Pharmacy Foundations Part 1
Primary NT of sympathetic nervous system
Norepinephrine (NE) and Epinephrine (EPI)
- Bind to adrenergic alpha and beta receptors
Primary NT of parasympathetic nervous system
ACh (acetylcholine)
- Bind to muscarinic receptors
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
224 Terms
Primary NT of sympathetic nervous system
Norepinephrine (NE) and Epinephrine (EPI)
- Bind to adrenergic alpha and beta receptors
Primary NT of parasympathetic nervous system
ACh (acetylcholine)
- Bind to muscarinic receptors
Primary NT of somatic nervous system
ACh (acetylcholine)
- Bind to nicotinic receptors
Catecholamine Metabolism
Breakdown Facilitated By MAO:
Tryptophan -> 5-HT -> metabolites
Tyrosine -> DOPA -> Dopamine -> NE -> EPI
Neutral Functional Groups
Hydroxyl or alcohol (primary)
Ketone
Aldehyde
Amide
Nitrate
Nitro
Aromatic (benzene) ring
Urea
Carbonate
Carbamate
Ether
Thioether
Acidic Functional Groups
Carboxyl
Phenol
Imide
Sulfonamide
Basic Functional Groups
Amine (primary)
Amine (tertiary)
Imine
Amidine
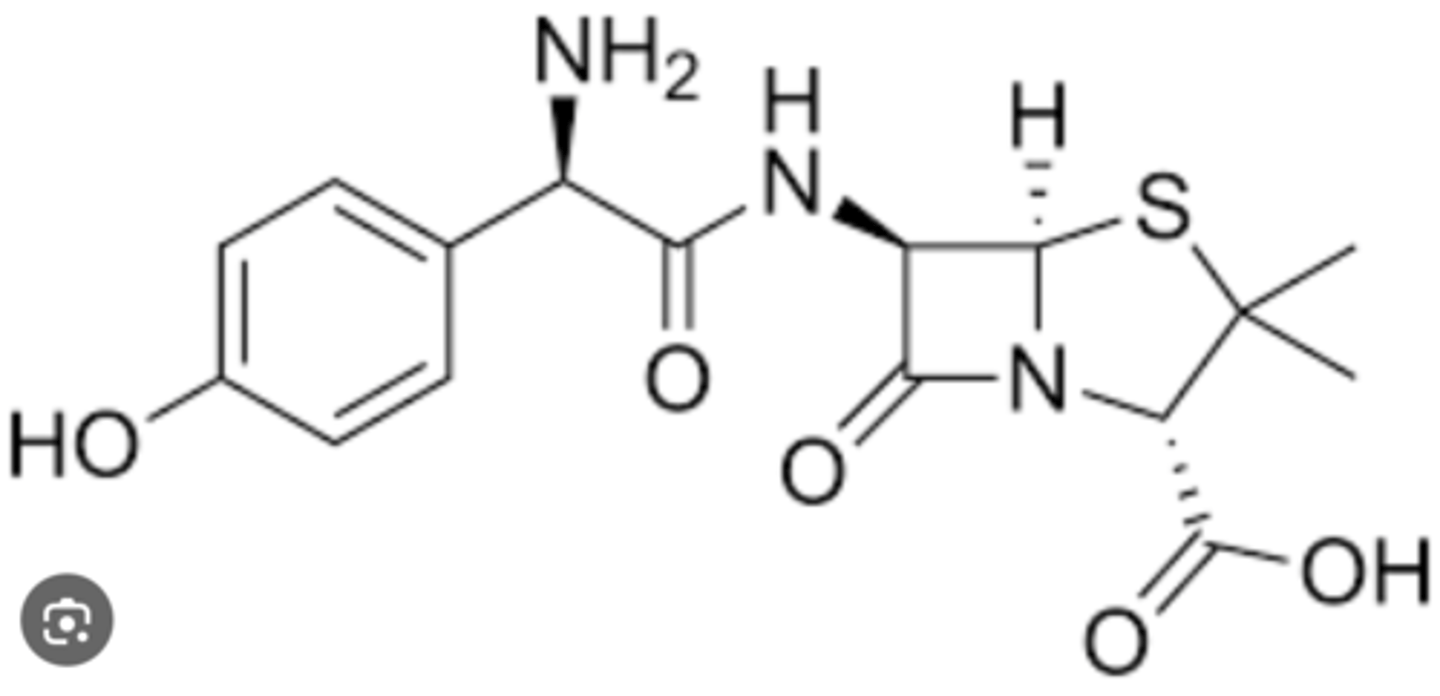
Amoxicillin Drug Structure
Beta-lactam fused to 5-sided ring
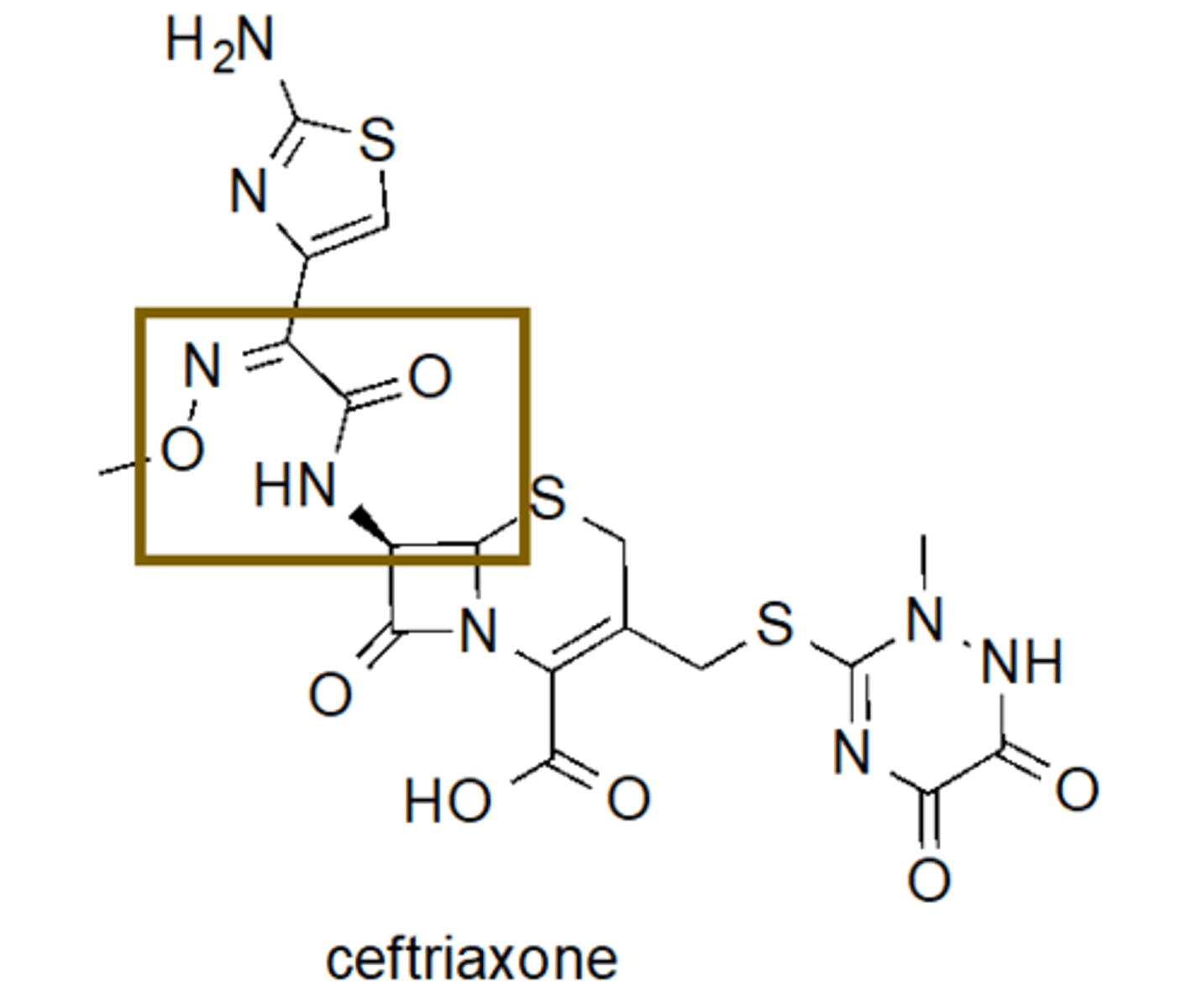
Ceftriaxone Drug Structure
Beta-lactam fused to 6-sided ring
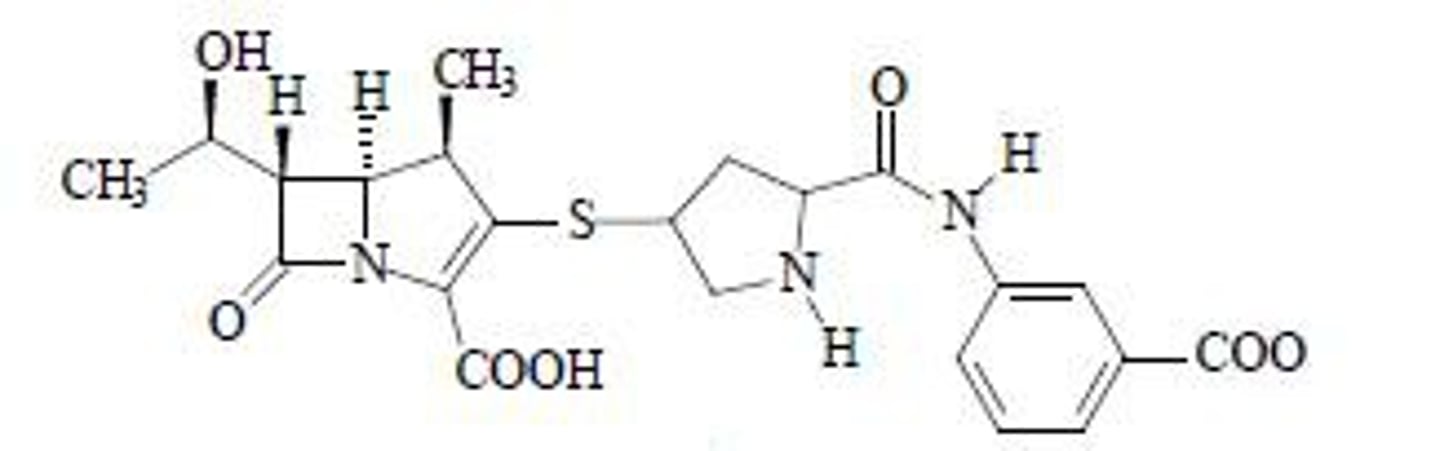
Ertapenem Drug Structure
Beta-lactam fused to 5-sided ring
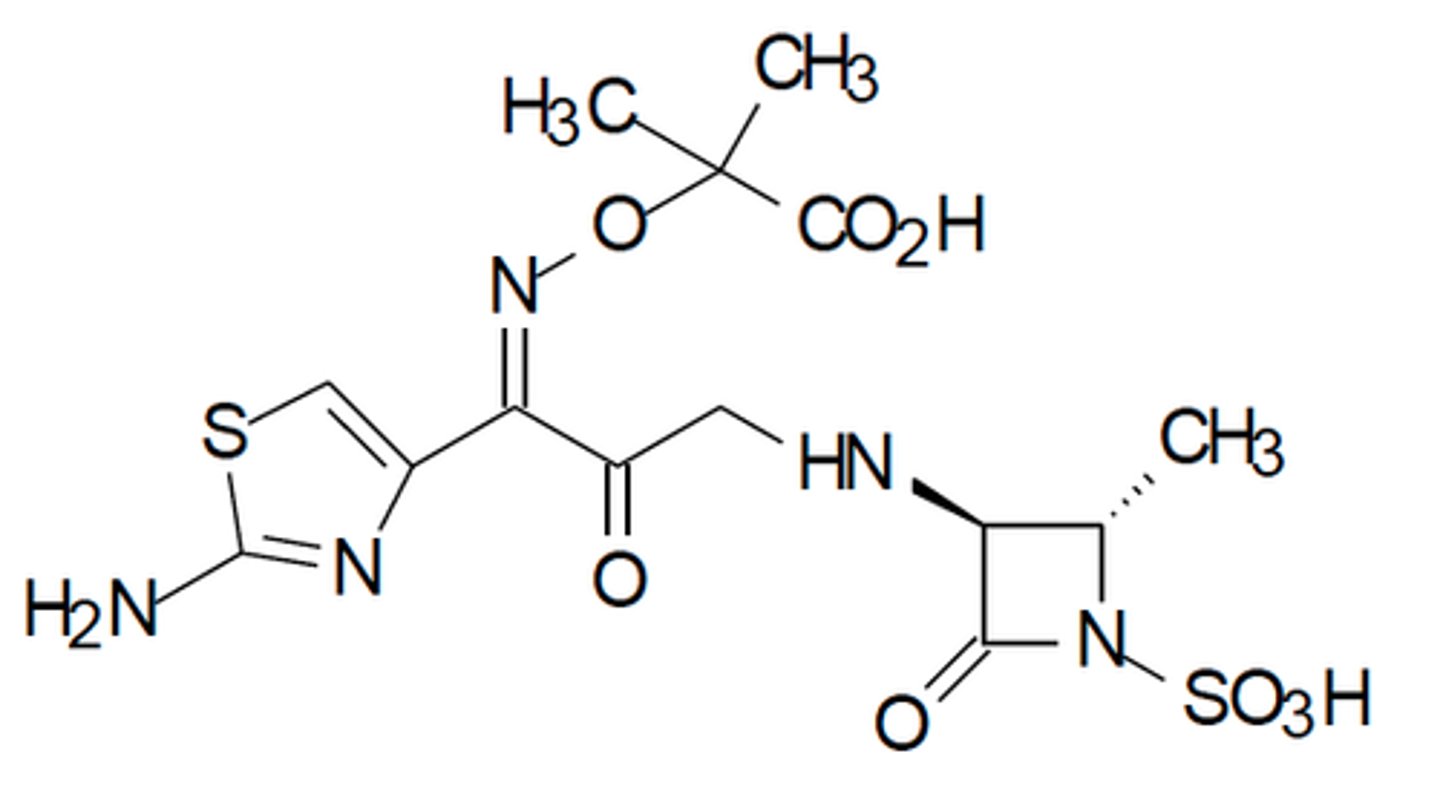
Aztreonam Drug Structure
Beta-lactam ring not fused to another ring
- Monobactam
- Not cross reactive with other abx
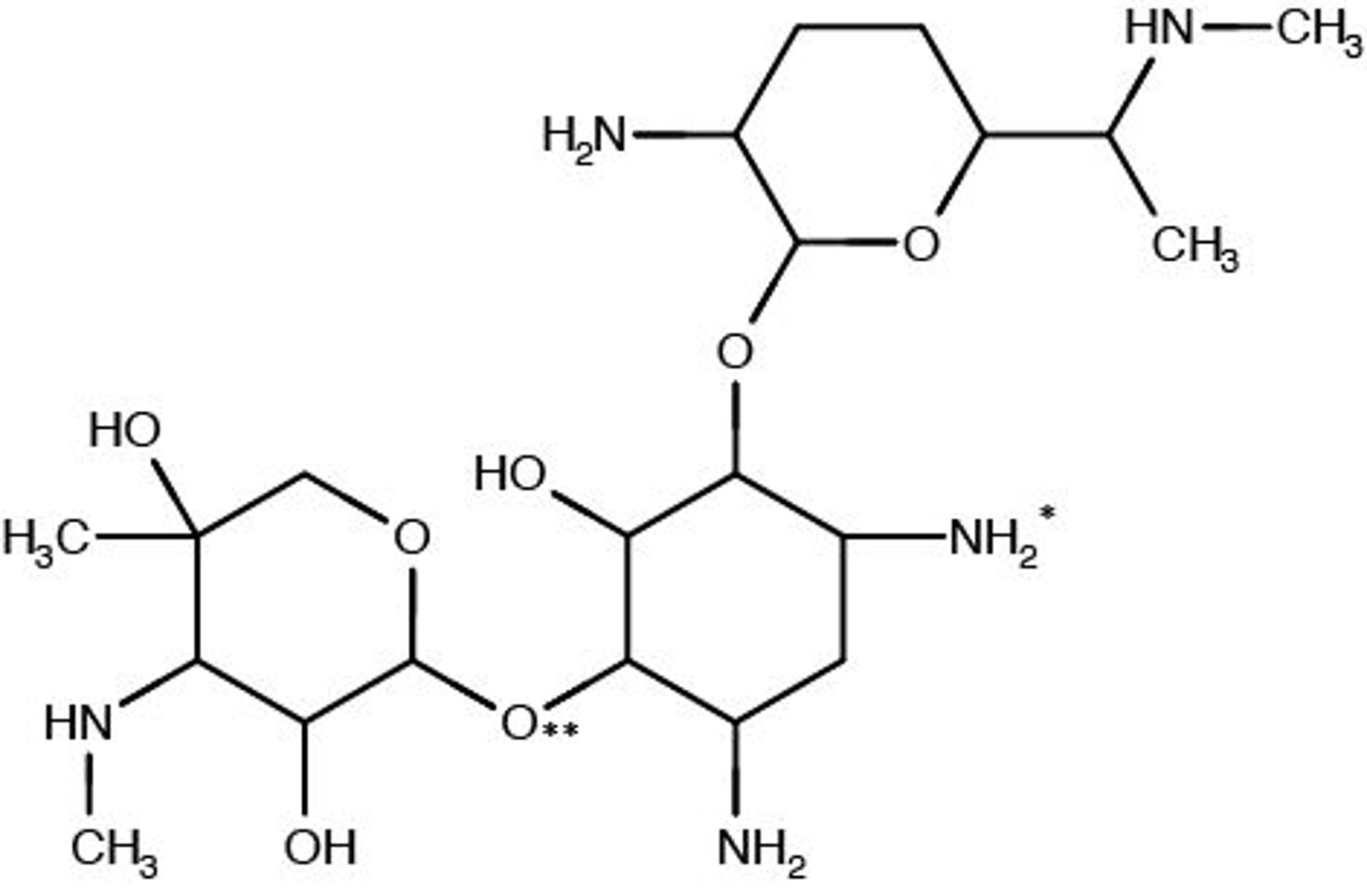
Gentamicin Drug Structure
Amine group (amino) and a sugar (glycoside) group
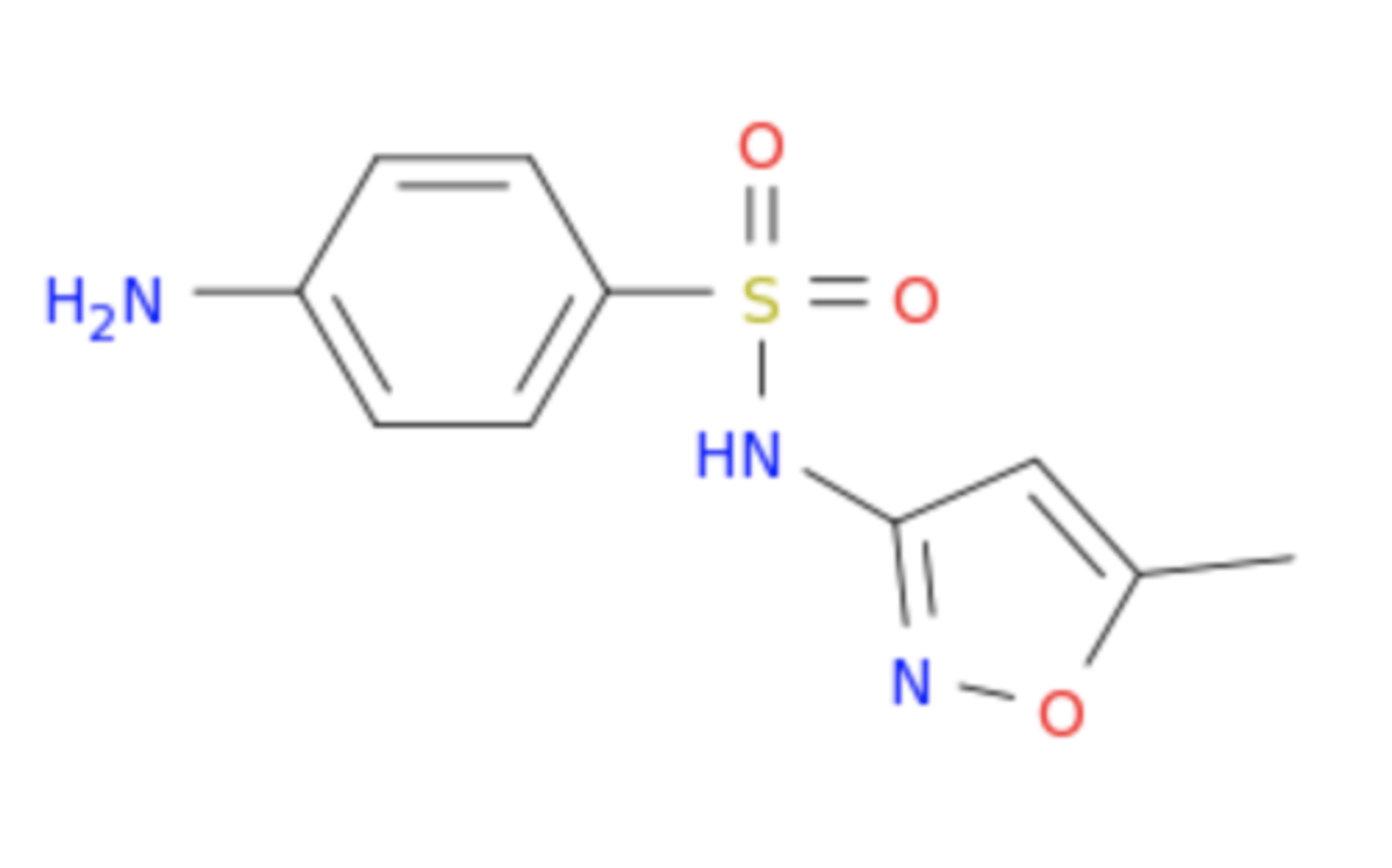
Sulfamethoxazole Drug Structure
Contains a sulfonamide group
- Cross-reactive with celecoxib
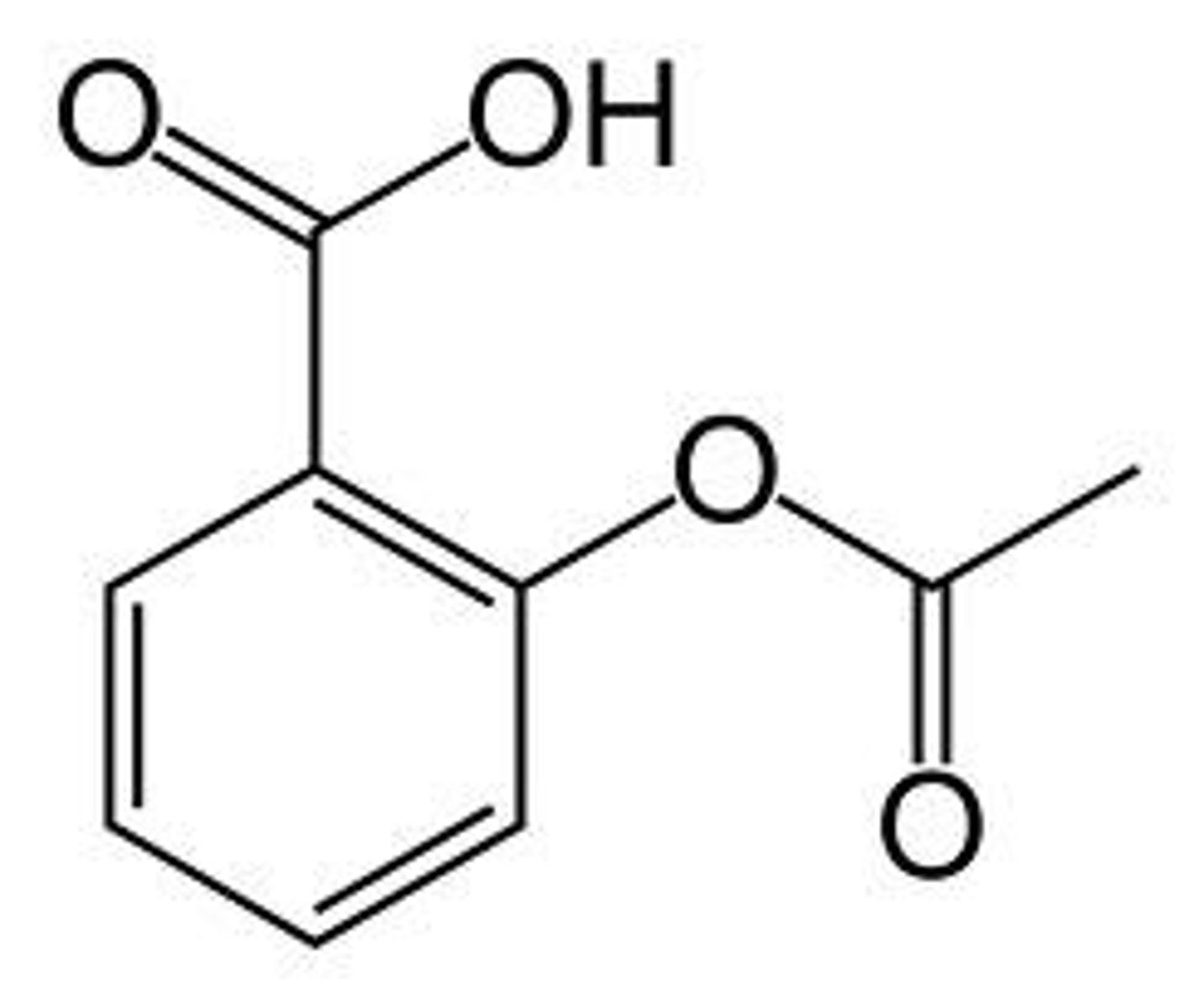
Aspirin Drug Structure
Has an acidic carboxyl group
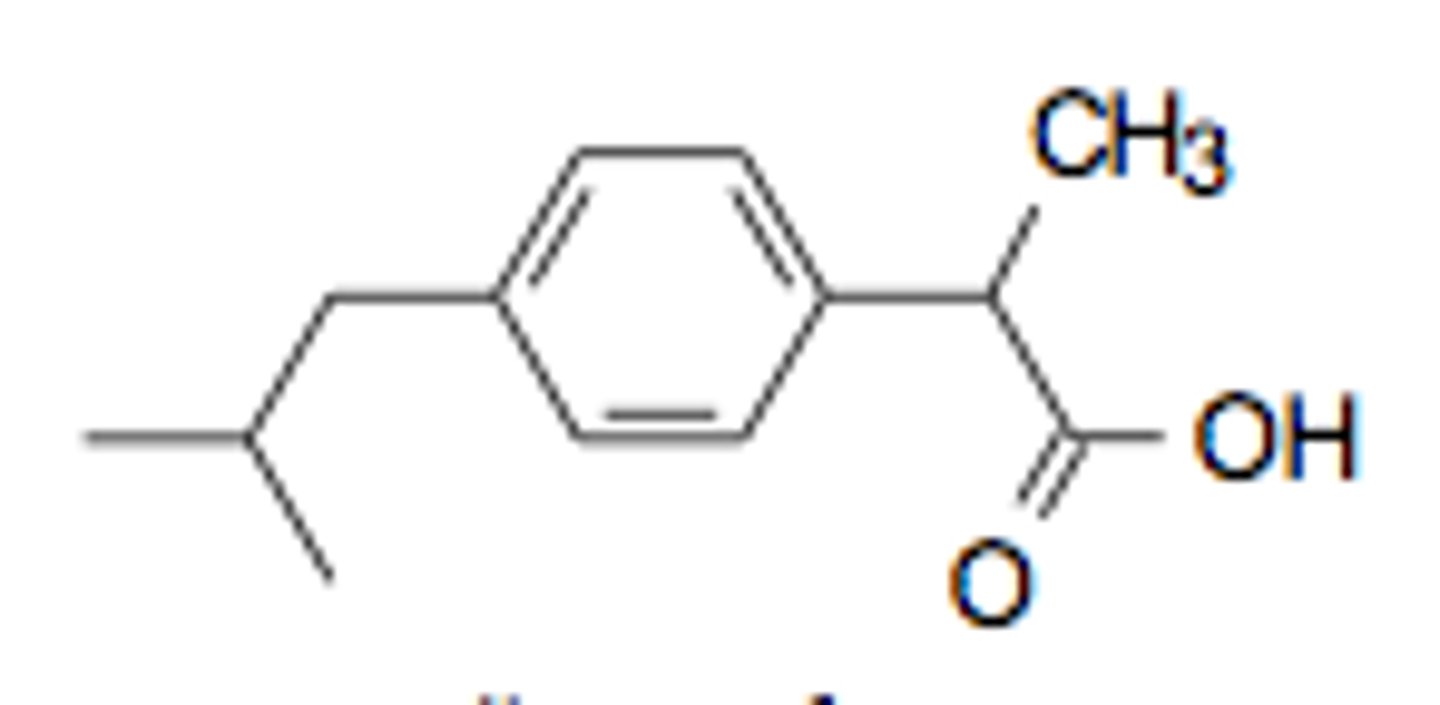
Ibuprofen Drug Structure
Has a carboxyl group
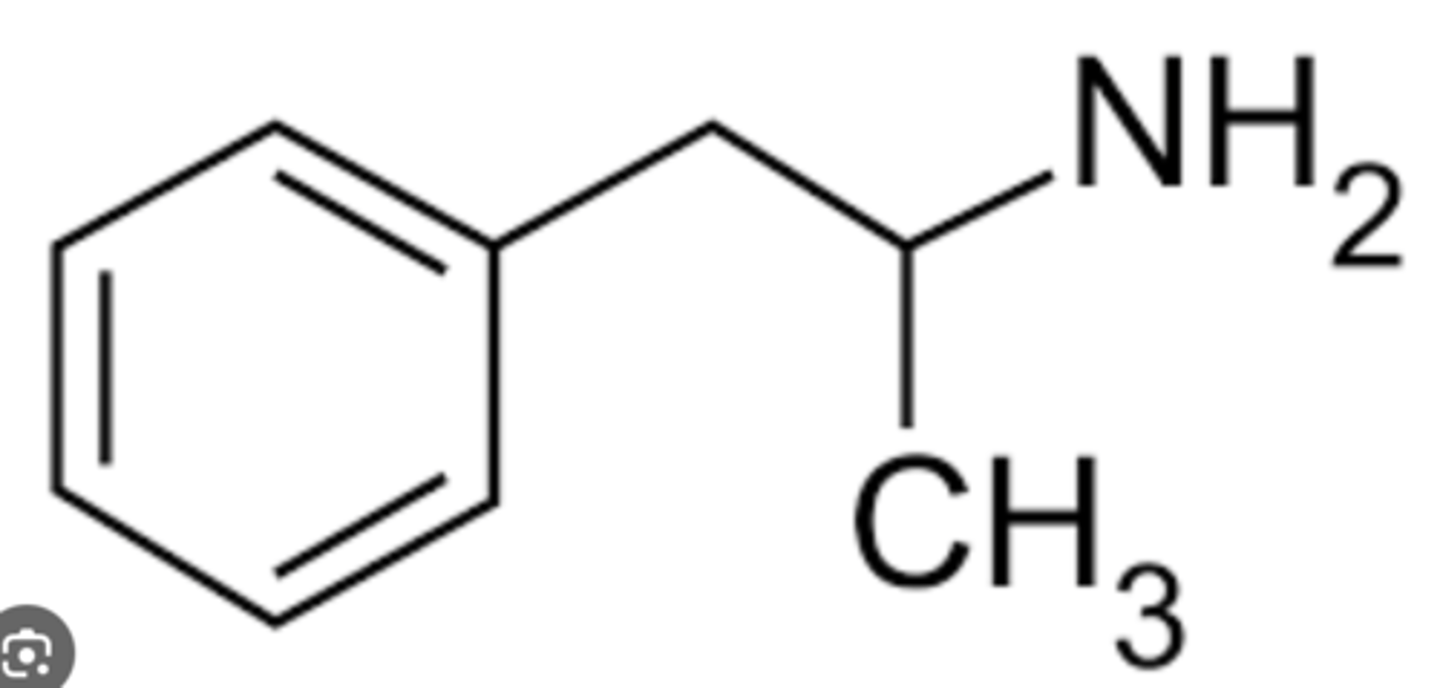
Amphetamine Drug Structure
Contains a primary amine functional group
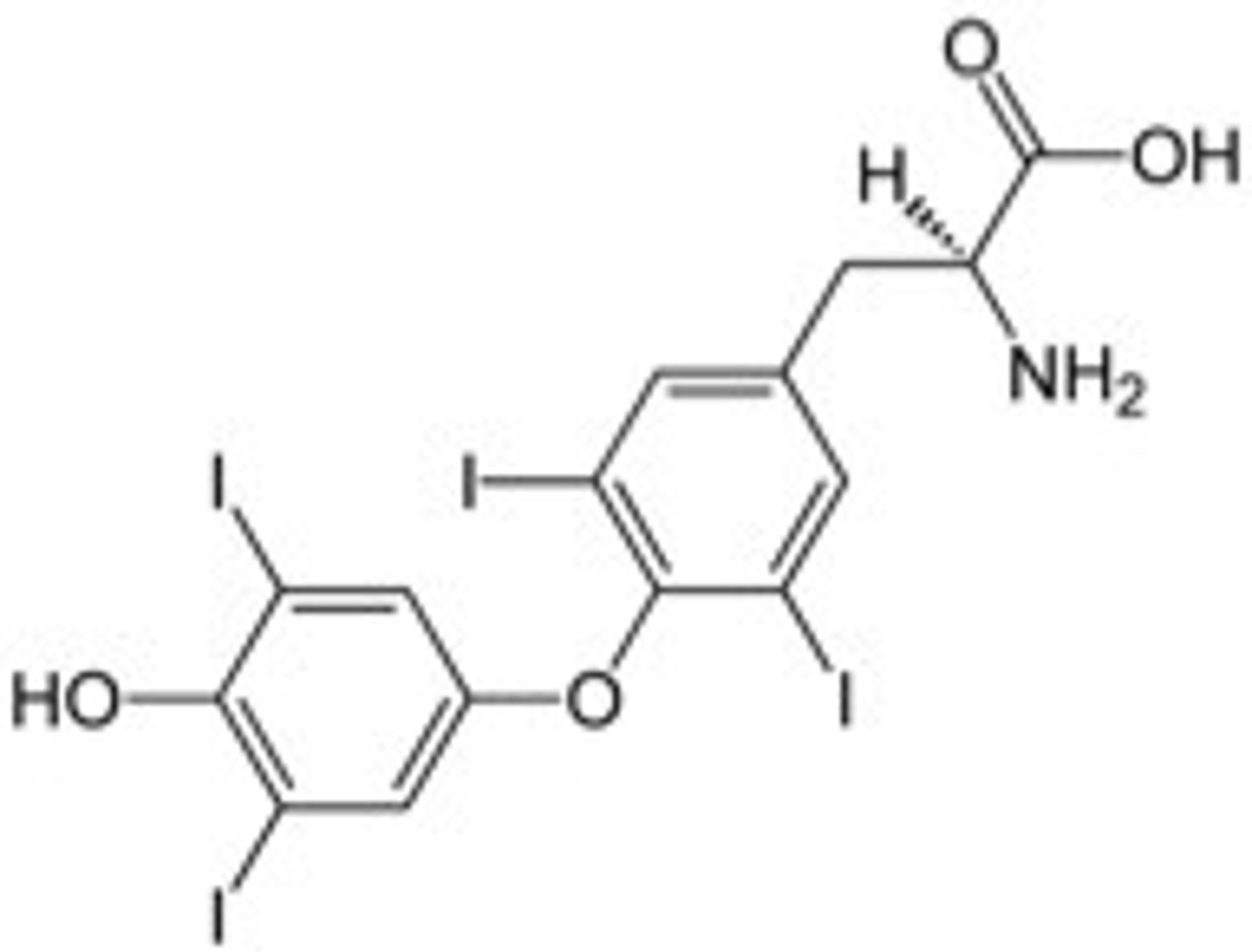
Levothyroxine Drug Structure
Has 4 iodine molecules (T4 thats converted to T3)
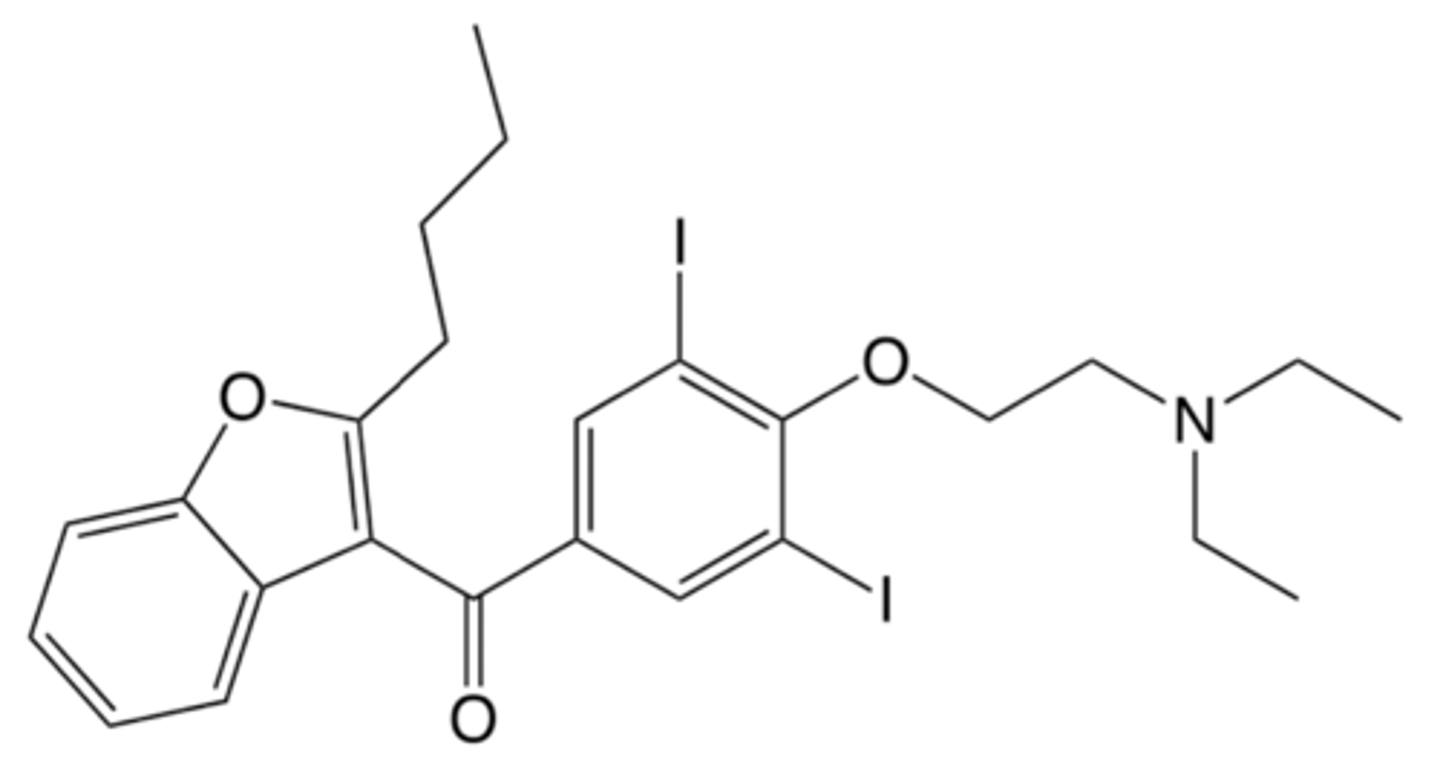
Amiodarone Drug Structure
Has 2 iodine molecules
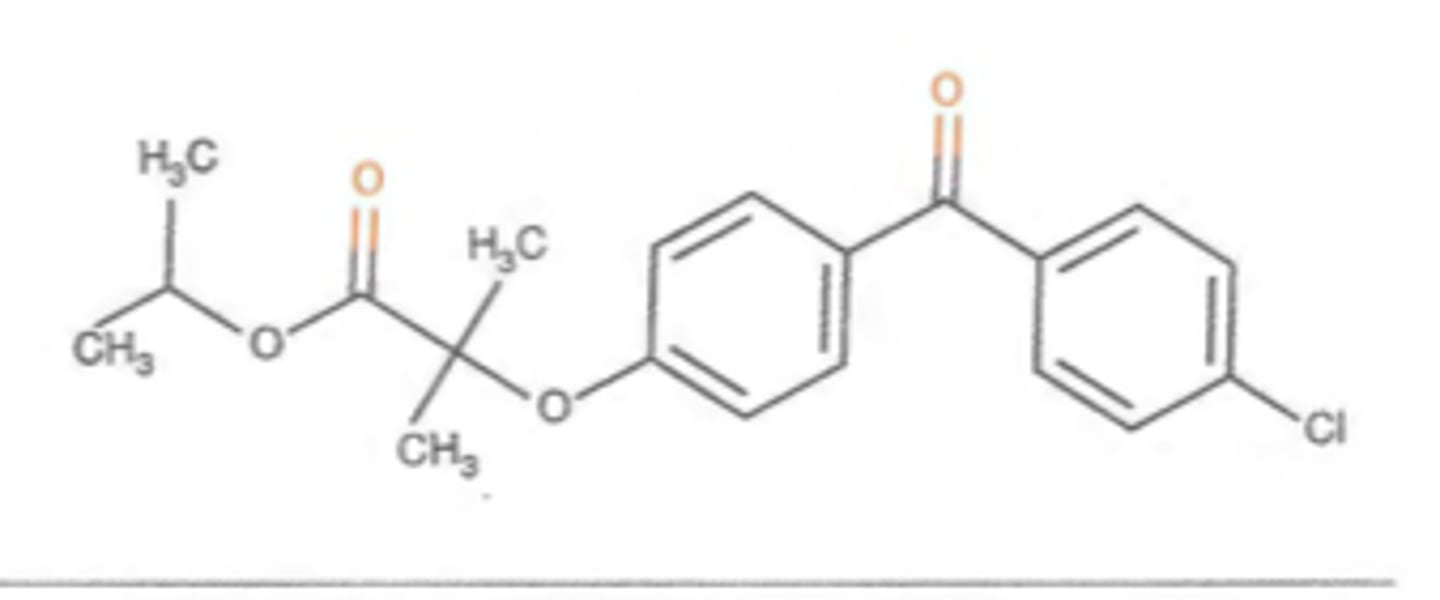
Fenofibrate Drug Structure
Contains ketone groups
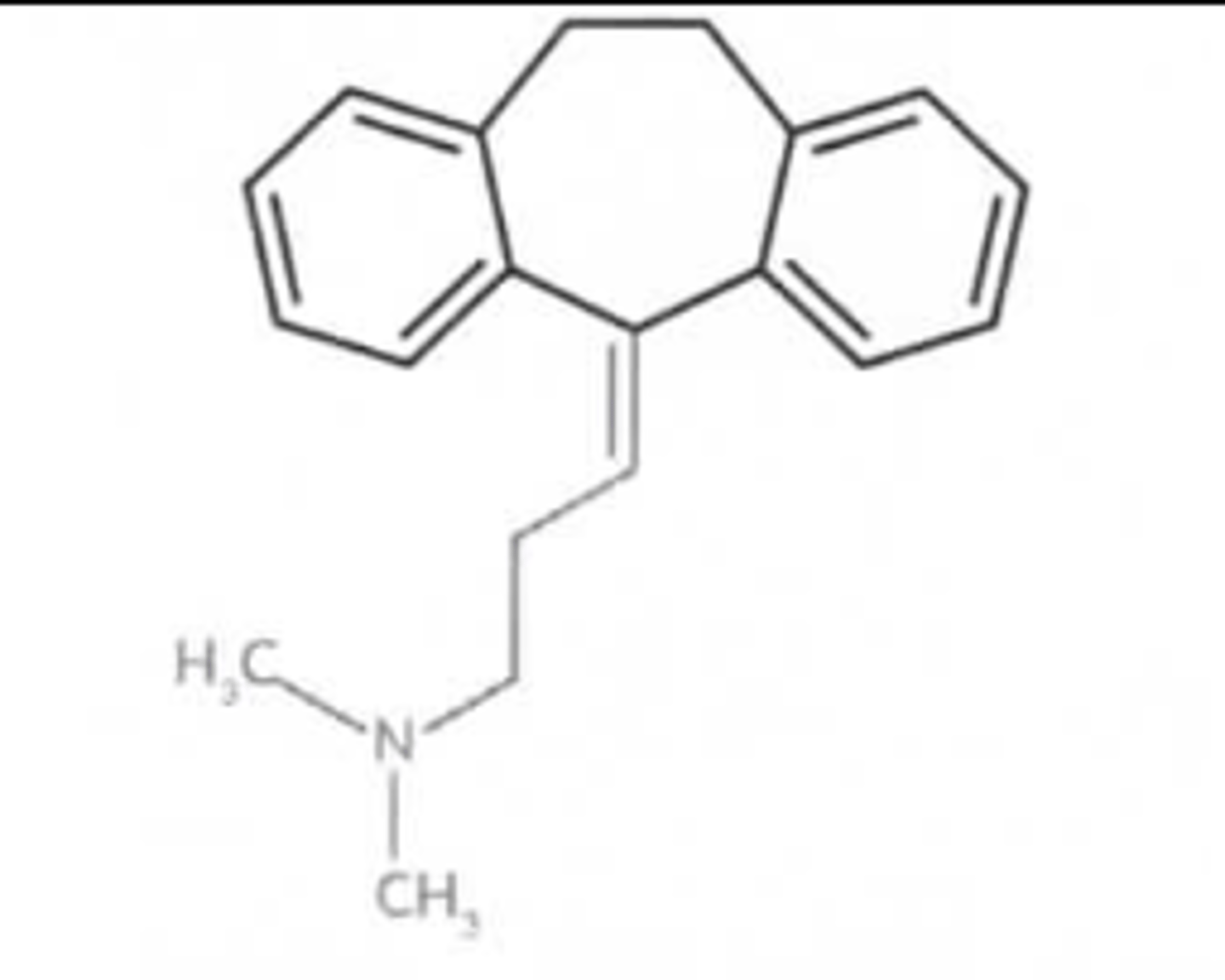
Amitriptyline Drug Structure
Three rings in it
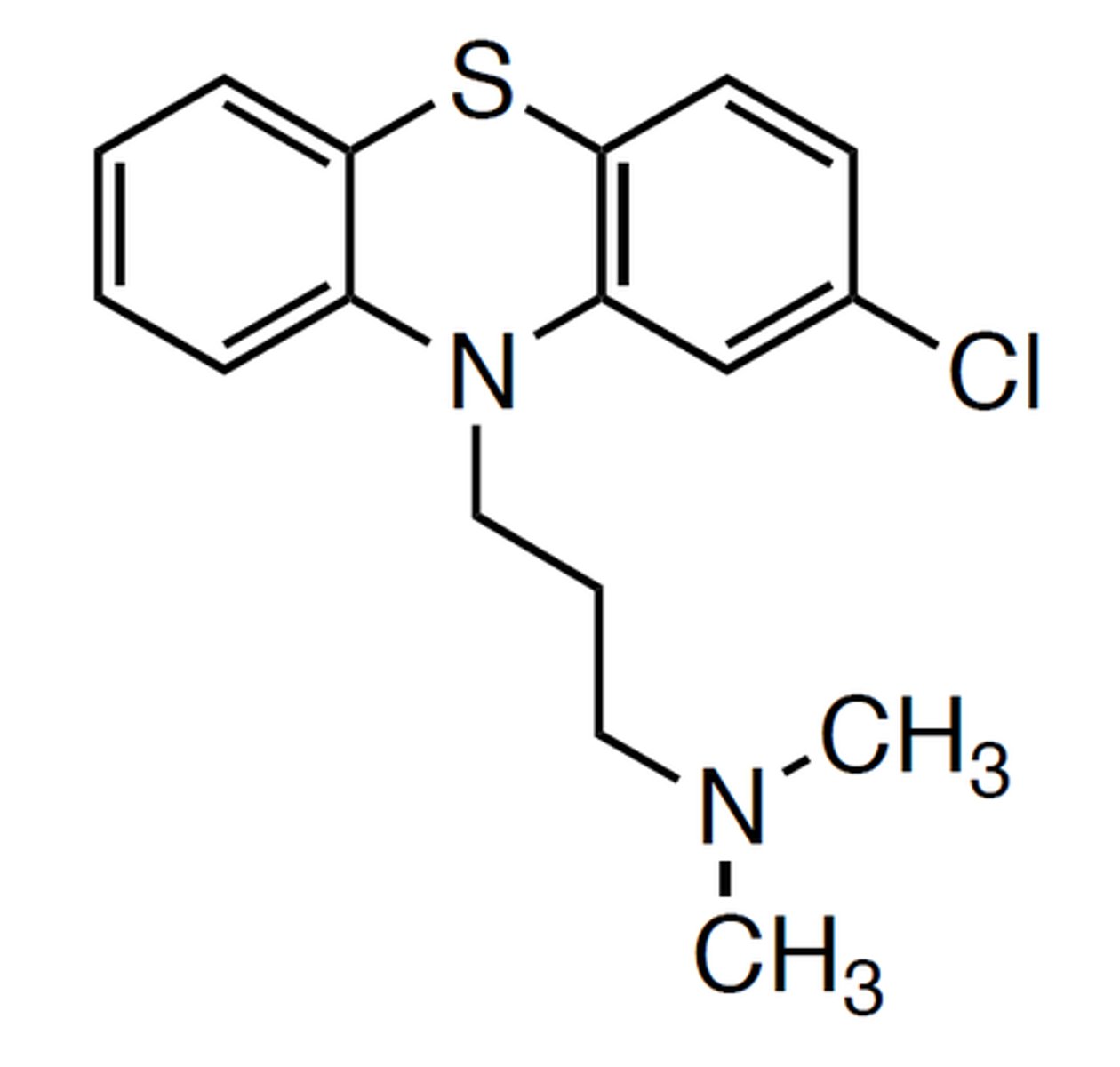
Chlorpromazine Drug Structure
Contains a thioether group
Drug Degradation: common chemical reactions that cause them to become unstable and degrade
Hydrolysis (water causes cleavage of molecular bond)
Oxidation-Reduction (electrons change = color change)
Photolysis (break of covalent bond from light exposure)
Most common functional groups to be oxidized/reduced
Hydroxyl group (OH) next to aromatic ring
Most common functional groups to be hydrolyzed
Ester (carbonyl to OR)
Amide (carbonyl to N)
Beta-Lactam ring
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body; mechanism of action
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion)
What drugs to separate from polyvalent cations (chelating agent)
FQs
Tetracyclines
Levothyroxine
Oral bisphosphonates
Cefixime
Capecitabine (prodrug)
Fluorouracil (active metabolite)
- 5-FU
Clopidogrel (prodrug)
Active metabolite
- CYP2C19 substrate
Codeine (prodrug)
Morphine (active metabolite)
- CYP2D6 substrate
Colistimethate (prodrug)
Colistin (active metabolite)
Cortisone (prodrug)
Cortisol (active metabolite)
Famciclovir (prodrug)
Penciclovir (active metabolite)
Fosphenytoin (prodrug)
Phenytoin (active metabolite)
Isavuconazonium sulfate (prodrug)
Isavuconazole (active metabolite)
Levodopa (prodrug)
Dopamine (active metabolite)
Lisdexamfetamine (prodrug)
Dextroamphetamine (active metabolite)
Prednisone (prodrug)
Prednisolone (active metabolite)
Primidone (prodrug)
Phenobarbital (active metabolite)
Tramadol (prodrug)
Active metabolite
Valacyclovir (prodrug)
Acyclovir (active metabolite)
Valganciclovir (prodrug)
Ganciclovir (active metabolite)
P-gp Substrates
Anticoagulants (apixaban, rivaroxaban)
Cardiovascular drugs (diltiazem, verapamil, digoxin)
Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, tacrolimus)
HCV drugs (sofosbuvir)
Others (colchicine)
P-gp Inducers
Carbamazepine
Phenobarbital
Phenytoin
Rifampin
St. John's Wort
P-gp Inhibitors
Anti-infectives: (clarithromycin, itraconazole, posaconazole)
cardiovascular drugs: (amiodarone, diltiazem, verapamil)
HIV drugs (cobicistat, ritonavir)
HCV drugs (ledipasvir)
Others (cyclosporine)
CYP-2C9 Inducers
Rifampin
St. John's Wort
CYP-2C9 Inhibitors
Amiodarone
Azole antifungals
Metronidazole
SMX/TMP
CYP-3A4 Substrates
Statins: lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin
Opioids: fentanyl, hydrocodone, oxycodone, methadone
Immunosuppressants/Anti-rejection: tacrolimus, cyclosporine, sirolimus
CV: nifedipine, amiodarone, amlodipine, bosentan, diltiazem, verapamil, eplerenone, ivabradine, quinidine, ranolazine, tolvaptan
Anticoagulants: apixaban, rivaroxaban, R-warfarin
HIV: NNRTIs
PDE-5i: avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil
Ethinyl estradiol
CYP-1A2 Substrates
R-warfarin
Theophylline
CYP-2C9 Substrates
S-warfarin
CYP-2C19 Substrates
clopidogrel
CYP-2D6 Substrates
- Analgesics (codeine, hydrocodone, meperidine, methadone, oxycodone, tramadol)
- Antipsychotics/Antidepressants
- Others (carvedilol, DM, flecainide, methamphetamine, metoprolol, propafenone, propranolol, tamoxifen)
If on warfarin and adding on amiodarone?
Decrease warfarin dose 30-50% depending on INR
If on digoxin and adding amiodarone?
Decrease digoxin dose by 50%
What increases digoxin toxicity risk?
Loop diuretics
Low potassium
High calcium
Which statins are metabolized by CYP3A4?
Simvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin (SAL)
- Simvastatin and lovastatin CI with strong CYP3A4i
How does valproic acid affect lamotrigine?
Decreases lamotrigine metabolism and increases levels which can cause SJS/TENS
- use Lamictal starter kit
Increased Serotonergic Toxicity Risk Meds
Antidepressants
MAOi
Opioids
Triptans
St. Johns wort, L-tryptophan
Buspirone
Lithium
Dextromethorphan
Increased Hyperkalemia Risk Meds
RAAS drugs
Potassium-sparing diuretics (amiloride, triamterene)
KCl
Tacrolimus, cyclosporine
SMX/TMP
Canagliflozin
Drospirenone-containing oral contraceptives
Increased QT Prolongation Risk Meds
Antiarrythmics (Class 1a, 1c, III)
Anti-infectives (hydroxychloroquine, azole antifungals, macrolides, quinolones)
Antidepressants (SSRIs, TCAs, mirtazapine, trazodone, venlafaxine)
1st and 2nd Gen Antipsychotics
Antiemetics (5-HT3 antagonists, droperidol, metoclopramide, promethazine)
Oncology (leuprolide, TKIs, arsenic trioxide)
Others (methadone, hydroxyzine, cilostazol, donepezil, loperamide, ranolazine, solifenacin)
Which SSRI is the safest for patients with CVD?
Sertraline
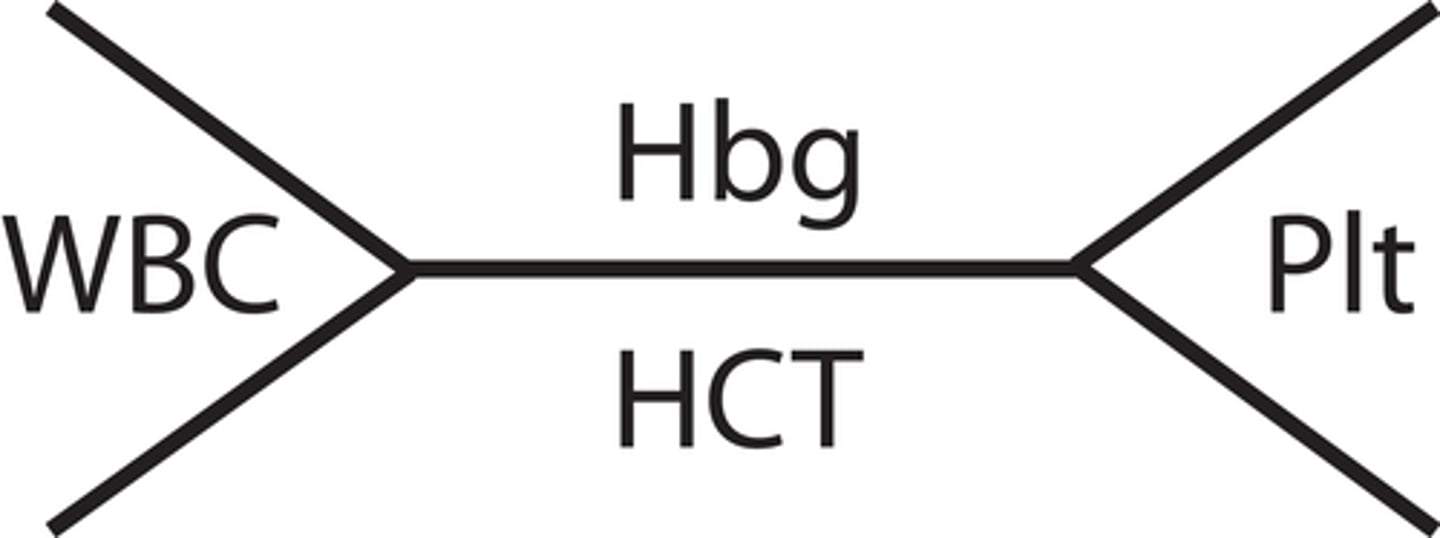
CBC (complete blood count)
a set of tests that include all WBC, RBC and platelet measurements.
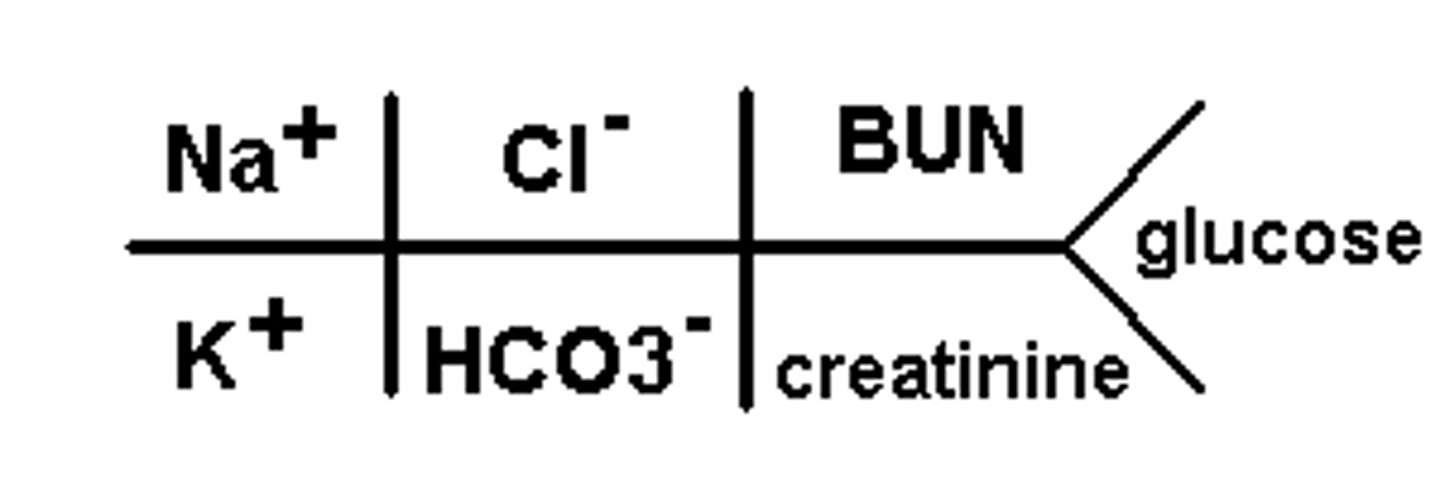
BMP (basic metabolic panel)
A group of 7-8 tests
Drug causes of agranulocytosis (decreased neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils)
Clozapine
PTU
Methimazole
Carbamazepine
SMX/TMP
Isoniazid
Procainamide
Causes of increased calcium
Vitamin D
Thiazides
Causes of decreased calcium
Long-term heparin
Loop diuretics
Bisphosphonates
Cinacalcet
Causes of decreased magnesium
PPIs
Diuretics
Amphotericin B
Causes of increased phosphate
CKD
Causes of increased potassium
RAAS drugs
Potassium-sparing diuretics (amiloride, triamterene)
KCl
Tacrolimus, cyclosporine
SMX/TMP
Canagliflozin
Drospirenone-containing oral contraceptives
Causes of decreased potassium
Beta-2 agonists
Diuretics
Insulin
Sodium Polystyrene Sulfate (SPS)
Causes of increased sodium
Hypertonic saline
Tolvaptan
Causes of decreased sodium
Carbamazepine
Oxcarbazepine
SSRIs
Diuretics
Desmopressin
Causes of decreased bicarbonate
Topiramate
Causes of increased BUN
Renal impairment and dehydration
Causes of increased WBCs
Systemic steroids
Causes of decreased WBCs
Clozapine
Chemotherapy
Carbamazepine
Immunosuppressants
Causes of increased eosinophils
Asthma, inflammation, parasitic infection
Causes of increased basophils
Hypersensitivity reaction
Causes of increased lymphocytes
Viral infections, lymphoma
Causes of decreased lymphocytes
Bone marrow suppression, HIV, systemic steroids
RBC average life-span
120 days
Causes of increased RBCs and Hgb
ESAs
Causes of decreased RBCs
Chemotherapy
Deficiency anemia (B12, folate)
Hemolytic anemia
Sickle cell anemia
Causes of increased MCV
B12 or folate deficiency
Causes of decreased MCV
Iron deficiency
Causes of decreased folic acid (folate)
Phenytoin/fosphenytoin
Phenobarbital/primidone
Methotrexate
Causes of decreased vitamin B12
PPIs
Metformin
Causes of decreased reticulocyte count
Untreated anemia
Bone marrow suppression
Coombs Test, Direct
Used to diagnose immune-mediated hemolytic anemia
Drug causes of immune-mediated hemolytic anemia
PCNs + cephalosporins
Isoniazid
Levodopa
Methyldopa
Quinidine
Quinine
Rifampin
Sulfonamides
G6PD Test
Used to determine if hemolytic anemia is due to G6PD deficiency
Food/Drugs that trigger RBC destruction with G6PD deficiency
Fava Beans
Dapsone
Methylene Blue
Nitrofurantoin
Pegloticase
Primaquine
Rasburicase
Quinidine
Quinine
Sulfonamides
What does Anti-Xa monitor?
LMWH (therapeutic dose - get peak level 4h after)
UFH (get level 6h after IV infusion starts)
What does PT/INR monitor?
Warfarin
What can falsely and actually increase PT/INR?
Falsely: daptomycin, oritavancin, telavancin
Actually: liver disease
What does aPTT or PTT monitor?
UFH (get level 6h after IV infusion starts)
What can falsely increase aPTT/PTT?
Oritavancin, televancin
Platelet lifespan and what can cause decreased platelets?
Average 7-10 days
Decreased by:
Heparin + LMWH
Fondaparinux
Linezolid
Valproic Acid
What can cause decreased albumin?
Cirrhosis
Malnutrition
What drugs are highly protein bound?
Warfarin
Calcium
Phenytoin