Larynx and Trachea
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Larynx
Voice production
Maintaining patent airway
Connects pharynx and trachea
C3-C6
Location of larynx
Epiglottis, thyroid, cricoid
Unpaired cartilages of the larynx
Cuneiform, corniculate, arytenoid
Paired cartilages of the larynx
Laryngeal prominence
Adam’s apple
Cricothyroid joint
Rotation and gliding of the thyroid cartilage
Changes in the length of the vocal folds
Cricoid cartilage
Level of C6 vertebra where:
carotid artery can be compressed
larynx and trachea join
pharynx joins esophagus
recurrent laryngeal nerve
only complete ring of cartilage
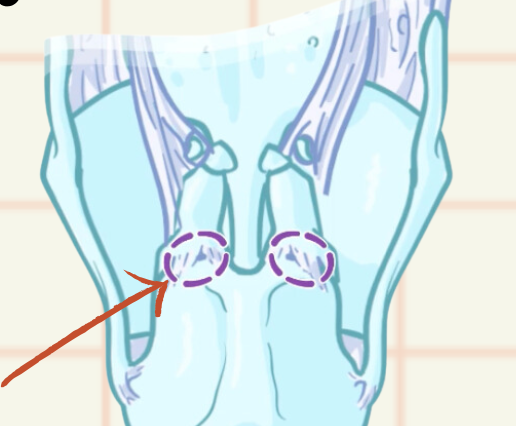
Arytenoid cartilage
Paired pyramidal cartilages
Articulate with superior border of cricoid
Cricoarytenoid joint
Slide toward or away from each other
Tilt anteriorly and posteriorly
Rotate
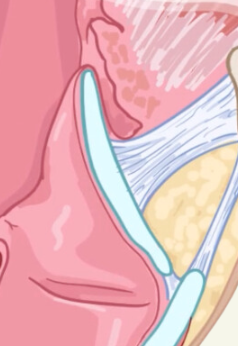
Conus elasticus
aka vocal ligament
Epiglottic cartilage
Posterior to the root of the tongue
Anterior to laryngeal inlet
Superior part of the anterior wall
Superior margin of the inlet
Epiglottic cartilage
Elastic cartilage that functions as a valve that closes of larynx during swallowing
Laryngeal inlet
Communicates with the laryngeopharynx
Level of the inferior border of cricoid
Laryngeal vestibule
Laryngeal inlet to vestibular folds
Middle part of the laryngeal cavity
Vestibular fold to vocal fold
Infraglottic cavity
Vocal fold to inferior border of cricoid
Laryngeal saccule
Lined with mucosal glands
Vocal folds
Produce audible vibrations when free margins are closed and air is pushed out of our lungs
Rima glottidis
The V-shaped opening formed between the true vocal cords, which permits the passage of air through the larynx
Narrow and wedge-shaped
Shape of rima glottidis during normal breathing
Wide and trapezoidal
Shape of rima glottidis during forced expiration
Slit-like
Shape of rima glottidis during phonation
Extrinsic muscles
Muscles that move larynx as a whole
Infrahyoid muscles (depress hyoid and larynx)
Suprahyoid muscles (elevate hyoid and larynx)
Intrinsic muscles
Muscles that alter length and shape of vocal folds and rima glottides
Abductors and Adductors
Sphincters
Tensors and Relaxers
Adductors
Lateral Cricoarytenoid Muscles and Transverse and Oblique Arytenoid are (?)
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles
Pull muscular processes anteriorly
Rotate anterior cartilages
Transverse and oblique arytenoid
Arise from one arytenoid and inserts to contralateral arytenoid
Pulls arytenoid cartilages together
Abductor
Posterior cricoarytenoid is an (?) muscle
Posterior cricoarytenoid
Arise from cricoid cartilage lamina and inserts into vocal process of arytenoid
Rotate vocal processes laterally
Tensor
Cricothyroid muscle is a (?) muscle
Cricothyroid muscle
Arise from the anterolateral part of the insert into the inferior margin and inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage
Tilt or pull the thyroid cartilage anteriorly and inferiorly
Vocal ligaments elongates and tightens
Raise pitch of voice
Relaxer
Thyroarytenoid muscles are (?) muscles
Thyroarytenoid muscles
Arise from the lower half of the posterior aspect of the thyroid cartilage and cricothyroid ligament and insert into the anterolateral arytenoid surface
Pull arytenoid cartilages anteriorly
Lower the pitch of the voice
Tensor and Relaxer
Vocalis muscle is a (?) muscle
Vocalis muscle
Lateral to the vocal ligaments
Origin: Lateral surface of the vocal process of arytenoid
Insertion: Ipsilateral vocal ligament
Acts during animated speech and singing by tensing and relaxing the vocal ligaments
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Innervation of all laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid muscles
External laryngeal nerve
Innervation of cricothyroid muscles
Superior laryngeal artery
Blood supply of the internal surface of larynx
Inferior laryngeal artery
Blood supply of mucous membrane and muscles of inferior part of larynx
Internal jugular vein
The superior thyroid vein drains into the (?)
Brachiocephalic vein
The inferior thyroid vein drains into the (?)
Internal laryngeal nerve
Runs with superior laryngeal artery
Supplies:
Sensory fibers to laryngeal mucous membrane of vestibule and middle laryngeal cavity
Superior surface of vocal cords
External laryngeal nerve
Posterior to sternothyroid muscle with superior thyroid artery
Supplies:
Cricothyroid muscle
Motor fibers
Inferior laryngeal nerve
Continuation of recurrent laryngeal nerve
Motor innervation to larynx
Sensory innervation to mucosa of infraglottic cavity
Trachea
Starts at inferior end of larynx (C6)
Ends at sternal angle (T4-T5)
Terminates into right and left bronchi
Tracheal cartilage
Incomplete cartilaginous ring
Deficient posteriorly