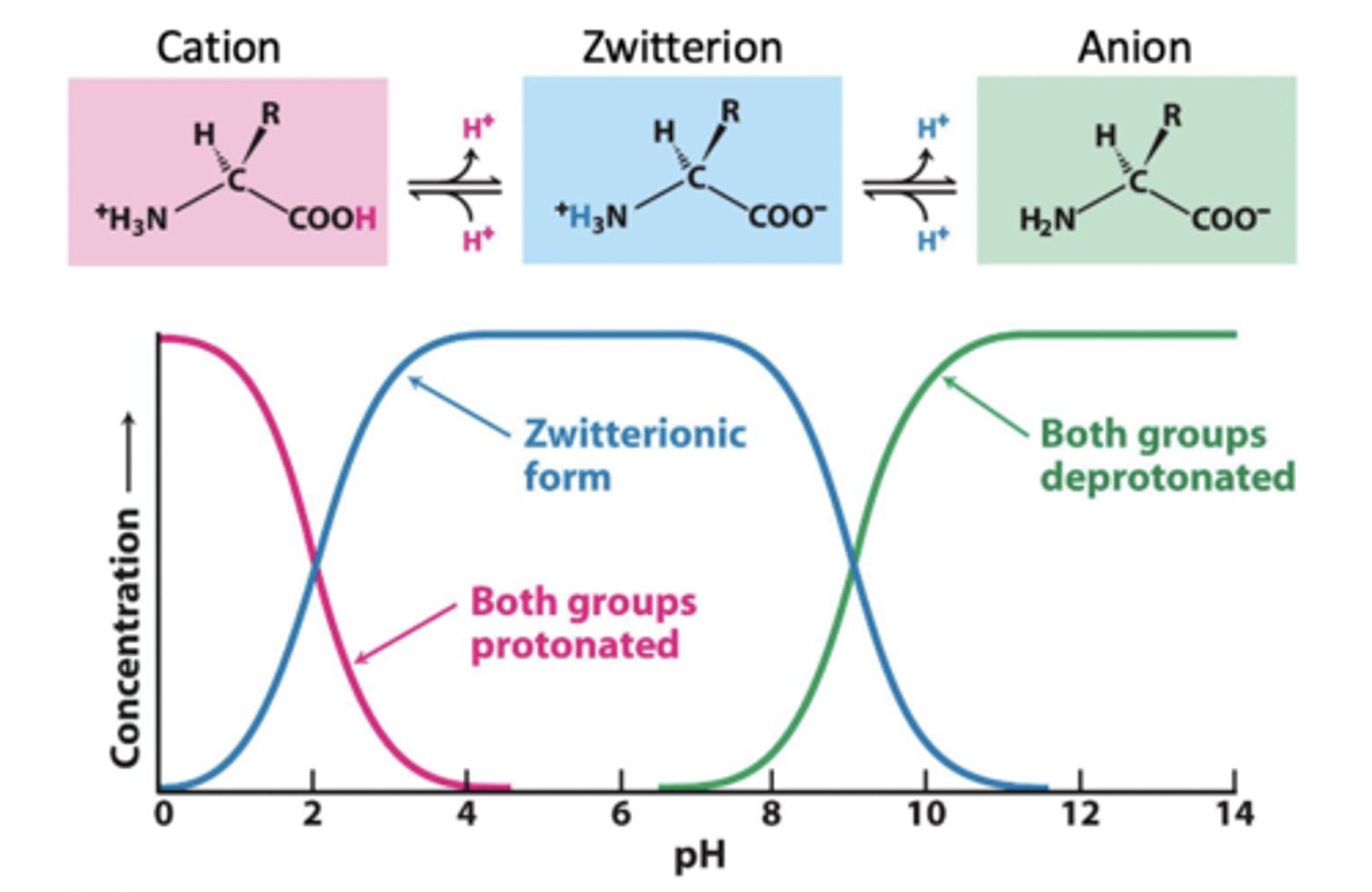
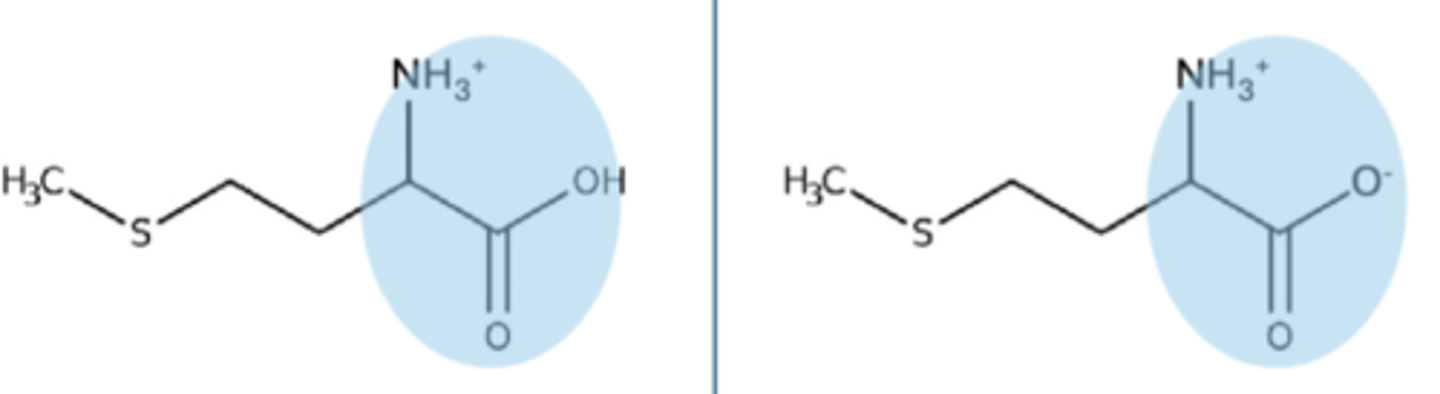
alpha carboxyl pKa
pKa is 2, if it is a pH above, it will lose a hydrogen
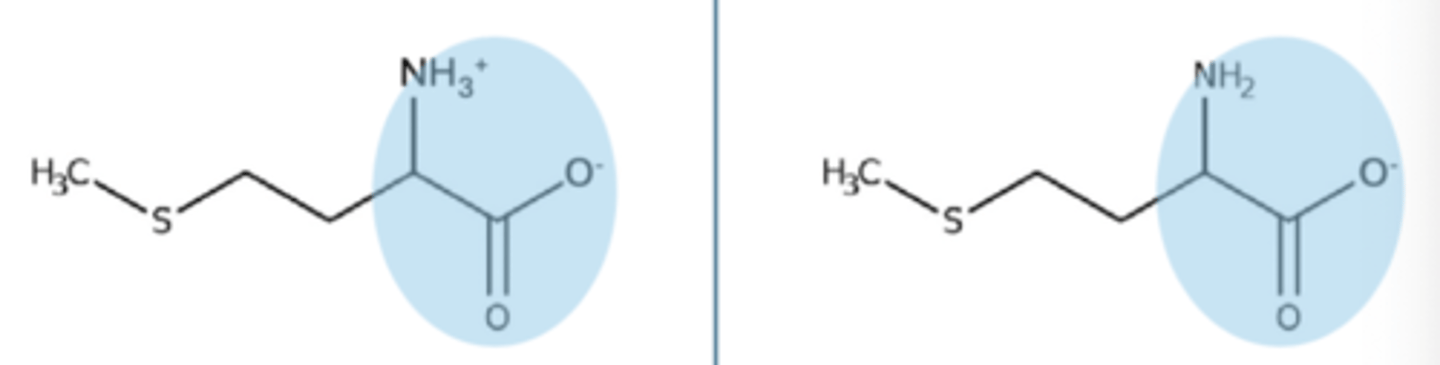
alpha amine pKa
pKA of 9, will stay protonated until you get above pH of 9, then it will lose a proton and become neutral NH2
pH calculation
__ = -log(H+)
pKa
reveals the pH cutoff for protonation of an ionizable functional group
below pKa cutoff
this means it is protonated
above pKa cutoff
this means it is deprotonated
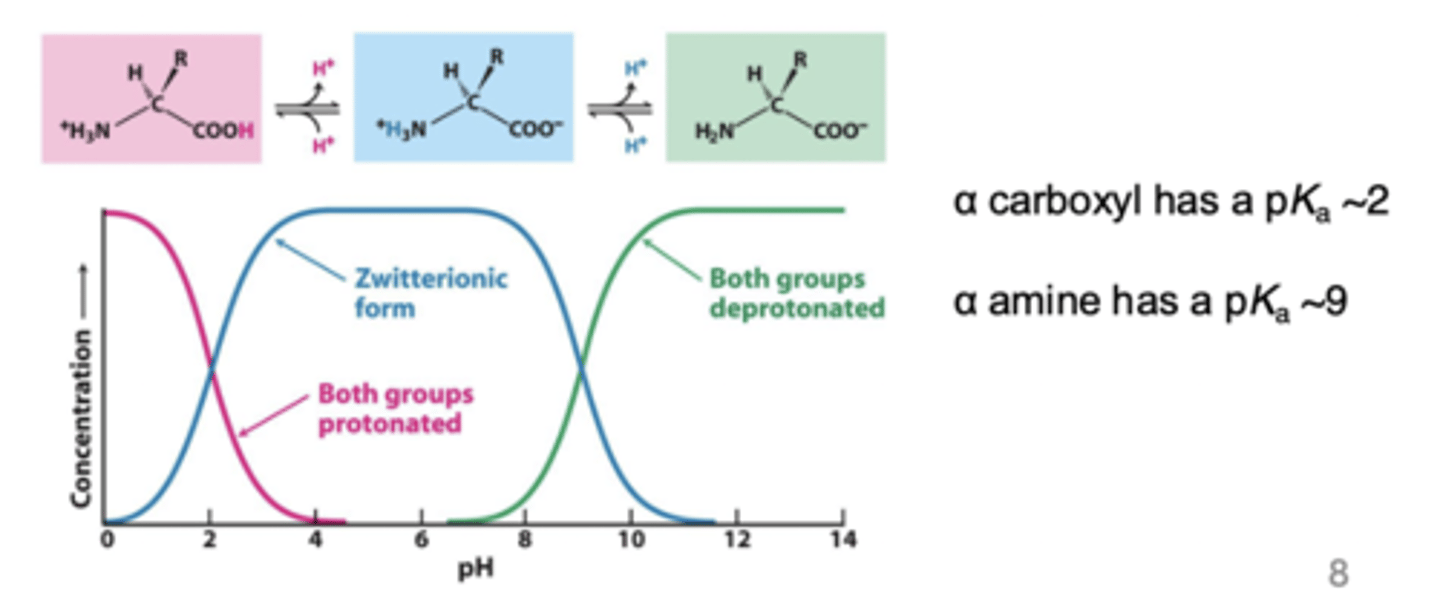
pH below 2 on a free zwitterion
+1 charge on zwitterion
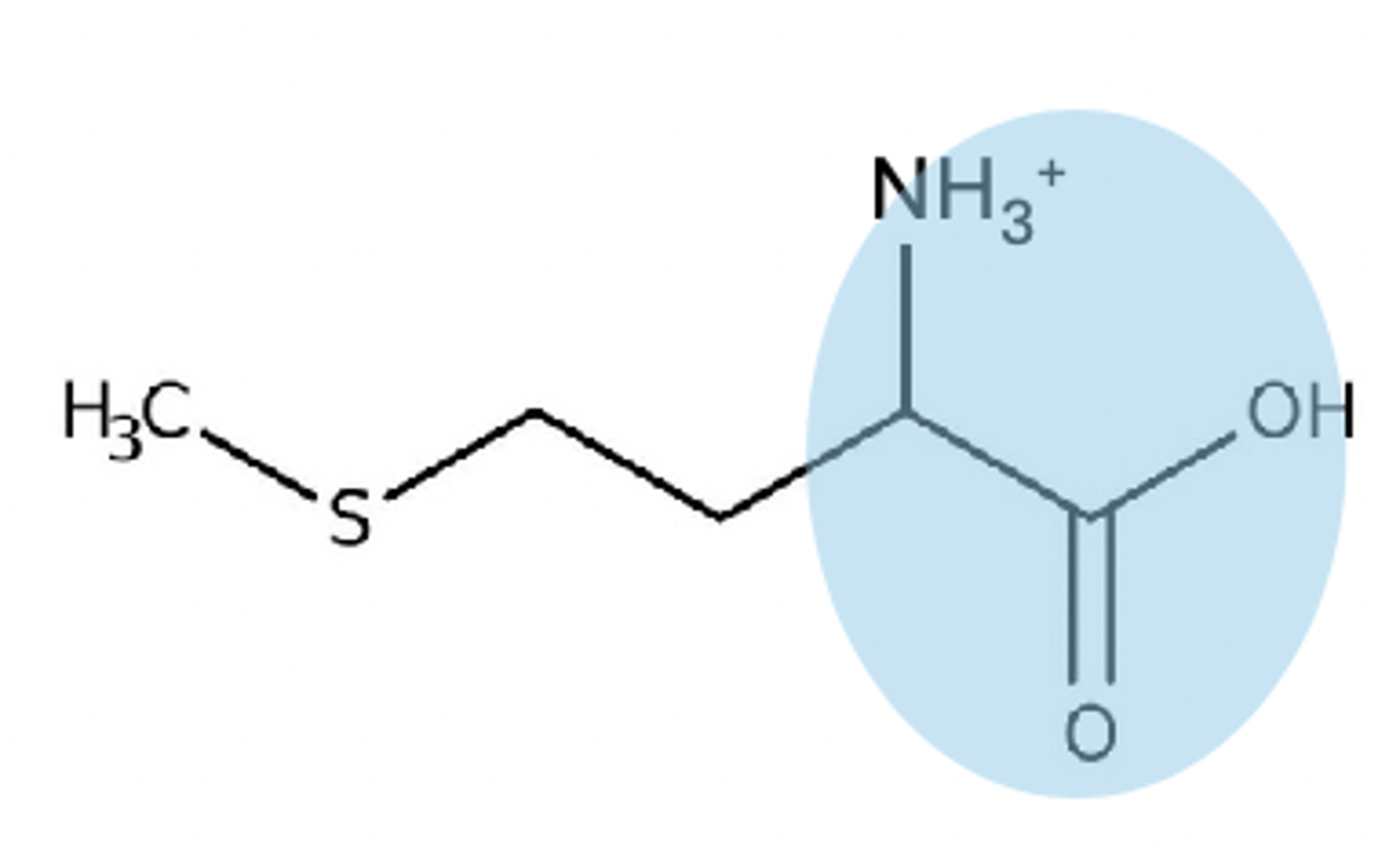
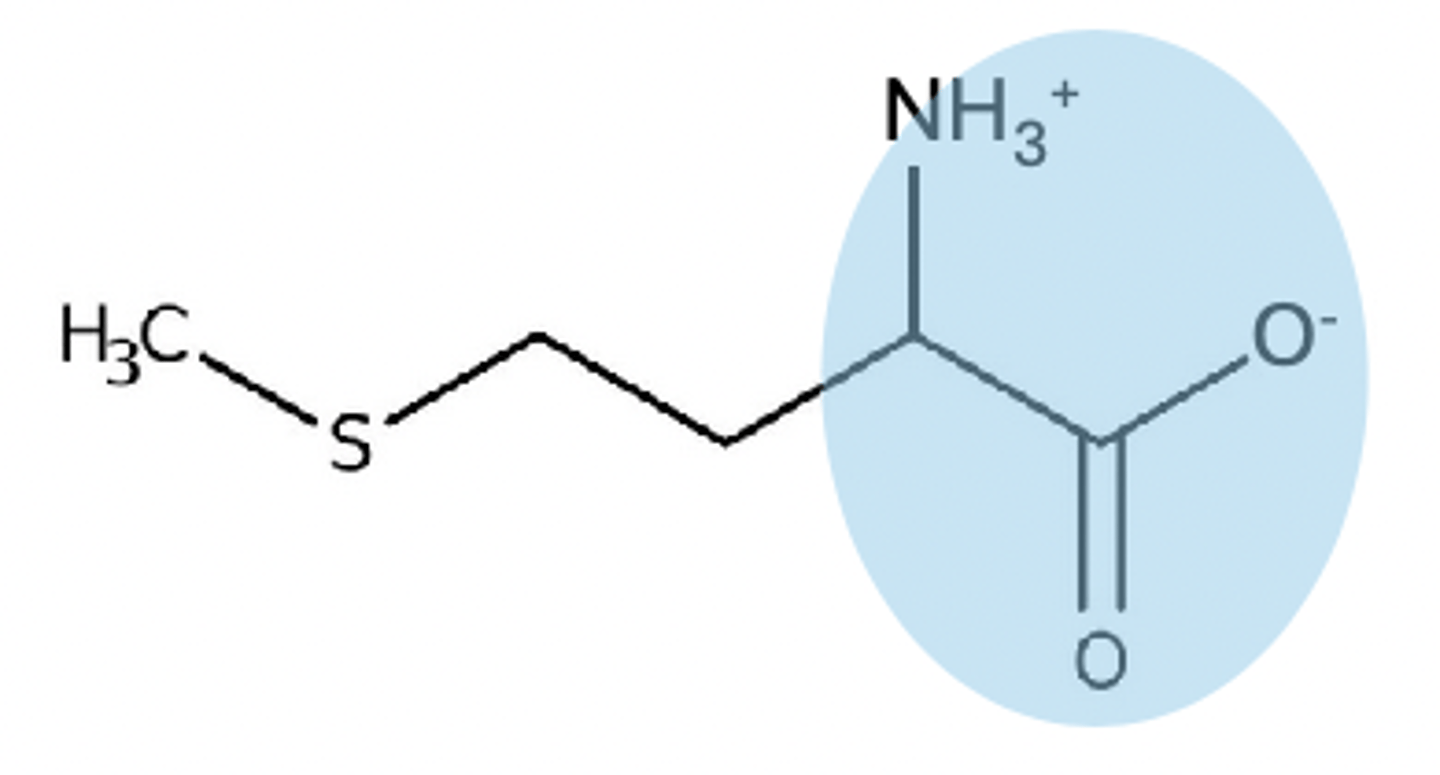
pH between 3-8 on zwitterion
no charge on zwitterion
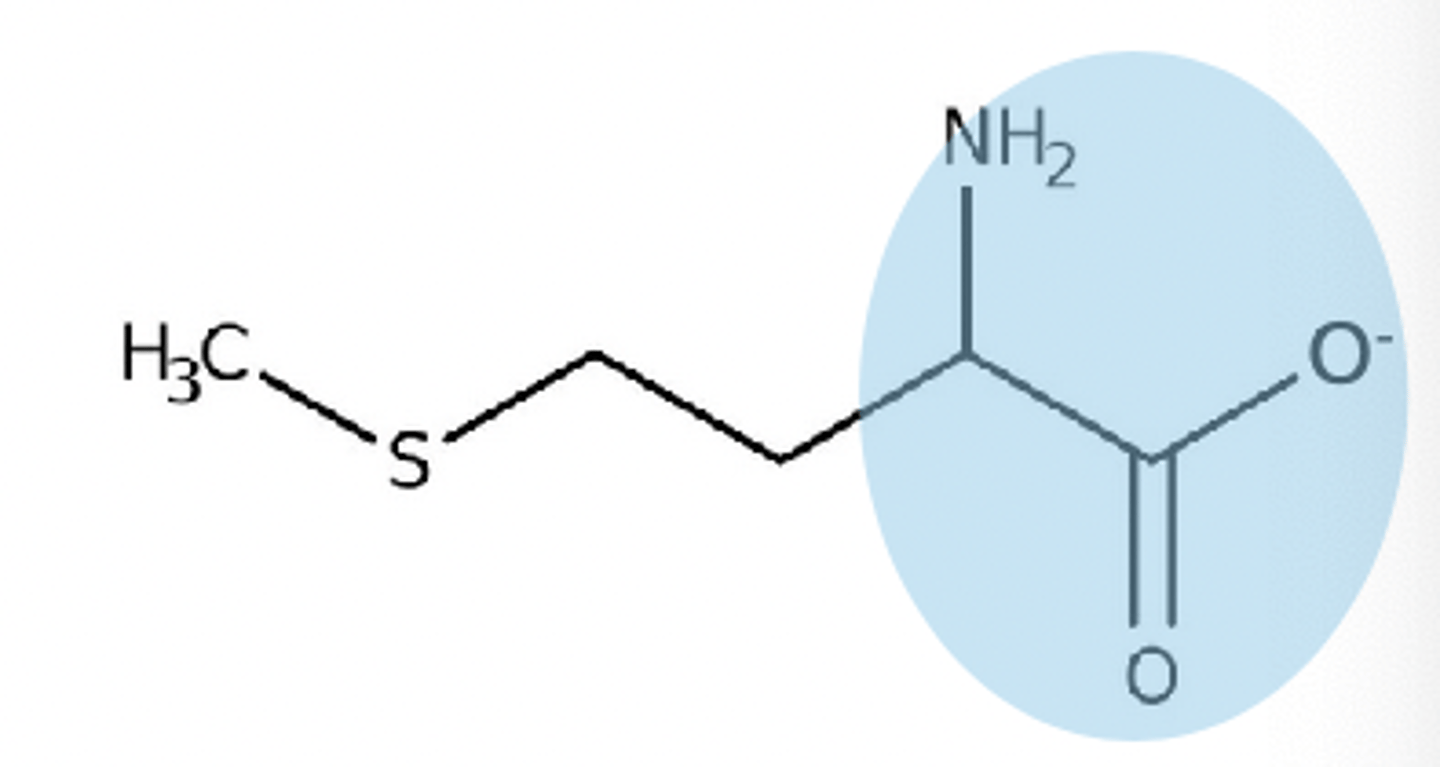
pH above 9 on zwitterion
-1 charge on zwitterion
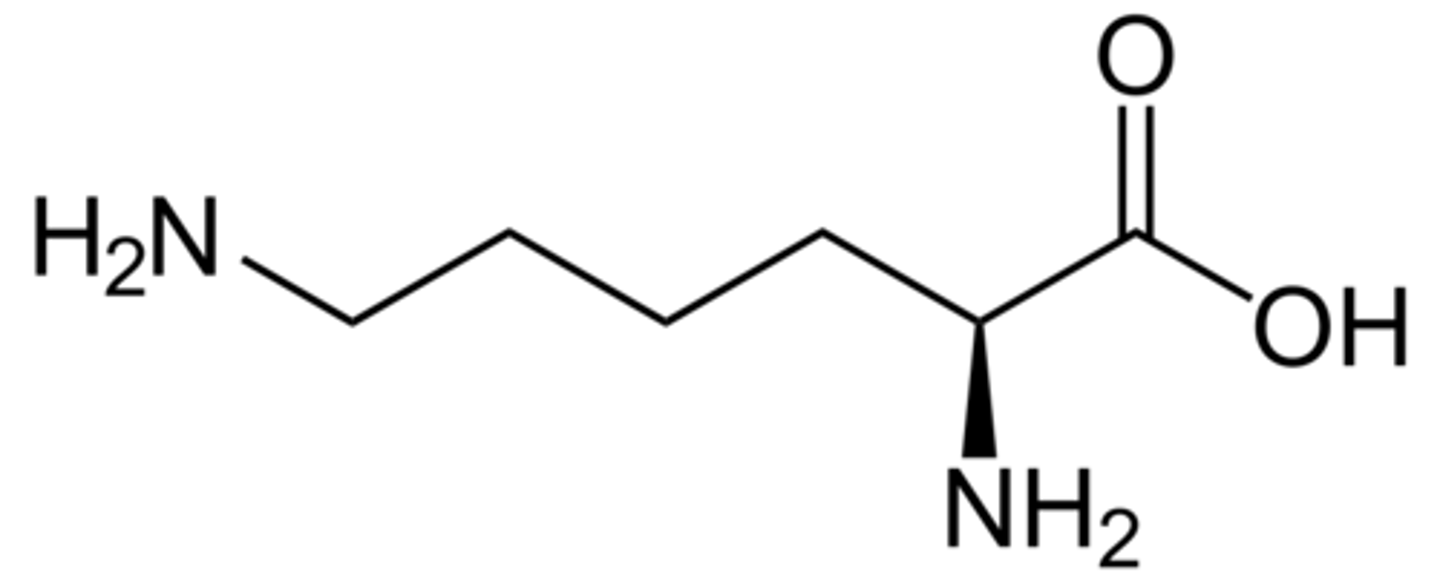
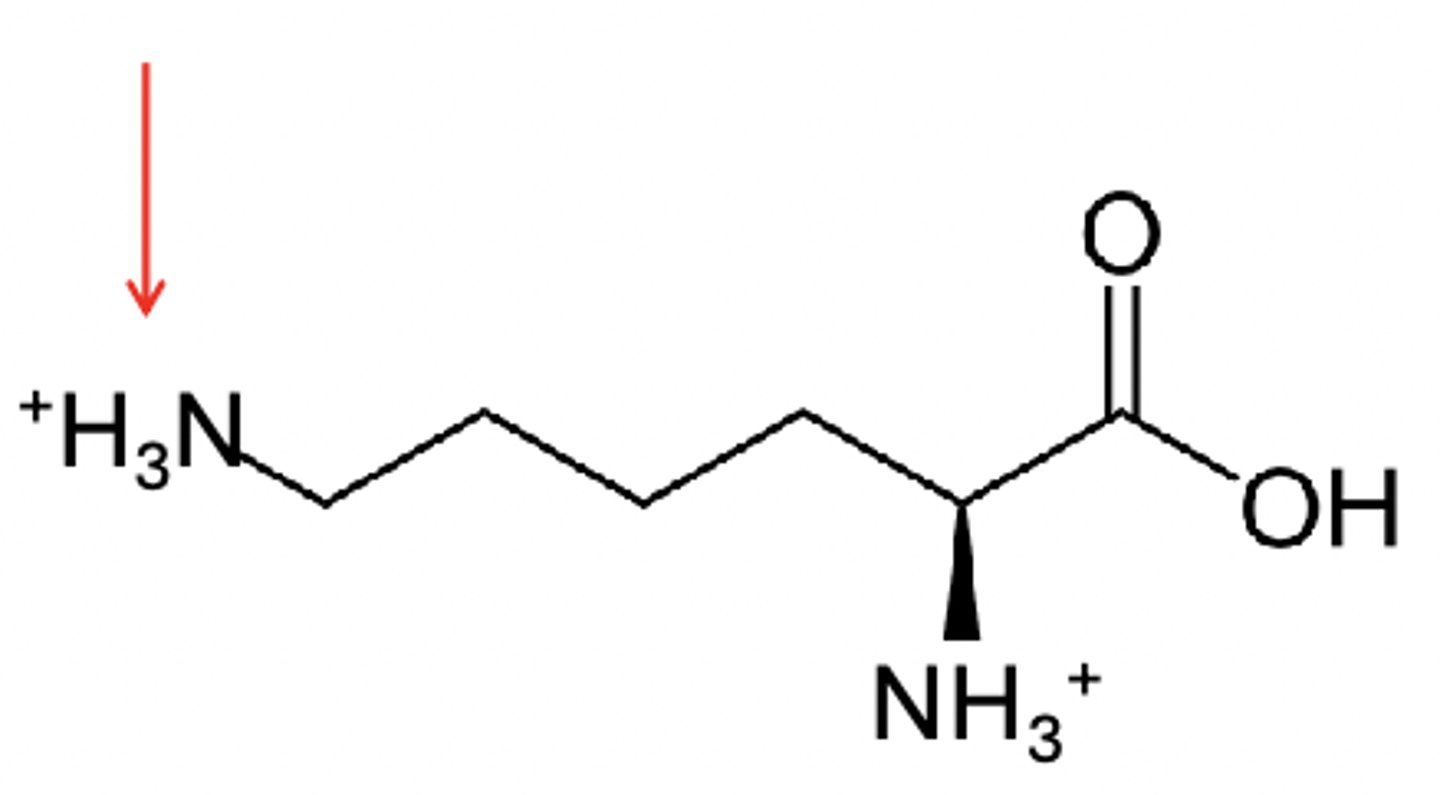
Lysine
the R group has a pKa of 10.8
Lysine in pH below 2
+2 charge on lysine
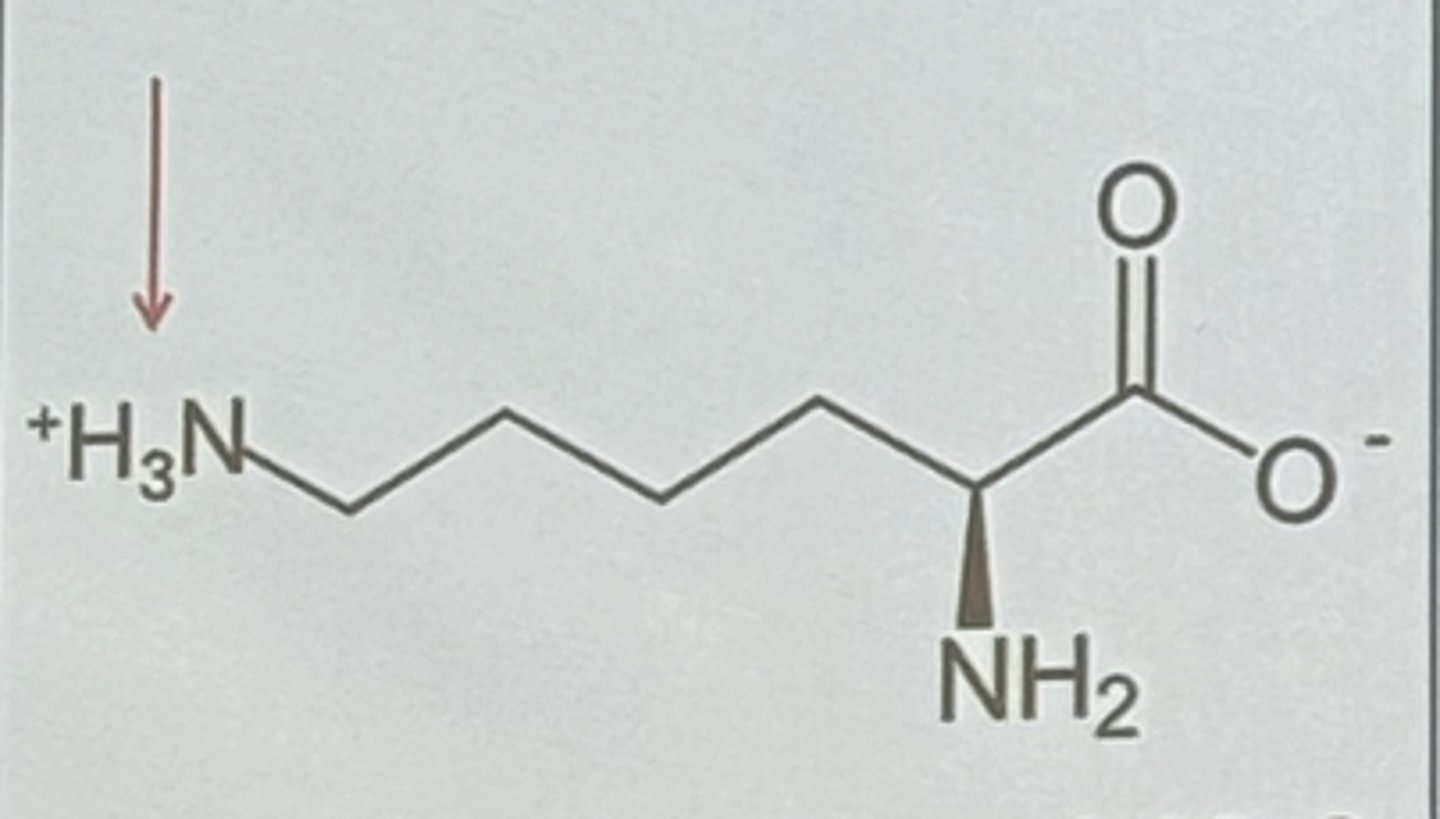
Lysine in pH between 9 - 10.8
no charge
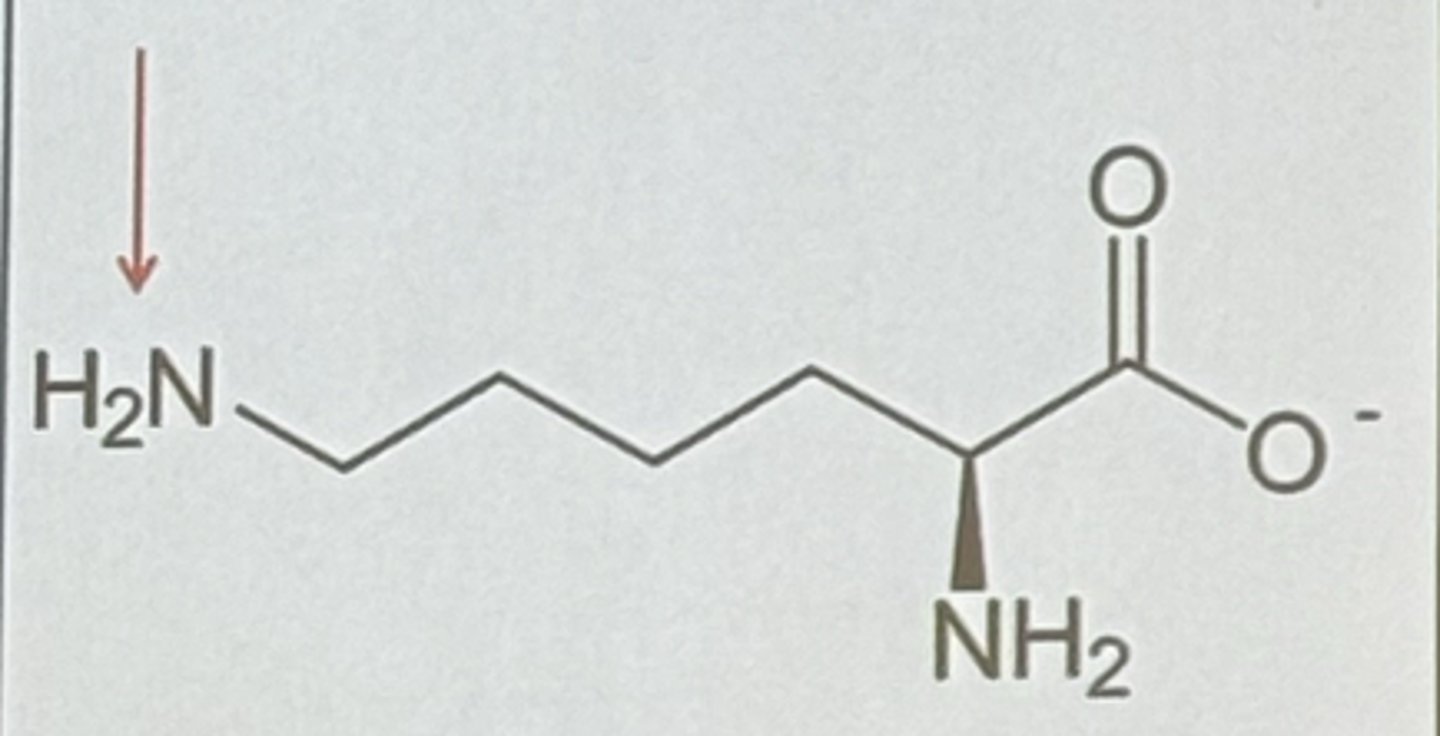
Lysine in pH above 10.8
-1 charge
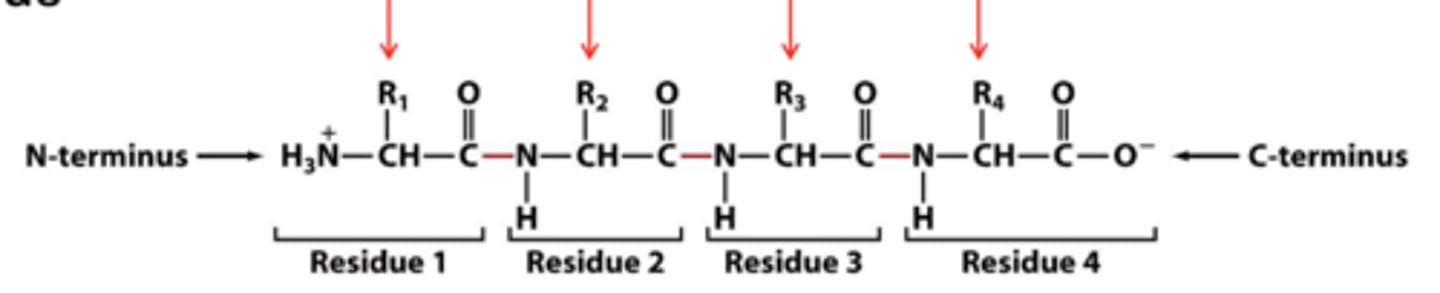
proteins have a net (overall) charge
_______ have a net (overall) charge
do not retain ionization states
because peptide bonds between carboxyl group of one amino acid and amine group of another, those groups (do or do not) retain ionization states
influence of ionization state on proteins
protein charge from amino acid ionizable side chains and terminal ends
(~95%)
what percent of naturally occurring proteins have a low net charge
highly charged proteins
ex. histones
positively-charged as primary structure about 24% lysine and arginine
charge enables interactions with negatively charged DNA
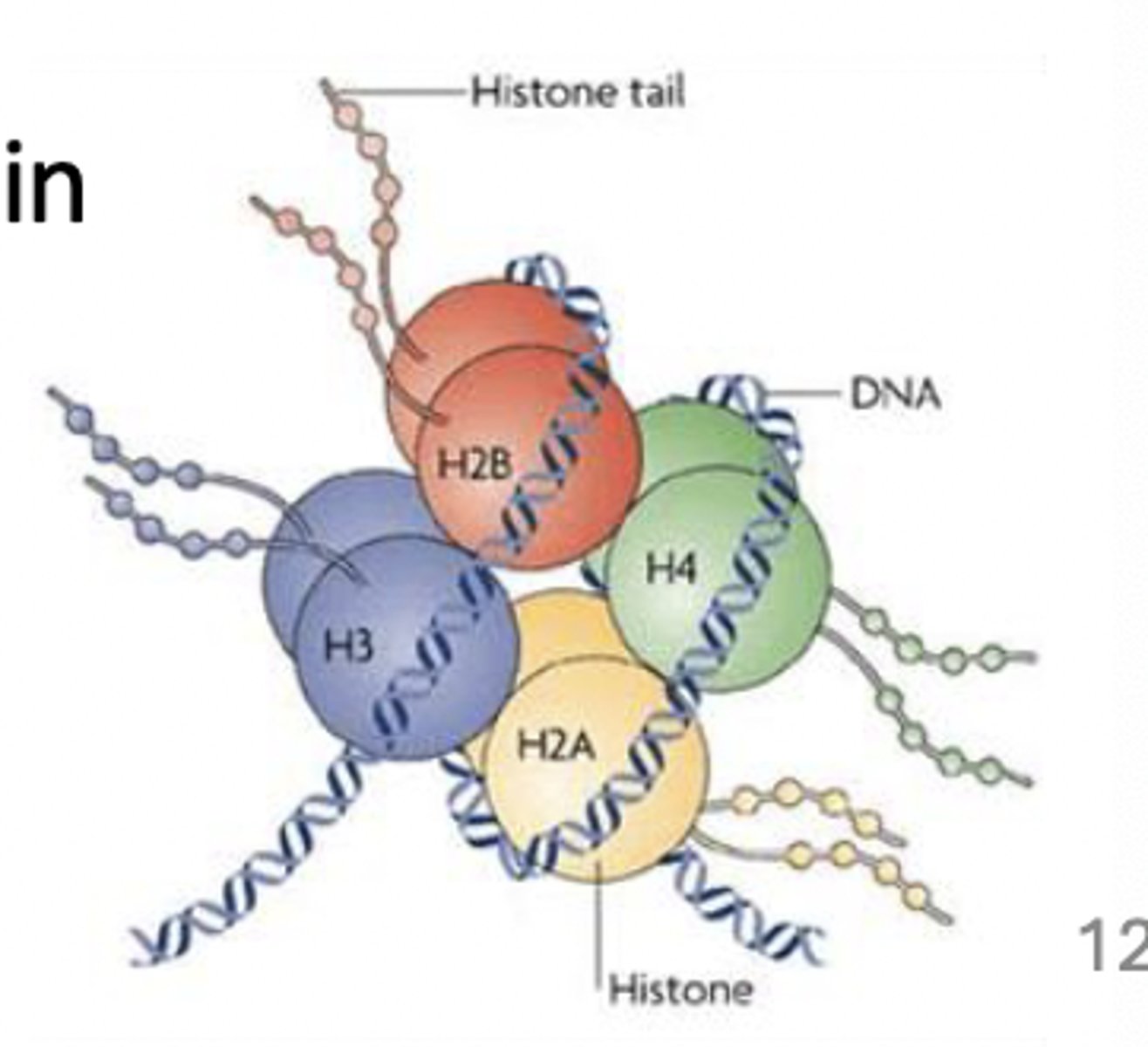
Acetylation and phosphorylation
these promo chromatin remodeling, as functional groups neutralize histones inherent charge and repel nucleic acid backbone
L amino acids and D amino acids
because of structure, most amino acids exist in two mirror-image form
configurational isomers
same chemical formula but differ in spatial arrangement / structure
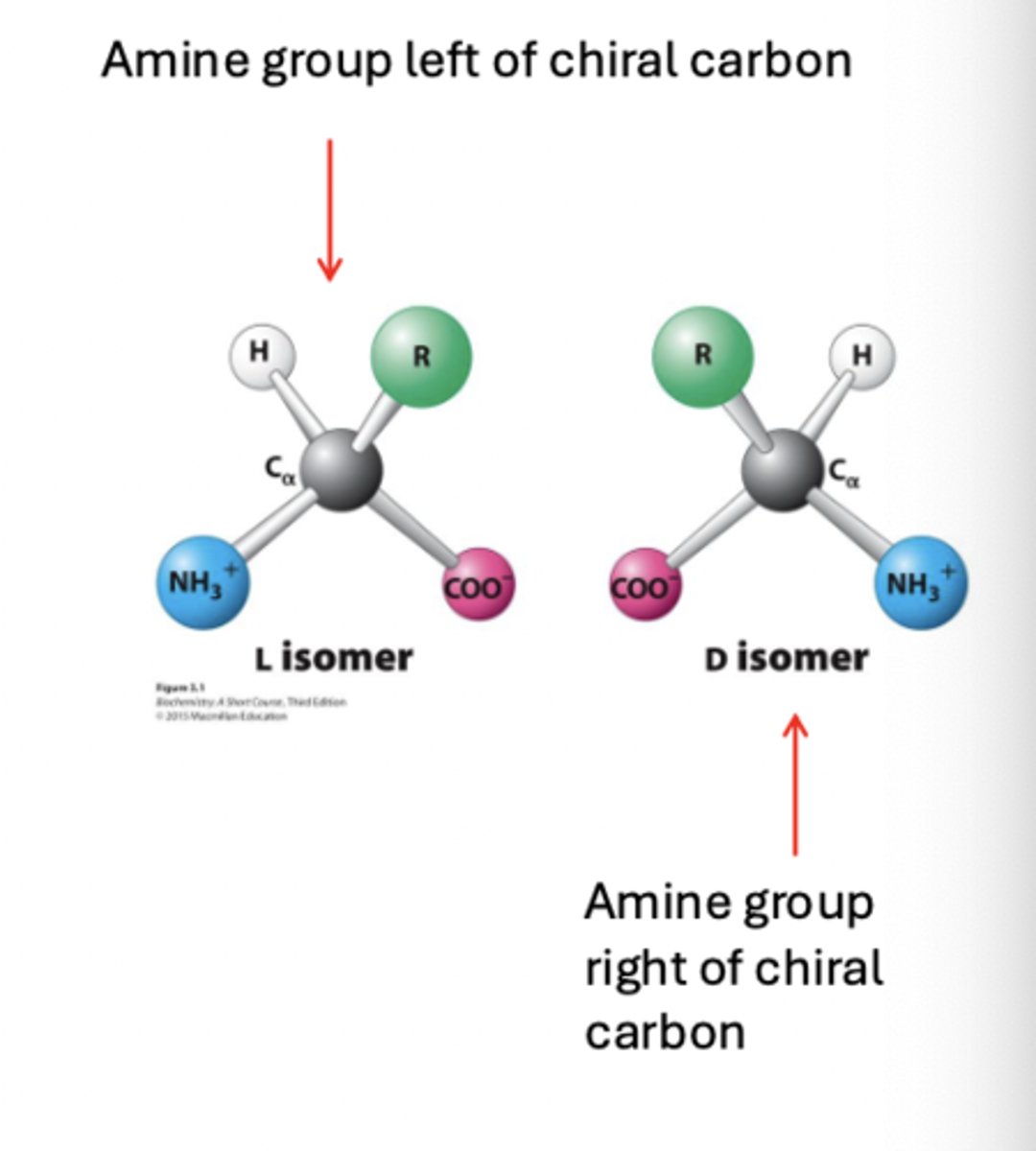
L amino acids
interestingly, only _ amino acids are constituents of proteins
- slightly more soluble in aqueous environments
- eukaryotic enzymes preferentially recognize this isomer
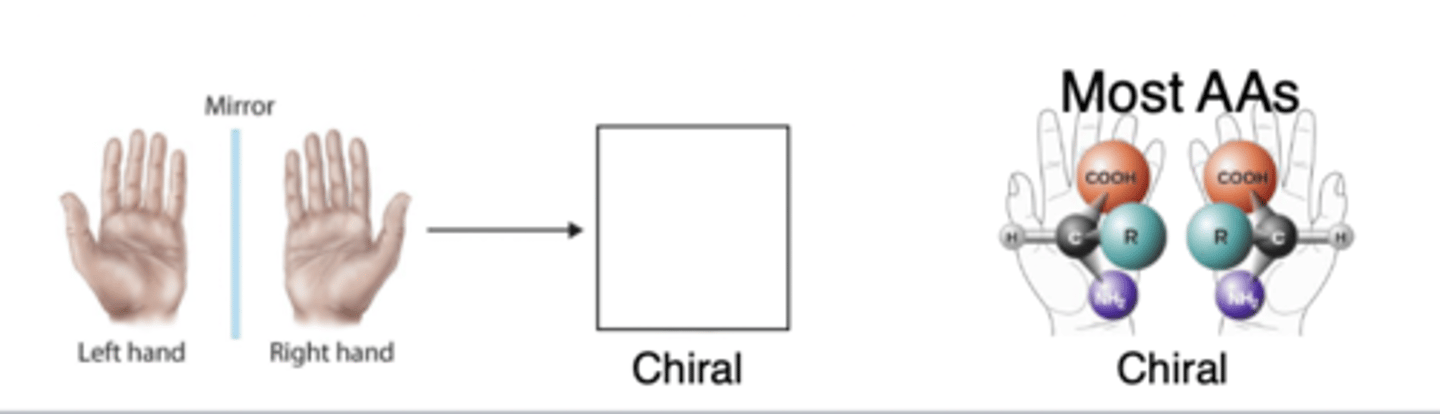
chirality
most amino acids also display optical isomerism due to this
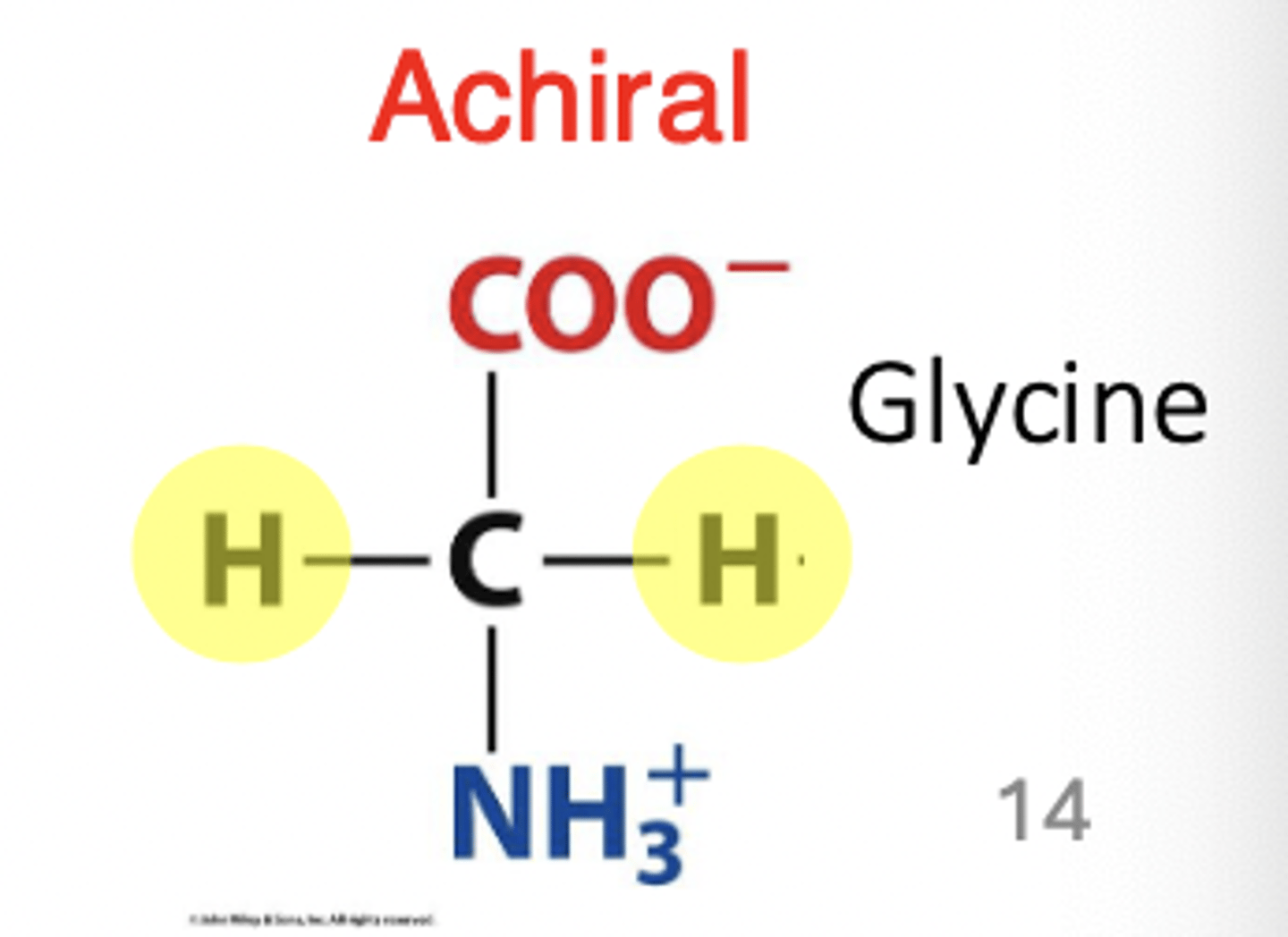
exception: glycine
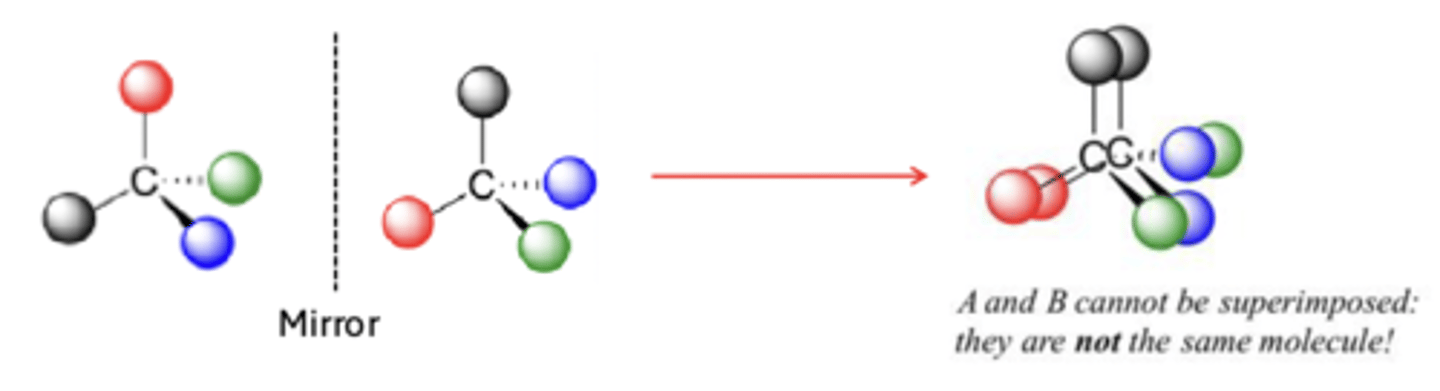
chiral
asymmetric in that structure and mirror image not superimposable
chiral examples
achiral example
stereocenters
chiral molecules contain 1 or more _____________ or chiral centers
- typically a tetrahedral or asymmetric carbon atom
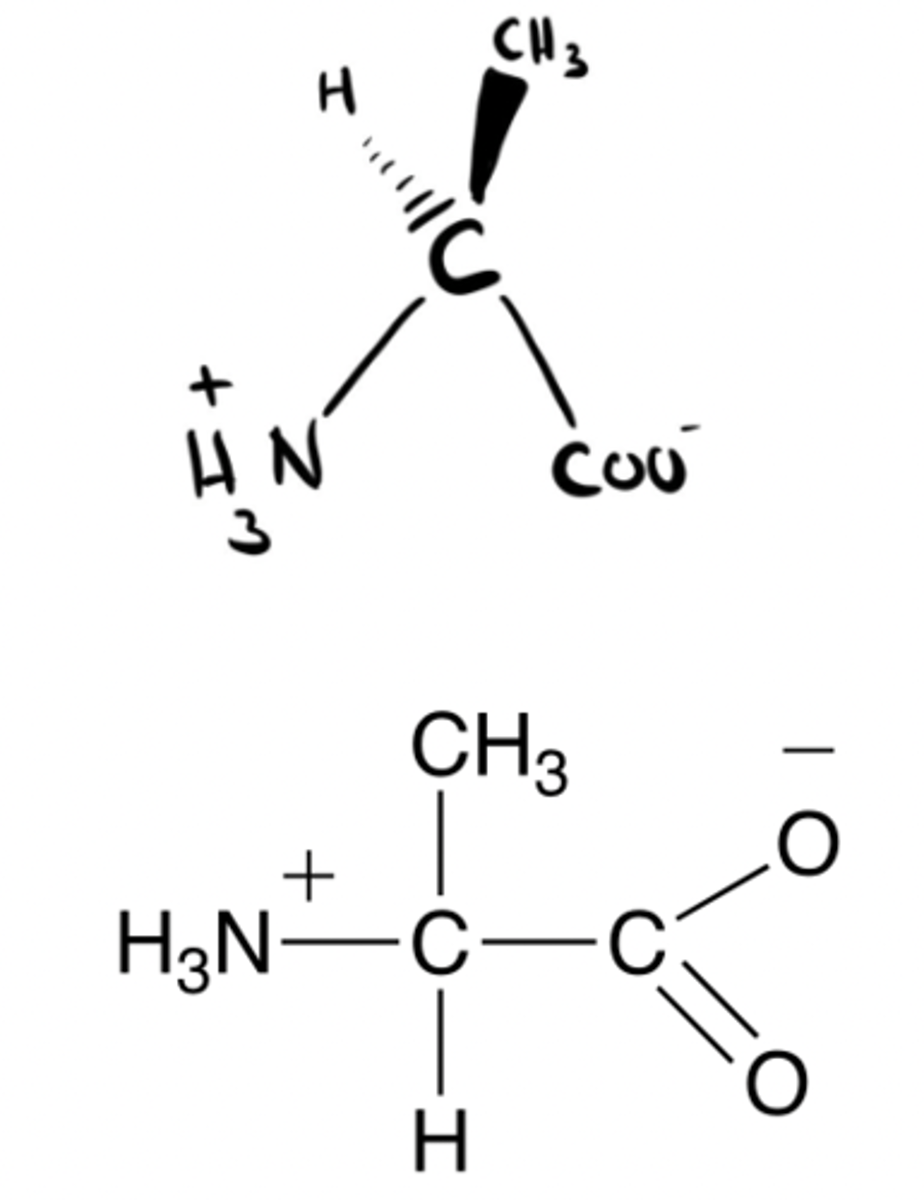
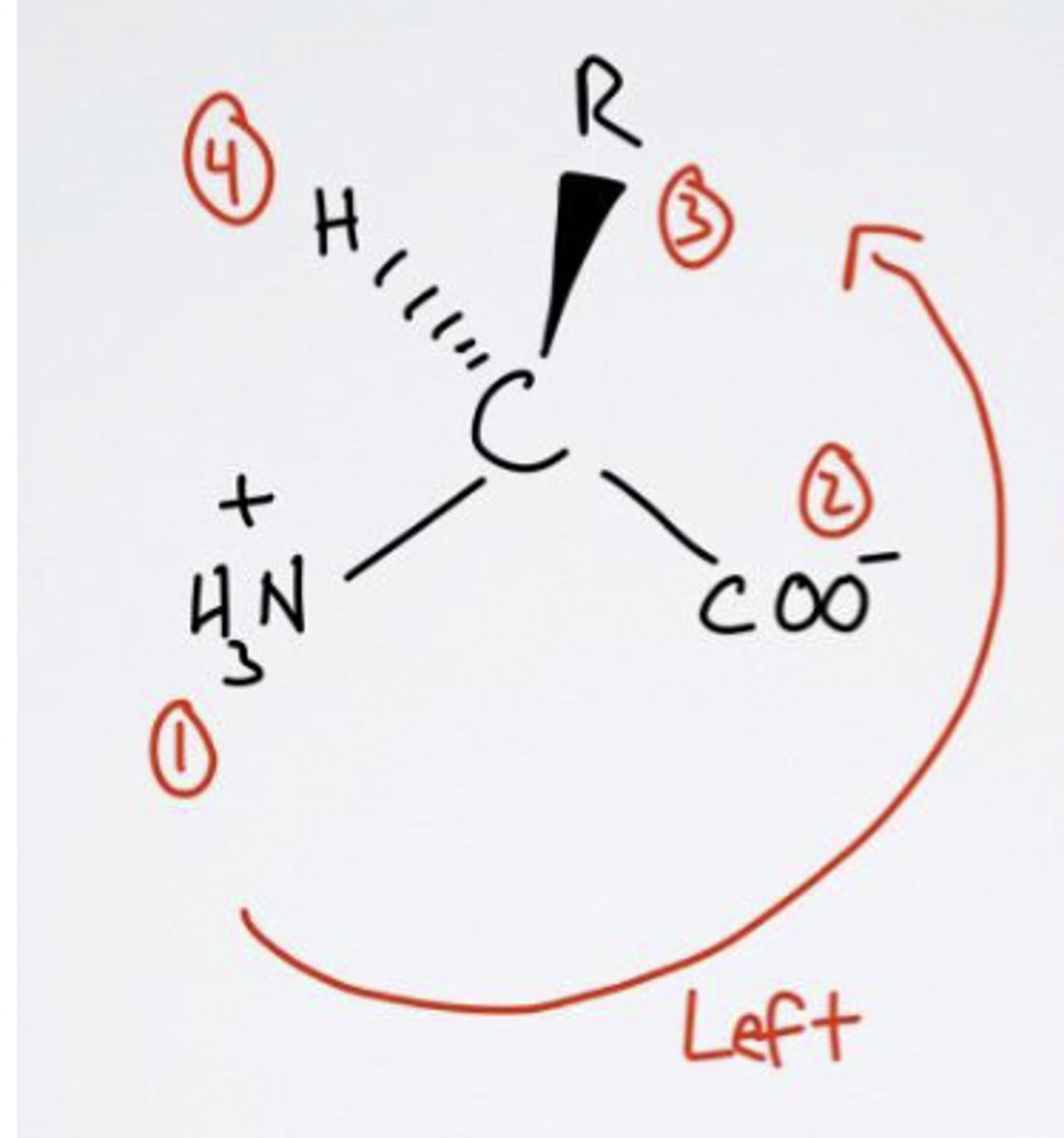
Left! L-isomer
L or D molecule?
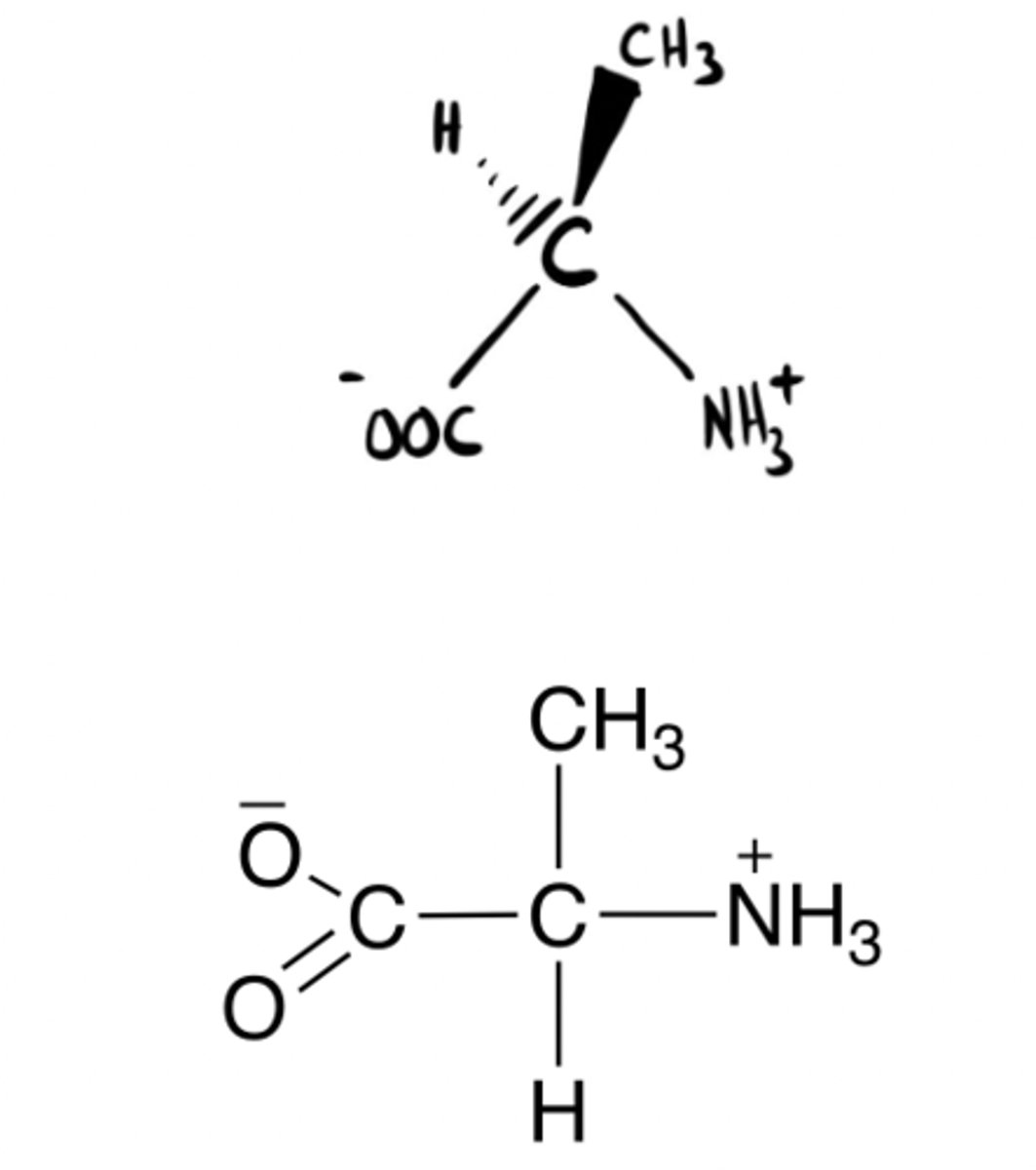
Right! D-isomer
L or D molecule?
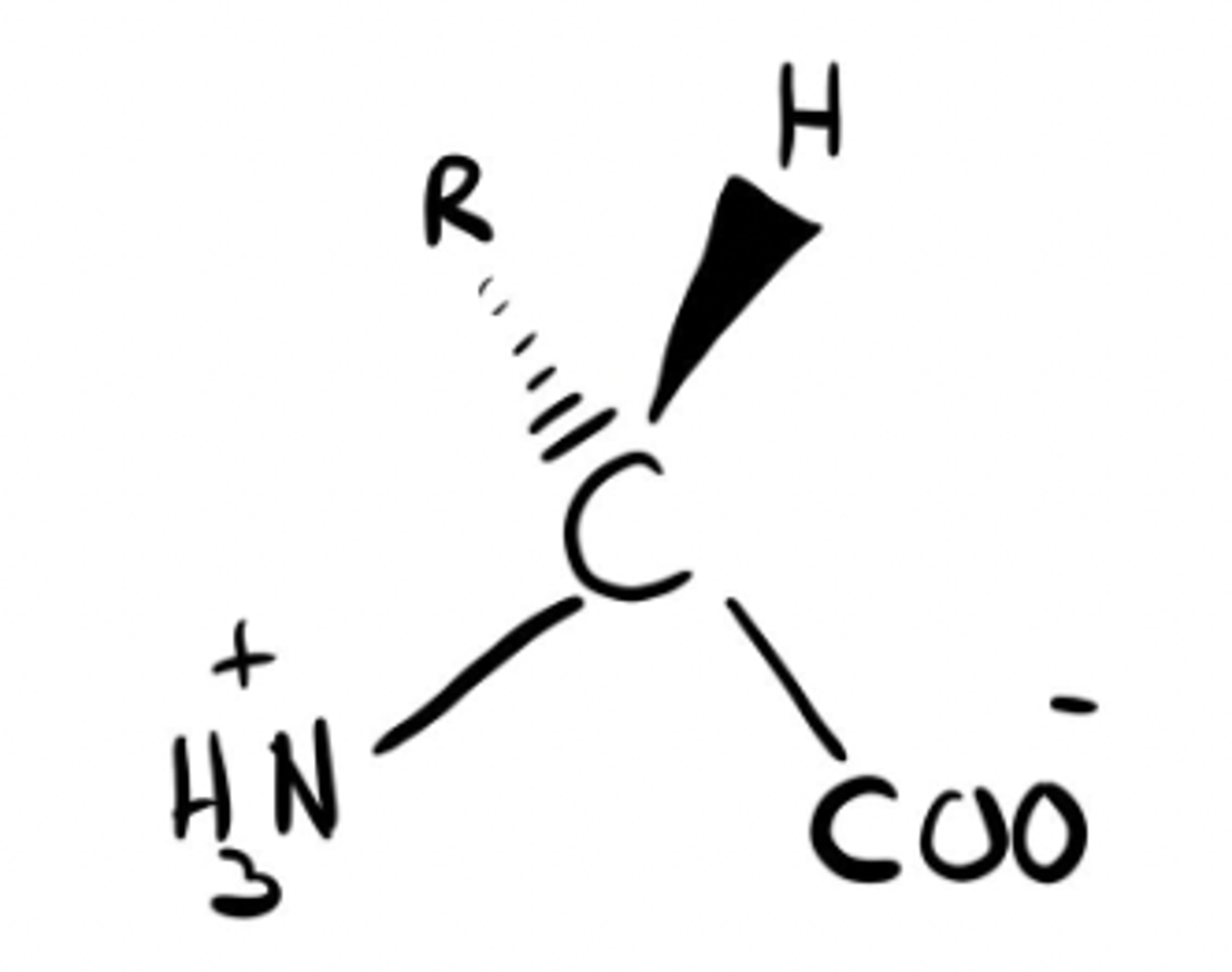
D-isomer
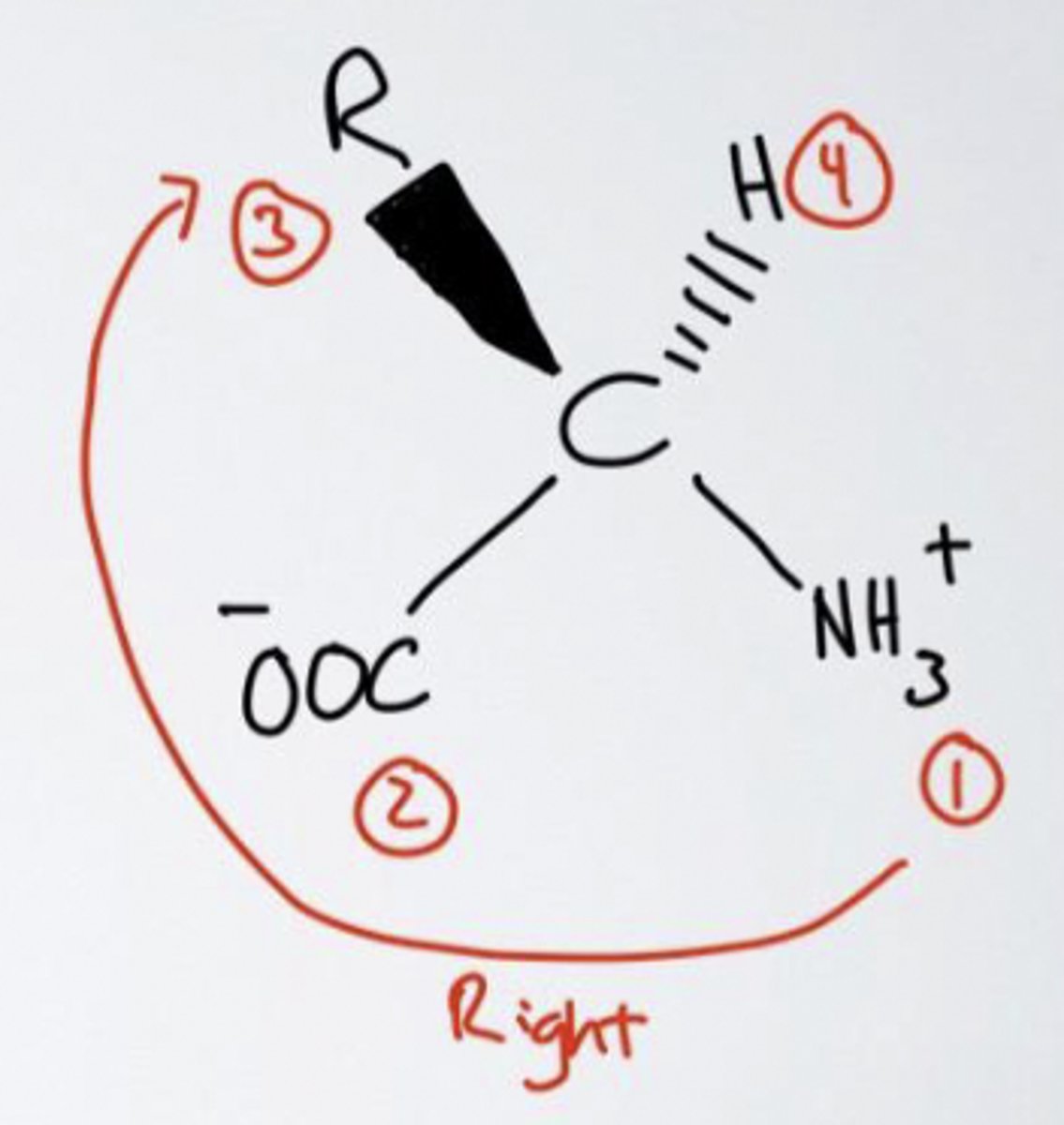
L-isomer
D-isomer
L or D isomer?
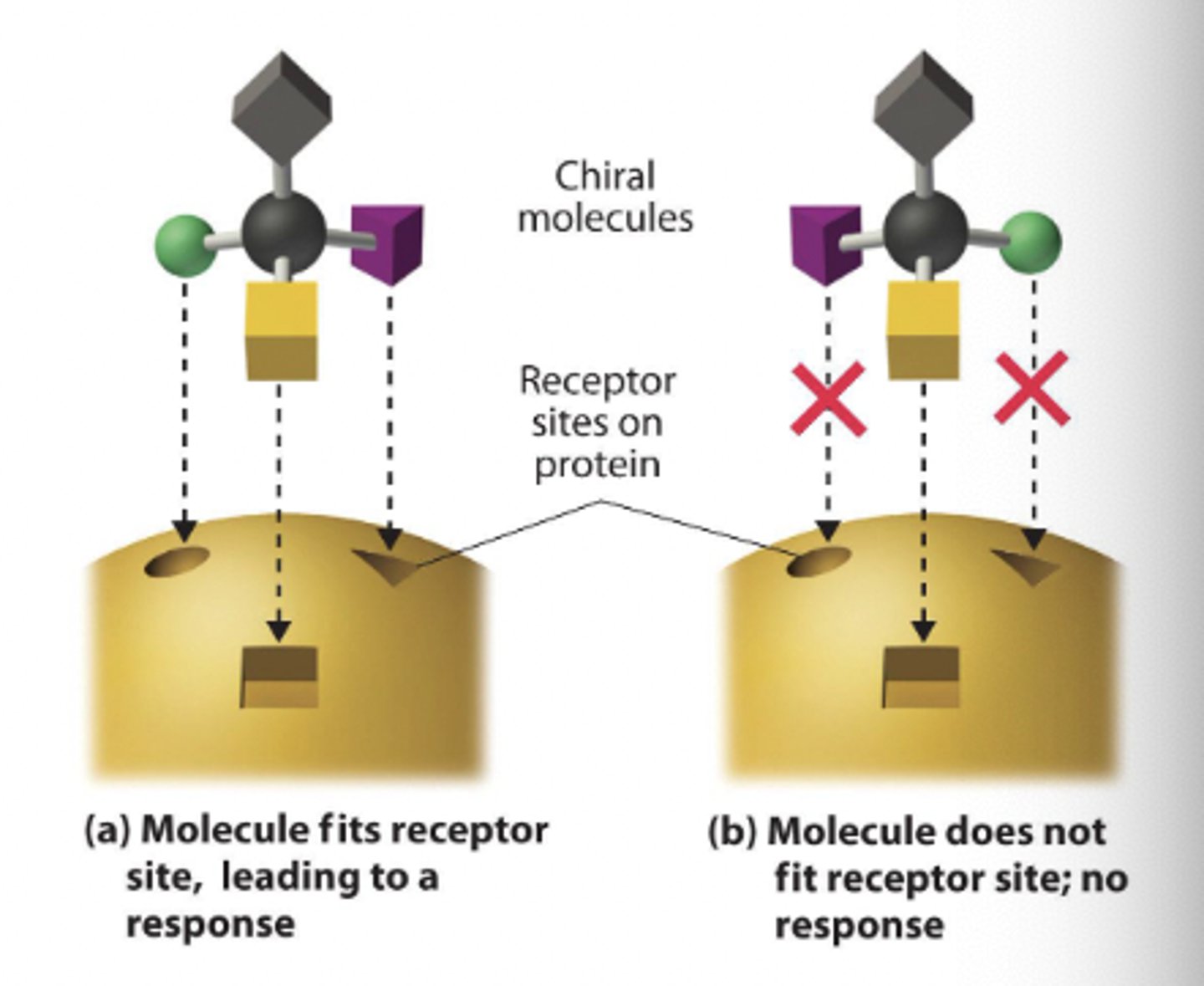
importance of isomers and chirality
fundamental components of receptor binding
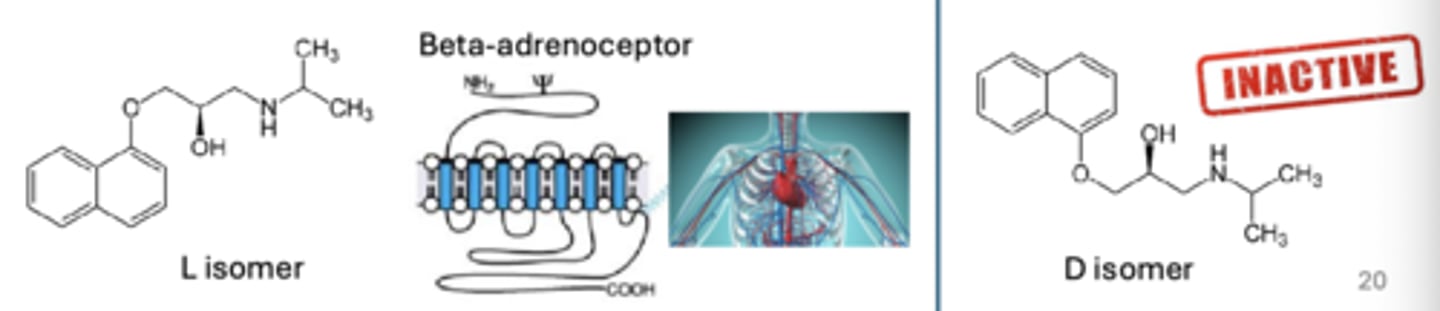
importance of isomers and chirality - drug efficacy
isomer selection means to maximize ____ efficacy
importance of isomers and chirality - proprandolol
a blood pressure drug
isomer selection
also means to minimize undesirable effects
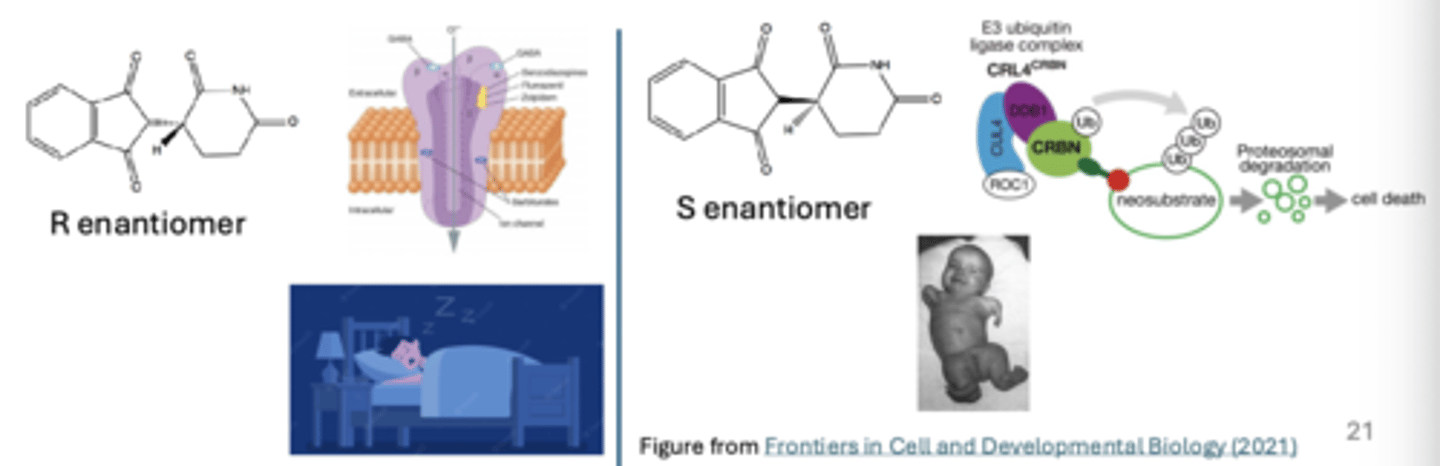
ex. Thalidomide is a synthetic sedative and hypnotic medication prescribed in the 1950's to treat anxiety, insomnia, and morning sickness in pregnant women