Cellular Adaptation and Cell Necrosis
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering definitions and key examples from the lecture on Cellular Adaptation and Cell Necrosis.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms

.

Cellular Adaptation
Normally reversible structural or functional changes that allow a cell, tissue, or organ to survive prolonged exposure to adverse or exaggerated stimuli.
Physiologic Adaptation
Normal, expected cellular adjustment to routine stimuli (e.g., uterine enlargement in pregnancy, thymic involution in childhood).
Pathologic Adaptation
Cellular adjustment to harmful stimuli that may progress to disease (e.g., cardiac hypertrophy from hypertension).
Atrophy
Decrease in the size of a tissue, organ, or entire body due to shrinkage of individual cells.
Physiologic Atrophy
Normal reduction in tissue size, such as thymic involution or post-menopausal endometrial thinning or breast and muscle atrophy
Pathologic Atrophy
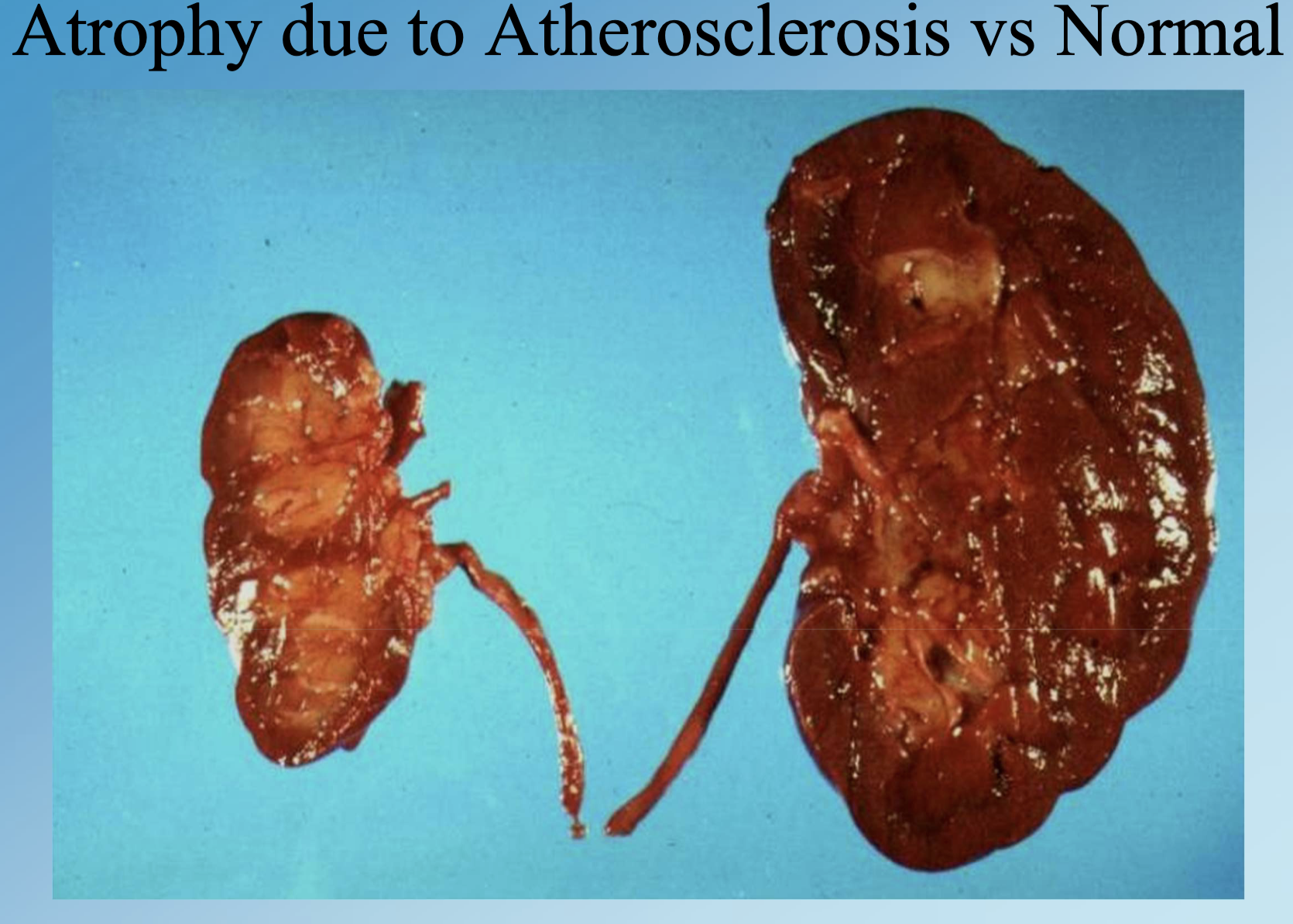
Size reduction from disease or lack of use, e.g., ischemic kidneys, testicular atrophy, Alzheimer brain shrinkage.
Hypertrophy
Increase in tissue or organ size due to enlargement of individual cells without added cell number.
Physiologic Hypertrophy
Adaptive enlargement from normal stimuli, such as skeletal muscle growth in weight training.
Pathologic Hypertrophy
Enlargement due to disease, e.g., concentric left-ventricular hypertrophy in systemic hypertension.
Hyperplasia
Adaptive increase in the number of cells causing organ or tissue enlargement.
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Estrogen-driven proliferation of endometrial glands resulting in thickened uterine lining.
Hyperplastic Polyp
Non-neoplastic proliferation of mucosal epithelium in colon or stomach forming a polypoid lesion.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Combined hyperplasia and hypertrophy of prostate stroma and glands leading to enlarged prostate.
Metaplasia
Reversible replacement of one differentiated cell type by another better suited to a chronic environment.
Squamous Metaplasia
Transformation of ciliated columnar bronchial epithelium to stratified squamous epithelium, often from smoking.
Barrett Esophagus
Glandular (intestinal) metaplasia of distal esophageal squamous epithelium induced by acid reflux.
Dysplasia
Disordered, precancerous growth with loss of uniformity and architectural orientation.
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
Graded cervical dysplasia detected by Pap smear, strongly linked to HPV infection.
Anaplasia
Undifferentiated, uncontrolled cellular growth—hallmark of malignant transformation. Cancer
Malignancy
Clinical synonym for anaplasia; includes carcinoma, cancer, neoplasm.
Cellular Pleomorphism
Variation in size and shape of cells and nuclei, a microscopic hallmark of anaplasia.
Hyperchromatic Nuclei
Dark-staining nuclei characteristic of anaplastic cells due to increased DNA content.
High N/C Ratio
Increase of nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio (~1:1) seen in malignant cells versus normal (~1:4–1:6).
Abnormal Mitotic Figures
Atypical or numerous mitoses indicating rapid, disordered cell division in cancers.
Necrosis
Death of cells or tissues within a living organism accompanied by inflammation.
Autolysis
Self-digestion of cells after organismal death, lacking inflammatory response.
Coagulative Necrosis
Most common necrosis; proteins denature yet cell outlines preserved (e.g., myocardial infarction).
Liquefactive Necrosis
Enzymatic digestion of tissue into liquid mass, typical in brain infarcts and abscesses.
Caseous Necrosis
Cheesy, yellow necrosis combining coagulation and liquefaction, classically in tuberculosis granulomas.
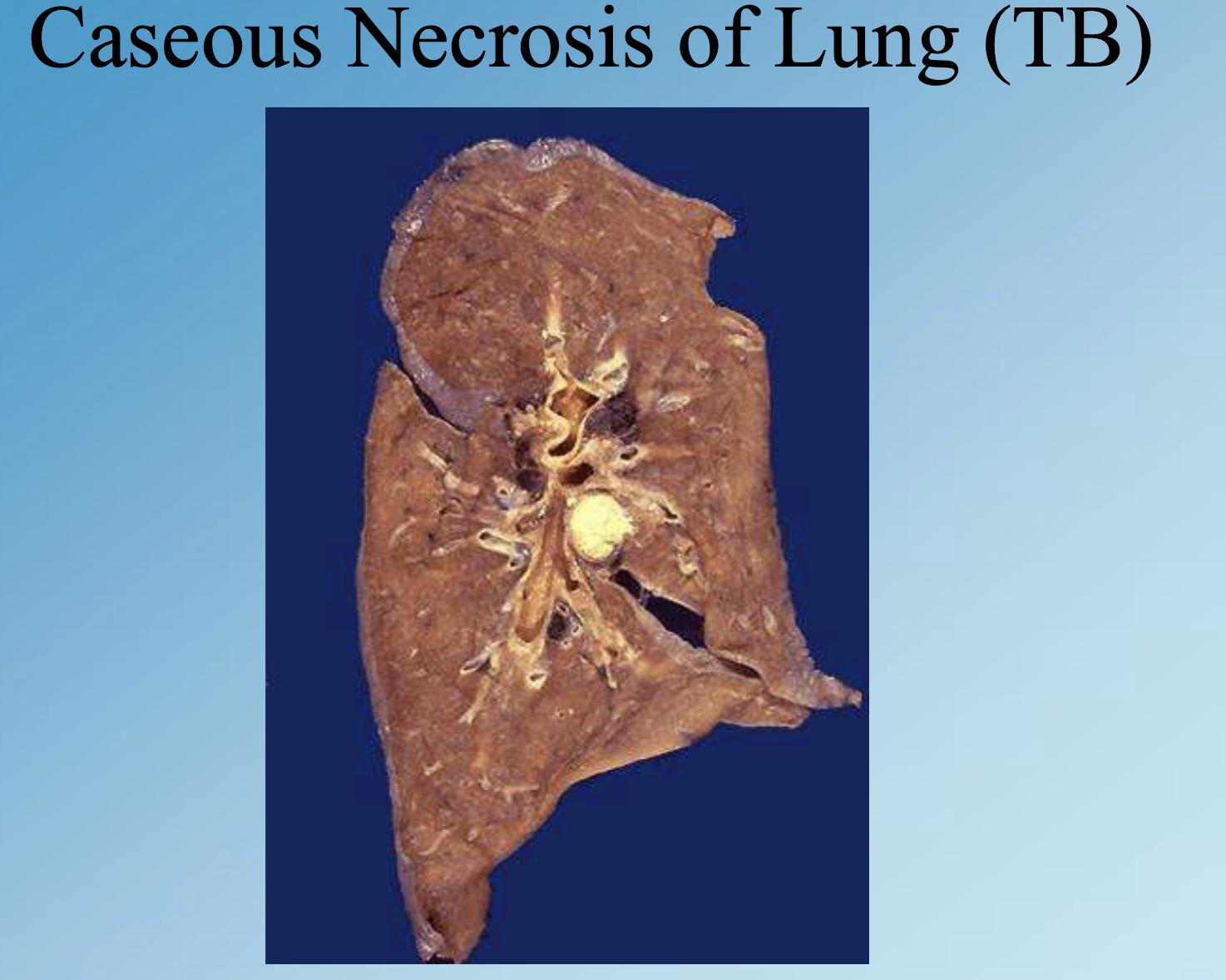
Ghon Complex
Primary TB lesion with caseous necrosis in lung and draining lymph nodes.
Fat Necrosis
Lipase-mediated fat destruction producing chalky soaps around pancreas or subcutaneous fat.
Wet Gangrene
Secondary bacterial infection of necrotic tissue leading to liquefaction and foul odor.
Dry Gangrene
Mummification and blackening of necrotic tissue due to dessication without infection.
Dystrophic Calcification
Calcium salt deposition in necrotic or injured tissues despite normal serum calcium levels.
Metastatic Calcification
Calcium deposition in normal tissues due to hypercalcemia or deranged metabolism.
Atherosclerotic Calcification
Dystrophic calcium deposition within atherosclerotic plaques, narrowing coronary arteries.
Calcified Aortic Stenosis
Dystrophic calcification of aortic valve cusps causing obstructed blood flow.
Tumoral Calcifications in Breast
Dystrophic microcalcifications around breast cancer detectable by mammography.
Hyperparathyroidism
Endocrine disorder producing hypercalcemia that predisposes to metastatic calcifications.
Calcium Oxalate Stone
Metastatic calcification forming renal, gallbladder, or bladder calculi due to salt precipitation.