combined FINAL + MIDTERM
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Q: What is business strategy?
A: How a firm competes within a particular industry or market.
Q: What is corporate strategy?
A: Decisions about firm scope—industries, markets, vertical integration, diversification, acquisitions, and resource allocation.
Q: Is Walmart’s cost leadership business or corporate strategy?
A: Business strategy.
Q: Is Coca-Cola acquiring bottlers business or corporate strategy?
A: Corporate strategy (vertical integration).
Q: What is product scope?
A: How specialized a firm is in its product range. Example: Tesla specializing in EVs.
Q: What is vertical scope?
A: How many supply-chain activities a firm performs. Ex: Shell is fully vertically integrated.
Q: What is geographic scope?
A: How widely a company operates geographically (McDonald's vs. In-N-Out).
Q: What are economies of scale?
A: Lower average costs from producing more of one product.
Q: What are economies of scope?
A: Cost savings from sharing resources across multiple products. Example: FedEx + Kinko’s.
Q: What is vertical integration?
A: Expanding into different stages of the value chain (acquisition or internal development).
Examples:
– Netflix creating originals
– Apple opening stores
– Comcast acquiring ABC
Q: What is diversification?
A: Entering new product lines/fields of operation.
Q: What is related diversification?
A: Expansion into similar businesses (car → trucks).
Q: What is unrelated diversification?
A: Expansion into different industries (tobacco → foods).
Q: Why do firms diversify?
A: Growth, risk reduction, economies of scale/scope, internal labor markets.
Q: What is a horizontal acquisition?
A: Acquiring a competitor (HP–Compaq, Albertsons–Safeway).
Q: When is M&A preferred over internal development?
A: When timing is critical, to gain unique resources, increase market share fast, acquire loyal customers.
Q: Are M&As always value-creating?
A: No — many fail (e.g., Quaker + Snapple).
Q: What is corporate governance?
A: System of relationships between management, board, shareholders, and stakeholders; sets objectives and monitors performance.
Q: What is an agency problem?
A: Conflict of interest between managers and shareholders.
Q: What is moral hazard?
A: When managers take risks/work less because their actions aren’t easily observed.
Q: How do we reduce agency costs?
A: Governance mechanisms and incentive alignment.
Q: Why are shareholders often short-term oriented?
A: Most are institutional investors seeking quick returns.
Q: What decisions does short-termism cause?
A: Cut R&D, avoid risky innovation, pressure CEOs to focus on quarterly results.
Q: What is the main criticism of shareholder value maximization?
A: Doesn’t account for environmental, social, or ethical factors; may harm sustainability.
Q: What is stakeholder theory?
A: Firms should consider all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
Q: What is CSR?
A: Corporate self-regulation and engagement in social/environmental good.
Q: How do companies implement CSR?
A: Reporting, ethics training, sustainability efforts, LEED standards, etc.
Q: What is a B-Corp?
A: Certified companies meeting high standards of social/environmental performance. (Ex: Etsy)
Q: What is strategic renewal?
A: Refreshing or replacing firm attributes to ensure long-term survival.
Q: What is incremental renewal?
A: Small continuous changes (J&J acquisitions; Intel chip generations).
Q: What is dynamic capability?
A: Ability to integrate, build, and reconfigure resources to adapt to change. Example: IBM.
Q: What is the 80-20 rule?
A: 80% of results come from 20% of causes (e.g., major customers drive most sales).
Q: Give examples companies that failed due to lack of adaptation.
A: Blockbuster, Borders, Nokia.
Q: What is competitor analysis?
A: Studying rivals to predict actions and shape strategic decisions.
Q: What are key elements of game-theoretic modeling?
A: Players, actions, payoffs.
Q: Payoff formula?
= (Price – Average Cost) × Sales.
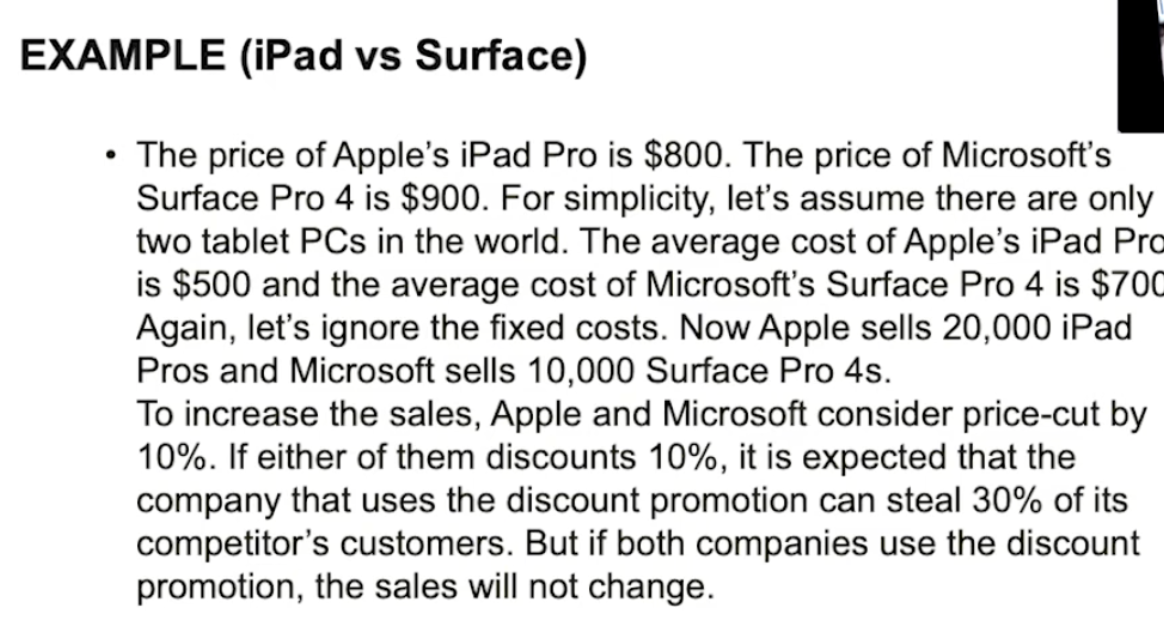
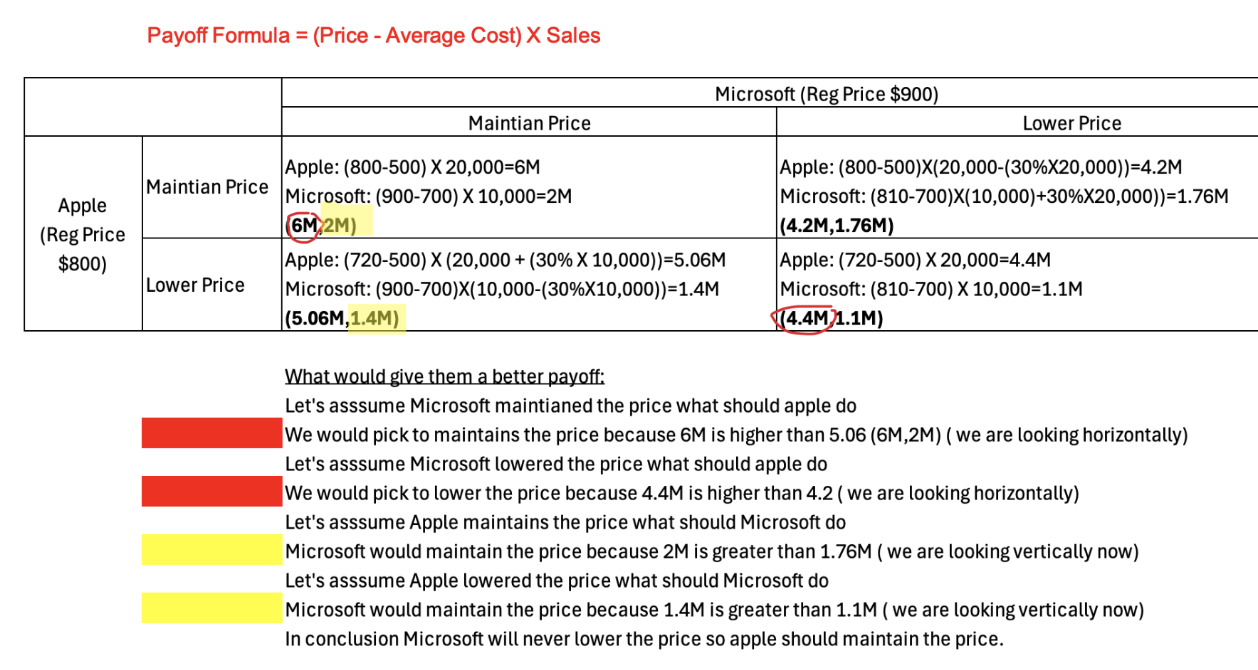
Q: What are limitations of competitive dynamics models?
A: Oversimplified, unrealistic assumptions, limited information, sensitive to payoffs.
What is strategy?
Strategy is the pattern of objectives, purposes, or goals and the major policies and plans for achieving these goals.
It defines what business the company is in and the kind of company it is or wants to be.
How does Porter differentiate operational effectiveness and strategy?
Operational effectiveness is about achieving excellence in individual activities
Strategy is about combining activities to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
What are economies of scale?
producing more reduces average cost
What is price sensitivity?
The degree to which the price of a product affects consumers’ purchasing behavior.
What are switching costs?
Any impediments or costs when changing business partners (sellers or buyers).
What are barriers to entry?
Obstacles that make it difficult to enter a market.
What is market concentration?
The degree to which a small number of firms hold a large market share.
Low HHI (Close to 0) = more comp and less concentration
High HHI (closer to 1) = less comp and more concentrated
What is the purpose of the Five Forces framework?
To understand how to capture a bigger slice of profit by positioning the company where competition is lower.
What is the unit of analysis in Five Forces?
Industry.
Why is defining industry boundaries important?
Because diversified firms may need multiple Five Forces analyses for different industries.
What are some limitations of Five Forces?
Views other parties only as threats, not allies.
Focuses on industries, not specific firms.
No guidance on weight or interactions of forces.
Ignores government and complements.
Industry boundaries can shift.
What is overall cost leadership?
A strategy to gain advantage through high efficiency, scale economies, cost control, and cost minimization, creating strong entry barriers.
What is differentiation strategy?
Charging a premium by offering unique value (design, brand, tech, service), increasing brand loyalty and reducing price sensitivity.
What is focus strategy?
Targeting a specific segment or buyer group. Implies limited overall market share.
What is RBV?
Views a firm as a collection of resources and capabilities. Competitive advantage arises from valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRIN) resources.
What is the role of capabilities?
Resources = what a firm has
Capabilities = what a firm can do with what it has
Competitive advantage = comes from capabilities, not just resources.
Why are resources “sticky”?
Because they are costly to transfer between companies.
What is a value chain?
A sequence of activities a firm performs to deliver a valuable product or service.
What is inbound logistics?
Movement of materials from suppliers to facilities
What is outbound logistics?
Moving final products to end users.
What is marketing and sales?
Creating and delivering value to customers.
What is service?
Keeping the product working effectively after sale.
What is procurement?
Acquiring goods or services externally.
What is HR management?
Recruiting, hiring, training, and managing personnel.
What is technological development?
Applying technology in transformation processes
What is infrastructure?
Activities like accounting, legal, finance, PR, quality assurance, and strategy.
What is vertical integration (VI)?
When a company adds another stage of production in the industry value chain (backward or forward)
What are advantages of VI?
More control over decisions
investments
information
production timing
capturing double margins
What are disadvantages of VI?
Costly entry
higher exit barriers
less flexibility increased debt risk
What are two-sided markets?
Economic platforms with two user groups providing network benefits to each other (e.g., platforms like credit cards or ride-sharing apps).
How is value flow different in two-sided networks?
Cost and revenue exist on both sides of the platform.
What is a network effect?
When the value of a product/service increases with the number of users.
What is critical mass?
The point where the value users receive is greater than or equal to the price paid.
Why do network effects lead to winner-takes-all markets?
Because increasing returns to scale allow a few platforms to dominate.
What are first-mover advantages?
The ability of pioneering firms to earn positive economic profits before competitors.
What are the main sources of first-mover advantages?
Technological leadership
Preemption of assets
Buyer switching costs
Brand reputation and awareness
Automobile industry:
Bargain Power of Suppliers
Intensity of rivalry
Bargain Power of Buyers
Threat of Subs
Threat of New Entrants
Bargain Power of Suppliers —> Moderate
Who are they? Many companies
switching costs of sup are low
supplier concentration is low
strong trade unions
Intensity of rivalry —>High
Who are they: other manuf
Exit barriers are high
product differences become difficult
Bargain Power of Buyers —> Moderate
WHo are they? You and me
Switching costs of buyers are low. However buyers desperately depnf on the products
Threat of Subs—> Low
Who are they? motorcycle manufacturers
Threat of New Entrants—> Low
economies of scale is veyr significant
brand identity/reputation is crucial
capital requirement are high
learning curve substantially matters
According to the five force framework, which one is true?
All else being equal, a firm in the fast growing industry will have strong bargaining power over its suppliers.
All else being equal, when buyers’ switching cost is high, a firm is more likely to have strong bargaining power over its buyers.
All else being equal, when suppliers have potential incentives to pursue forward integration (such as technology similarity), a firm is more likely to have strong bargaining power over its suppliers.
All else being equal, when exit barrier of incumbents is high, the intensity of rivalry is less likely to be high.
2
Which one is explaining the condition of higher exit barrier?
When physical assets can be easily used in other industries
When the business does not require a high level of capital investment
When core technology of this industry cannot be applied to other industries
3
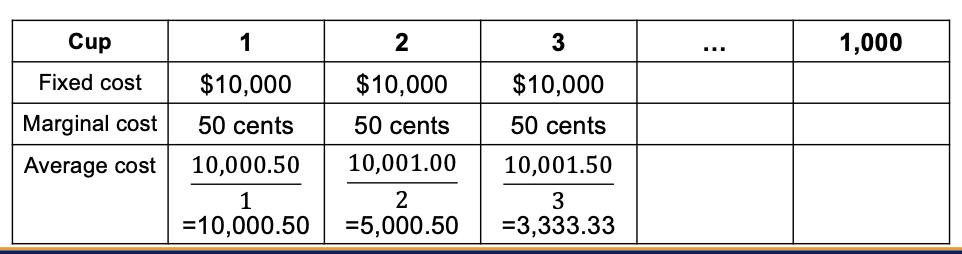
Economies of Scale Problem
A company wants to start a mobile coffee truck business.
The initial fixed cost of the coffee truck and equipment is $10,000.
The marginal cost per cup of coffee (coffee grounds and water) is $0.50.
Calculate the average cost per cup if the company sells:
a. 1 cup of coffee
b. 2 cups of coffee
c. 3 cups of coffee
d. 1,000 cups of coffeeExplain how the average cost per cup changes as the number of cups produced increases.
Based on your calculations, explain how this example shows economies of scale