3 Radiation Safety and Protection
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
what is the main source of exposure for most people ?
naturally occurring background radiation (US average 3.1 mSv/yr)
what is the main source of background radiation? (IMPORTANT)
radon (a gas released from ground that enters home and buildings)
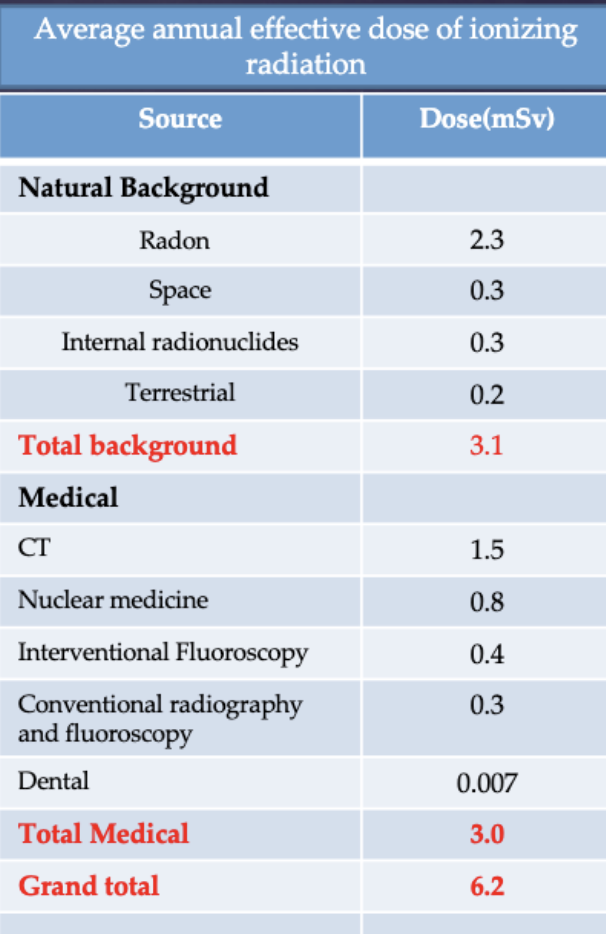
is the amount of background radiation related to increased cancer?
no. No evidence of increased cancers from these high natural levels
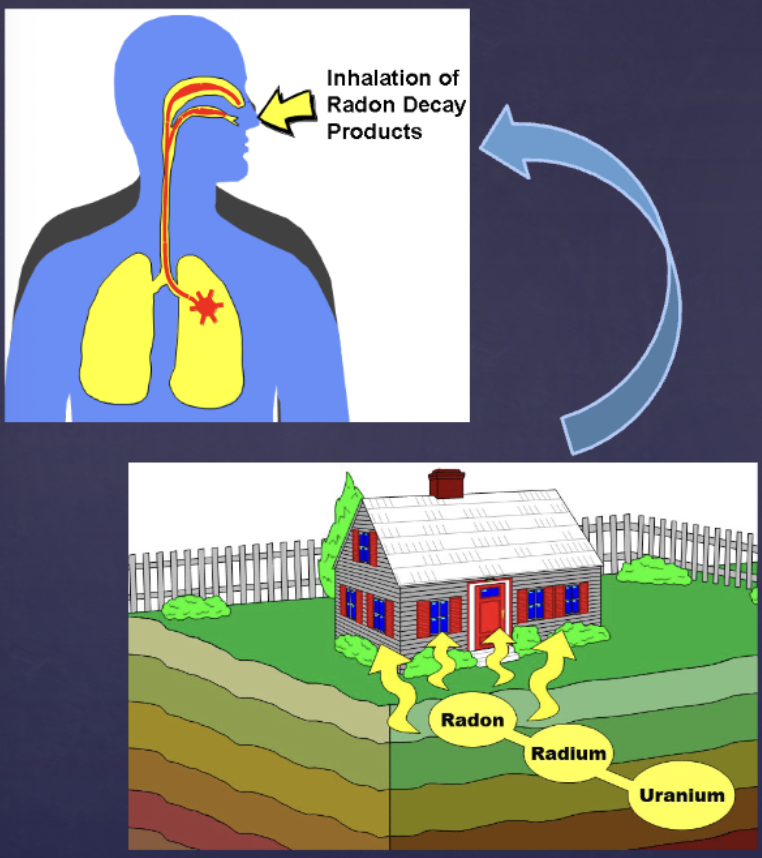
how does radon cause damage (specifically lung cancer)?
Radioactive decay products of radon emit alpha particles that affect cells in the lung
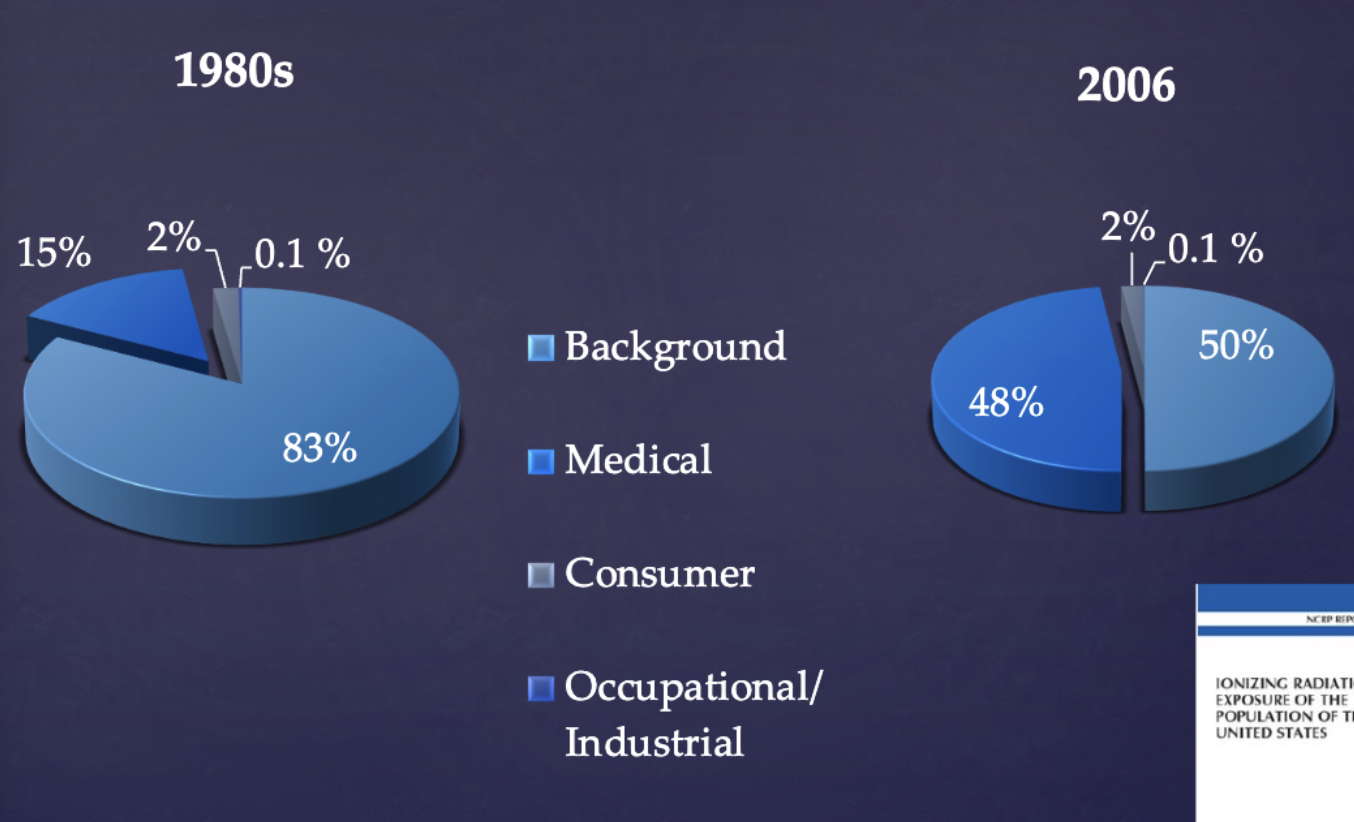
how has exposure of natural vs man made radiation changed from the 1980s to 2000s?
how has medical exposure of patients to radiation changed from the 1980s to 2000s?
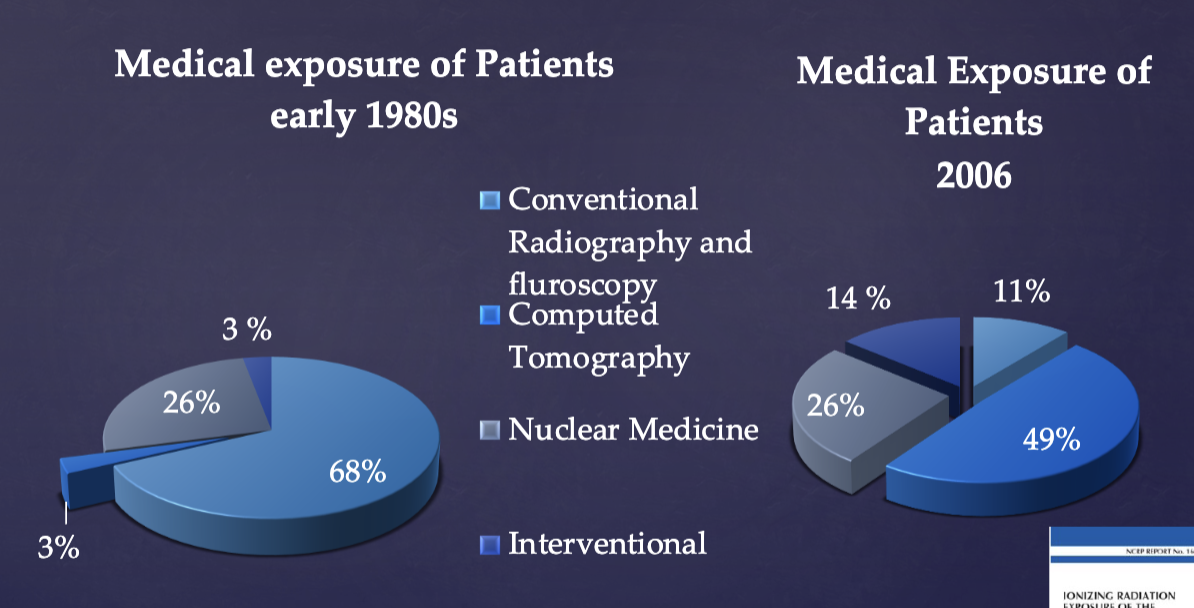
in health care, how much radiation exposure comes from dental?
VERY LITTLE
what is the annual effective dose limit for occupational persons relative to stochastic effects? (IMPORTANT)
50 mSv (this would be if we took radiographs WITH the pt inside the machine every time)
what is the annual effective dose limit for occupational persons relative to deterministic effects?
150 mSv → lens of eye
500 mSv → skin, extremities
what is the annual effective dose limit for nonoccupational (public) persons relative to stochastic effects? (IMPORTANT)
5 mSv for infrequent exposure
what is the annual effective dose limit for nonoccupational (public) persons relative to deterministic effects?
50 mSv → lens, skin, extremities
what is the annual effective dose limit for embryo/fetus (nonoccupational (public) persons)? (IMPORTANT)
0.5 mSv equivalent dose/month
what are the 3 guiding principles in radiation protection?
principle of justification
principle of optimization
dose limitation
which guiding principle states dentist should identify situations where the benefit from diagnostic radiation exposure likely exceeds the risk of harm?
principle of justification
what is the most effective way to reduce unnecessary exposures?
reduce unnecessary radiographic examinations (principle of justification)
radiographs should be prescribed only after what 2 questions are asked?
clinical evaluation (susceptibility to dental disease)
patient needs
(not at preset intervals)
t/f: Radiographic exposures are necessary only when, in the dentist’s judgment, it is reasonably likely that the patient will benefit by the discovery of clinically useful information in the radiograph
true
which guiding principle states dentists should use every reasonable means to reduce unnecessary exposure to their patients and themselves?
principle of optimization
principle of optimization is often referred to as (what acronym)…?
ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle of radiation protection
what is the dose limit for individuals exposed for diagnostic purposes (patients)?
THERE ARE NO DOSE LIMITS FOR individuals exposed for diagnostic purposes
what dose the guiding principle of dose limitation state?
Dose limits are used for public and occupational exposures
applies to dentist and their staff that are occupationally exposed but does not apply to patients
according to ADA guidelines, how should radiographs be prescribed for new patients?
4 bitewings + pano or periapical images (but only do so AFTER seeing the pt to determine what they need)
according to ADA guidelines, how should radiographs be prescribed for recall patients?
bitewings every 6-12 months (caries risk) or 12-24 months (no caries risk)
what are the 3 speed groups of radiographs?
D (slowest), E, F (fastest)
Film of a speed slower than which speed should NOT be used for dental radiographs?
E
E-speed film is how much faster than D?
twice as fast (hence uses half the dose)
F speed film results in % less exposure than E speed?
20-50% (equal or slightly more exposure than digital sensors)
t/f: digital sensors use equal or greater dose savings compared to F-speed films
true
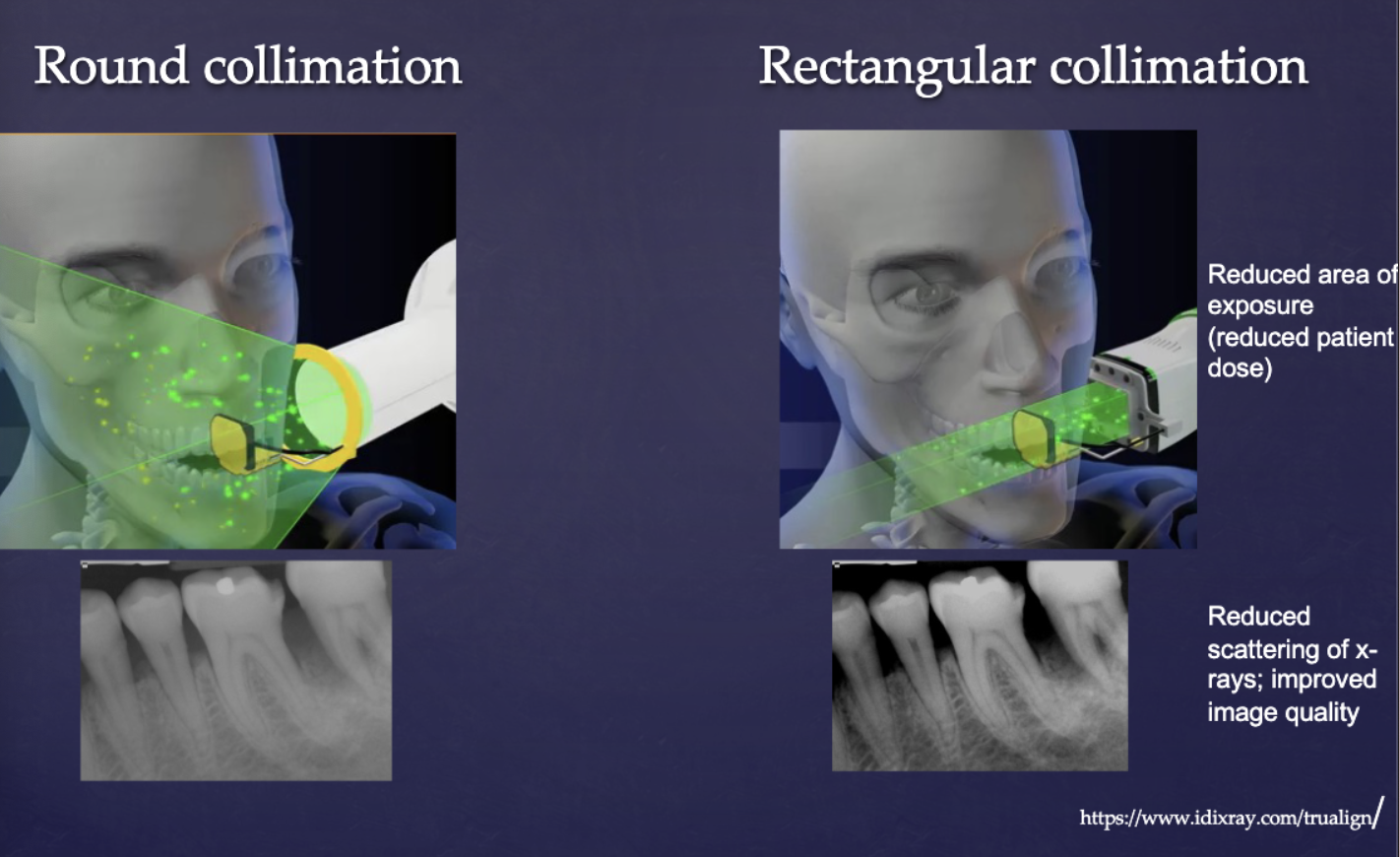
how does rectangular collimation affect radiation dose compared to a circular one?
decreases radiation (dose reduction almost 5-fold/60% reduction)
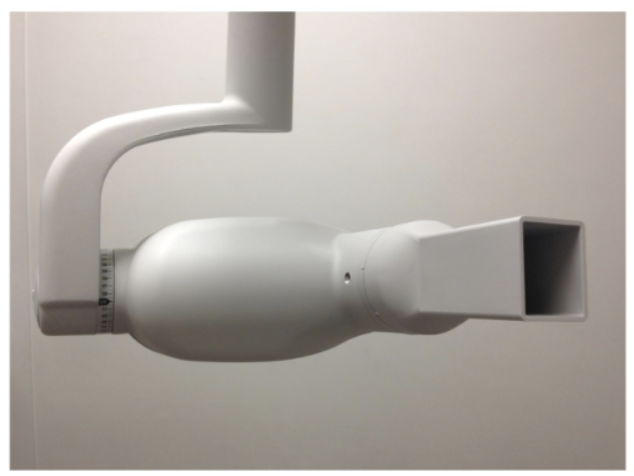

what are the benefits of using a rectangular collimation?
dose reduction achieved is almost 5 fold (60% reduction)
improved image contrast (reduced fogging caused by scattered photon)
pt’s skin surface exposure field is < 7 cm diameter
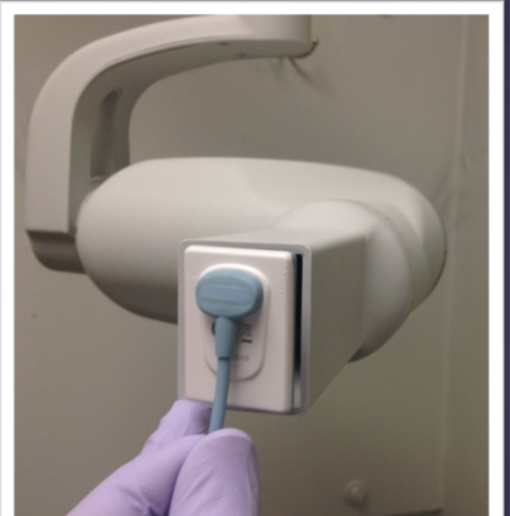
what is this device?
rectangular position indicating device (PID)
rectnagular collimation leads to a dose reduction of almost _____
five fold (60% reduction)
what does rectangular position indicating device (PID) do?
limits size of the x-ray beam to the size of intraoral sensor reducing unnecessary exposure
what does filtration do in radiograph devices?
removes low energy x-ray photons from the x-ray beam
why are low energy photons bad?
increase patient dose without contributing to image information
per most state regulations, pt’s skin surface exposure field should be < ___ cm in diamter
7 cm (achieved using rectangular collimators)
3 mm of aluminum (filtration) leads to a % reduction in exposure
80%
what are leaded aprons/collars used for?
reduce exposure to gonads and thyroid gland
are leaded aprons necessary?
not necessary if all NCRP recommendations are followed
Shielding of the gonads, pelvic structures, and fetuses during all dentomaxillofacial radiographic imaging procedures is not recommended
Thyroid collar is not recommended during intraoral , panoramic, cephalometric and CBCT
Follow Federal, State or Local regulations regarding the use of Lead Apron
(according to ADA)
Source-to-skin distance or Focal spot to film distance (FFD) is controlled by…?
the length of the position indicating device (PID) of x-ray tube
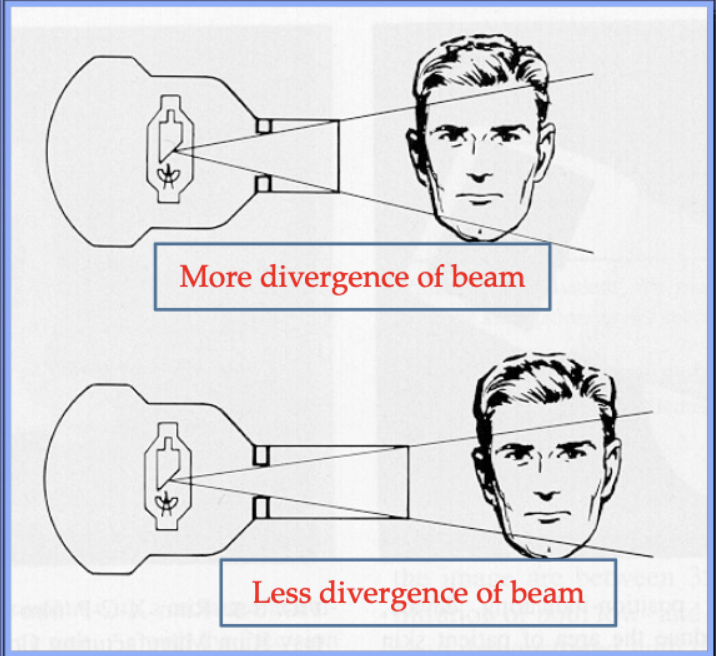
a Source-to-skin distance or Focal spot of 16” vs 8” decreases exposure by %?
10-25%
what combination of intensifying screens and speed group is recommended for extraoral imaging?
rare-earth intensifying screens + high speed screen film (>400)
(significant dose reduction)
t/f: significant dose reduction for extraoral imaging is seen with digital sensors compared to screen films.
false. no significant dose reduction for extraoral imaging is seen with digital sensors compared to screen films.
this is due to significant dose reduction already achieved with intensifying screen-screen film combination
source-to-skin distance or focal spot to film distance (FFD) is controlled by…?
length of position indicating device (PID) of xray tube)
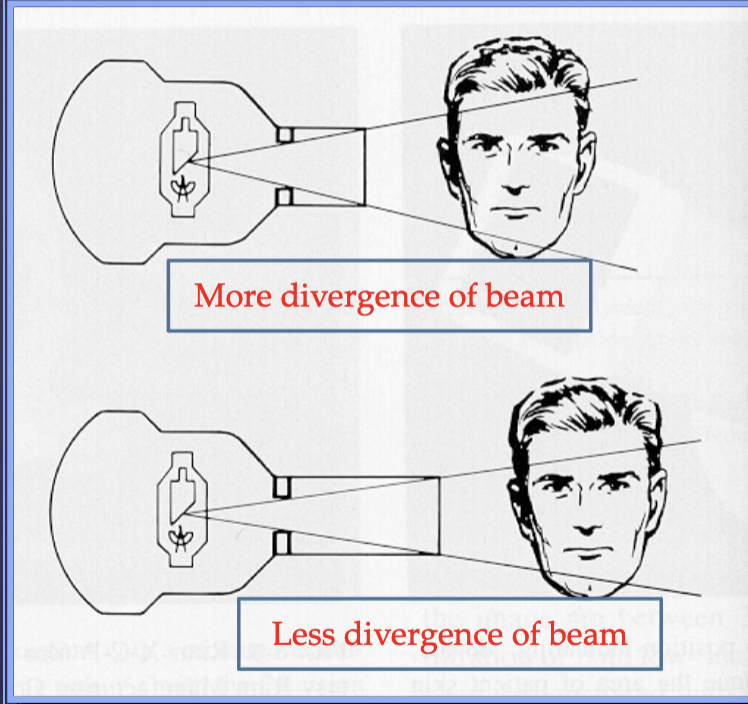
a 16” vs 8” source-to skin distance or FFD decreases exposure by %
10-25%
why does a 16” vs 8” source-to skin distance or FFD decrease exposure by 10-25%?
reduction in exposed tissue volume as the xray beam is less divergent
this icnreases image quality (sharpness, fog)
what do film and sensor holders do?
aligns receptor to collimated beam reducing unacceptable images (cone cutting)

which colors of film/sensor holders are for posterior PA vs anterior vs bitewings?
yellow → posterior PA
blue → anterior PA
red → bitewing

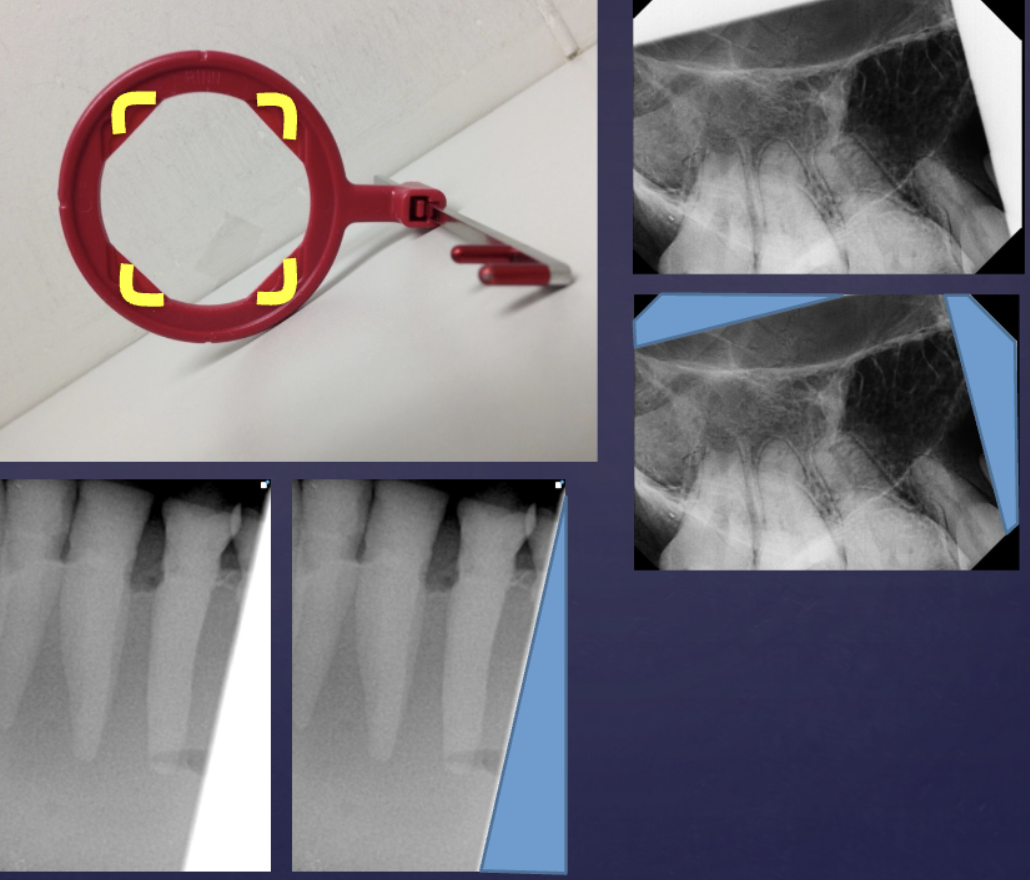
what are the yellow reference marks for?
Reference marks for aligning PID of X-ray tube to prevent cone-cuts
Operating potential of dental x-ray machines must range between ____kVp but should range between ____ kVp
50 and 100 kVp
60 and 80 kVp
what are the benefits of using a high kVp?
reduces patient dose
what are the pros/con of using a low kVp?
reduce beam intensity which requires increased exposure time
beam w more low energy photons that increases risk but not useful in making image
improves image contrast
what is the amperage and time settings for optimal quality radiographs?
miliampere seconds (mA-s)
what does miliampere-second settings control?
radiographic density (quantity of xrays produced)
what is the significance of having miliampere-second settings set to optimal quality radiograph levels?
Overexposures/underexposures result in repeat exposures
The dentist should evaluate radiographs under appropriate conditions for analysis and diagnosis. What setting is appropriate for digital radiographs?
on a computer screen in a darkened room
what must be accurate and posted alongisde xray machines in a dental office?
technique chart
protecting personnel during radiograph imaging involves operatory construction and shielding. where should the operator stand?
outside operatory
behind a barrier (leaded)
if no barrier, use position-and-distance rule
what is the position-and-distance rule?
distance: at least 6 ft from source
position: 90-135 degrees from primary xray beam
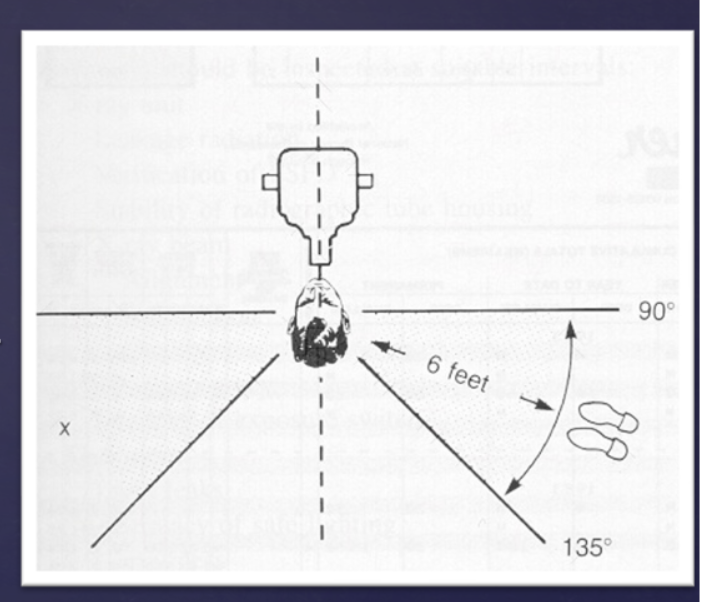
can the operator hold sensor receptor holder during exposure?
no. For uncooperating patients/minors, patient’s caregiver or guardian/parent can hold the sensor holder. Appropriate shielding should be provided to the caregiver
t/f: Neither operator nor patient should hold the radiographic tube housing during exposure
true
t/f: Personnel monitoring devices should be provided to dental office personnel operating x-ray machines to monitor exposure
true
what are 2 examples of personnel monitoring devices?
film badge
TLD (thermoluminescent dosimeter)
what is a film badge and how does it work?
type of personnel monitoring device
• Special type of sensitive film in a special holder with metallic filters
• Attached to external area
• Reasonably accurate (~20 mR)
• Not for periods of longer than 1 month

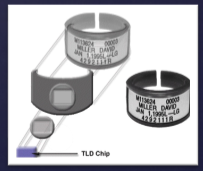
what is a TLD and how does it work?
type of personnel monitoring device
• Lithium fluoride crystal
• Absorb energy which will be read by a special reader
• Reusable
• More sensitive and accurate (~5 mR)
_______ protocols for x ray machine, imaging receptor, film processing, lead aprons should be developed and implemented in every dental practice
Quality assurance
________ for dentists and staff is important to learn about Safety updates, equipment that can decrease radiation exposure and improve diagnostic quality of radiographs
Continuing education
how should you respond to patien’ts concern/anxiety about radiation exposure?
allow patient to express thoughts fully
Acknowledge and show that you understand their apprehension
tell patient why you need radiographs-detect interproximal caries, extent of periodontal bone loss suggested by probing on clinical exam, painful tooth etc
Describe numerous measures you take to reduce patient exposures- digital sensors, rectangular collimation
Finally, make comparisons that patients will understand (background equivalent exposure)
explain you will only make exposures that you specifically need to make diagnosis
For new patients- assure you will contact their previous dentist to obtain previous radiographs to avoid repeat exposures
Always discuss benefits when discussing risks with
patients