L5 - Discriminant Analysis
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is discriminant analysis?
prediction of groups when groups are known a priori (supervised clustering)
How do we denote the g populations/groups/categories?

What would the different populations be and what would X be in case we look at diseases?
Populations can be different diseases, and predictors can be the symptoms of a patient (X)
What would the different populations be and what would X be in the Swiss bank notes example?
Populations are whether banknotes are forged or genuine, and predictors are measurements of the banknotes
What is a discriminant rule d?

When is discrimination more accurate?
if Πj has high concentration of its probability in Rj
What is the idea of the maximum likelihood discriminant rule?
Allocate X to a group which gives the largest likelihood to X
The idea of the maximum likelihood discriminant rule is to allocate X to a group which gives the largest likelihood to X. Write this down mathematically.
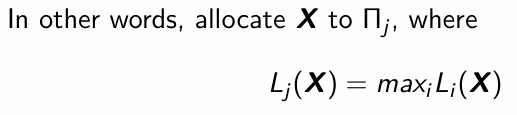

What do we do if X = 0? What if X = 1? Explain.

What does LDA stand for?
Linear discriminant analysis
What are the LDA assumptions?

Give the theorem about linear discriminant analysis.


How is this calculated again?
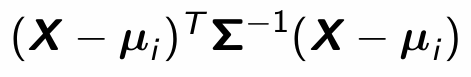

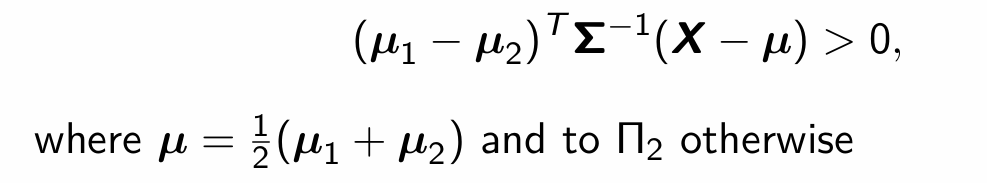

Prove this
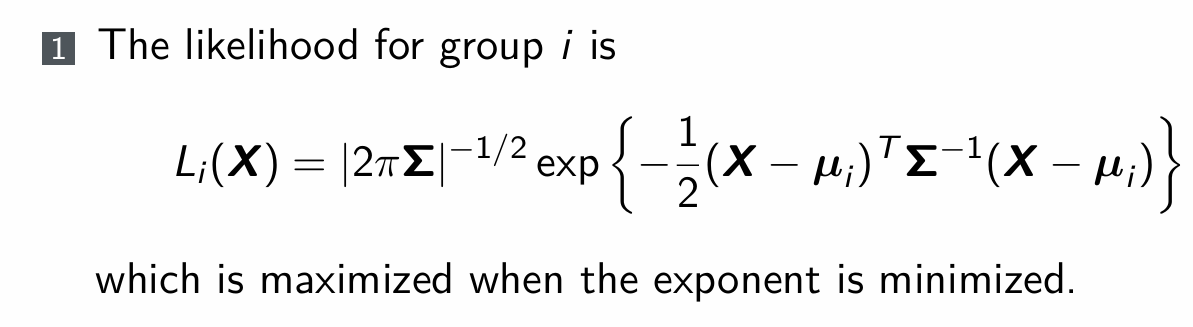

What to do when this assumption is not correct?
Quadratic discriminant analysis
What is the likelihood for group i?
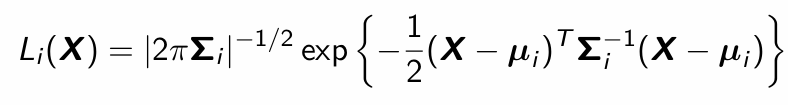
What is the discriminant function (including prior information)?
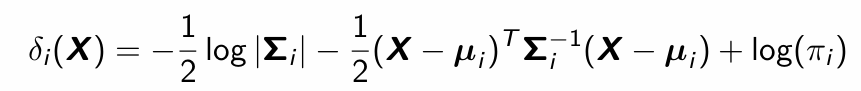
Why is it called quadratic discriminant analysis?
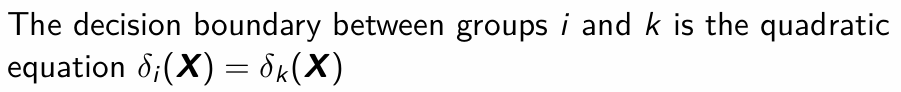
What is the discriminant (classification) rule for quadratic discriminant analysis?
assign X to Πj when δi(X) is maximized
What is the practical issue with QDA?

What is a solution to the practical issues we face when applying QDA?

What is Bayes discriminant rule?

If no prior probabilities are available then Bayes discriminant rule …
is the same as ML discriminant rule.
If g =2 then the discriminant function (1) is shifted by …
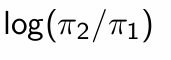
A randomized discriminant rule d involves allocating observation X to a population j with probability … [symbol]
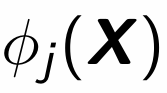

What can we say about these?

What is the deterministic allocation rule? phi_j(X) = …
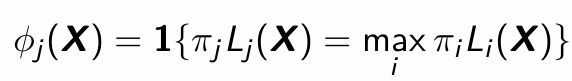
The probability of allocating X to population Πi when it comes from Πj is pij = …
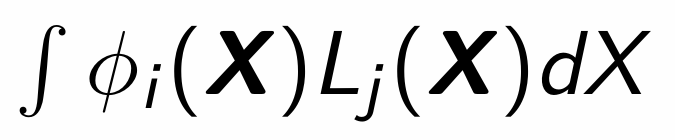
When is a discriminant rule admissible?

Which theorem fo you know about admissibility of discriminant rules?
All Bayes discriminant rules (including the ML rule) are admissible
What if we do not want or cannot use a parametric form of the distribution of the populations? Can we find a reasonable discrimination rule in this case?
Yes, with Fisher’s idea!
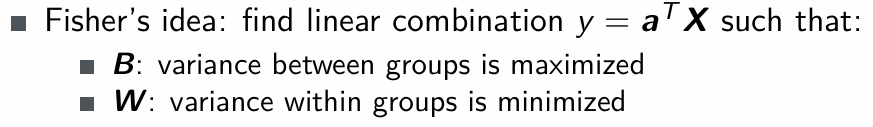
How do we calculate B (Between group sum of squares?
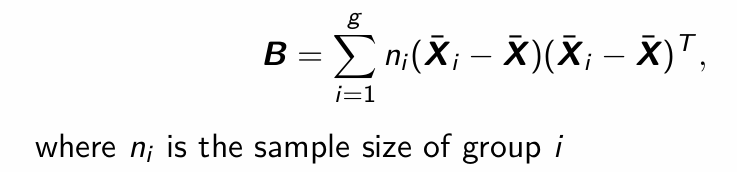
How do we calculate W (Within group sum of squares)?
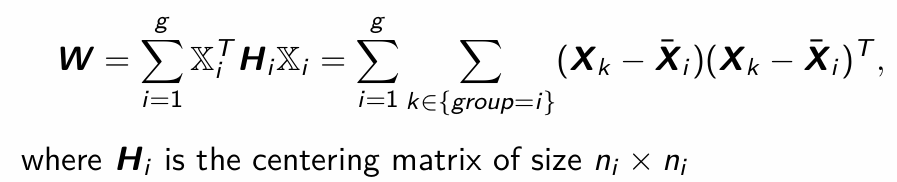
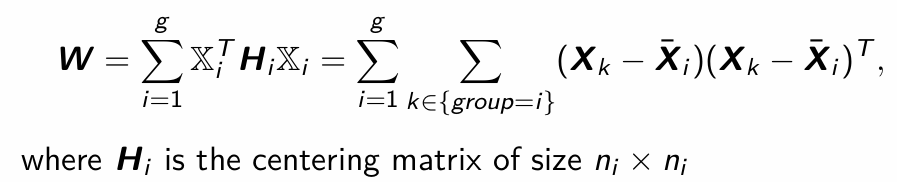
What does this H matrix look like?
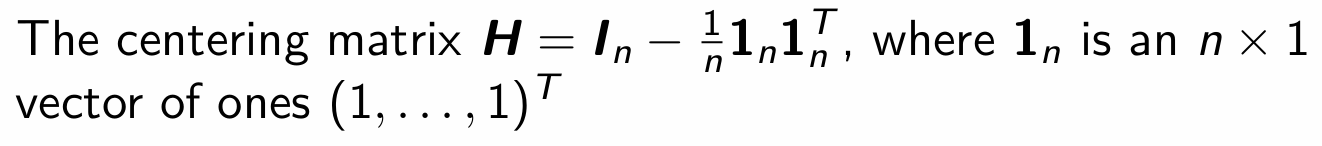
What is the maximization we do with Fisher’s linear discriminant function?
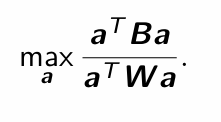
What is the solution to this maximization problem (Fisher)?

What is the discriminant score of Fisher’s linear discriminant function?

What is the general form of Fisher’s rule?
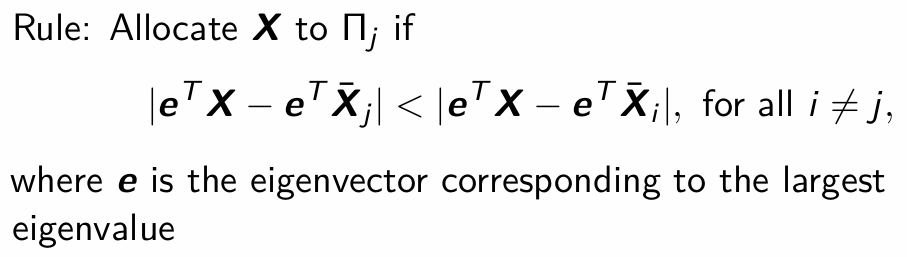
What is Fisher’s rule in the case of two groups?
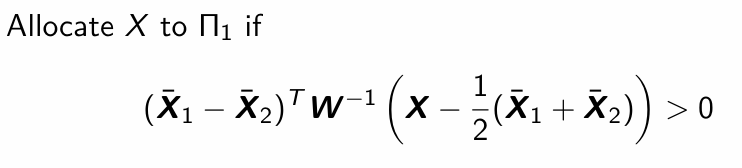
Compare Fisher’s discriminant rule to the Maximum Likelihood discriminant rule.
For g = 2: Same as ML rule but not based on multivariate normality! Although, the mathematical justifications are different.
For g ≥3: the rules are (in general) different from ML rules
Let us incorporate the misclassification costs into the discriminant rule. How do we define the loss function in this course?

Suppose that d is an allocation rule then the risk function is defined by …
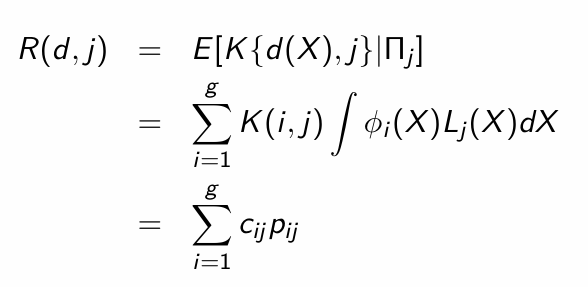
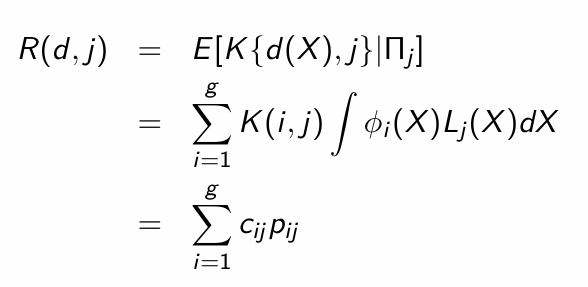
Give an interpretation of the risk function.
It is an expected loss, given that the observation comes from Πj
How do we compute the Bayes risk?
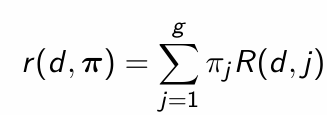
What is the interpretation of the Bayes risk?
The posterior expected loss
What is the Bayes rule?
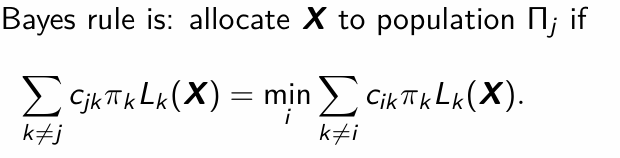
The classical approach for discriminant analysis is to use sample mean and sample (co)variance estimators of µ and Σ. We know that they are very sensitive to outliers. What to do?
We can simply use the robust estimators
Which robust estimators should we use for discriminant analysis?

Croux et al. (2008) shown that the first order influence function of the classification error rate vanishes. What does this mean?
This roughly means that the loss of efficiency from the use of robust estimators is not transferred to the performance measure
→ The use of robust methods for classification is worthwhile
What to take away from this lecture?
