Ch 1-3 Review
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Computer programs also known as ___. (1.1)
Software
The major operations performed by all sizes of computer include ___. (1.1)
input, processing, and output
Visual Basic, C++, and Java are all examples of computer ___. (1.1, 1.2, 1.3)
programming languages
A programming language’s rules are its ___. (1.1)
syntax
The most important task of compiler or an interpreter is to ___. (1.1)
translate programming language statements into machine language
Which of the following is temporary, internal storage? (1.1)
computer memory
Which of the following pairs of steps in the programming process is in the correct order? (1.3)
code the program, translate it into machine language
What is the program development cycle? (1.3)
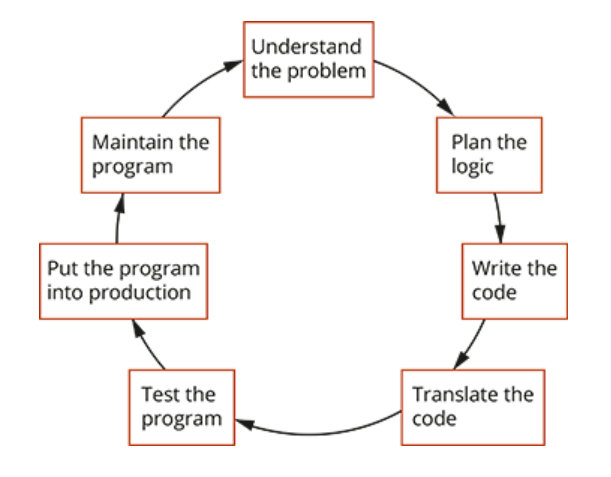
A programmer’s most important task before planning the logic of a program is to ___. (1.3)
Understand the problem
The two most commonly used tools for planning a program’s logic are ___. (1.3)
flowcharts and pseudocode
Writing a program in a language such as C++ or Java is known as ___ the program. (1.3)
coding
An English-like programming language such as Java or Visual Basic is a ___ programming language. (1.3)
high-level
Which of the following is an example of a syntax error? (1.3)
misspelling a programming language word
Which of the following is an example of a logical error? (1.3)
dividing by 3 when you meant to divide by 30

The parallelogram is the flowchart symbol representing the ___. (1.4)
either input or output

In a flowchart, a rectangle represents ___. (1.4)
processing
In flowchart, the decision symbol is a ___. (1.4)
diamond
The term of ‘eof’ represents ___. (1.5)
a generic sentinel value
When you use an IDE instead of a simple text editor to develop a program, ___. (1.6)
some help is provided
When you write a program that will run in a GUI environment as opposed to a command-line environment ___. (1.6)
the logic is very different
As compared to procedural programming, with object-oriented programming, ___. (1.7)
the programmer’s focus differs
What does a declaration always provide for a variable? (2.1)
A name, a data type, and a value.
A variable’s data type describes all the following except ___. (2.1)
the scope of the variable
The value stored in an uninitialized variable is ____. (2.1)
garbage
The value 3 is a ___. (2.1)
numeric constant
The assignment operator ___. (2.1)
is a binary operator.
Multiplication has a lower precedence than ___. (2.2)
parentheses
Which of the following is not a term used as a synonym for module? (2.3)
object
Modularization ___. (2.3)
facilitates reusability
What is the name for the process of paying attention to important properties while ignoring nonessential details? (2.3)
abstraction
Every module has all of the following except ___. (2.4)
local variables
Programmers say that one module can ___ another, meaning that the first module causes the second module to execute. (2.3)
call
The more that a module’s statements contribute to the same job, the greater the ___ of the module. (2.4)
function cohesion
In most modern programming languages, a variable or constant that is declared in a module is ____ in that module. (2.4)
global
Which of the following is not a typical housekeeping task? (2.4)
printing summaries
Which module in a typical program will execute the most times? (2.4)
the detail loop
A hierarchy chart tells you ___. (2.4)
which modules call other modules
What are nonexecuting statements that programmers place within code to explain program statements in English? (2.5)
comments
Program comments are ___. (2.5)
neither required in a program nor a form of external documentation.
Which of the following is valid advice for naming variables? (2.5)
To make names easier to read, separate long names by underscores or capitalization for each new word.
A message that asks a user for inputs is a(n) ___.
prompt
Snarled program logic is called ___ code. (3.1)
spaghetti
The three structures of structured programming are ___. (3.2)
sequence, selection, and loop
A sequence structure can contain ___. (3.2)
any number of tasks
Which of the following is not another term for a selection structure? (3.2)
loop structure
A ____ expression has one of two values, often expressed as true or false. (3.2)
Boolean
Placing a structure within another structure is called ___ structure.
nesting
Attaching structures end to end is called ___. (3.2)
stacking
When an action is required if condition is true, but no action is needed if it is false, you use a ___. (3.2)
single-alternative selection
To take action repeatedly as long as a condition remains true, you use a ___. (3.2)
loop
When you must perform one action when a condition is true and a different one when it is false, and then the program continues, you use a ___. (3.2)
dual-alternative selection
Which of the following attributes do all three basic structures share? (3.2)
They all have one entry and one exit point.
Which true of stacking structures? (3.2)
When you stack structures, you cannot nest them in the same programs.
When input data in a loop within a program, the input statement that precedes the loop ___. (3.3)
is called a priming input
A group of statements that executes as a unit is a ___. (3.2)
block
Placing a decision within a loop is ___. (3.2)
an acceptable structured programming technique
In a selection structure, the structure-controlling condition is ___. (3.2)
tested once at the beginning of the structure
When a loop executes, the structure-controlling condition is ___. (3.2)
tested either before or after the loop body executes
Which of the following is not a reason for enforcing structure rules in computer programs? (3.4)
Structured programs usually are shorter than unstructured ones.
Which of the following is not a benefit of modularizing programs. (3.4)
If you use modules, you can ignore the rules of structures.
Which of the following is true of structured logic? (3.6)
Any task can be described using some combination of the three structures: sequence, selection, and loop.