Finals - Separation of Particles from a Gas
Filtration
This is the most common method for removing very fine particles from gas streams.
FALSE
In filtration, the gas stream is led through a filter, which is often a woven or compressed fibrous, cloth-like material.
TRUE or FALSE. In filtration, the gas stream is led through a filter, which is often a woven or expanded fibrous, cloth-like material.
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Filtration
This is the most common method for removing very fine particles from gas streams.
FALSE
In filtration, the gas stream is led through a filter, which is often a woven or compressed fibrous, cloth-like material.
TRUE or FALSE. In filtration, the gas stream is led through a filter, which is often a woven or expanded fibrous, cloth-like material.
High efficiency
What is an advantage of filtration?
oscillating pressure drops
wear of the filter material
handling and disposal of spent filter cartridges or bags.
Give some disadvantages of Filtration (3)
Wet scrubbers
In this cleaning method, droplets are either directly sprayed into the incoming dusty gas or the gas is allowed to shear a source of liquid into droplets.
FALSE
The particle-containing droplets have a larger diameter than the dust particles, which allows them to be separated more easily from the gas streams in inertial type separators.
TRUE or FALSE. The particle-containing droplets have a smaller diameter than the dust particles, which allows them to be separated more easily from the gas streams in inertial type separators.
FALSE
Wet scrubbers can have a high efficiency for small particle sizes
TRUE or FALSE. Wet scrubbers can have a high efficiency for large particle sizes.
Centrifugal and cyclonic devices
These gas cleaning devices utilize centrifugal force to separate particles from a fluid based on density or size.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. Centrifugal and cyclonic devices both utilize centrifugal force to separate particles from a fluid based on density or size, but they differ in their application and structure.
The collected product remains dry and, normally, useful
Can be used under extreme processing conditions, in particular at high temperatures and pressures and with chemically aggressive feeds
Advantages of Centrifugal or cyclonic devices
A low efficiency for particle sizes below their ‘cut size’ when operated under low solids-loading conditions
Usually has higher pressure loss than other separator types
Disadvantages of Centrifugal or cyclonic devices
Swirl tubes
This is a type of centrifugal or cyclonic device that has an axial inlet with swirl vanes and a cylindrical body shape.
Cyclones
This is a type of centrifugal or cyclonic device with a tangential inlet (‘slot’ or ‘wrap-around’) and a cylinder-on-cone body shape.
FALSE
Particles in the gas are subjected to centrifugal forces which move them radially outwards, against the inward flow of gas and towards the inside surface of the cyclone on which the solids separate
TRUE or FALSE. Particles in the gas are subjected to centrifugal forces which move them radially inwards, against the outward flow of gas and towards the inside surface of the cyclone on which the solids separate

read lang
read lang

Reverse flow cyclone
In this type of cyclone, the gas enters through a tangential inlet at the top of the cyclone body, shaped to create a confined vortex gas flow.
Uniflow cyclone
In this type of cyclone, the gas enters at one end of the body and leaves at the other end.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. In reverse flow cyclone, the clean gas exits through a central pipe also at the top of the body.
FALSE
The uniflow cyclone is less frequently used in industry because it is a much less practical design.
TRUE or FALSE. The uniflow cyclone is more frequently used in industry because it is a more practical design.
High efficiency designs
What classification of cyclones based on the body size are characterized by long bodies in addition to small openings?
High efficiency designs
This design of a cyclone allows for high recovery rates at higher pressure drops.
High rate designs
What classification of cyclones based on the body size are characterized by shorter bodies in addition to larger openings?
High rate designs
This design of a cyclone allows for a larger volume with lower capture rates or pressure drops.
Total pressure drop
The radial pressure gradient, combined with the frictional pressure losses at the gas inlet and outlet and losses due to changes in flow direction, make up the ________________.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. This pressure drop, measured between the inlet and gas outlet, is usually proportional to the square of the gas flow rate through the cyclone.
Inlet contraction
Particle acceleration
Barrel friction
Gas flow reversal
Exit contraction
The total pressure drop is calculated by summing the five pressure drop components associated with a cyclone. What are the five (5) components?
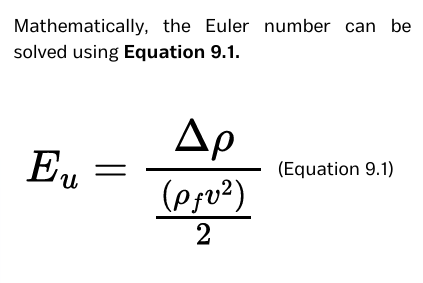
Euler number (Eu)
This represents the ratio of pressure forces to the inertial forces acting on a fluid element.
Euler number (Eu)
This is a resistance coefficient relates the cyclone pressure drop (Δp) to a characteristic velocity (v).
FALSE
The value of Euler number is practically constant for a given cyclone geometry and is independent of the cyclone body diameter.
TRUE or FALSE. The value of Euler number is practically constant for a given cyclone geometry and is dependent of the cyclone body diameter.
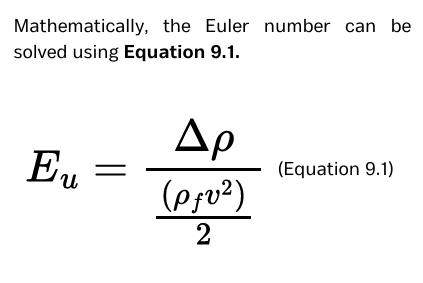
formula for Euler number
formula for Euler number
Characteristic velocity (v)
This can be defined for gas cyclones in various ways. The simplest and most appropriate definition is based on the cross-section of the cylindrical body of the cyclone.
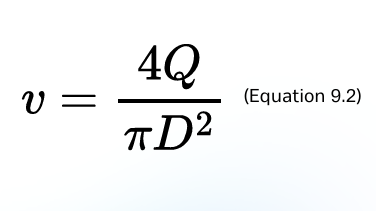
formula for Characteristic velocity
formula for Characteristic velocity
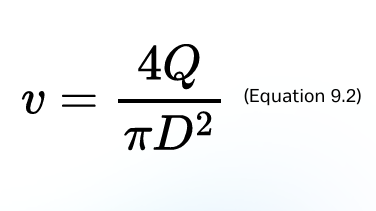
Drag
Buoyancy
Centrifugal Force
What are the forces that act on a particle that follows a circular path? (give 3)
Equilibrium orbit
The balance between drag, buoyancy, and centrifugal force determines the __________ adopted by the particle.
Drag force
This force is caused by the inward flow of gas past the particle and acts radially inwards.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. The centrifugal and buoyancy forces acting on the particle moves with a tangential velocity at a given radius.
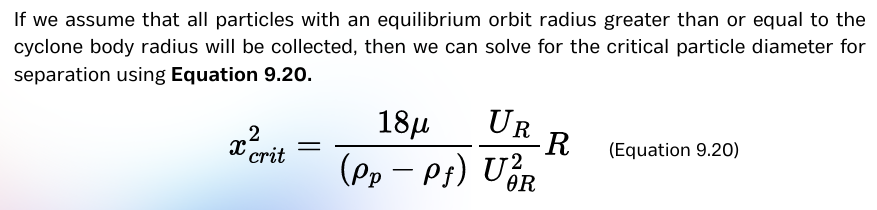
familiarize
familiarize
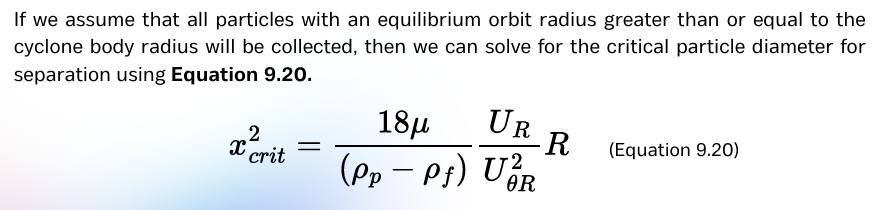
Ideal grade efficiency
This analysis predicts that all particles of size less than the xcrit are not collected.
S-shaped
The collection efficiency curve of a cyclone typically follows an ____ pattern.

read lang
read lang

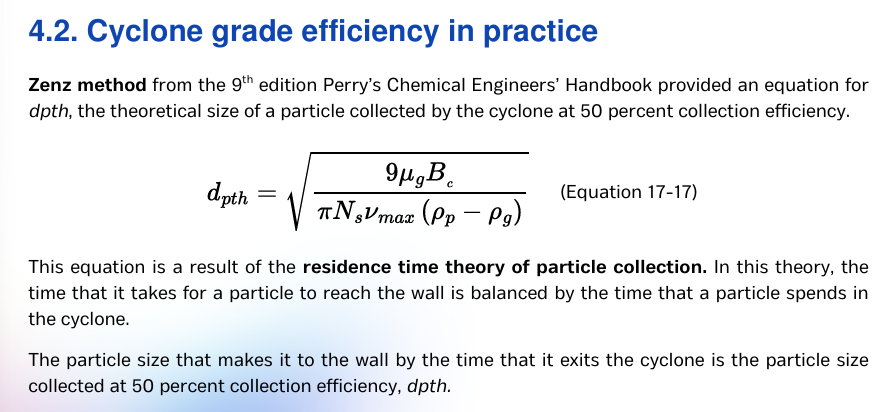
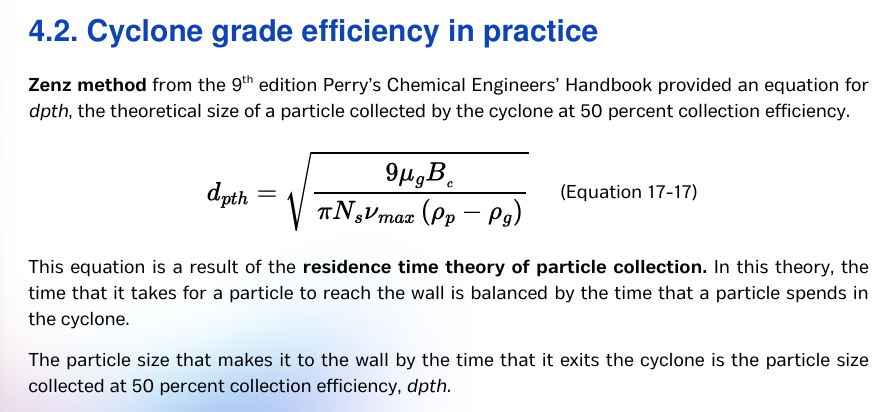
read lang
read lang
Total Efficiency
The ____________ of separation of particles from gas, is defined as the fraction of the total feed which appears in the coarse product collected.
Grade efficiency
The efficiency with which the cyclone collects particles of a certain size is described by the ____________.
Stokes number
The scale-up of cyclones is based on a dimensionless group, _________, which represents the ratio of the force required to redirect a particle to the drag force available for that redirection.

TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. The greater the value of Stokes number, the greater the tendency for particles to impact with the airway walls and so be captured.
FALSE
For large industrial cyclones, the Stokes number is independent of Reynolds number.
TRUE or FALSE. For large industrial cyclones, the Stokes number is dependent of Reynolds number.
5 g/m3
For suspensions of concentration less than about __ g/m3, the Stokes number is constant for a given cyclone geometry
FALSE
One of the most important characteristics of gas cyclones is the way in which their efficiency is affected by pressure drop (or flow rate).
TRUE or FALSE. One of the most important characteristics of gas cyclones is the way in which their efficiency is affected by pressure rise (or flow rate).
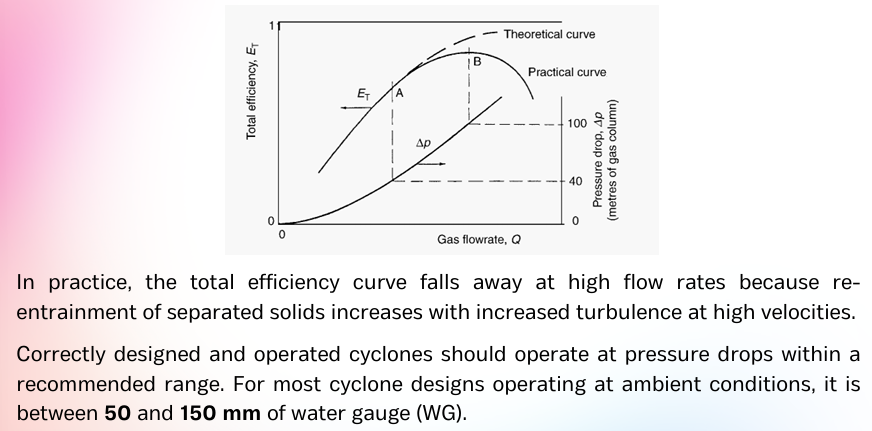
read lang
read lang
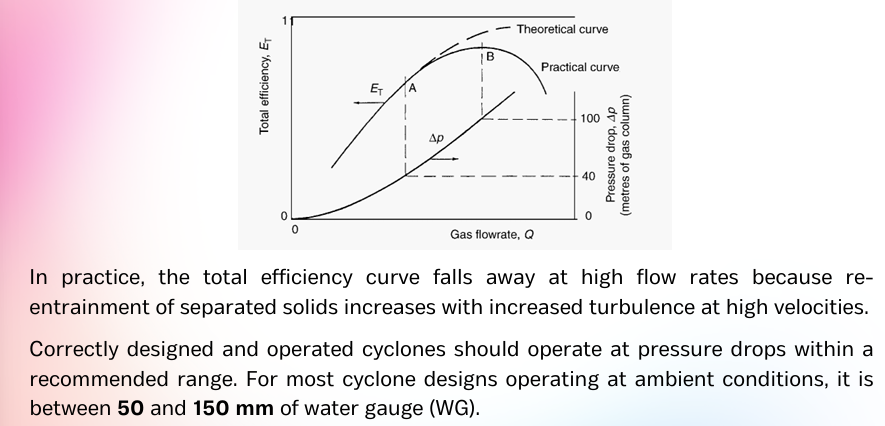
50 and 150 mm
Correctly designed and operated cyclones should operate at pressure drops within a recommended range. For most cyclone designs operating at ambient conditions, it is between _____ and _____ mm of water gauge (WG).
Dust loading
One of the important operating variables affecting total efficiency is the concentration of particles in the suspension.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. High dust loadings lead to higher total separation efficiencies due to particle enlargement through agglomeration of particles.
5 g/m³
High dust loadings (above about ____ g/m³) lead to higher total separation efficiencies due to particle enlargement through agglomeration of particles.
High efficiency cyclones
These cyclones give high recoveries and are characterized by relatively small inlet and gas outlet orifices.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. The high rate designs have lower total efficiencies, but offer low resistance to flow.
High rate cyclones
These cyclones have large inlets and gas outlets, and are usually shorter.
Abrasion
_________ in gas cyclones is an important aspect of cyclone performance and it is affected by the way cyclones are installed and operated as much as by the material construction and design.
FALSE
Within the cyclone body there are two critical zones for abrasion:
in the cylindrical part just beyond the inlet opening and
in the conical part near the dust discharge.
TRUE or FALSE. Within the cyclone body there are three critical zones for abrasion.
Attrition
This is known to take place on collection in gas cyclones but little is known about how it is related to particle properties, although large particles are more likely to be affected by attrition than finer fractions.
Attrition
This is also known as break-up of solids
Attrition
This is most detectable in recirculating systems such as fluidized beds where cyclones are used to return the carry-over material back to the bed.
Blockages
________ is typically the result of excessive solids accumulation at the cyclone’s outlet and is among the most frequent operational issues.
Diplegs
In fluidized beds with internal cyclones, ‘________’ are used to return the collected entrained particles into the fluidized bed.
Diplegs
These are vertical pipes connected directly to the solids discharge orifice of the cyclone extending down to below the fluidized bed surface.
Connecting cyclones in series
This is often done in practice to increase recovery. Usually the primary cyclone would be of medium or low efficiency design and the secondary and subsequent cyclones of progressively more efficient design or smaller diameter.

read lang
read lang

Near the bottom of the cylindrical section of the cyclone
Where does the direction of the flow of vortex reverses inside the cyclone body?