plants, roots, leaves, stems, hormones, tropisms, and PSN
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
vascular tissue
inner of roots, stems, leaves (xylem and phloem)
2
New cards
dermal tissue
outer layer of roots, stems, leaves
3
New cards
ground tissue
roots, stems, leaves
4
New cards
meristematic
rapid growth, mitosis
5
New cards
functions of roots
absorb water and dissolved nutrients, anchor the plant, hold the plant upright
6
New cards
functions of stems
transports substances through plants, holds leaves upright/support, heigh
7
New cards
functions of leaves
photosynthesis, pores exchange O2 and CO2 while conserving H2O
8
New cards
epidermis
outer covering of a root
9
New cards
root hairs
projections from the epidermis that provide surface area for absorption
10
New cards
endodermis
layer between cortex and vascular cylinder
11
New cards
osmosis
water gets into the root by ----------
12
New cards
Casparian strip
located in the endodermis, prevents water from moving backwards
13
New cards
transpiration
movement of water through the plant
14
New cards
xylem moves
one way
15
New cards
sieve tubes
conducting strands in phloem cells
16
New cards
translocation
movement of organic substances within a plant from source to sink
17
New cards
phloem moves
two ways
18
New cards
parenchyma
thin cell walls, large central vacuoles, thing layer of cytoplasm
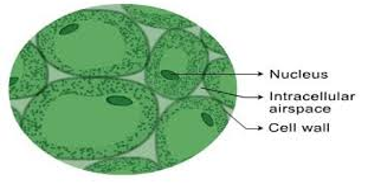
19
New cards
collenchyma
strong, flexible cell walls that support large plants
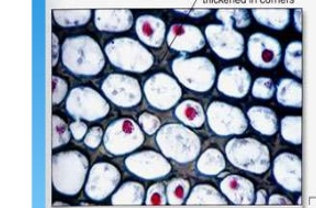
20
New cards
sclerenchyma
extremely thick, rigid cell walls that make tissue tough and strong
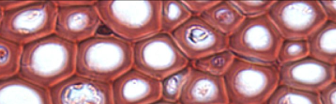
21
New cards
woody stems
trees and shrubs, such as pines, oaks, roses, and hollies
22
New cards
heartwood
wood in the center of a mature stem or tree trunk, xylem within it can no longer conduct water, so they provide support
23
New cards
sapwood
lies outside heartwood, contains vessel cells that can conduct water
24
New cards
dormancy
condition in which a plant or seed remains inactive
25
New cards
Carbon dioxide, water
reactants for PSN
26
New cards
sugars, oxygen
products of PSN
27
New cards
Calvin Cycle
inorganic carbon is incorporated into organic molecules