AP physcolgy prgessvie uint quizlet
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
- *Q:* What is the term for retrieving information without cues
A:* Recall
- *Q:* What type of memory is used to identify previously learned information
*A:* Recognition
- *Q:* What is the process of learning something more quickly when you have learned it before
*A:* Relearning
- *Q:* What are the three types of memory
*A:* Sensory Memory, Short-Term Memory, Long-Term Memory.
- *Q:* Which memory strategy involves grouping information into manageable units
*A:* Chunking
- *Q:* What phenomenon describes the tendency to forget rapidly after learning
*A:* Forgetting Curve
- *Q:* What is the inability to form new memories called
*A:* Anterograde Amnesia
- *Q:* What is the effect when old information disrupts recall of new information
- *A:* Proactive Interference
- *Q:* What is the systematic process for investigating ideas called
*A:* Scientific Method
- *Q:* In an experiment, what is the factor manipulated by the researcher
*A:* Independent Variable (IV)
- *Q:* What do we call the outcome measured in an experiment
*A:* Dependent Variable (DV)
- *Q:* What is the purpose of a control group in an experiment
*A:* To provide a baseline for comparison.
- *Q:* What is validity in the context of research
A:** How well a test or experiment measures what it intends to measure.
- *Q:* What refers to the consistency of a measure over time
*A:* Reliability
- *Q:* What are confounding variables
*A:* Other variables that could influence the DV but are not controlled for.
- *Q:* Why is informed consent important in research
*A:* It ensures participants are aware of what the study involves and agree to participate.
- *Q:* What is the Misinformation Effect
*A:* When memories are altered by misleading information.
*Q:* What is the purpose of chunking in memory
*A:* Chunking is a strategy that groups information into manageable units to enhance memory retention.
*Q:* Define neuroplasticity
A:* Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, especially after injury.
*Q:* What is the difference between proactive and retroactive interference
A:** Proactive interference occurs when old information disrupts the recall of new information, while retroactive interference occurs when new information disrupts the recall of old information.
*Q:* What are confounding variables
are factors other than the independent variable that could influence the dependent variable in an experiment.
*Q:* What is the scientific method
A:* The scientific method is a self-correcting process for evaluating ideas through observation and experimentation.
*Q:* What are dependent variables
A:while the dependent variable (DV) is the outcome measured in response to the IV.
*Q:* What is the forgetting curve
A:** The forgetting curve illustrates the decline of memory retention over time, showing rapid forgetting that levels off.
*Q:* Define emotional intelligence (EQ)
is the ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions effectively in oneself and others.
*Q:* What role does the control group play in an experiment
A:** The control group is not exposed to the independent variable; it serves as a benchmark to compare the effects of the independent variable on the experimental group.
What is the purpose of random assignment in a study is to
Reduce the potential of confounding variables
what is retrograde amnesia
when you can't recall memories from your past.
What is classical conditioning
The process of classical conditioning can explain how we acquire phobias. For example, we learn to associate something we do not fear, such as a dog (neutral stimulus), with something that triggers a fear response, such as being bitten (unconditioned stimulus).
What is hindsight bias
o the tendency to perceive past events as more predictable than they actually were .
Availability Heuristic
Judging how likely a certain event is to happen based on how easily information regarding this topic is available.
A researcher finds a strong positive correlation between hours studied and exam scores What can be inferred
There is a relationship but causation cannot be determined
The Hawthorne effect
is when participants alter behavior simply because they are aware they're being observed.
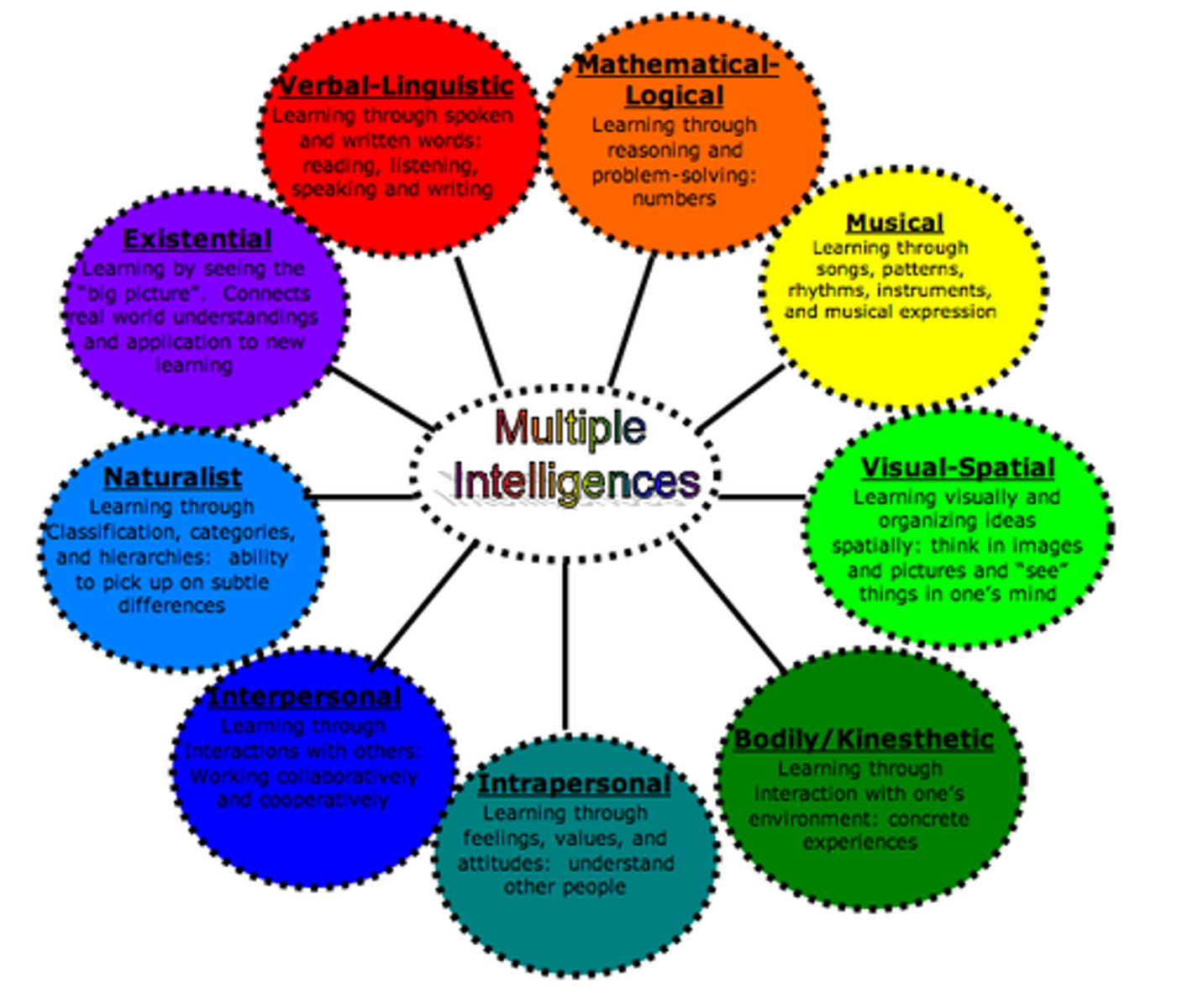
Gardener's Intelligence Theory
no such thing as single unified intelligence. linguistic, musical, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal and intrapersonal by a guy named garnner
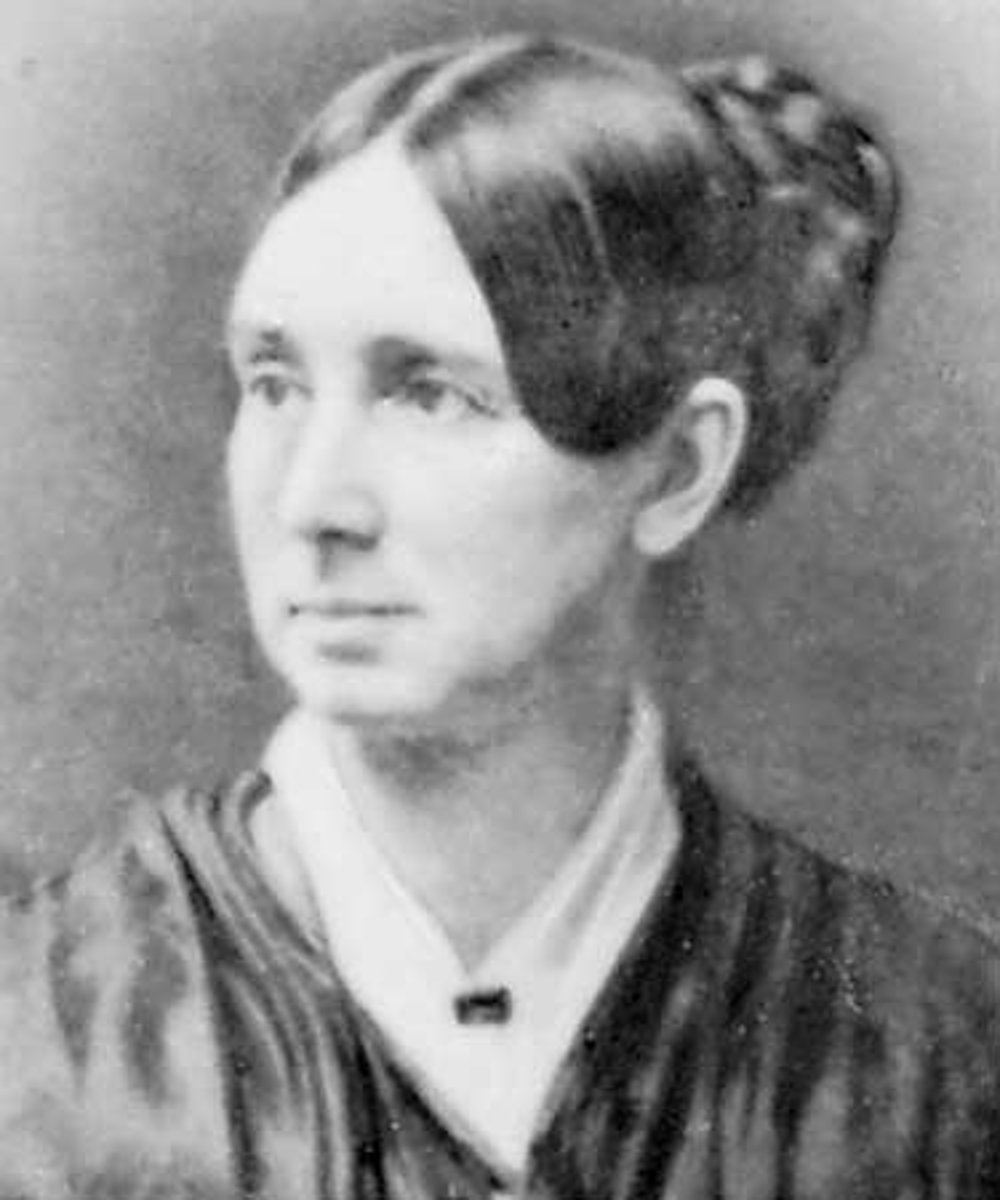
Dortha Dix
Union nurse famous for reforming prisons and mental hospitals

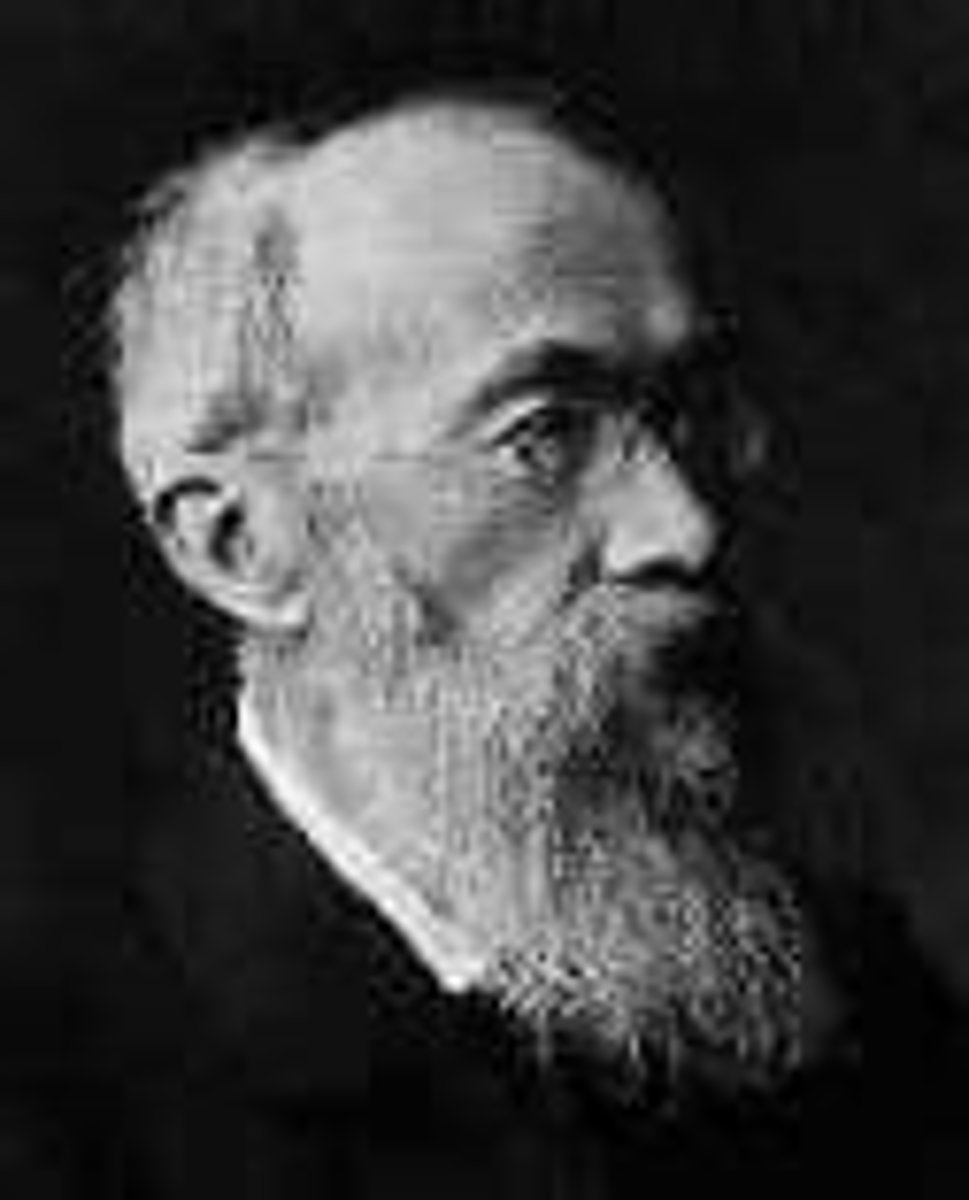
Wilhem Wundt (1832-1920)
-viewed psychology as a science
-observe + EXPERIMENTATION = psychology
-first experiment on how people hear a sound faster than being aware of what the sound means (hitting a telegram key when a ball hit a hall)
* opened the first psychology laboratory in Germany in 1879

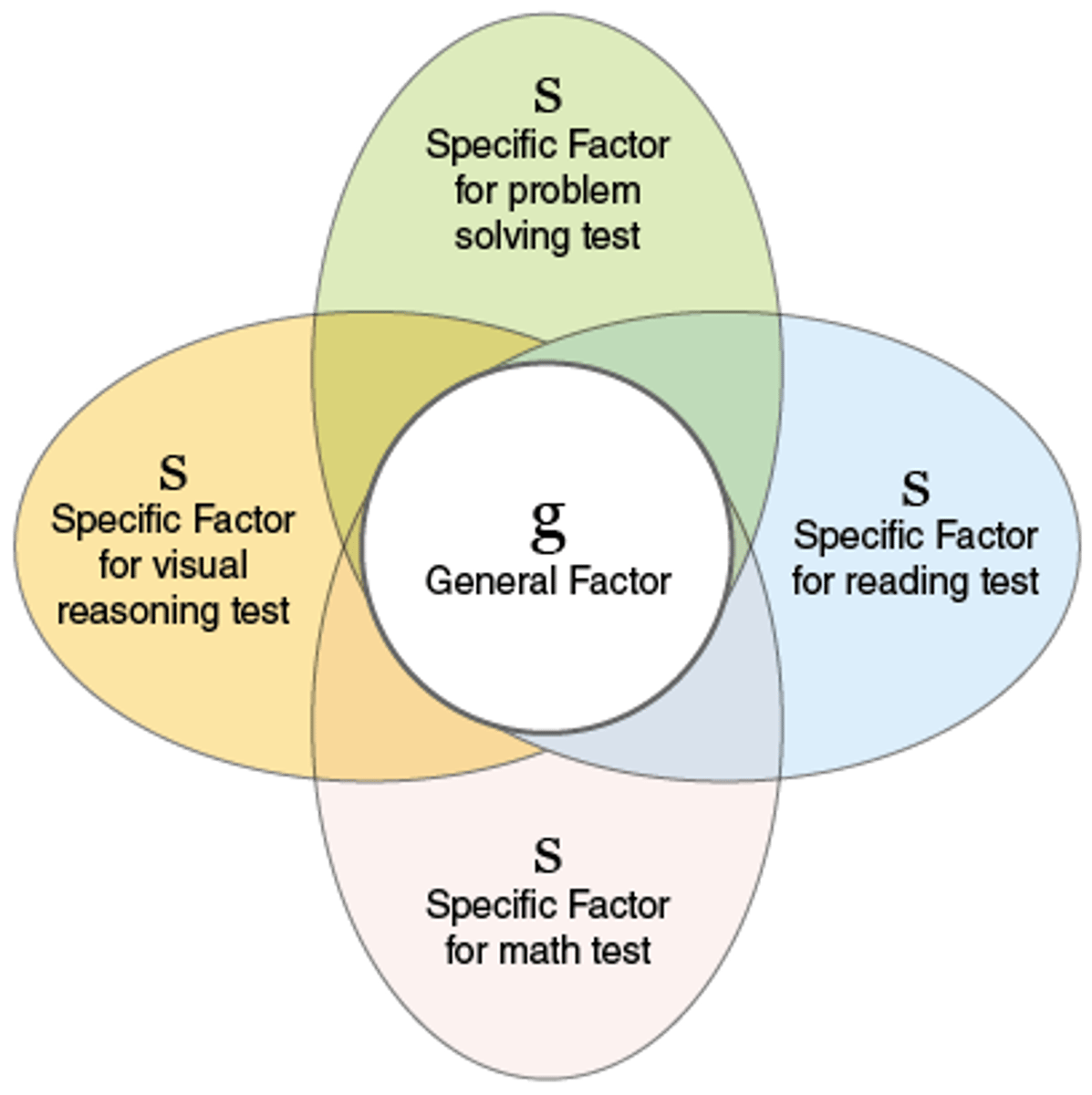
Spearman general intelligence
Intelligence is made up of a number of mental abilities (factors)
g factor broad reasoning and problem-solving
s factor represents specific intelligence
Bandra
expanded on the ideas of behaviorism and introduced new concepts
As genetics between girls become similar
Heritability is lower
As genetics between the groups become dissimilar
Hair ability becomes higher
Twin Studies
Research method in psychology that compares identical and fraternal twins to study the influence of genes and environment on behavior and traits
What is the primary purpose of twin studies in psychology?
To determine the relative influence of genetics and environment on various traits and behaviors
What is a limitation of twin studies?
They may overestimate genetic influences due to the shared prenatal environment of twins
What assumption do twin studies rely on, which has been criticized?
The "equal environments assumption" - that identical and fraternal twins experience similarly similar environments
Skewed Curves
A distribution that is not symmetrical, where one tail is longer or fatter than the other.
What is a characteristic of skewed curves?
They are not symmetrical.
Nature vs. Nurture
name for a controversy in which it is debated whether genetics or environment is responsible for driving behavior
What is the function of acetylcholine (ACh)?What happens if acetylcholine (ACh) malfunctions?
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory.malfunction With Alzheimer's disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate.
What is the function of dopamine?What happens if there is an oversupply and undersupply of dopamine?
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. (undersupply)It is linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson's disease. oversupply linked to schizophrenia.
What is the function of serotonin?What happens if there is an undersupply of serotonin?
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. It is linked to depression.
What is the function of norepinephrine?What happens if there is an undersupply of norepinephrine?
Helps control alertness and arousal.It can depress mood.
What is GABA?
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter.
What happens if there is an undersupply of GABA?
An undersupply of GABA is linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
What is glutamate?
is a major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory.
What happens if there is an oversupply of glutamate?
igt can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures.
What are endorphins?
Endorphins are neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure.
What happens if there is an oversupply of endorphins due to opioid drugs?
An oversupply of endorphins with opioid drugs can suppress the body's natural endorphin supply.
action potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
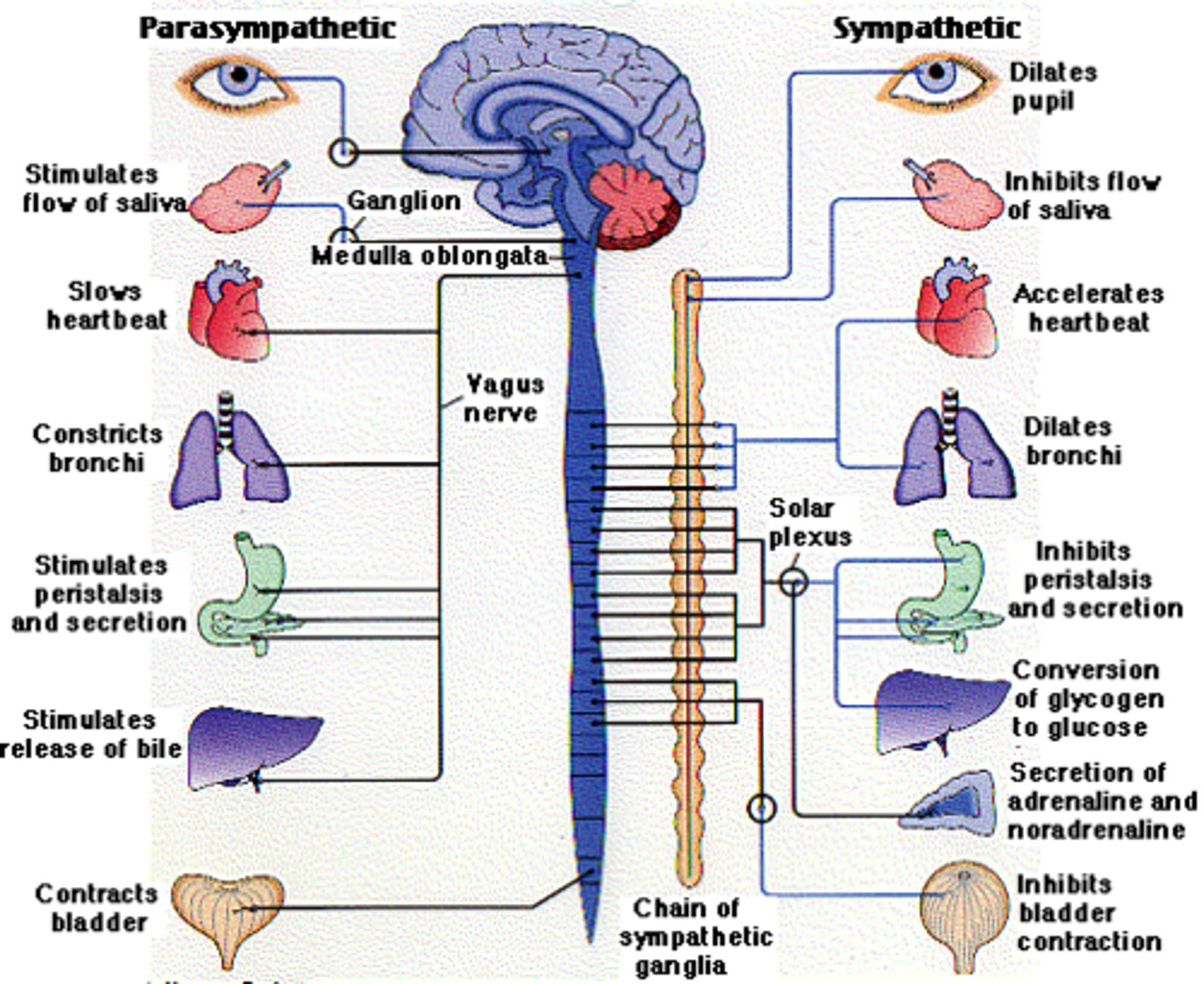
sympathetic nervous system vs. parasypathic
While your sympathetic nervous system carries signals that put your body's systems on alert, your parasympathetic carries signals that relax those systems.