PHARYNX & TONSILS
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
how long is the pharynx
12-14 cm
describe the pharynx using 2 words
musculomembranous tube
which tracts does the pharynx connect
the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract share a common path through the pharynx
course of the pharynx
the pharynx extends between the nasal cavity and the entrances to the larynx and in continuation with the osesophagus
what type of tissue is the pharynx partially surrounded by
the pharynx is partially surrounded by muscle
where is the pharynx in relation to the larynx
the pharynx is posterosuperior to the larynx
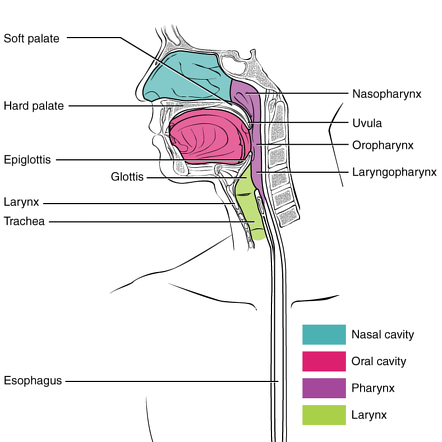
what are the divisions of the pharynx
regions of the pharynx
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
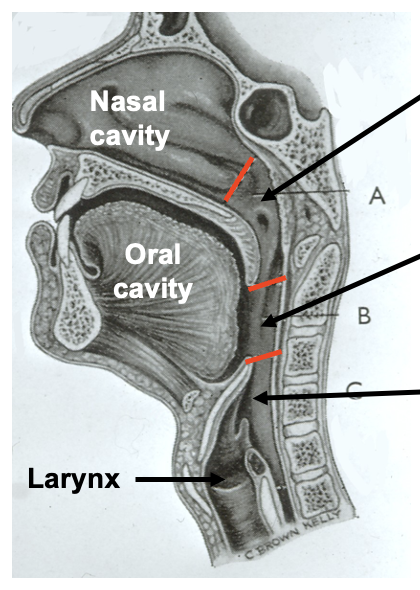
important point about the divisions of the pharynx
divisions of the pharynx are only descriptive
not demarcated by physical borders, only anatomical landmarks
nasopharynx: borders
nasopharynx
extends from behind the nose/ nasal cavities
to the soft palate
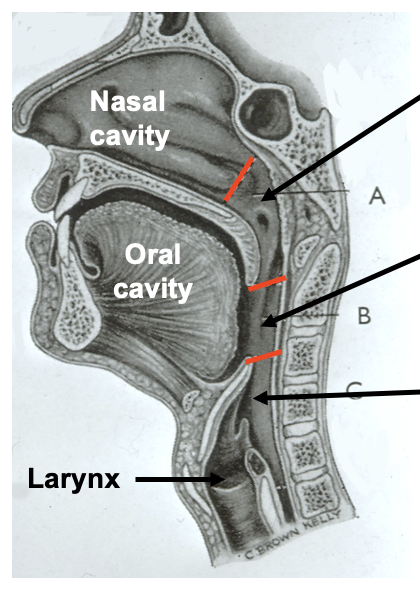
nasopharynx: which tract is it a part of
the nasopharynx is a functional part of the respiratory tract
nasopharynx: what structures does it contain
pharyngeal tonsils/ adenoids
opening of auditory tubes (Eustachian)
the tubal tonsils
oropharynx: borders
oropharynx
from below the soft palate
to the tip of the epiglottis
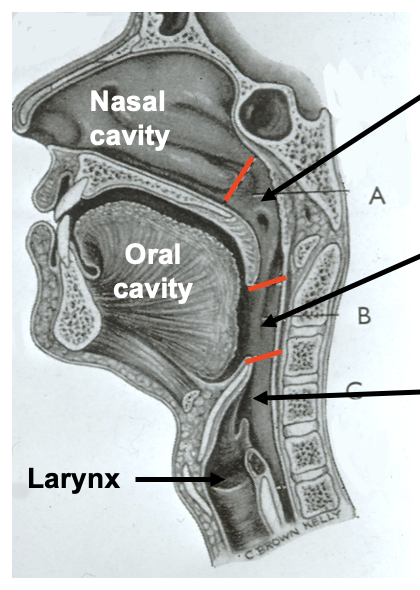
oropharynx: how does it open into the mouth
via the oropharyngeal isthmus/ faucial isthmus
demarcated by the palatoglossal arch - anterior border of oropharynx
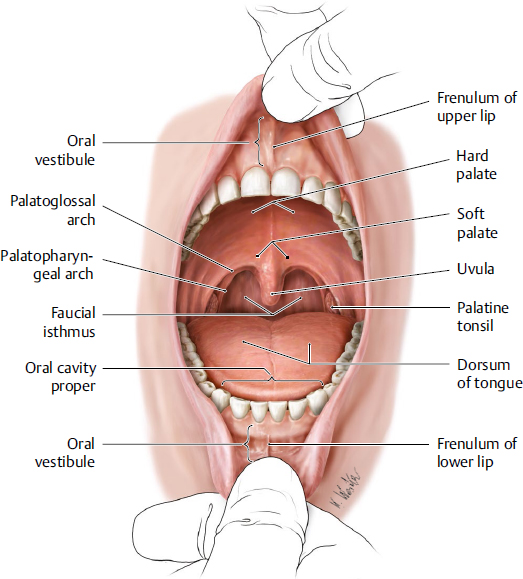
oropharynx: what does its lateral wall consist of
palatopharyngeal arch
palatine tonsil
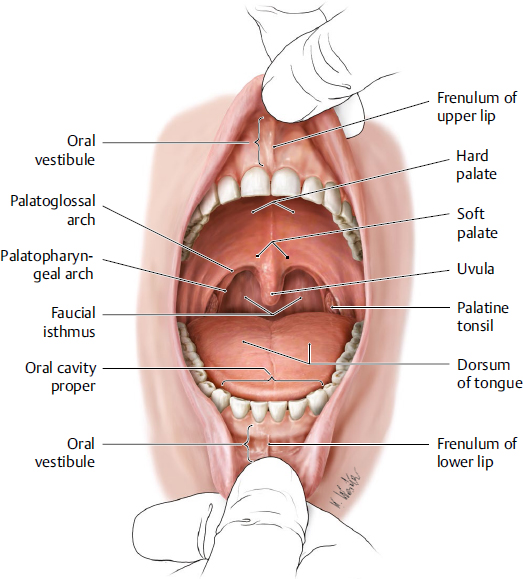
oropharynx: which vertebrae is it level with posteriorly
body of the second cervical vertebrae
upper part of the third cervical vertebrae
laryngopharynx: borders
laryngopharynx
from the tip of the epiglottis
to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage
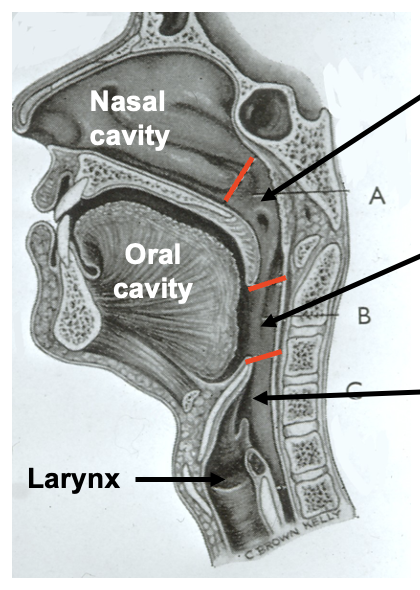
laryngopharynx: at which vertebrae is the cricoid cartilage level with
the cricoid cartilage lies at the level of C6
laryngopharynx: what structure is anterior to it
the entire length of the larynx
laryngopharynx: what structure is it continuous with
the laryngopharynx is continuous with the oesophagus
laryngopharynx: laryngeal inlet
laryngopharynx: at which vertebrae is it level with posteriorly
the laryngopharynx extends posteriorly from the third to the sixth cervical vertebrae
AT REST
laryngopharynx: what occurs during swallowing
the laryngopharynx is elevated considerably by the hyoid elevators i.e. suprahyoid muscles during swallowing
what is another term for swallowing
deglutition
name the pharyngeal constrictor muscles
three pairs of pharyngeal constrictor muscles
superior constrictor
middle constrictor
inferior constrictor incl. cricopharyngeus (part of inferior constrictor)
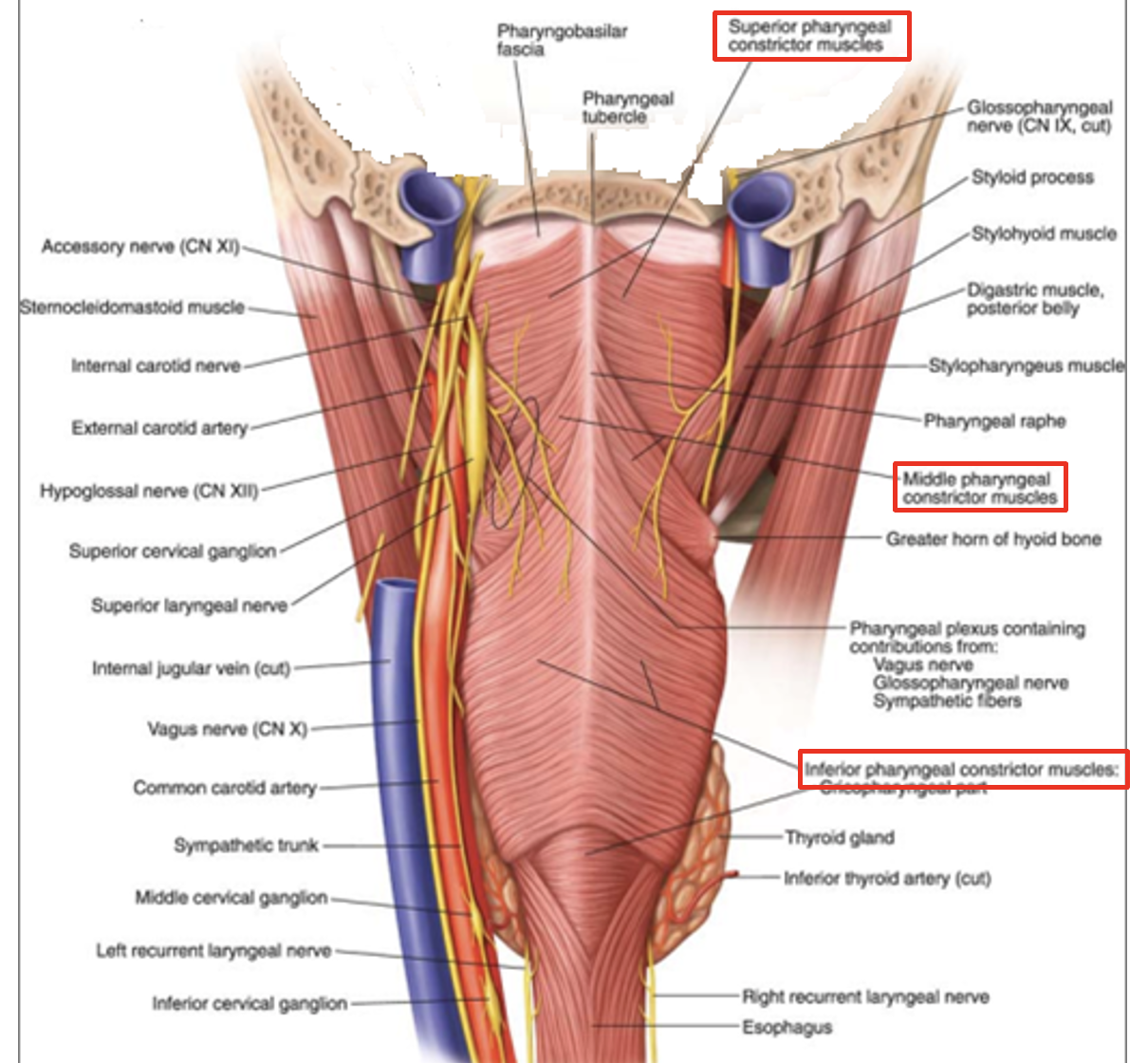
function of pharyngeal constrictor muscles
sequentially constrict the pharynx to propel the bolus of food down towards the oesophagus
pharyngeal constrictor muscles: structure
pharyngeal constrictor muscles are circular but not fully closed anteriorly
posteriorly the muscles are joined at the midline via the fibrous pharyngeal raphe
name the pharyngeal longitudinal muscles
three pairs of pharyngeal longitudinal muscles
stylopharyngeus
salpingopharyngeus
palatopharyngeus
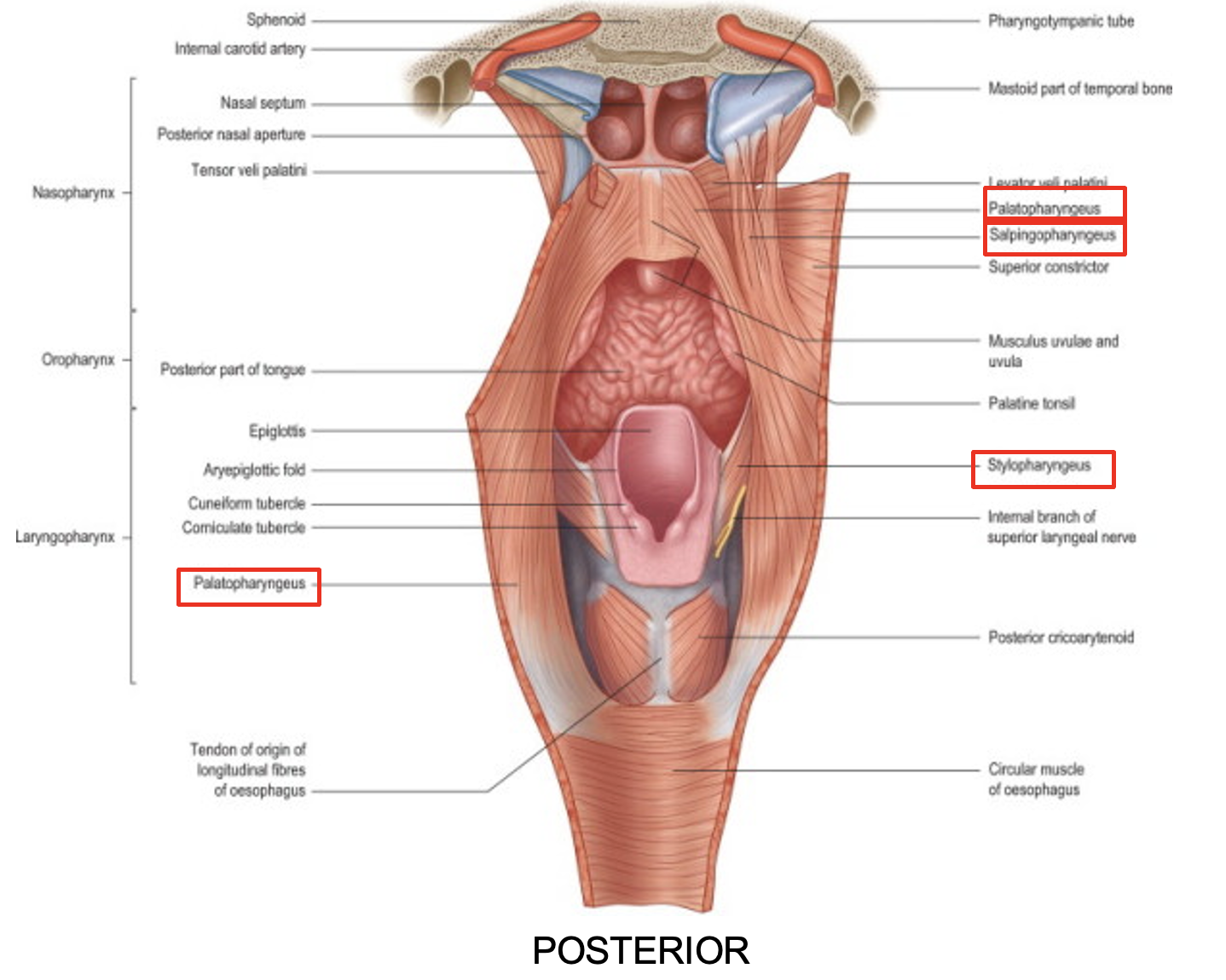
function of the pharyngeal longitudinal muscles
elevate the larynx
shorten and widen the pharynx during swallowing
which structure is the pharynx innervated by
the pharynx is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus (branches of CN IX and CN X)
where is the pharyngeal plexus located
the pharyngeal plexus of fine nerves spread under the lining (sensory innervation) and muscles (motor innervation) of the pharynx
which nerves form the pharyngeal plexus
pharyngeal branches of the glossopharyngeal nerves (CN IX)
pharyngeal branches of the vagus nerves (CN X)
branches from the external laryngeal nerve (branch of the superior laryngeal nerve which is a branch of the vagus)
sympathetic fibres from the superior cervical ganglion
pharyngeal sensory innervation: which nerve supplies sensory innervation to the pharynx
the pharynx receives sensory innervation from the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
pharyngeal sensory innervation: the maxillary nerve
the maxillary nerve (CN V2)
supplies sensory innervation to the anterior and superior aspect of the nasopharynx
pharyngeal sensory innervation: the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve
the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (CN X)
supplies sensory innervation to the inferior aspect of the laryngopharynx (surrounding the beginning of the larynx)
pharyngeal motor innervation: which nerve innervates the pharyngeal muscles
all of the muscles of the pharynx are innervated by the vagus nerve (CN X)
pharyngeal motor innervation: which pharyngeal muscle is the exception to being innervated by the vagus nerve
the stylopharyngeus muscle (longitudinal) receives motor innervation from the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
clinical applications: general consequence of damage to pharyngeal innervation
damage to the nerve supply of the pharynx causes swallowing problems i.e. dysphagia
clinical applications: consequences of damage to glossopharyngeal nerve
damage to glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) - SENSORY SUPPLY
difficulty initiating swallowing
clinical applications: consequences of damage to vagus nerve
damage to vagus nerve (CN X) - MOTOR SUPPLY
difficulty in smooth transit of material from mouth to oesophagus
which structure contains the auditory/ Eustachian tube
the auditory/ Eustachian tube opens into the nasopharynx
which structures do the auditory/ Eustachian tube connect
the auditory/ Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx
functions of the auditory/ Eustachian tube
the auditory/ Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx to:
equalise pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane
drain fluid from the middle ear
tonsils: describe their structure
tonsils structure
accumulation of lymphoid tissue (lymphocytes)
tonsils: describe their location
tonsils location
tonsils lie under the mucosa lining the pharynx
tonsils: function of the lymphoid tissue
lymphoid tissue function
protective to gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tracts
lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to bacteria and their toxins
tonsils: what physical changes occur during infection
during infection (viral/ bacterial) the tonsils enlarge
tonsils: state the groups of tonsillar tissue
4 groups of tonsillar tissue
palatine tonsils - paired
pharyngeal tonsils/ adenoids - unpaired
lingual tonsils - paired
tubal tonsils - paired
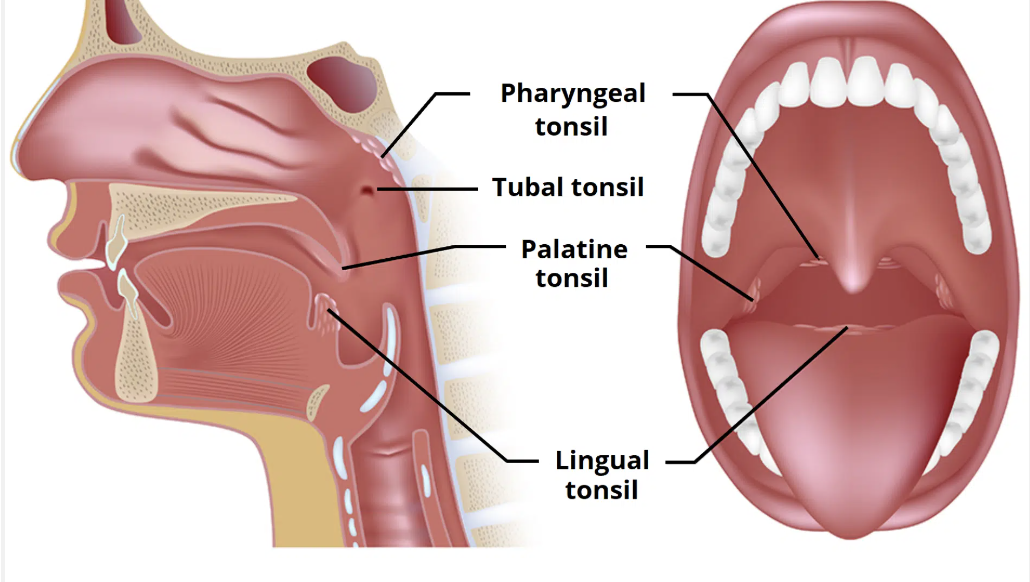
tonsils: palatine tonsils location
palatine tonsils location
between the palatoglossal (anterior) and palatopharyngeal (posterior) arches
oropharynx
tonsils: pharyngeal tonsils/ adenoids location
pharyngeal tonsils/ adenoids location
the posterior wall of the nasopharynx
tonsils: lingual tonsils location
lingual tonsils location
underneath the mucosa of the posterior 1/3 of tongue
tonsils: tubal tonsils location
tubal tonsils location
around the entrance to the auditory/ Eustachian tube
MAY OR MAY NOT BE PRESENT
tonsils: which two types are variable in size
pharyngeal tonsils/ adenoids
tubal tonsils
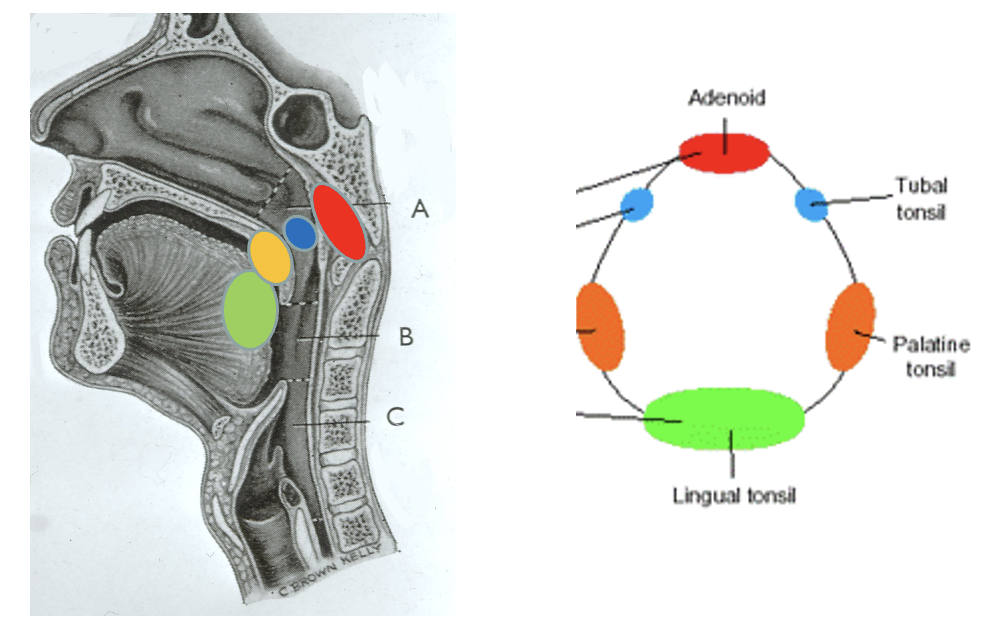
what is this diagram showing
Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring
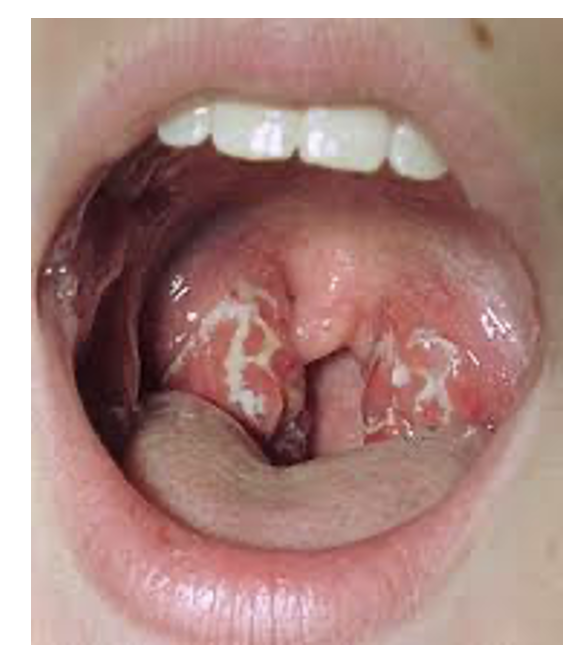
what does this image show
palatine tonsil infection
bacterial infection
very enlarged
cream coloured streaks on top is pus
outline chronic tonsillar enlargement
chronic tonsillar enlargement
interferes with oral and nasal function (difficulty in articulation)
affects children especially
tonsils in children are larger than adult tonsils so if enlarged it can cause considerable blockage
outline pharyngeal tonsil/ adenoid enlargement
pharyngeal tonsils/ adenoids enlargement
interferes with soft palate elevation
can cause sinusitis
can cause auditory tube dysfunction » middle ear infections
can cause sleep apnea
patients experience open mouth breathing
hyponasality - distorted and congested sounding speech
outline palatine tonsil enlargement
palatine tonsil enlargement
interferes with soft palate elevation
hypernasality - nasally sounding speech
common consequences of pharyngeal/ adenoid and tubal tonsillar enlargement
pharyngeal/ adenoid and tubal tonsillar enlargement
prevent auditory tube opening » middle ear infections/ otitis media/ glue ear
outline tonsillectomy
tonsillectomy
surgical procedure to completely remove the (palatine) tonsils - can sometimes be lingual
decreasing in frequency
which conditions are tonsillectomies used for
chronic tonsillitis and complications
sleep apnea