6.2 - ATP (energy production / resynthesis)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is ATP and where is it stored
High-energy molecule
Stored in muscle cells and other body parts
Energy currency for biological work
What is ATP made up of
Adenosine
Three inorganic phosphate groups
High-energy chemical bonds
How long does stored ATP last during physical activity
1–2 seconds
What happens after the initial ATP stores are used
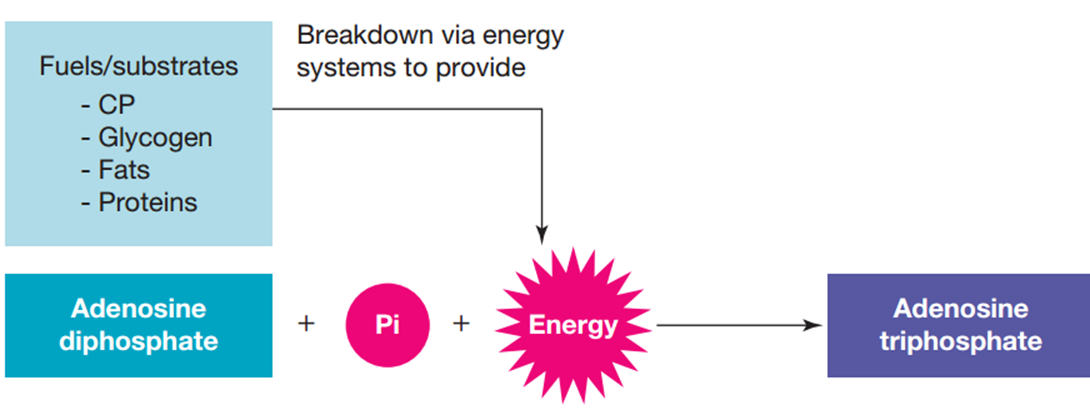
ATP must be resynthesised using chemical and food fuels
How much ATP is stored in the average human body
50–100 grams
How much ATP is used by the body in 24 hours
50–75 kilograms
Where is the energy in ATP stored
In the bonds between the three phosphate groups
Especially in the bond between the outer phosphate
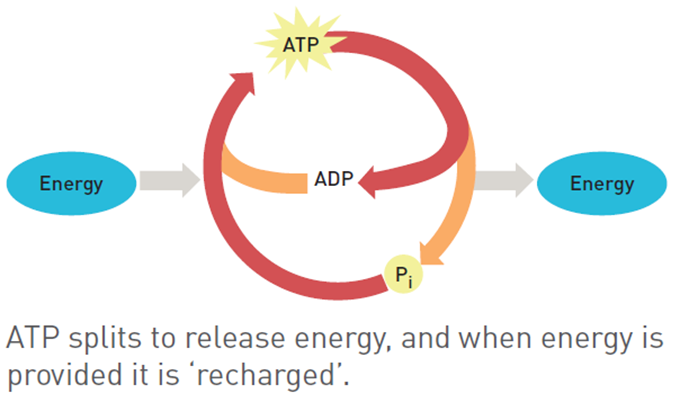
When is the energy released
when the bonds are broken
usually occurring in the bond between the outer phosphate
What are the by-products when ATP is broken down for energy
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)
Pi (Inorganic Phosphate)
What is ATP resynthesis (phosphorylation)
Adding a phosphate to ADP to form ATP
ADP + Pi + Energy ↔ ATP
What is aerobic metabolism
ATP resynthesis with oxygen
What is anaerobic metabolism
ATP resynthesis without oxygen
What is required for ATP resynthesis
what for
Energy
to connect the phosphate group back to ADP to create ATP
(ADP + Pi + Energy ↔ ATP)
What energy fuels or substrates help resynthesise ATP (present within the muscle)
Phosphocreatine
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
How long can these fuels support ATP resynthesis during physical activity
As long as sufficient fuel/substrate stores are available