Module 12
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:44 AM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
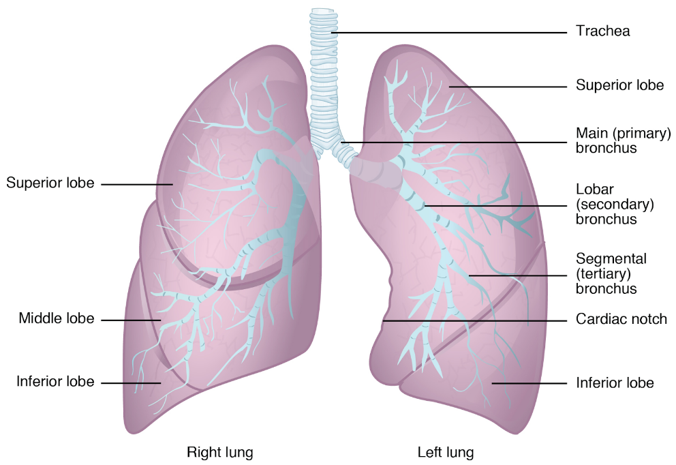
respiratory system function
* supply body tissues with oxygen\\
* dispose of CO2
* dispose of CO2
2
New cards
respiration includes…
* pulmonary ventilation
* gas exchange
* gas exchange
3
New cards
alveoli
* saclike dilation
* site of gas exchange with the blood
* big surface area in contact with capillaries for quick diffusion
* site of gas exchange with the blood
* big surface area in contact with capillaries for quick diffusion
4
New cards
elasticity
tendency of a structure to recoil to its initial dimensions after being distended
5
New cards
acidosis
increase in H+ concentration of the blood that lowers pH
6
New cards
type 1 alveolar cell
forms continuous layer lining the air-facing surface of the pulmonary alveoli
7
New cards
hypoventilation
plasma concentration of CO2 is abnormally increased, inadequate pulmonary ventilation
8
New cards
boyle’s law
pressure of given quantity of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume
9
New cards
alkalosis
decrease in H+ concentration of blood that raises pH
10
New cards
partial pressure
pressure of a particular gas in a mixture
11
New cards
transpulmonary pressure
pressure difference keeping the lungs against the chest wall
12
New cards
diaphragm
primary muscle of ventilation
13
New cards
lung compliance
change in lung volume per change in transpulmonary pressure
14
New cards
chemoreceptor
receptor sensitive to chemical changes such as pH, O2, CO2
15
New cards
deoxyhemoglobin
produced when oxyhemoglobin releases oxygen
16
New cards
ventilation
exchange of air between atmosphere and alveoli
17
New cards
oxyhemoglobin
oxygen bound on hemoglobin
18
New cards
hyperventiliation
high rate and depth of breathing resulting in a decrease in blood CO2 concentration below normal
19
New cards
intrapleural space
potential space between the visceral and parietal linings
20
New cards
surfactant
reduces surface tension between fluid and alveolar surface, increases lung compliance
21
New cards
intrapulmonary space
space within air sacs and airways
22
New cards
type 2 alveolar cell
pulmonary cells that produce surfactant
23
New cards
pulmonary ventilation
exchange of air between atmosphere and alveoli
24
New cards
components of gas exchange
* external respiration
* internal respiration
* internal respiration
25
New cards
external respiration
* movement of O2 from lungs into blood
* CO2 from blood to lungs
* CO2 from blood to lungs
26
New cards
internal respiration
* movement of O2 from blood into tissue cells
* CO2 from cells into blood
* CO2 from cells into blood
27
New cards
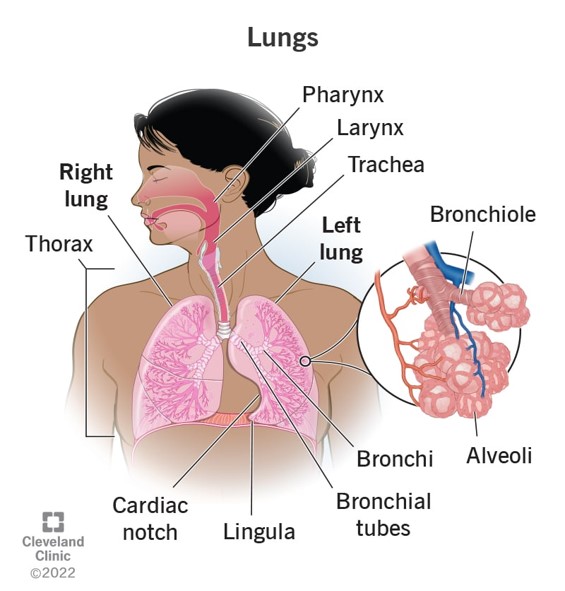
upper airway
air comes in and travels to larynx
28
New cards
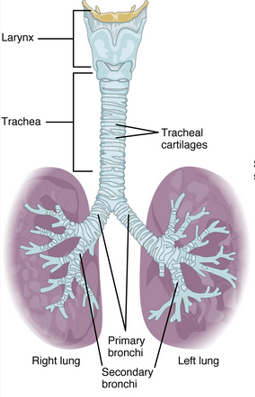
air way ends at the
alveolar sacs
29
New cards
respiratory zone
where gas exchange happens
30
New cards
conducting zone
everything else
31
New cards
epithelial surfaces contain…
cilia
32
New cards
cilia
secrete mucus and keep lungs clear of particulate matter
33
New cards
particulates
dust, foreign contaminants
34
New cards
in the respiratory zone the air is…
* 37 degrees C
* temp and moisture is constant
* temp and moisture is constant
35
New cards
respiratory system located in …
thorax (neck to diaphragm)
36
New cards
lungs
passive, elastic, volume fluctuates
37
New cards
all pressures are relative to…
atmospheric pressure (760mm Hg at sea level)
38
New cards
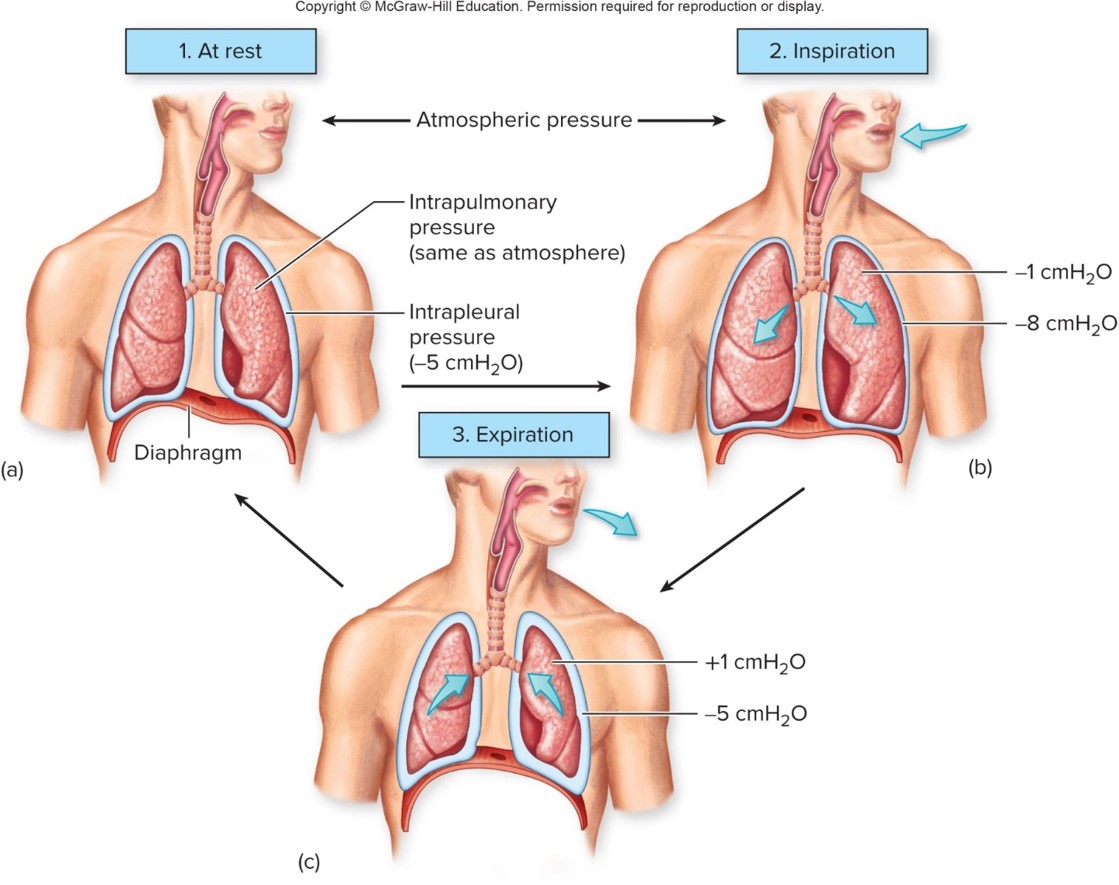
inverse relationship between
pressure and lung volume
39
New cards
intra-alveolar pressure (intrapulmonary)
changes to drive movement of air
40
New cards
pressure equation
P(transpulmonary) = P(alveolar) - P(intrapleural)
41
New cards
intrapleural pressure is always less than
alveolar pressure
42
New cards
intrapleural pressure
pressure in pleural space
43
New cards
inspiration initiated by
motor neurons firing APs to intercostal muscles and diaphragm
44
New cards
most important inspiratory muscle
diaphragm
45
New cards
active movement
inspiration
46
New cards
expiration initiated by
motor neurons decrease APs to diaphragm and intercostal muscles, causing them to relax
47
New cards
passive movement
expiration
48
New cards
role of nervous system
* receive info
* processes and responds
* processes and responds
49
New cards
respiratory rhythm generated in…
medulla oblongata
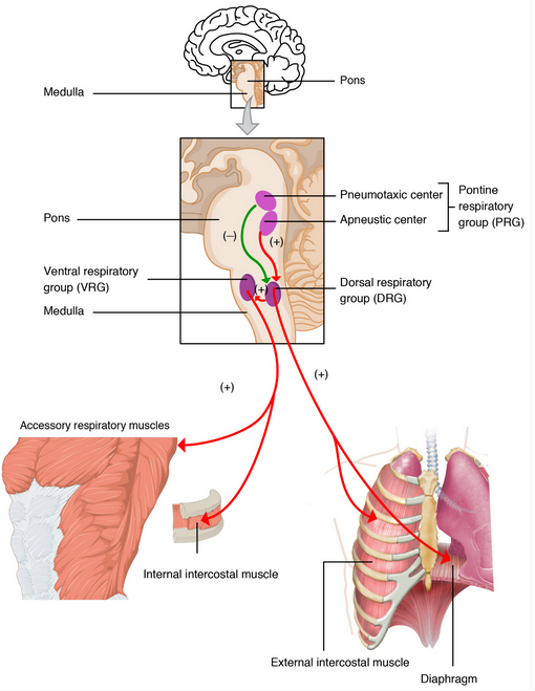
50
New cards
motor neurons
breathing depends on these muscle movements, especially diaphragm
51
New cards
carotid bodies
strategically located to monitor oxygen supply to brain
52
New cards
peripheral cemoreceptor
responding to changes in H+ concentration
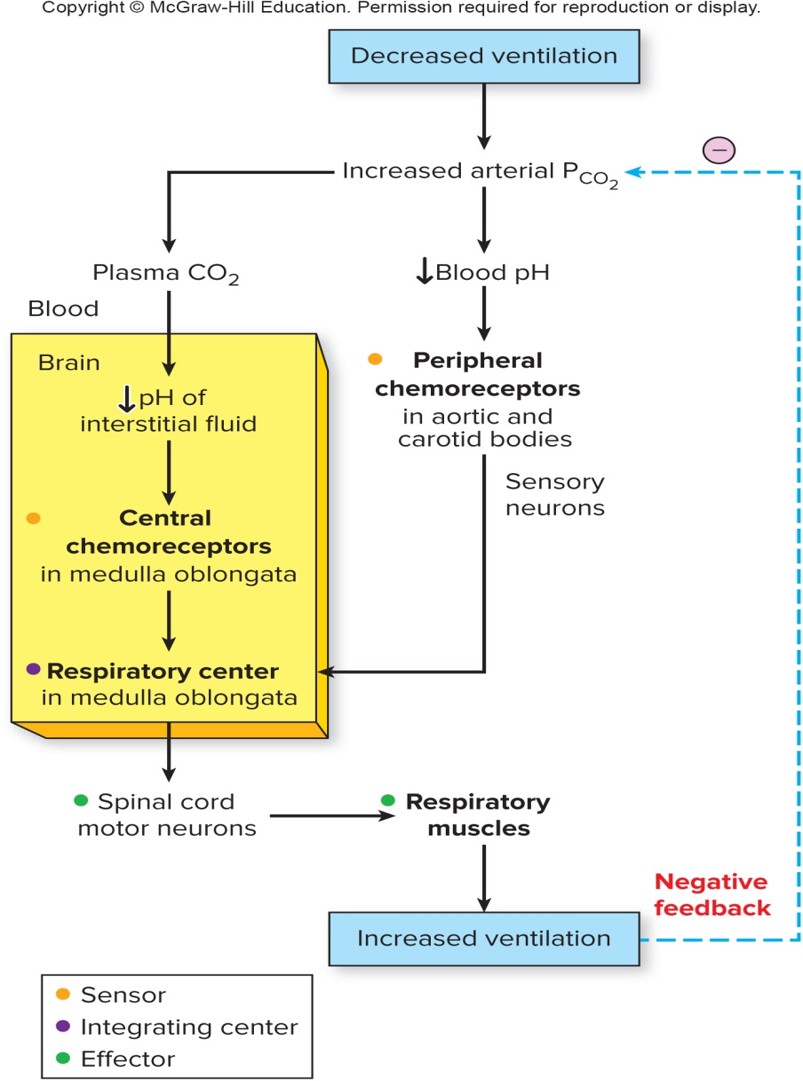
53
New cards
input from receptors modifies
rate and depth of breathing
54
New cards
when muscles contract in chest wall
chest expands
55
New cards
during inspiration…
diaphragm contracts downward and the thoracic cavity is larger
56
New cards
dalton’s law
the pressure each gas exerts is independent of the pressure of other gases
57
New cards
oxygen diffuses from
alveoli to plasma (high to low concentration)
58
New cards
during exercise
the O2 gradient from blood to tissue increases
59
New cards
2 forms of oxygen in blood
* dissolved in plasma and erythrocyte cytosol
* combined with hemoglobin molecules in erythrocyte
* combined with hemoglobin molecules in erythrocyte
60
New cards
heme
iron-containing pigment, binding site
61
New cards
factors affecting movement of O2 on hemoglobin to tissues
* concentration
* affinity (changes in pH or temp can affect affinity)
* affinity (changes in pH or temp can affect affinity)
62
New cards
affinity should be
sufficient to hold bond of O2 to the iron on hemoglobin but not so high that it prevents unloading
63
New cards
only dissolved O2 contributes to
pressure of O2 of the blood
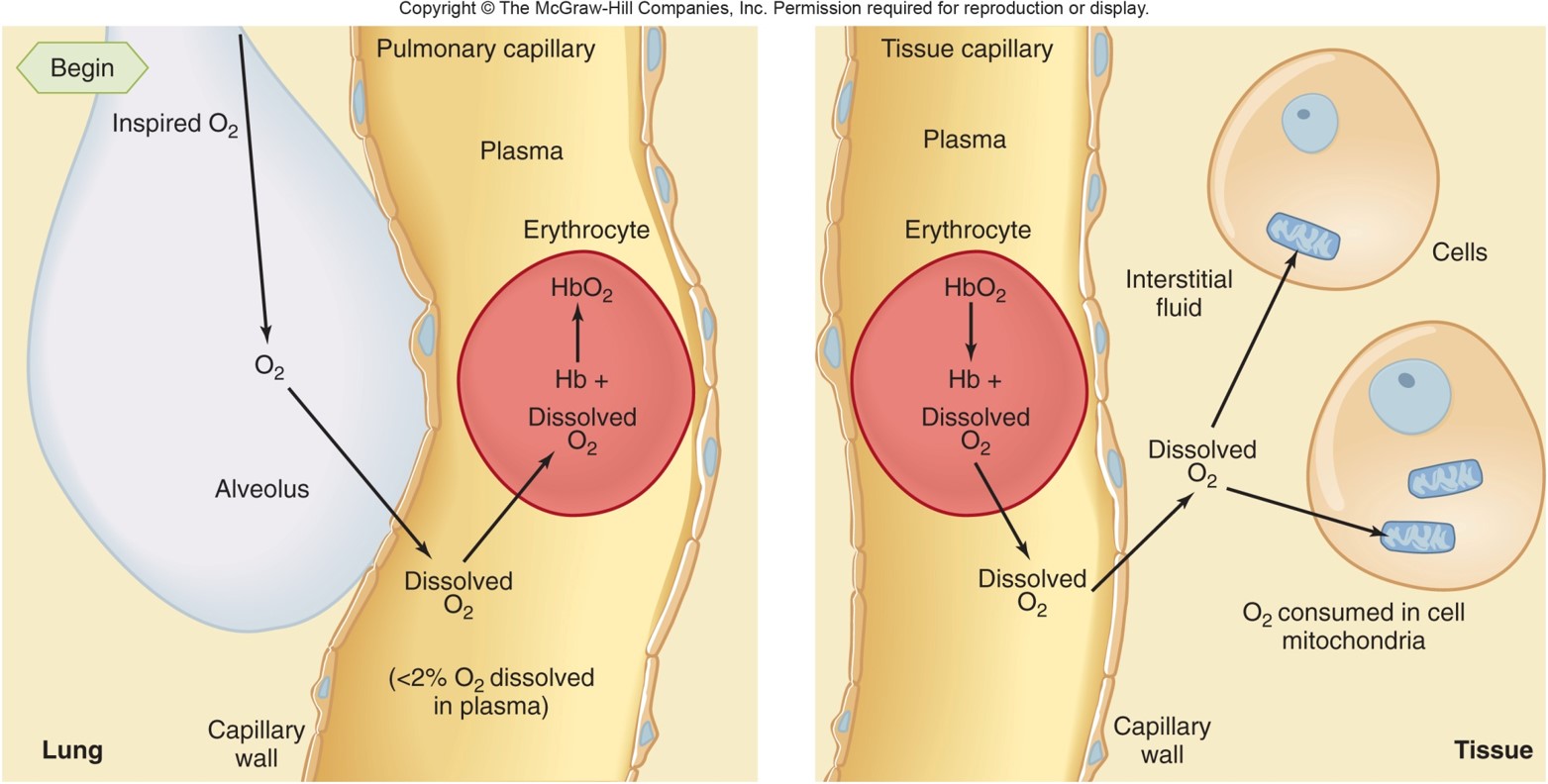
64
New cards
CO2 produces
H+ which causes toxicity
65
New cards
forms of transport for CO2
* 10% dissolves in plasma
* some react with hemoglobin
* 60-65% is converted to HCO3-
* some react with hemoglobin
* 60-65% is converted to HCO3-
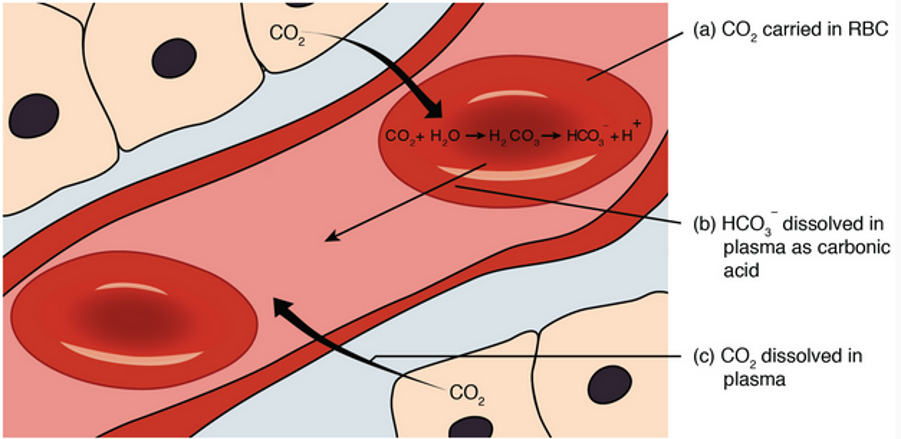
66
New cards
CO2 movement in tissues and lungs
* chloride shift retains electrical neutrality of cell
* H+ in red blood cell buffered by deoxyhemoglobin, H+ in plasma buffered by bicarbonate moving out
* bicarbonate builds up, leaves down its gradient
* Cl- is attracted into cell with movement of bicarbonate and trapping of H+
* H+ in red blood cell buffered by deoxyhemoglobin, H+ in plasma buffered by bicarbonate moving out
* bicarbonate builds up, leaves down its gradient
* Cl- is attracted into cell with movement of bicarbonate and trapping of H+
67
New cards
range for pH of blood
7\.35-7.45
68
New cards
blood pH maintained thru
* lungs regulate CO2
* kidneys regulate bicarbonate
* kidneys regulate bicarbonate
69
New cards
respiratory acidosis
arterial H+ concentration increased due to CO2
70
New cards
respiratory alkalosis
results from decreased arterial CO2 pressure and H+ concentration