Geriatrics -Neurologic System
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
Neuro system: overall ___% decline per year starting at age 30
1
ACH decrease leads to
typical age related memory changes
NE decrease leads to
cognitive decline
Dopamine decrease lead to
motor and cognitive decline
serotonin decrease leads to
mood and cognitive changes
GABA decrease leads to
cognitive decline
loss of dendritic spines lead to ______________ loss
synapses
true or false: total number of neurons decline over time
true
areas in the CNS that are impacted by typical aging are _____________
variable!
substantia nigra and locus ceruleus lose _______%
35
lumbosacral anterior horn cells, sensory ganglion cells, putamen, and purkinje lose at most _________%
25
vestibular nuclei and inferior oliver lose __________%
HARDLY ANY
white matter changes with age found in _____-_____% of community dwelling elderly
50-98
white matter changes related to decrease in ______________ density over time
myeline
white matter changes can lead to age-related changes in _____________ and ______________
gait, cognition
grey matter changes thought to be driven by decline in circulating serum ____________ levels
BDNF
grey matter changes more prevalent in what areas?
frontal lobe, temporal lobe, cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and insula
atherosclerosis
Pesence is highly variable and seems to be more related to BP control, lipid levels, and genetics than a product of aging
basilar arteries become ______________ and more TORTUOUS
larger
cerebral blood flow and cerebral metabolic rate ____________
decline
blood flow to brain declines by _____% by age 80
20
true or false: ventricles get smaller with age and sulci become less pronounced
FALSE, opposite
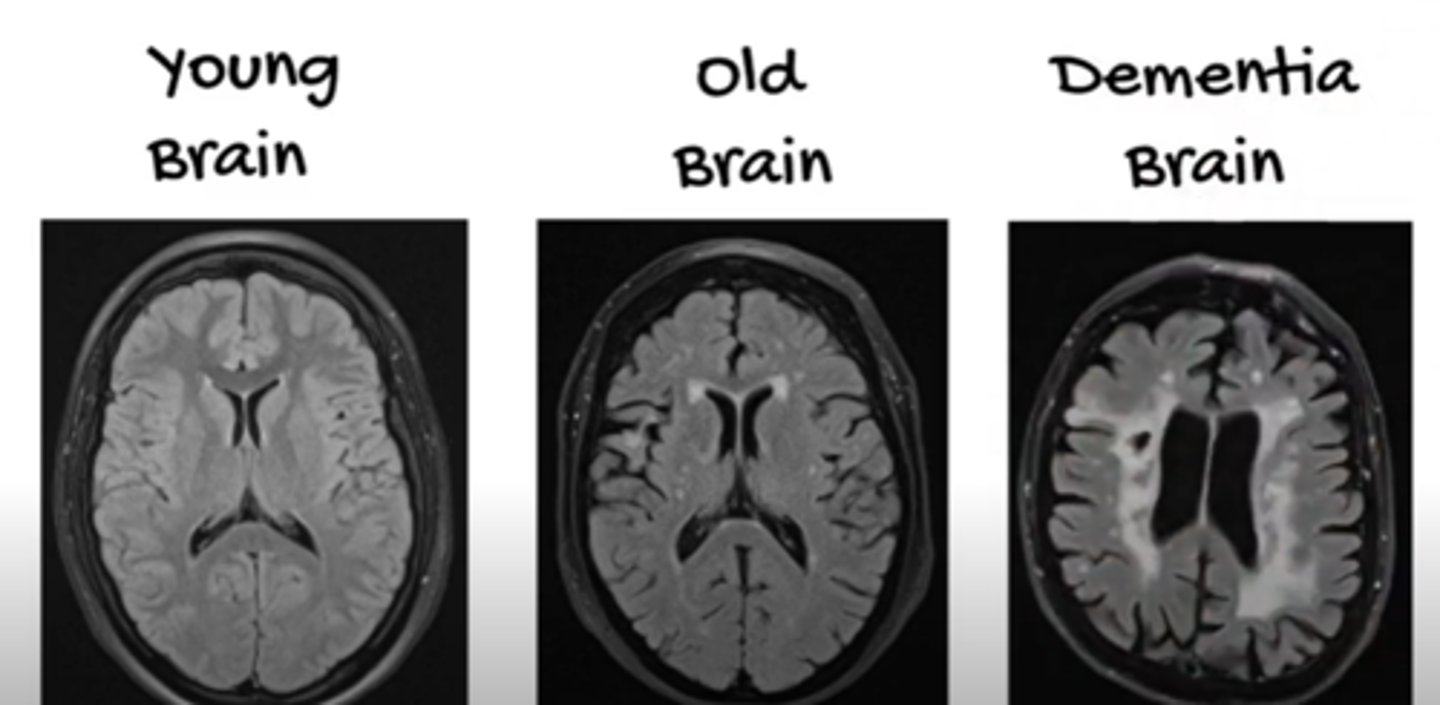
true or false: 10-15% decline in brain weight by age 80
true
true or false: our view on typical cognitive changes can impact how neurological events (TBI, stroke) are recognized
true
nerve conduction speeds decrease with aging, starting between age _____ and _____
30-40
nerve conduction changes are driven by what two things?
loss of myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers, decrease in myelin with maintained nerve fibers
true or false: motor and sensory nerves decrease in number
true
which is more effected by peripheral nerve loss? UE or LE?
LE
_____% decline in number of fibers in nerves by age 80
37
do older adults become hyporeflexic or hyperreflexic?
hypo
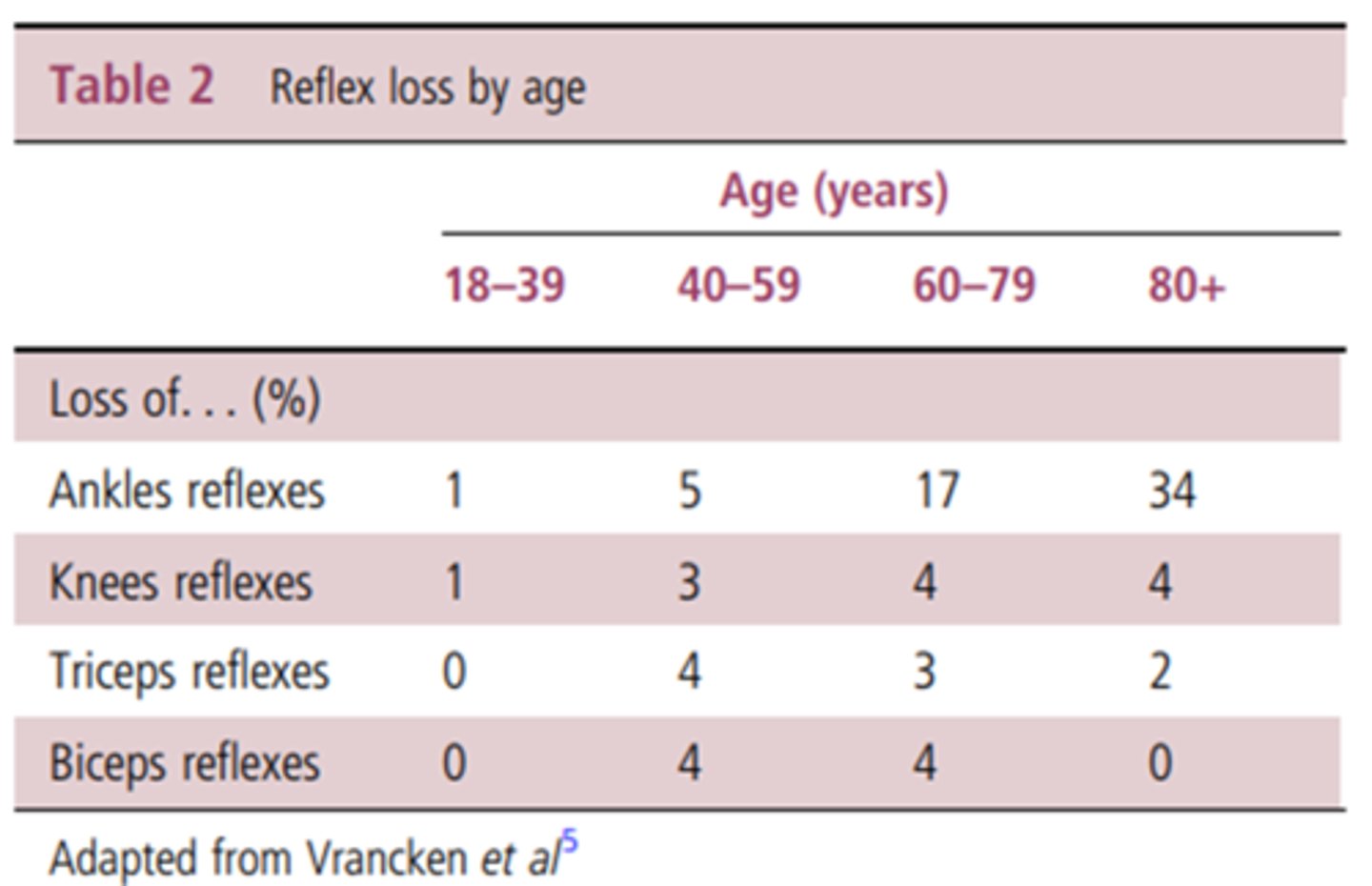
LE or UE more effected by hyporeflexia?
LE
t or f: with age, decreased vibratory sense, joint position, and response to tactile input
true
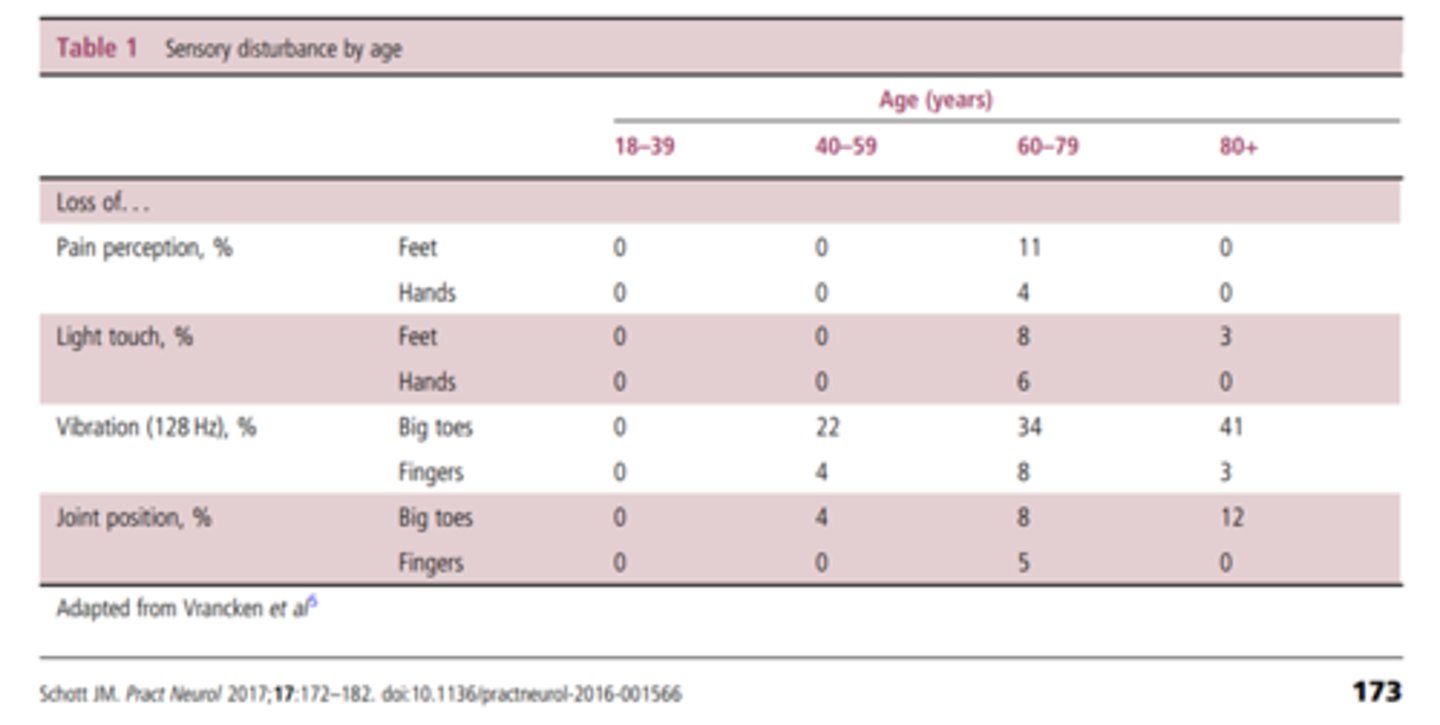
t or f: older adults are more impacted by extremes of hot and cold
true
pain perception?
we dont really know
t or false: 40% have smell enhancement by age 80
no (loss)
what causes smell loss?
meds, smoking, cancer tx, alzheimers, PD
decreases sense of taste due to what?
decreased number/size taste buds, decreased saliva production
what can decreased taste lead to:
malnutrition, excess salt and sugar intake
____% decline in number of taste buds by age 80
64
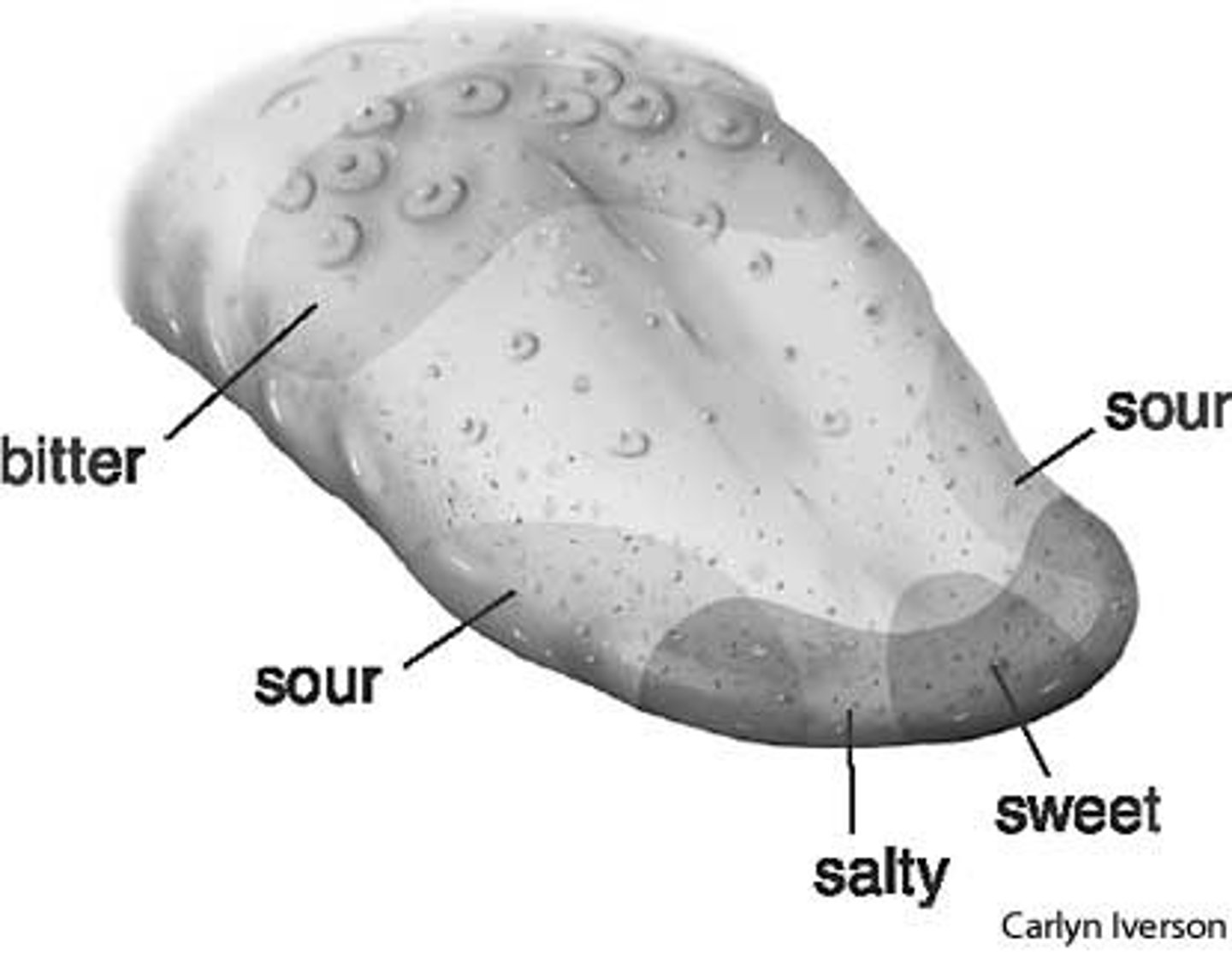
presbycusis=
age related hearing loss
why are their hearing changes: due to decreased number of _______________ cells in the organ of ___________
hair, Corti
what is speech discrimination?
ability to tell if two sounds are the same or different
uncorrected hearing loss is correlated to ____________ decline
cognitive
how should you speak to a patient with hearing loss?
lower, slower
lens becomes more ___________, begins around age 40
rigid
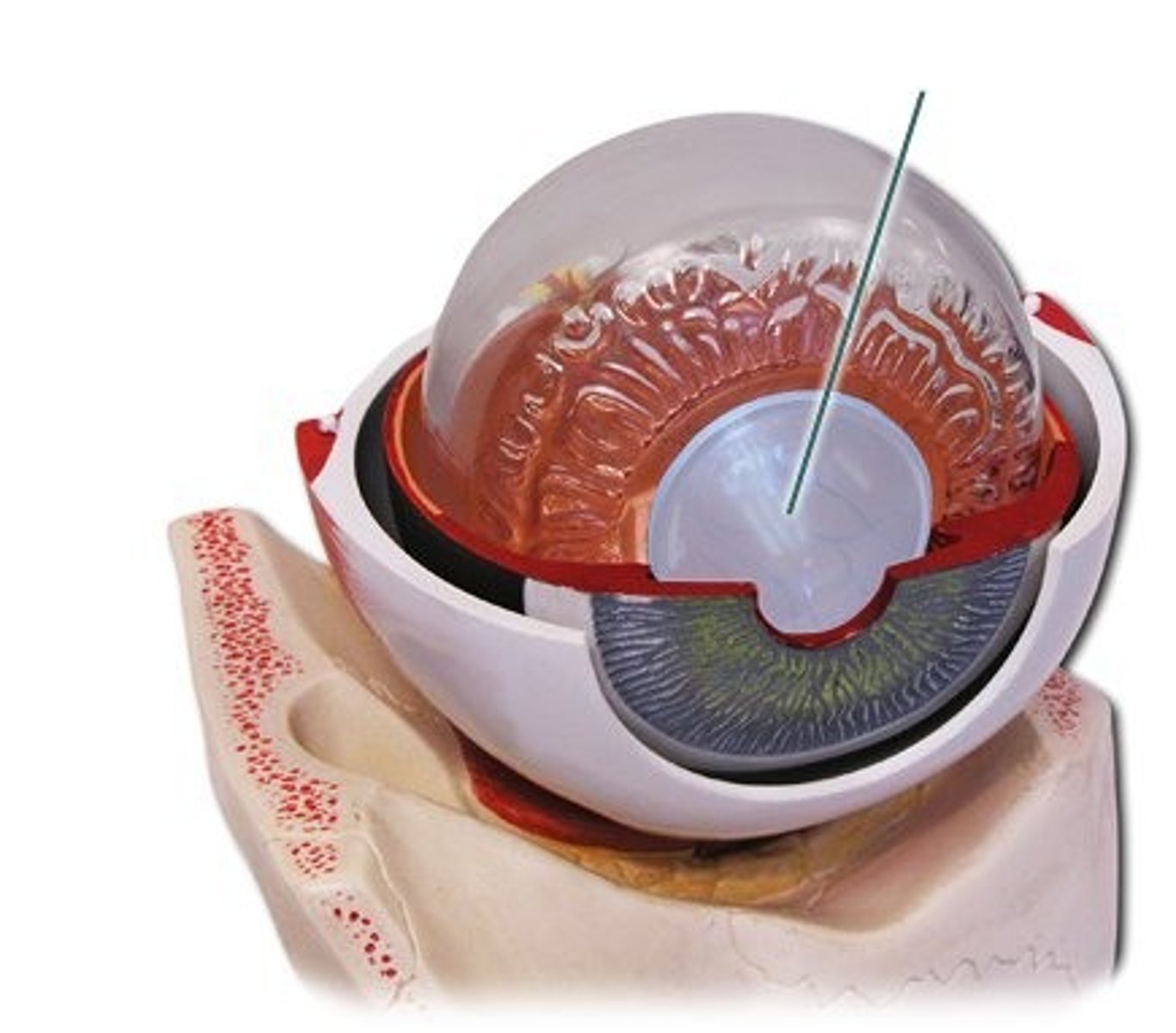
rigid lens: leads to _________________ deficits
accomodation
impact of rigid lens:
need bifocals, readers
presbyopia
impaired vision as a result of aging
glare
causes problem

increased/decreased? tear production
decreased (dry eye)
causes of vestibular changes
vestibular, medication, cardiogenic
vestibular deconditioning
you tend to stop spinning in circles, cartwheels, etc. as you get older
presence of _________________ increases risk of falls
BPPV
when doing testing with BPPV: testing should be _______________
slower
agility?
declines starting in 30s
typical gait changes w/age:
wider BOS, slower, stoops, less arm swing, more time in double limb stance, less confidence
gait changes mean what?
increased work in walking, increased risk for falls
sleep cycle ___________
shortens
sleep schedule:
early morning waking, more frequent night-time waking
why are there sleep changes?
changes in circadian rhythms, decreased sleep homeostasis, social engagement, lifestyle, environment, medical co-morbities, medications, sleep disorders
stage 1 and 2 sleep
non-REM
SWS = slow wave sleep
deep non-REM sleep important for MEMORY consolidation
REM=
rapid eye movement
WASO
wake after sleep onset
sleep latency
how long until you fall asleep
t or f: significant mood changes are typical with aging
FALSE
exception to mood changes with aging?
perimenopause and menopause
if notable changes in mood or mood swings are noted, look for underlying cause like:
mental health, dementia, medications, underlying condition
1/4 of people over the age of 65 are considered to by socially ______________
isolated :(
social isolation significantly increases chances of _________ ____________
premature death
social isolation: _________% increased risk of dementia
50%
t or f: loneliness and social isolation are the same
false
definition of meaning
"psychological concept linked to the feeling we get when our thoughts, emotions, and actions make a difference and matter to others. Significance in our lives."
definition of purpose
"Journey we embark on, what we perceive as our calling, or the potential we believe we have for our lives."
t or f: unsuccessful or non-attempts at finding meaning and purpose tend to lead to higher rates of depressive symptoms
true
how to find meaning in later life:
•Meaning reflectivity
•Finding and constructing
•Mindset
•Viewing aging as a strength and source of wisdom
•Creative pursuits
•Exploring new activities
•Family life
•Volunteering or continued employment
•Learning something new (or many things)
•Setting new goals
______________ attention remains intact, ___________________ gradually decline
selective, divide attention
___________________ memory shortens
working
long term memory:
general concept remain, but context, dates, and people involved tend to be lost
semantic memory (facts):
preserved
procedural memory:
preserved
prospective memory:
requires use of calendars and lists, without these impairment is noted
perception
intact ,deficits related to sensory impairments
speech and language
preserved and MAY IMPROVE
with decision making, rely heavily on __________________________________ rather than new info
prior knowledge
with decision making, rely heavily on ______________ opinion
expert
executive control (planning, organization, coordination, implementation):
decline w age
t or f: intelligence remain with age
true
crystallized intelligence
improves w age
fluid intelligence
Analyze novel problems, identify patterns and relationships that may cause problems, extrapolate using logic, decline with age
recommendations for preventing abnormal cognitive decline w aging:
aerobic ex, crossword, socially active, cognitively active, stop smoking, minimize alcohol, minimize risk of head injury
is neuroplasticity possible in older age?
yes, but takes more time, work, and practice
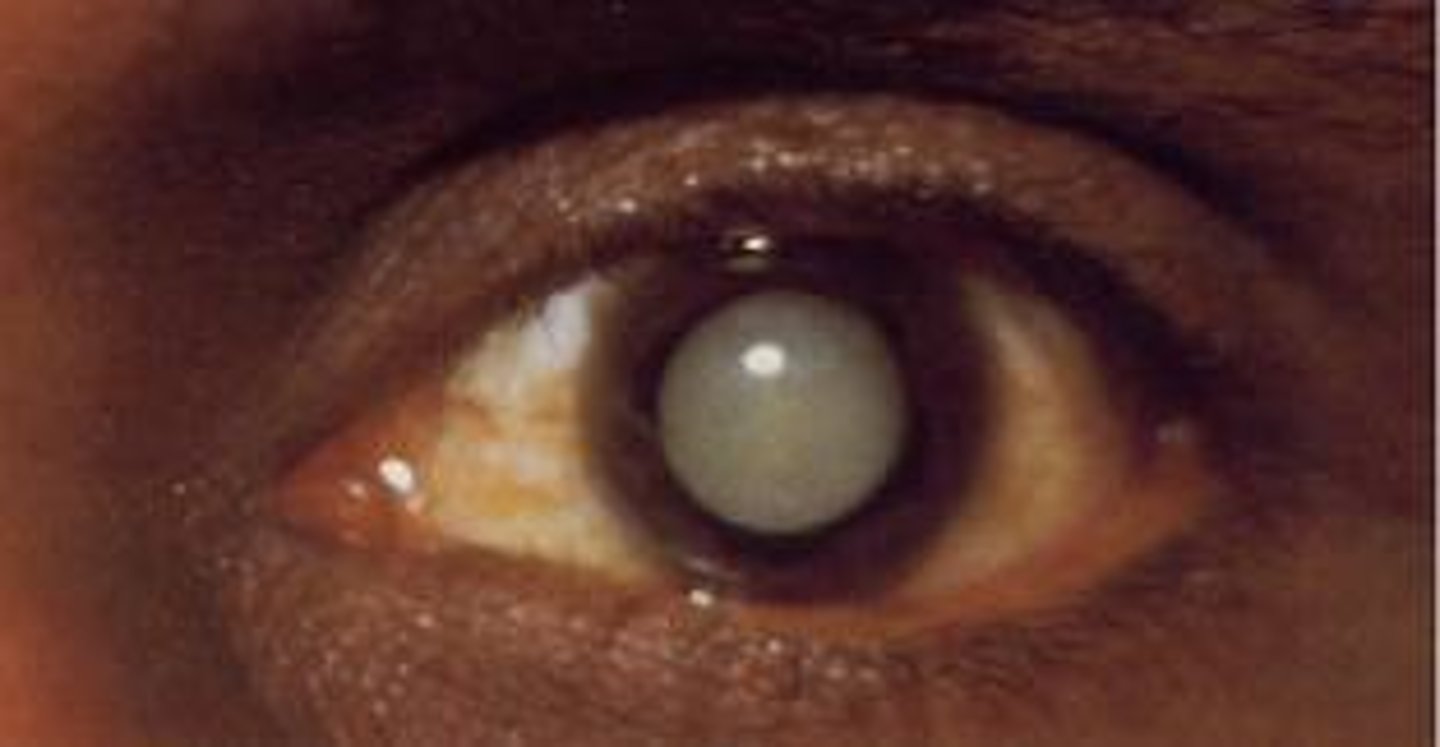
cataracts
clouding of the lens
glaucoma
increased intraocular pressure

macular degeneration
loss of central vision

t or f: any visual issue puts people at higher risk for falls
true
risk factors for cataracts
age, DM, smoking, alochol, fam hx, eye injury, no sunglasses, steroids
symptoms of cataracts
develop over time, cloudy vision, colors faded, problems seeing at night, halo around lights, diplopia
leading cause of blindness in developing countries?
cataracts
t or f: in the US and developed nations, surgery removes clouded lens and replaces it
true